1. Tumors of the transparent septum
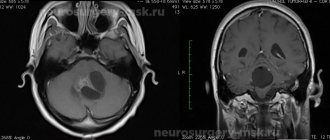
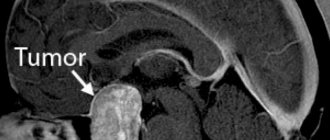
Among brain tumors localized in the area of the septum pellucidum
, the most common are ganglioneuroma and central neurocytoma.
Ganglioneuroma
, or otherwise ganglioma, gangliocytoma is a benign tumor usually reaching small sizes - up to 4 cm. Ganglioneuroma is formed mainly by glial cells and does not have a capsule. Neoplasms tend to infiltrate into the spinal canal and posterior mediastinum.
Central neurocytoma
It is also a benign tumor and is quite rare - in only half a percent of cases of the total number of brain tumors. The usual location of neurocytoma is the lumen of the lateral ventricles closer to the area of the transparent septum. Central neurocytoma is characterized by slow growth and does not have a tendency to become malignant. This pathology affects both men and women in the age range from 15 to 40 years.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Septal agenesis: symptoms
Agenesis of the septum pellucidum is a serious congenital pathology of brain development caused by improper development of the corpus callosum in the fetus. This is a very rare anomaly of the central nervous system, caused mainly by hereditary factors, genetic mutations and insufficient supply of nutrients to the embryo. Another reason may be toxic drugs that a woman takes during pregnancy.
At birth, children with this pathology are practically no different from healthy ones; clinical signs begin to appear at the age of 2-3 months.
The main symptoms of agenesis of the cavity of the transparent septum include:
- formation of cystic cavities in brain tissue;
- atrophy of the auditory and optic nerves;
- fits and seizures;
- microencephaly.
As a rule, this malformation of brain development is preliminarily diagnosed in the second trimester of pregnancy (after 18 weeks) and is confirmed by a set of diagnostic measures after birth. An ultrasound examination of the newborn's brain, CT scan of the head, and, if necessary, MRI and neurosonography are performed.
2. Symptoms of tumors of the transparent septum
The most characteristic of tumors of this localization is damage to the hippocampus, the cortical center of smell. It causes olfactory disturbances
associated with difficulty recognizing odors and olfactory hallucinations.
In addition, the general symptomatic picture is not much different from the signs that are usually characteristic of most brain tumors:
- increased intracranial pressure;
- headache, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- clouding of consciousness;
- muscle weakness, paralysis of the upper/lower limbs;
- visual disturbances;
- poor coordination of movements, unsteady gait;
- mental disorders.
Visit our Neurosurgery page
Causes and mechanism of formation
A capsule with liquid inside can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital form of Verga's cyst:
- diagnosed in young children in 60% of cases, and in cases of prematurity in almost all;
- in this case, it is almost always asymptomatic and is often diagnosed accidentally;
- usually does not require treatment and is eliminated in 75% on its own;
- The cause of the cavity is pathology of fetal development, intrauterine infection and injury.
Acquired form of cyst:
- occurs during life due to head injuries, concussions, cerebral hemorrhages, inflammatory and infectious lesions of the central nervous system;
- this form can develop to large sizes, thereby causing health complications;
- To avoid worsening the situation, the acquired form must be systematically observed and treated.
3.Diagnostics and treatment
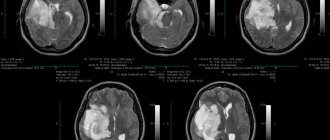
Diagnosis of tumors is carried out using both MRI and CT
, and using special methods -
electromyography and electroneurography
.
This helps assess the condition of the patient's neuromuscular system. In addition, neuro-lumbar puncture
for histological analysis.
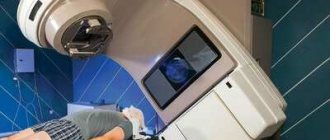
surgery is used to remove central neurocytoma.
using transcranial access. However, this is not always possible due to the deep location of the tumor. In this case, radiation therapy is used.
Today, an innovative technique is used to remove a tumor using a cyber-knife - targeted, high-precision irradiation of a tumor with powerful beams of ionizing flux.
. It is envisaged that a high dose of radiation accumulates exclusively in tumor tissues, making them nonviable, but without affecting healthy tissues.
Regarding the diagnosis and treatment of ganglioneuroma
, then there are certain features. A clear diagnostic sign can be an increased concentration of norepinephrine, dopamine and prostaglandins in the urine and blood serum. Treatment of the tumor in most cases is carried out conservatively, or more precisely, by administering a special medicinal solution designed to cause sclerosis of the tumor. If the desired effect is not achieved, it is surgically removed. It should be noted that there are cases of random disappearance of ganglioneuroma without medical intervention.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diagnostics
Pathology in a child can be detected during pregnancy
The pathology is diagnosed in the 2-3 trimester of pregnancy. During the prenatal period, it is quite difficult to identify brain abnormalities, since the fetus may assume a position that does not allow a clear view of all brain structures. The anomaly can be determined by ultrasound from the 18th week of pregnancy, not earlier. After birth, encephalography, ultrasound, CT, and MRI are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis.
The structures of the cranial cavity in children from birth with possible agenesis can be examined using neurosonography. The procedure is carried out through an open fontanel. Thanks to neurosonography, it is possible to examine the structures of the brain. Ultrasound can detect pathology in the brain even if it is not accompanied by symptoms. Thanks to computed tomography, it is possible to assess the condition in detail and identify possible disorders in the brain, as well as identify possible formations.
If agenesis of the septum pellucidum and corpus callosum is suspected, an MRI is performed.
This method complements neurosonography and makes it possible to detect the absence of a septum and changes in the structure of the ventricles of the brain. Magnetic resonance imaging helps determine the nature of the lesion, the absence of a transparent septum and other pathologies that cannot be determined by ultrasound. If agenesis is partial, then it is even more difficult to identify pathology.
Can it develop into cancer?
In extremely rare cases, a benign Verge's cyst degenerates into a cancerous tumor. This occurs if the tumor develops as a result of a pathological lesion of another organ.
Only acquired cysts of the transparent septum of the brain are susceptible to malignancy. If a malignant transformation has occurred, then rapid growth occurs, squeezing adjacent healthy tissues and blood vessels.
The danger of this condition is that such a cancer progresses rapidly, and treatment practically does not give any result, which is why the patient dies. Therefore, it is important not to delay treatment and contact a specialist at the first symptoms.
Types of damage to the transparent septum of the brain
The human brain contains many interesting and thoroughly unstudied components, one of which is the transparent septum of the brain. It includes two rather thin sheets of brain tissue that form the slit-like space, and separates the anterior part of the brain from the structures of the corpus callosum. Normally, the cavity of the transparent septum is square-shaped and contains cerebrospinal fluid. Let us consider the types of pathology of this formation, the tactics of managing patients with various diseases.
Diagnostic value of brain structure
The transparent septum of the fetal brain is one of the criteria for assessing the formation and degree of brain development in an unborn baby. Expectant mothers regularly undergo ultrasound examinations to identify possible developmental disorders of the child.
When examining the head on the monitor, the presence of a septum, the size of the gap between its sheets, and the correspondence of the size to the duration of pregnancy are studied. In the second half of pregnancy, its dimensions are 1.8–9.4 mm. If pathology is suspected, the study is carried out dynamically. After the birth of a child, it is recommended to conduct neurosonography through the fontanel to confirm or remove the diagnosis of a defect in the transparent septum of the brain in newborns.
Features of the course of a cyst of the transparent septum
One of the most common diseases is a cyst of the transparent septum. It is formed when free circulation is disrupted and cerebrospinal fluid accumulates in the septum area. The features of this pathology are:
- predominantly asymptomatic;
- the presence of a cyst in approximately half of full-term babies and in almost all children who were born earlier than expected;
- in most cases, it is eliminated on its own, without requiring therapy.
The pathology can be congenital and result from fetal developmental disorders, congenital anomalies, or infections. The acquired disease is provoked by head injuries, concussions, inflammatory and infectious lesions of brain tissue, and hemorrhages in brain structures.
A congenital cyst in the form of an enlarged cavity in the transparent septum of the brain in an infant has no clinical signs. If the pathology occurs after inflammation or injury, the cyst can grow and cause symptoms:
- bursting headache that occurs when brain structures are compressed;
- dysfunction of the visual and auditory analyzers - the patient complains of decreased quality of vision and poor hearing;
- There may be a sensation of noise in the head.
As the size of the cyst increases, other manifestations appear, which depend on the location of the pathological focus.
Treatment of cysts of the transparent septum of the brain includes medical and surgical approaches. The medications prescribed include diuretics and medications that help resolve hematomas, scars and adhesions. Their task is to eliminate the “blocks” that form the cyst and reduce its size.
Medicines are also used to improve cerebral circulation and central nervous system activity. If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical treatment is used - the adhesions and capsule are cut endoscopically, eliminating the cyst. Dangerous consequences of the disease include a tendency to form secondary adhesions, hydrocephalus, and stroke.
Absence or underdevelopment of the cerebral septum
There is another type of disease - agenesis of the transparent septum of the brain, which consists of the absence of space (cavity) between the sheets of the septum. This structural brain disorder occurs as one of the severe congenital brain abnormalities. Its reasons may be:
- hereditary factor, various mutations;
- maternal infections, taking certain medications (Phenytoin, Trimethadione and others) in the first weeks after conception;
- to a lesser extent, malnutrition and alcohol abuse have an effect.
The pathology manifests itself in a baby older than 3 months; before this age he does not have any disorders. The basic symptoms of the disease include:
- formation of microcephaly;
- porencephaly - the formation of cavities, cysts filled with cerebrospinal fluid;
- atrophy (destruction) of the auditory and optic nerves;
- problems with the formation of convolutions.
Sick children are also characterized by early puberty and the occurrence of pathological seizures such as epilepsy.
Important! In the case of partial agenesis, the prognosis is quite favorable, the children grow and develop under the supervision of a neurologist.
Therapy is used mainly symptomatically to improve well-being and eliminate epileptic seizures and convulsions, calm the baby, and relieve tension. With the development of exclusively insufficiency of the septum pellucidum, children have a chance for a full life; if multiple brain defects are present, then the prognosis is unfavorable.
(1 ratings, average: 2.00 out of 5)
Symptoms and diagnosis
A congenital cyst of the transparent septum of the brain in the absence of growth is devoid of symptoms, but if it develops or its acquired form, then its small size causes the following symptoms:
- headache of a compressive nature, arising from compression of brain tissue;
- decreased vision and hearing functions;
- the occurrence of auditory hallucinations such as noises and ringing;
- increased blood pressure;
- tremor of the limbs.
Over time, more severe symptoms appear, the nature of which depends on the location of the tumor.
Since the acquired form of Verge's cavity tends to develop uncontrollably, it should be constantly monitored. For this purpose, the following is periodically performed:
- MRI of the brain;
- computed tomography of the head.
Using these procedures, it is possible to carry out differential diagnosis to determine whether it is a cyst or a tumor. When a contrast agent is administered intravenously, the tumor accumulates it, and the capsule remains inert.
As additional examination procedures in which a cyst of the cavity of the transparent septum is visible, the following are carried out:
- Fetal ultrasound;
- ECG of the heart;
- blood pressure control in order to determine the risk group for the development of stroke after which neoplasms are formed;
- blood test to detect infection.
Cyst of the transparent septum of the brain in the photo is shown by arrows
If an MRI shows growth of the tumor, additional measures are taken to determine the cause of its development. First of all you should:
- determine the location of the inflammatory process and the quality of blood clotting;
- identify disturbances in the functioning of the circulatory system; to do this, examine the blood flow in the vessels of the head using ultrasound, which makes it possible to find places of ischemia where capsules develop;
- identify possible autoimmune diseases;
- check the blood for cholesterol in order to determine the predisposition to atherosclerosis, which is the reason for the formation of cysts;
- They check cardiac activity using ECHO-CG to check for abnormal heart rhythms or identify signs of heart failure.
For procedures and consultations, you should contact a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Forecast
If Verge's cyst was diagnosed at an early stage, then in this case the prognosis is favorable. If there is no growth, special treatment is not even required.
The patient should only be periodically examined with MRI. As the cystic formation progresses, the prognosis worsens.
If the capsule is single-chamber, then the operation provides an almost 100% guarantee of healing. With multiple walls and cavities, even after surgical removal there remains a risk of relapse.
At advanced stages, a cyst sometimes degenerates into a cancerous tumor, which often leads to death, so it is important to seek help in time to prevent dangerous consequences.