- What is brain cancer
- First manifestations and symptoms
- Possible treatment
- Stages of brain cancer
- Prognosis for brain cancer
Malignant brain tumors (BM) are not the most common type of cancer. But such diseases are more life-threatening for patients, as they directly affect a vital organ. Brain cancer is confidently associated in people’s minds with an incurable disease, however, methods for diagnosing and treating malignant neoplasms of this localization have rapidly developed over the last decade, which makes it possible to successfully cope with such a disease.
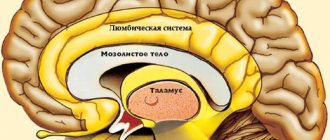
What is brain cancer?
A malignant tumor or cancer is a disease that begins with a mutation. If a cell begins to grow uncontrollably, a benign or malignant neoplasm occurs in the body. A tumor made from malignant cells is especially dangerous: its components lose the properties of their “native” tissue, multiply non-stop and spread metastases (mutant cells) throughout the body.
There are many types of malignant tumors of the brain, but they can be divided into two groups:
- primary, which initially develop in the brain (from cells of the medulla, meninges, pituitary gland, cranial nerves, embryonic tissue in children, etc.);
- secondary or metastatic, which are brought into the brain from the outside (from a tumor in the lung, breast, etc.).
Breast cancer occurs more often in men than in women. This disease is diagnosed more often in children than in adults. Paying attention to the early signs of brain cancer can save lives and keep you healthy.
Survival of patients with breast carcinoma who develop brain metastases is closely related to the subtype of carcinoma. The same applies to the location of metastases.
HAMBURG. Approximately 30% of patients with metastatic breast cancer develop metastases to the brain despite systemic therapy. After lung cancer, breast cancer ranks second among malignant neoplasms, which in most cases metastasize to the brain. In general, malignant tumors are more often located in the brain than primary tumors.
The increasing incidence of brain metastases in patients with breast cancer is likely due in part to the fact that it is now possible to provide better control of the disease outside the skull. This is also facilitated by improving the quality of imaging diagnostics. However, at the same time, the increasing incidence of brain metastases also indicates the inability of the current treatment regimen to prevent tumor spread to the brain.
In order to raise awareness of the clinically important group of patients whose breast cancer has metastasized to the brain, leading breast centers in Germany have united under the auspices of the German Breast Group to jointly conduct the “Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer Network Germany” (BMBC) study. Recently, a research group led by Isabelle Witzel from the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf published in the European Journal of Cancer (2018; online August 9) an analysis of data from 1,712 breast cancer patients with brain metastases from 2000 to 2021 gg.
The average age of women was 56 years (22-90). 48% of women were diagnosed with HER2-positive tumors, 21% with triple-negative breast cancer, and 31% with luminal breast cancer (hormone receptor positive, HER2 negative). The proportion of HER2-positive brain metastases decreased during the study period; in 2000-2009 it was 51%, and in 2010-2015. - 44%. The number of cases of luminal types of cancer, on the contrary, increased proportionally from 28% to 34%.
Metastases were localized in the anterior cranial fossa (31%), in the posterior cranial fossa (23%), or in both cranial fossae. Leptomeningeal metastases were diagnosed in 9% of patients. 54% of metastases in the posterior fossa were HER2-positive, 60% of leptomeningeal metastases were of the luminal type.
92% of patients had at least one attempt at local therapy. 28% of patients underwent surgery, and 94% of patients received radiation therapy after surgery. 64% of patients received radiation therapy, which included stereotactic treatment (7%), whole-brain irradiation (89%), or both.
After diagnosis of brain metastases, the average life expectancy of patients remained 7.4 months. 38% survived the first year. The average survival time for patients with HER2-positive tumors was a maximum of 11.6 months, compared with 5.9 months for patients with luminal tumors and 4.6 months for patients with triple-negative metastases. With anti-HER2 therapy, the average life expectancy of patients with HER2-positive tumors was 17.1 months; without such treatment, patients lived an average of 7.2 months.
“The prognosis for patients whose breast carcinoma has metastasized to the brain depends largely on the tumor subtype,” summarizes Witzel and her colleagues. The results highlight the urgent need to improve treatment and prevention strategies for such metastases in women with breast cancer.
The average life expectancy for breast cancer patients with HER2-positive brain metastases was 11.6 months. With luminar type of tumors, the life expectancy of patients was 5.9 months, in the presence of triple-negative metastases - 4.6 months.
Contact us
The Center for Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Cancer at the City Clinical Hospital of Solingen is one of the most famous and modern not only in Germany, but in Europe. If you have any doubts about your health, please contact our specialists for advice: Email: [email protected] Tel.: +49 212 5476913 Viber | WhatsApp: +49 173-2034066 | +49 177-5404270 For your convenience, please save the phone number in your phone book and call or write to us for free on WhatsApp, Viber or Telegram. Applications made on weekends or holidays will be processed on the first business day. In urgent cases, request processing is carried out on weekends and holidays.
First manifestations and symptoms
The first signs of breast cancer are not highly specific, but their appearance requires an unscheduled consultation with a doctor. Among these symptoms:
- Headache. This malaise is a typical cerebral sign of a progressive tumor.
- Movement disorders. The arm begins to bend poorly, the leg ceases to obey, and hypertonicity of some muscles appears.
- Nausea and vomiting. This general cerebral sign of brain cancer can appear outside of meals, including on an empty stomach. Sometimes a wave of uncontrollable gushing vomiting comes without preliminary nausea, suddenly and reflexively.
- Dizziness. The main reason for this symptom is increased intracranial pressure. The discomfort is complemented by tinnitus and hearing impairment.
- Mental signs. Patients note a feeling of stupefaction, attention weakens, and memory and perception are dulled. There may be a decrease in criticality, deterioration in associative thinking, lethargy and indifference.
The way brain cancer manifests itself also depends on the location of the tumor. Before signs of increased intracranial pressure appear, the patient often experiences an epileptic syndrome. Convulsive tonic-clonic seizures manifest themselves in brain cancer of different locations, but most often such symptoms are typical for damage to the frontal lobes.
Types of brain tumors
Brain tumors are classified according to histological and topographic principles. Depending on the type of cells that make up the formation, there are:
- Meningiomas
are formed from the endothelial tissues of the meninges. This type accounts for more than a quarter of all brain tumors, most of which are benign.
- Gliomas
are a group of neoplasms of neuroectodermal origin, that is, developed from glia, the cellular structures that are the precursors of neurons.
- Astrocytomas are infiltrative tumors with a low degree of malignancy. Develops from astroglial cells that are part of the gray matter of the brain.
- Sarcoma
is a malignant tumor formed from mutated connective tissue cells.
Based on the site of formation, brain tumors are divided into:
1. Cerebellar tumors.
About a hundred histological varieties of neoplasms of this localization are known, accounting for up to 30% of all types of brain tumors. Even benign neoplasms pose a danger to life, since when they grow, they infringe on the brain structures responsible for blood circulation and respiration.
· Frontal lobe tumors.
They are represented by both benign and malignant gliomas and meningiomas. Their main symptom is movement disorders.
2. Temporal tumors.
Primary tumors of this location in most cases are adenomas and astrocytomas that develop from Schwann (glial) cells. Temporal tumors as secondary lesions can occur during metastasis of a malignant tumor of the eye (retinoblastoma), kidney (hypernephroma), skin (melanoma), etc.
3. Brain stem tumors. These are most often glial or neuronal-glial tumors. They are treated with chemotherapy and radiation - surgery here is dangerous, since this area of the brain is responsible for vital functions. Distinctive symptoms of this type of neoplasm are disturbances in hearing, swallowing and skin sensitivity. Brain tumors in children often have exactly this, the most dangerous, localization. Usually these are astrocytomas or blast tumors prone to cystic degeneration
4. Pituitary tumors.
The rarest type of brain tumor, occurring in one in a thousand people. Neoplasms develop on the anterior or posterior lobe of the gland and in most cases are benign adenomas.
Possible treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the type of tumor, its location and size. Doctors analyze the stage of the disease, the patient’s condition and the presence/absence of metastases, conduct tests and diagnostic procedures.
The optimal treatment option is complete removal of cancer cells. Advances in neurosurgery make it possible to perform low-traumatic and highly effective interventions on the brain. But the problem is that removing cancer tissue can be very difficult. GM neoplasms are prone to diffuse growth, they spread to nearby structures and tissues. For imaging, doctors use modern optical medical equipment and contrast agents.
Treatment may also include:
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- brachytherapy;
- stereotactic radiosurgery.
Patients are required to be prescribed medications that can reduce symptoms of brain cancer and support the body. Inoperable cancer requires palliative supportive treatment.
Causes of brain tumors
Factors that may be associated with an increased risk of developing a brain tumor include:
— Presence of any type of tumor in a family history;
— Some types of genetic syndromes;
— Exposure to ionizing radiation (this applies to both professional activities and treatment with radiation therapy);
— Exposure to chemicals, in particular acrylonitrile, formaldehyde and vinyl chloride;
- Injuries in the head area.
Stages
Doctors distinguish 4 main degrees of brain cancer:
- The neoplasm is small in size, does not affect or compress nearby structures, and does not metastasize.
- The tumor noticeably increases in volume, can disrupt the activity of nearby healthy areas, and also germinate into them; there are no metastases.
- The neoplasm is moderately aggressive, often inoperable, and can produce single metastases.
- The neoplasm reaches a significant size, affects other parts of the organ and gives distant metastases.
The rate of tumor progression depends on the type of cancer. Sometimes cancer develops very slowly, while other tumors are extremely aggressive.
Diagnosis of brain tumors in Israel
The screening program for a brain tumor includes:
— Test blood tests, clinical and advanced;
— Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF);
— X-ray, angiography and echoencephalography of the brain;
— Determination of fields of view;
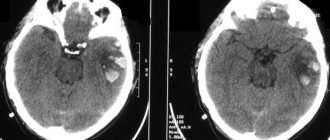
- Navigation tomography - computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. MRI is considered the most effective method for diagnosing tumors, as it allows you to obtain a detailed layer-by-layer image of the organ.
— Biopsy followed by microscopic and histological analysis of a tissue sample;
— Electrocardiography;
— Chest X-ray;
— Consultations with a neuro-oncologist, radiotherapist, anesthesiologist.
PET-MRI device has been installed at the Assuta clinic
allowing for full visualization of the brain and identification of microscopic molecular changes at the initial stage. The PET-MRI method is currently considered the most promising and effective way to diagnose brain tumors.
Prognosis for brain cancer
If a tumor is detected at an early stage of development, after which the correct complex treatment (surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy) is selected, more than 60% of patients can be saved. Late stages of brain cancer or inoperable tumors allow only 30% of patients to survive more than 5 years. However, some types of tumors are more aggressive - glioblastoma reduces the chance of five-year survival to 5%, but some patients can live with the disease for years. Therefore, it is simply unrealistic to accurately predict how long a patient will live after diagnosis. Even in case of successful treatment, a person after brain cancer remains at risk, because the tumor can recur.
Treatment of a brain tumor in Israel
When choosing treatment methods, the type and size of the tumor, the stage of its development, as well as the patient’s health condition are taken into account. For operable tumors, the surgical method of craniotomy resection is most often used - the tumor is excised with access through small holes cut into the skull.
In Israel, operations to remove a brain tumor are often performed under local anesthesia.
After resection of the tumor, a sample of its tissue is sent for rapid analysis to determine the degree of malignancy. The rehabilitation period is usually two weeks. If the tumor is found to be malignant based on the results of histopathology, the patient is prescribed postoperative chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Malignant brain tumors of stages 3 and 4 are mostly inoperable, with the exception of some types of temporal tumors. Then the patient is prescribed several cycles of local irradiation of the tumor or a course of chemotherapy. Drugs that inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells are taken orally or administered intravenously.
At the moment, it has become possible to simultaneously treat several brain tumors (up to 10) thanks to the technology that the Assuta clinic was the first in the world to implement. This unique procedure makes it possible to target several tumors with radiation in one session without affecting healthy areas. This highly effective and safe procedure does not require anesthesia or hospitalization.
Why is it worth coming to Germany for brain cancer treatment?
In addition to the general reasons and advantages of treatment in Germany, which we described in this section of the site, in Germany doctors never refuse to treat patients who have already come to their clinic for treatment. If the doctors agreed to accept you for treatment, then they will not send anyone home to die, but will fight to the end. When making decisions about the need to use a particular technique, German doctors proceed from the patient’s condition and the appropriateness of treatment, but they never refuse further treatment simply because of the patient’s age, as is often the case in other countries. If it becomes obvious that it is no longer possible to stop the progression of the disease, the patient is offered a well-thought-out palliative program to alleviate suffering and relieve pain as much as possible.
Brain tumor stages
Benign tumor
goes through three stages of development:
· Initiation stage - as a result of gene mutation, some cells gain the ability to reproduce rapidly;
· Promotion stage - a small tumor focus is formed from mutated cells;
· Progression stage - the tumor begins to increase in size without losing clear boundaries.
The degree of development of a malignant brain tumor
is established according to the international classification, depending on the size and prevalence of the tumor.
· Stage I
– the tumor focus has clear boundaries and measures no more than 2 cm. The only sign of a brain tumor in the early stage may be a persistent headache.
· Stage II –
the tumor size exceeds 2 cm, a single metastasis is possible. Due to the increase in intracranial pressure during this period, nausea and vomiting may occur.
· Stage III
- the process of malignant degeneration involves neighboring tissues, secondary tumor foci are possible in the lymph nodes. At this stage, symptoms characteristic of a particular localization of nooplasma appear. It depends on what functions the area of the brain affected by the tumor is responsible for.
· IV stage
- large-scale damage to brain tissue has occurred, the tumor is growing rapidly, has spread to surrounding tissues, multiple secondary foci (metastases) can develop in any organ.