Methods for plastic surgery of a bone defect of the skull
A bone defect in the skull is a hole in it that forms after neurosurgical intervention on the organs of the central nervous system or as a result of trauma.
Let's talk in more detail about skull defects in medical practice. After removing a section of bone and creating a hole in the skull, patients experience not only psychological discomfort, but also the so-called “trepanned skull syndrome.” In both cases, the hole must be closed with an implant. And now about everything in more detail.
Consequences after craniotomy
The severity of the consequences in the postoperative period depends on the reason for the operation, the age of the patient, and the presence of concomitant diseases. If neurological disorders were not immediately detected after trepanation, this does not mean that they will definitely not arise in the future. If the cerebral cortex is damaged, hearing and vision impairment of varying severity, up to complete loss, may occur.
The consequence may be a stroke due to thrombosis or thromboembolism. During trephination for abscesses, pathogenic flora may spread through the membranes of the brain, which will lead to meningitis and encephalitis. After many hours of anesthesia, disorders of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are possible. If the neurovascular bundles are damaged, numbness, complete loss of sensitivity, and movement of certain areas of the skin, muscles, and limbs are possible. Postoperative consequences can manifest themselves in the form of mental and behavioral disorders.
Consequences of skull defects
The bones of the skull not only protect the brain from mechanical damage. The absence of one area can cause a lot of unpleasant symptoms or complications for the patient. It is their presence that serves as a direct indication for surgical plastic surgery.
It could be:
- Headache. It occurs not only at the site of the defect, but also affects other areas. Most often, the symptom intensifies or occurs when there is a change in atmospheric pressure and air temperature. The so-called meteosensitivity appears.
- "Astheno-neurotic syndrome." These include complaints of absent-mindedness, decreased concentration, difficulties in solving intellectual problems, frequent mood swings, decreased ability to withstand stress and tolerance to alcohol.
- Protrusion of the contents of the skull outward. When coughing or sneezing, physical stress or exertion, part of the brain substance can protrude through an opening in the skull, under the skin. This leads to traumatization of internal tissues at the edges of the bone defect.
- Symptomatic epilepsy.
- Mental disorders.
Consequences
Complications of the postoperative period can be caused by brain damage even before treatment, the quality of surgery and subsequent medical care, and the characteristics of the patient’s body .
Consequences of the trepanation procedure
Opening the cranial frame can cause swelling of the brain matter near the surgical site, and cause temporary neurological impairment . The nature of the disorders and their manifestations (lack of balance, paralysis, speech problems, blurred vision and other changes) depend on the location of the edema. Most often, the deviations disappear after the swelling disappears. Protracted, deep and extensive disruption of the tissue structure leads to the persistence of negative changes for a long time, sometimes throughout life .
During surgery, many blood vessels are damaged , as a result of which the surgical area may bleed for a long time. To avoid critical consequences, doctors install drainage to remove blood from the cavity of the cranium. Otherwise, the accumulating mass may touch the nerve fibers and cause seizures. Continuous bleeding becomes a reason for repeated surgery.
An inevitable consequence of trepanation is deformation of the cranial frame at the site of surgical actions. In the area of incisions, connective and bone tissue cells often grow and a colloidal scar is formed. To eliminate a cosmetic defect, one has to resort to plastic correction of the skull bones . As a rule, young people take this step.
General complications after surgery
Compliance with antiseptic rules practically prevents infection from entering the brain cells during the operation. Problems arise during the wound healing period . With proper care, it is possible to effectively extinguish inflammatory processes and avoid complications.
The risk of infection in the postoperative period threatens internal organs : lungs, bladder, intestines. This is due to the limitation of the patient’s activity. The following preventive measures are recommended: special diets, therapeutic exercises, and adherence to a daily regimen. In critical situations, antibiotics are prescribed.
Another acute problem of the postoperative period associated with limited mobility and pathological biochemical processes in the body is the formation of blood clots in the circulatory system. Most often they form in the vessels of the lower extremities. Such a formation can clog blood vessels, block blood flow, and cause a malfunction of various organs. As a preventive measure, therapeutic massage, compresses and anticoagulants are prescribed.
Postoperative therapy involves taking many medications (painkillers, anticonvulsants and other drugs), the effect of which is shocking. Side effects of taking large doses of drugs include digestive disorders, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, mental instability and a number of other manifestations.
After surgery, patients often feel severe emotional discomfort , fall into a depressed state, and need moral support. In most cases, the participation of loved ones is sufficient; in difficult situations, the help of a psychotherapist is required.
Long-term consequences of surgical intervention manifest themselves in the form of the following pathologies:
- Stroke.
- Asthenia.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Memory disorder.
- Impaired speech skills.
- Deterioration of hearing and visual acuity.
- Frequent headaches.
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Infectious diseases.
Cranioplasty
This is the name of the operation to restore the tightness of the skull. It is designed to restore the brain’s protection from external influences, normalize blood and lymph flow, eliminate the above symptoms, cosmetic defects and relieve psychological discomfort.
The essence of the procedure is to close the hole in the skull with an implant. A competent neurosurgeon will help you understand the great variety of implants offered by medicine today and choose the best one. Fill out an application on the website or call us to get advice from a leading specialist to choose the right implant and discuss the features of the upcoming operation.
We will tell you what types of cranioplasty implants there are and how the operation to install them is performed.
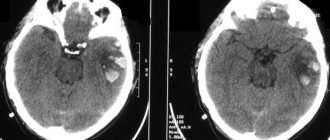
1. Reasons for the formation of defects in the skull bones
Defects of the skull bones
– a pathology characterized by the absence of a segment of cranial bone tissue. Defects are divided by location area, damage location, and size.
Causes of formation of skull bone defects
Traumatic brain injury may contribute to the occurrence of a cranial defect.
received as a result of an accident, a fall from a height,
a blow to the head, or a gunshot wound
.
Another cause of the defect is resection of a bone segment
as a result of craniotomy.
Iatrogenic intervention (trephination with removal of part of the bone tissue) is a consequence of pathologies such as a tumor, brain abscess and other types of suppuration, post-traumatic or spontaneous hematoma inside the skull.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Implants
There is a list of mandatory qualities that they must have:
- sufficient strength;
- biocompatibility;
- ease;
- plastic;
- do not cause infectious complications;
- do not have a carcinogenic effect.
Implants can be made from the patient's own bone (autografts) or artificial (xenografts).
Autografts
This is bone that has been temporarily removed to access the patient's brain tissue. If the bone needs to be preserved to close a skull defect later, it is placed under the skin of the patient's abdomen or anterior outer thigh. If such preservation is not possible, other techniques using the person’s own bone tissue are used. And if it is impossible to replace the defect with autografts, they resort to materials replacing them.
Xenografts
The so-called “artificial bones” are made of metal (aluminum or titanium), using methyl methacrylate or hydroxyapatite.
Each of the mentioned implants has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, hydroxyapatite can be used for defects up to 30 square centimeters. This material is completely biocompatible. And it is able to turn into its own bone tissue after 18 months with small defects. And the risk of infectious complications for this type of implant is the lowest among similar ones.
Titanium is the least likely to cause local inflammatory reactions. And from it it is possible to recreate lost fragments of the facial skeleton, the base of the skull, the vault and the walls of the orbit. This is done using simulation and neuronavigation in the preoperative period.
The doctor will help you understand the variety of implants, as well as find out what the latest medical developments in the field of implantology are, during an in-person consultation. Fill out an application on our website and we will make an appointment with a leading specialist in the field of neurosurgery.
In each specific case, it is important to take into account not only the direct benefits for a person, but also the aesthetic and psychological aspects. As well as restrictions imposed on the patient in connection with the choice (for example, a metal implant does not allow the patient to subsequently resort to MRI examination).
3.Reconstruction of the skull bones
In modern medicine, the main method of reconstructing the skull bones is cranioplasty.
. This is a plastic surgery during which the resulting defects in the cranial bone and dura mater of the brain are closed with an artificial implant.
The need for cranioplasty is determined by the presence of the following symptoms and indications:
- post-traumatic epileptic seizures;
- cerebral (speech, motor) disorders;
- cosmetic restoration;
- prevention of re-damage.
The operation is contraindicated
with the development of an intracranial infection, the presence of a foreign body in the brain, or with a serious condition of the patient.
In the course of eliminating defects in the skull bones using cranioplasty with the surgical production of an implant, first of all, the scar of the meninges is dissected with minimal risk of damage to brain tissue. The most effective fusion with bone tissue is achieved by precisely matching the graft to the size and shape of the defect. The implant is placed behind the exposed edges of the lesion and securely fixed to avoid future displacement.
3D computer visualization technology is used to prepare the implant during surgery.
.
Based on a three-dimensional image of the skull, using laser stereolithography
. Then the missing segments and their molds are reconstructed.
Formatted implants are sterilized before use.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!