Treatment of cerebral ischemia in newborns
The goal of treatment is to restore normal blood circulation in the brain tissue, prevent pathological changes and eliminate the consequences of ischemia. For stage 1 disease, treatment usually involves prescribing massage to improve blood circulation.
For diseases of the 2nd and 3rd degrees, drug therapy and surgery are used to remove a blood clot in the vessel and restore the structure of the vascular bed. In difficult cases, the baby undergoes a rehabilitation course of intensive therapy.
How does cerebral ischemia occur?
In 70% of cases, ischemia occurs in the fetus in the womb and is associated with the formation of a blood clot in one of the vessels supplying the brain, or with insufficient development of the vessel. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in premature babies whose vascular system is not yet fully formed.
As a result, an insufficient amount of blood enters the vital organ, and with it, oxygen. Delay in providing medical care leads to damage to larger areas of the brain, cerebral hemorrhage and other serious consequences.
Classification of hemorrhages in newborns
Subarachnoid hemorrhage in a newborn
One of the most common types of hemorrhages in children is subarachnoid. Its cause is the rupture of blood vessels inside the arachnoid and soft membranes of the brain. Most often, the cause may be prolonged labor. If the problem is not recognized in time, an inflammatory process begins due to the breakdown of blood at the site of bleeding.
Main symptoms:
- Overexcitement, poor sleep;
- Constant crying;
- Strabismus;
- Increased head volume;
- Convulsions;
- Neck muscle tension.
With immediate detection of the disease and proper treatment, hemorrhage leaves no consequences.
Subdural hemorrhages in newborns
Subdural hemorrhage in newborns is caused by rupture of venous vessels.
This type of damage is caused by acute trauma. It leads to an outpouring of blood into the area between the dura mater and the brain. A hematoma forms, which rapidly increases and compresses the brain. The consequences of such a pathology are very dangerous and can lead to death.
In addition to injuries, aneurysms and brain tumors can lead to subdural bleeding.
The most common causes of this hemorrhage are the following:
- The fruit is too large;
- Rigidity of the uterus (in women giving birth for the first time and during late labor);
- The rapidity or protracted nature of labor;
- Vacuum extraction or turning of the baby during labor;
- Prematurity (too soft skull bones).
Symptoms of subdural bleeding in newborns:
- Muscle tension in the back of the head;
- Throwing back the head;
- Non-response of the pupil to light;
- Bradycardia;
- Cramps.
The condition of a child with this pathology is serious; death can occur within two days.
With immediate diagnosis and removal of the hematoma, in half of the cases it is possible to save the newborn a full life. The rest experience serious damage to the neurological system, hydrocephalus and death.
Intraventricular hemorrhage in a newborn
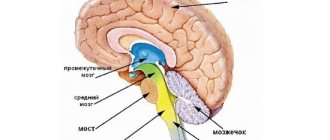
Asphyxia and hypoxia lead to the development of intraventricular hemorrhage in infants. At risk are premature babies whose circulatory system and structural parts of the brain are not fully formed. In babies born prematurely, the head contains the germinal matrix, a structure that later turns into the framework of the brain. With IVH, the process of transformation of the matrix is disrupted, which leads to a delay in the development of the child
This pathology has four degrees of severity. In the first two, there are no symptoms or consequences of the disease, and its presence is diagnosed only by tomography and sonography. In the third and fourth degrees, hydrocephalus begins, the spread of bleeding to brain tissue, and, as a result, neurological changes.
Subependymal hemorrhage in newborns
Subependymal hemorrhage occurs due to cerebral hypoxia. Symptoms in newborn babies include:
- Hand hypotension;
- Mild changes in excitement and lethargy;
- Excessive eye mobility;
- Unsharp tilting of the head.
An indicative sign of this condition is repeated attacks of apnea. To identify the disease, the baby undergoes neurosonography. It is not always possible to recognize SEC in the first hours of life. Often, symptoms appear in the second week or even several months after birth. A prolonged course of the disease leads to the formation of a cyst in the brain.
Parenchymal hemorrhage in a newborn
A complication of IVH can be blood entering the brain. This process is called parenchymatosis.
The pathology begins due to brain damage from a viral infection or blood clotting disorders in the child (difference in the Rh factors of the baby and the mother). Causes may include asphyxia or birth trauma.
With such bleeding there is a high risk to the baby's life. If the outcome is positive, after the hematoma resolves, a cyst forms, which occupies the affected area of the brain. This process leads to serious neurological impairment and developmental delays.