Causes of pain
A headache that spreads to the skin at the roots of the hair is a characteristic sign of fungal, bacterial, metabolic diseases, as well as an allergic reaction to external irritants. Some people have highly sensitive skin, so they are more susceptible to such manifestations. Diagnostic results may reveal disorders that require an individual treatment regimen.
Skin diseases
Pain that intensifies when you touch the scalp is a typical symptom of skin diseases. They can be triggered by a fungal or bacterial infection, metabolic disorders and other factors. Most diseases present with similar symptoms. The patient presents with problems such as itching in the scalp, redness of the skin, the appearance of microdamages and rashes. It is possible to determine what caused these symptoms only based on test results.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic disease of autoimmune origin. Its main cause is a disruption of the immune system, which leads to the appearance of inflammatory lesions on the skin. The disease can manifest itself on any part of the body, including the head. Its characteristic symptoms:
- the appearance of voluminous spots that connect with each other and form plaques;
- itching, inflammation of the skin;
- relapsing course, with alternating periods of remission and relapses;
- in some cases - joint damage.
The disease can occur with varying degrees of severity, even in one patient. Relapses are often triggered by changes in weather conditions, stress, disruption of the daily routine and concomitant diseases. It is important that psoriasis is not transmitted through household, contact, or airborne transmission.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrhea is a skin disease that is characterized by scaling, inflammation, flaking, itching and pain. The scalp is a typical location because there are a large number of sebaceous glands. Seborrheic dermatitis often occurs in children and adolescents, as well as in older adults. Its appearance is associated with disruption of the skin glands, diseases of the immune system, as well as with the vital processes of a fungal infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp occurs more often in those with oily skin. To reduce its manifestations, it is recommended to choose suitable care products, normalize your diet and sleep schedule. Your doctor may also prescribe antifungal medications if seborrhea is caused by an increased activity of a fungal infection.
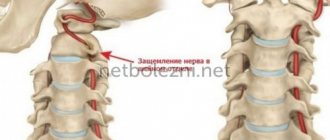
Violation of innervation and blood circulation
If your scalp often hurts, itching and discomfort appear, you should consult a neurologist. This symptom may be associated with the high sensitivity of nerve endings located in the scalp area. Discomfort increases when touching the skin, combing the hair and while caring for it. Doctors recommend massage and, if necessary, sedatives based on herbal extracts.
Poor blood circulation in the scalp can be caused by mechanical factors. The blood vessels are compressed if you wear hats that do not fit properly, or use bulky hairpins. Lovers of high hairstyles and ponytails also often complain of pain and increased sensitivity of the skin at the end of the day.
Other reasons
Painful sensations are not normal. If your skin hurts, develops a rash, or has other alarming symptoms, it is important to see a doctor and get tested. Tests can show different diseases that occur with similar symptoms.
- Pediculosis is a disease caused by lice and nits. Infection occurs through contact and household routes and is possible even among those people who carefully monitor hygiene. To get rid of pests, pharmacies offer a wide range of shampoos and medicinal products against lice. They do not harm the hair and scalp and are suitable for use in adults and children.
- Fungal infection is a common cause of itching and soreness. The pathogen is found on the skin of most people, but is activated only under favorable conditions. The fungus reproduces at high temperatures and humidity, with limited access to oxygen. If it appears on the scalp, you need to use antifungal ointment and choose hats only from natural materials.
- Atopic dermatitis is a disease that is more common in children and goes away with age. Its exact cause has not been established, but exacerbation is associated with poor diet, stressful situations, and hormonal disorders. The patient’s condition is corrected through proper nutrition, scalp hygiene and selection of an appropriate set of care products.
- Allergic reactions - can occur when using various shampoos, soaps, balms and other hair and scalp care products. Within a few hours after the procedure, pain, itching and discomfort appear. It is important to choose skincare products that do not cause allergies, and if your health suddenly worsens, take an antihistamine and consult a doctor.
Some people have very sensitive scalps. They experience pain when combing or braiding their hair or wearing hats. This can lead to intense headaches and the development of chronic migraines. It is important to determine the cause of pain and take timely measures to reduce discomfort.
Causes of pathology
It is no coincidence that hair is called an indicator of a person’s overall health. If they fall out, split, break, or don’t shine, the reasons may be hidden inside the body. The same applies to uncomfortable sensations in the follicles of curls. Sometimes this is a symptom of such ailments:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- other diseases accompanied by circulatory disorders associated with vascular spasms. Even sinusitis impedes blood circulation;
- furunculosis;
- migraine;
- dermatological diseases - psoriasis, seborrhea, etc.;
- exacerbation of herpes;
- pinched nerve.
It is important to exclude other dysfunctions of the body that provoke pain in the hair roots:
- changes in hormonal levels (pregnancy, menopause, other reasons). It is a frequent “culprit” of deterioration of hair condition;
- stress - a person is in constant tension, which causes the feeling of a helmet on the head;
- deficiency of vitamins, minerals;
- overwork, exhaustion. Often an additional symptom of this condition is numbness in the tips of the fingers and toes.
However, even a healthy person can have pain at the roots of their strands. Most often this happens due to:
- abrasions, wounds in a certain area (on the back of the head, on the top of the head);
- burns due to inaccurate dyeing, curling of hair or using a curling iron in the root zone;
- changing the parting. Hair gets used to the same position, so at first it may hurt;
- tight styling - a high ponytail or bun usually causes unpleasant symptoms in the crown area. For some women, pain occurs due to regular wearing of such a hairstyle, for others it is possible even after the first styling (for example, if the primary source of the problem is circulatory disorders or other ailments);
- dry scalp and dandruff;
- extension of curls - pressure on the follicles increases;
- allergic reaction to shampoo or other cosmetics;
- a bad comb, the teeth of which injure the epidermis;
- prolonged exposure to cold, which provokes vasoconstriction. This can cause pain in the root zone;
- piles of hairpins, hairpins, heavy accessories in the hair;
- wearing a small, ill-fitting, or tight headdress.
Some women note that most often the roots of their dirty hair hurt. Excess sebum in itself does not cause pain, so the following theses can explain the reason:
- Wanting to disguise not too clean strands, girls do not let them down, but collect them in a ponytail. This hairstyle can disrupt normal blood circulation in the root zone.
- Oily, contaminated skin is a place for the development of pathogenic microflora. If there are microcracks or damage on the skin, this is fraught with dermatological ailments, as a result of which the hair follicles begin to hurt.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
It is impossible to treat scalp pain at home. This symptom can be caused by various factors that require an individual approach to treatment. The doctor examines skin scrapings and hair follicles under a microscope; general and biochemical blood tests may also be needed. Based on the examination and laboratory results, a treatment regimen is prescribed. It may include the following steps:
- antifungal ointments and tablets;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- preparations against lice and nits, as well as other pathogens of dermatitis;
- proper nutrition - you should choose healthy foods with plenty of vitamins, avoid fatty foods, excess salt and spices;
- refusal of any products that cause allergies and irritation of the skin at the hair roots.
The Clinical Brain Institute has all the conditions for comfortable diagnosis and treatment of pain in the scalp. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the correctness of the diagnosis - for this purpose, our center has high-quality, modern equipment. Experienced doctors will select a set of drugs and procedures that will help get rid of pain and discomfort.
What to do if you have an allergic reaction to shampoo
The main thing is to stop using the cosmetic product that provoked the hyperreaction.
The consequences can be eliminated with the help of popular medications that are sold in any pharmacy. These are antihistamine tablets, ointments with cortisol.
If symptoms do not subside, consult a specialist. He will conduct allergy tests and determine what could cause the body’s reaction and prescribe more effective therapy.
Since the allergy itself is extremely difficult to cure completely, you will have to more carefully check the composition of shampoos and avoid the presence of an irritant in them. Then the quality of your life will remain at the same level.
If allergies occur to popular products with different compositions, it is recommended to use special hypoallergenic or baby shampoos.
A good option would be to use high-quality treatments for your hair type. Such shampoos and balms are presented in the ALERANA® series. They contain proteins, natural growth stimulants, and components that promote hair restoration. Active ingredients: plant extracts, provitamins B5, and natural hair growth stimulator Procapil®*. It actively nourishes hair follicles, making hair grow faster.
Prevention methods
Some reasons why the scalp hurts are associated with heredity and chronic diseases, but others are acquired. Their occurrence can be prevented by following simple recommendations from doctors:
- watch your diet, give up fast food, fatty foods and sweets;
- choose quality shampoos and other cosmetics;
- use a comb with soft teeth that do not injure the scalp;
- do not tie your hair in tight hairstyles;
- avoid stress, if necessary, select herbal-based sedatives;
- normalize your sleep, work and rest schedule.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of headaches and scalp soreness. The doctors of our center are experienced specialists in a narrow and broad profile. They will determine the reason why your scalp hurts and prescribe effective treatment. However, it is important for the patient to take responsibility for his own health: consult a doctor on time, and then take the prescribed medications as scheduled.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 6 votes
Share article on social networks
How to treat scalp diseases?
Having determined the reasons and made an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will definitely prescribe treatment. If the problem is hormonal imbalance, then, most likely, the first treatment will be prescribed drugs that optimize the level of hormones in the blood according to the patient’s gender. Physiotherapy, head massage and ointments that stimulate hair growth can also be prescribed as additional therapy.
Accordingly, immune-dependent alopecia is treated with the prescription of immunomodulators or drugs that eliminate the root cause of such a reaction of the immune system to the cells of the hair follicles.
If hair loss occurs due to stress, the patient is advised to get proper rest, avoid traumatic situations and take sedatives.
The fight against hair nodule diseases will primarily involve changing your hair care style and introducing substances into the body that help strengthen hair. Among them are tocopherol, retinol, phytin, gelatin (animal protein), vitamin F, etc. But in any case, you cannot prescribe any treatment yourself. This can lead to worsening scalp problems and other undesirable health effects.
Circulatory disorders
If your hair hurts at the roots after being in the cold without a hat, then the reason is most likely insufficient blood supply to the follicles, which occurred as a result of vasospasm from the cold.
Active instructions will help with hair loss and scalp pain
Several techniques will help you cope with the problem:
- Dry heat (wear a hat or scarf);
- Warm shower or bath;
- Scalp massage;
- Masks that improve blood circulation and warm.
If your hair roots hurt and your hair is constantly falling out, then you should use masks regularly. These can be home remedies with red pepper, mustard, onion, sea salt, etc. They will not only improve blood circulation, but also nourish. Also massage your scalp regularly. Special scrubs can also help. But if the hair loss is severe, consult a trichologist. As a result of proper therapy, not only will the unpleasant sensations in your roots go away, but your hair itself will become radiant and healthy.
Types of hair thinning in women
Androgenetic (androgenic) alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common cause of hair loss in both men and women: it accounts for over 90% of all alopecia. Androgenetic alopecia does not impair a person’s physical health in any way. This is an exclusively cosmetic problem, but it significantly impairs the quality of life, causing psychological discomfort.
Androgenetic alopecia is found in people whose hair follicles are genetically sensitive to androgens (male hormones). In the presence of such sensitivity, dihydrotestosterone has a negative effect on the hair follicles, as a result of which they decrease in size, thin out and die over time.
Androgenetic alopecia changes the hair growth cycle. The active growth phase (anagen) is shortened, and the resting phase (telogen), when the hair does not grow, lengthens. The ratio of anagen to telogen periods becomes less than 8:1, with the norm being 12:1. With each cycle, the anagen phase becomes shorter and shorter, while the telogen phase remains the same. Changes in the hair growth cycle lead to shortening of the overall hair length. Over time, the size of hair follicles decreases. Normal, healthy, thick hair is replaced by thin (vellus) hair that appears unhealthy and sparse.
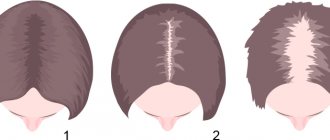
Female hair loss pattern
With androgenetic alopecia in women (female pattern of hair loss), the volume of hair in the frontoparietal zone decreases. Thinning on the crown is rare.
There are three stages of hair loss in women (according to the Ludwig scale): Stage 1 is characterized by noticeable thinning of hair in the frontoparietal zone and widening of the parting, while the marginal hairline remains unchanged. Stage 2 is diagnosed when there is severe hair thinning in the frontoparietal area. Stage 3 , in which hair in the frontoparietal zone is completely lost, is extremely rare.
Ludwig scale
Thinning in the central parting area
Thinning in the side parting area
Unlike men with androgenetic alopecia, women with the same diagnosis do not lose hair as intensely and abundantly, so there are practically no completely bald women. In addition, androgenetic alopecia begins to appear in women at a later age than in men and is more treatable.
The influence of hormones (androgens) on hair growth and loss
The effect of androgens on hair loss in men has been thoroughly studied and fully proven. As for women, in some cases there is indeed a relationship between hair loss and increased levels of male hormones in women (hyperandrogenism). In addition to hair loss, hyperandrogenism can also manifest itself with symptoms such as acne, hirsutism (increased facial and body hair), and menstrual irregularities. However, all these manifestations can occur even with normal levels of male hormones. Thus, hair loss that follows a female pattern is not always a consequence of hyperandrogenism. Genetic factors play a leading role in hair thinning in both women and men.
Treatment
Therapy with external and internal means
The most effective treatment for stopping hair loss and restoring hair growth is the following regimen: - Androgen receptor antagonists - cyproterone acetate (used in Europe and Canada) and spironolactone (used in the USA). These substances work to stop hair loss. — Hair growth stimulants – minoxidil, nitrolipins (Regeus).
Preparations containing these substances are applied externally directly to the areas of hair thinning and/or taken orally. The regimen and duration of treatment are determined individually. The earlier therapy is started, the higher its effectiveness. In later stages, when conservative treatment does not help, hair transplantation or the use of concealers is recommended.
Injections
The treatment method for androgenetic alopecia is based on the natural activation of regenerative processes. The essence of the method is to use your own cells, namely platelet-rich plasma. The drug is administered intradermally or subcutaneously, the course lasts at least 3 months. The treatment regimen is selected individually. Injection of platelet-rich plasma leads to the activation of key growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor (TGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). This cascade of reactions leads to regeneration and repair and ultimately to the restoration of the physiological cycle of hair follicles.
Traditional methods of treating alopecia
There are many folk recipes for increasing hair thickness. The most popular of them are scalding masks based on pepper. In the scientific and medical community, this method of treating alopecia is treated with skepticism and humor. Pepper, although it increases blood flow while applying the mask, cannot thus restore the normal functioning of the hair follicles. Using traditional recipes is not only useless, but can also be dangerous for the skin. However, some people are confident in the effectiveness of such remedies. Here you can read where these beliefs come from: https://regeus.ru/blog/it-will-help-a-folk-remedy-to-stop-hair-loss-and-regain-hair-density
Hair loss due to menopause
A separate and fairly common type of alopecia in women is hair loss due to menopause. At the same time, the level of androgens (male hormones) in women can be either elevated or within normal limits. The classic treatment for alopecia caused by menopause is oral finasteride or dutasteride (prohibited for use in women in the Russian Federation). The dose and regimen are selected individually.
Diffuse alopecia
Other names: telogen effluvium, symptomatic alopecia, telogen effluvium hair loss. Telogen effluvium hair loss is characterized by the loss of more than 100 hairs per day, with hair falling out evenly over the entire surface of the scalp. Of the hair shed, most of it is in telogen rather than anagen.
Causes
Acute telogen effluvium occurs in childhood after infections, as well as in women from 30 to 50 years old and can last 3-6 months. In women of any age (including the elderly), acute telogen effluvium can occur against the background of androgenetic alopecia and aggravate its course. In such cases, the patient is given two diagnoses at once: androgenetic alopecia and diffuse alopecia, although this is quite rare.
“In my practice, there was such a case, and the patient was convinced that the doctors simply could not understand what was wrong with her, that the diagnoses differed and this aggravated her psychological state (and this could aggravate hair loss). Please trust your doctors, ask questions, study scientific articles if you don't believe anyone. The effectiveness of treatment depends on this. Fortunately, such types of diagnostics as trichoscopy and trichogram help in making both diagnoses.”
Elizaveta Dubinskaya Dermatologist, trichologist
Provoking factors for diffuse hair loss: surgical interventions, hospitalization, taking certain medications (neuroleptics, anticoagulants, interferons). If diffuse hair loss continues for more than 6 months with exacerbations, then a diagnosis of chronic telogen effluvium is made. There are two forms of such alopecia: - primary idiopathic, predominant in women before menopause; - secondary, occurring against the background of systemic chronic diseases (especially against the background of hypothyroidism), as well as against the background of conditions such as nutritional deficiency, stress, depression, malignant neoplasms. Young patients with seborrheic dermatitis also experience increased hair loss in the telogen phase, but this issue still requires clarification of the cause-and-effect relationship.
Diagnosis and treatment
The differences between diffuse and androgenetic alopecia are not always obvious; moreover, cases of transition from diffuse to androgenetic alopecia have been recorded (Sinclair et al., 2004). Non-invasive diagnostic methods: hair traction test, hair washing test, dermatoscopy and trichogram are sufficient to establish most diagnoses. Histological examination may help but is rarely required. To treat telogen effluvium, it is important to quickly identify and, if possible, eliminate the triggering factors. No special acute treatment is required, and most patients recover spontaneously within six months. The prognosis for chronic telogen effluvium is uncertain; spontaneous improvement may occur after several years.
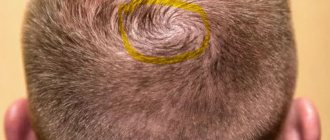
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is a chronic disease of the hair follicles, manifesting itself in the form of round, non-scarring foci of hair loss on the head, and less often on the body.
Causes
Many authors consider the autoimmune nature of the disease, when cells of the immune system attack hair in the growth phase. The interaction of aggressive lymphocytes with hair follicle cells, abnormal expression of certain tissue antigens, and the initiation of apoptosis (programmed cell self-destruction) contribute to the development of autoimmune inflammation.
Among the factors contributing to the development of the disease: genetic predisposition, microcirculatory and immune disorders, endocrine and metabolic disorders, adverse environmental influences. In addition, nervous system disorders at various levels play an important role. The literature has now accumulated a lot of data indicating various emotional disorders, the presence of hypothalamic pathology and autonomic disorders in patients with alopecia areata.
How does alopecia areata manifest?
Clinical picture: - presence of alopecia foci on the skin with clear boundaries; - the presence of stumps of hair in the lesion in the form of an exclamation mark and a “loose hair zone” at the border of the lesion (active stage); - detection during microscopic examination of hair epilated from the lesion of dystrophic proximal ends in the form of a “broken rope”; - the presence of light vellus hair in the growth area (in the regression stage); - sometimes along one edge of the lesion there are fragments of hair in the form of an exclamation mark, and on the opposite - the growth of thin hair; - detection during examination of nails of signs of onychodystrophy: thimble-shaped indentations, longitudinal striations, changes in the free edge in the form of wavy patterns.
If the disease is less than 1 month old, the following subjective symptoms may occur: hyperemia, burning, itching in the area of hair loss.
Treatment
Considering the autoimmune mechanism for the development of baldness, the main therapeutic direction is immunosuppression.
In very severe forms, drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids are prescribed orally. For milder forms, external treatment with drugs of the same group is used. Intradermal injections of diprospan are used simultaneously with the main line of therapy.
The course of the disease is often unpredictable; pathogenetic therapy does not always promote hair restoration and does not guarantee that there will be no relapses. To maintain hair growth, treatment must be continued until complete remission occurs.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the effectiveness of cryotherapy for the treatment of alopecia areata.
The effectiveness of cryotherapy for alopecia areata
Cryotherapy, a treatment with liquid nitrogen for the treatment of alopecia areata, is not widely used, although cryotherapy machines are available in dermatology offices.
The possibility of using cryotherapy in the treatment of alopecia areata was described back in 1986. The therapeutic effectiveness of surface cryotherapy has been proven in various studies. For example, studies have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment of alopecia areata with cryotherapy (1 treatment every 2 weeks for 12 weeks) and 0.05% clobetasol propionate lotion. It was shown that despite the lack of complete hair restoration (>95%), the response to treatment was 80% and 91.5%, respectively. This indicator is considered very worthy, taking into account the almost complete absence of side effects with cryotherapy, in contrast to clobetasol propionate. In a large study conducted on more than 350 patients, it was shown that 61% of respondents experienced restoration of normal guard hair growth, and at the initial stage of the disease and short intervals between procedures (no more than 2 weeks), the proportion of positive results was higher.
A large retrospective study published in 2006 found that 68.6% of 153 patients with alopecia areata achieved significant hair improvement, including terminal hair growth within 12 weeks of treatment. In 2021, a prospective study was conducted to compare the effectiveness of superficial cryotherapy and topical steroids as a therapeutic option. It was shown that 73% of patients experienced hair growth after cryotherapy (including 13% who experienced complete restoration of the lesion). Along with the general clinical improvement, the number of terminal (guard) hairs on the treated part of the head significantly increased by 1.6 times, in contrast to the control part, on which no significant changes were observed. Of course, one should remember the possibility of spontaneous remission, which occurs in 34% ~ 50% of patients during the first year of the disease. However, it cannot be ignored that the positive treatment results obtained in the various studies described can be interpreted as a significant therapeutic effectiveness of cryotherapy in the treatment of alopecia areata.
Thus, due to the minimally painful nature of the damage during the procedure and minimally invasive effects, superficial cryotherapy has been found safe and effective in the treatment of alopecia areata.
Traction alopecia
Traction alopecia is hair loss due to external traumatic action on the hair follicle. The main reasons for the development of the disease: frequent tugging, improper combing and addiction to tight hairstyles, including tight ponytails, frequent twisting of hair into buns, tight curlers, backcombing, dreadlocks. As a rule, the most affected hair is along the forehead, on the back of the head and temples, in the parting area, between the braids.
At the initial stage, traction alopecia may manifest itself as soreness of the scalp. At this stage, the disease is easily treatable: it is enough to eliminate the traumatic factor, change the hairstyle, and hair growth is restored on its own. However, if the problem is neglected, irreversible processes may begin; the disease will progress to the stage of cicatricial alopecia, when the hair follicles cease to exist. Unfortunately, with cicatricial alopecia, no remedies will help restore hair growth.
What hairstyles are most likely to cause traction alopecia?
Dreadlocks
Once you have dreadlocks, a person can wear them for several years. To achieve this hairstyle, hair - natural and synthetic - is twisted together to lengthen and add volume. Because of this, the weight of the hair and the load on the hair follicle increases. In addition, the hair is constantly tense: stretched and fixed in one direction - this leads to its excessive fragility and breakage. If you decide to get dreadlocks, there is a risk that you will remove them along with all your hair. This is perhaps the most dangerous hairstyle.
Braids
Tight weaving of hair, joining in different directions, fixing in rows and lines when creating complex patterns severely injures the hair and provokes hair loss. Beautiful, complex weaves can be done sometimes, but for a daily hairstyle it is better to choose something else.
Bouffant
Backcombing also injures and damages strands, overloads the roots and can lead to hair loss. Hairstyles that require backcombing are also best done on special occasions and not overused. Otherwise, in an effort to have a voluminous hairstyle, you can lose this volume irrevocably.
Postpartum hair loss
Hair loss in women due to pregnancy, childbirth, and lactation is a normal physiological process caused by hormonal changes in the body. Treatment during this period is ineffective. Normally, hair growth should recover on its own within a year after giving birth. If after a year the hair is still falling out intensively and losing volume, this is an alarming symptom: it is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible.
Other types of hair loss in women
Unfortunately, hair loss is still a poorly studied area by science. In our article we have listed the main ones, but there are still many other types of hair loss that are extremely rare.