Causes of long-term headaches
Soreness is a natural reaction of the body to inflammatory processes, insufficient blood supply, spasms and other factors. The headache is called cephalgia. It can have different origins, and therefore requires an individual approach during treatment. Thus, there are several types of long-term cephalalgia:
- vascular – occurs as a result of acute and chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, as well as when blood pressure regulation is disturbed;
- nervous – caused by stress, lack of rest, intense exercise;
- infectious – provoked by poisoning with various substances;
- tension pain – associated with spasms of muscles and blood vessels.
The exact cause of the headache is determined based on the results of a complete examination. At home, it is impossible to carry out an informative diagnosis, as well as to select an effective treatment.
Tension headaches
The causes of cephalalgia can be different, but the most common of them is tension headache. They are associated with spasms of muscles and blood vessels in the neck and head. The reasons include staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time with your head fixed, or working at a monitor without breaks. Pain can also be triggered by constant nervous tension, stress, and abnormal physical activity. As a result of these factors, tension and spasm of the neck muscles occur, which compress the blood vessels and nerves. This leads to several symptoms:
- severe headache - it spreads over the entire surface of the head and is of a compressive nature;
- dizziness, general weakness;
- constant drowsiness, decreased concentration.
If a person has a headache for several days, a week or more, it is worth reconsidering the work and rest regime. Symptoms often go away if you avoid stress and ensure proper sleep. During sedentary work, be sure to take short breaks for neck exercises and general warm-up.
Migraine
Common causes of long-term cephalalgia include migraines. This is a chronic disease that is often hereditary. Doctors name several conditions for its development. The pain is caused by vascular spasms, as a result of which the brain receives insufficient oxygen. It can also occur with increased sensitivity of brain cells. They react to external stimuli, while affecting pain centers.
Migraine often manifests itself as a severe, throbbing headache that covers one side of the head. Shortly before the attack begins, a “migraine aura” may occur. This is a characteristic set of symptoms that indicate the imminent onset of the acute phase:
- nausea, dizziness, general weakness;
- the appearance of dark spots and circles before the eyes (visual hallucinations);
- tinnitus, hearing loss;
- increased heart rate, increased sweating.
A migraine attack lasts from 3–4 hours to several days and weeks. Symptoms are individual for each person. Thus, an aura appears in only a fifth of patients, and a headache will not necessarily affect only half of the head. If the disease worsens frequently, the doctor will prescribe special medications against migraines - cephalgia does not go away after taking conventional painkillers. It is also useful to maintain a sleep schedule, include large amounts in the diet, and avoid stress and sudden changes in climatic conditions.
Poisoning
Intoxication causes headaches as often as other causes. There are several types of poisoning, depending on the substance that provoked it. Thus, food intoxication can be caused by low-quality food or substances that are not suitable for ingestion. Poisoning by heavy metals, medications, alcohol, and volatile poisons is also distinguished. Toxins can enter the human body through bites of animals, snakes and insects due to helminth infestation.
Cephalgia is not the only sign of poisoning, but may precede the development of the full picture. You should immediately consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur after contact with hazardous substances, consumption of low-quality products, animal or insect bites:
- dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- disruption of the digestive system;
- severe abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature;
- other specific signs.
Treatment for poisoning must begin as quickly as possible. It is important to tell your doctor about all foods you have eaten and other substances you have come into contact with today or recently. For some types of poisoning, there are antidotes - they must be taken as quickly as possible to neutralize the effect of the toxins. In other cases, various detoxification methods are prescribed, including drip administration of electrolyte solutions, gastric lavage and others. Treatment takes place at home or in a hospital, depending on the degree of poisoning.
Injuries and their consequences
Cephalgia is one of the first manifestations of traumatic brain injury. Even in everyday life, you can get a severe bruise or concussion, but more often they happen due to falls and accidents. These injuries are dangerous because they affect the condition of brain structures and can cause long-term complications. Immediately at the time of injury, as well as several hours after it, characteristic symptoms appear:
- acute pain, which can be localized in a specific area or affect the entire surface of the head;
- dizziness, nausea and vomiting;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of dark spots and circles before the eyes;
- loss of consciousness is a sign that you need to urgently seek medical help.
After a traumatic brain injury, a headache can bother a person constantly or manifest itself in short attacks. In many patients, it worsens in response to changing weather conditions, stress, physical activity and other factors. The pain goes away on its own after rest, and also responds to painkillers.
Increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial hypertension is a common disorder. This is a complex indicator that cannot be measured at home, and the diagnosis is often made based on the clinical picture and indirect examinations. Intracranial pressure includes the pressure of blood in the cerebral vessels, the fluid of the cerebral ventricles and the brain tissue itself. The disease is often congenital, but can occur at any age due to injuries and chronic vascular pathologies. It causes characteristic symptoms:
- prolonged headaches that are concentrated in the temples or spread to the entire surface of the head;
- sensation of pulsation inside the skull;
- deterioration of hearing and vision;
- general weakness.
With intracranial hypertension, the patient often has a headache. The disease is chronic and manifests itself in attacks. They can be triggered by an increase in atmospheric pressure or other changes in weather conditions. The treatment is comprehensive, aimed at reducing pain and removing excess fluid. The regimen includes painkillers, diuretics (diuretics) and medications to improve blood flow to the brain.
Diseases of the cervical spine
If you often have a headache, this may also indicate diseases of the spine. The vertebral artery passes here - its path lies through the openings on the processes of the vertebrae, so it is normally protected from damage by bone tissue. However, with some disorders, the vertebrae change their correct position and compress an important vessel that carries blood to the brain. At the same time, irritation of the spinal nerve roots occurs, which provokes an exacerbation of the pain syndrome.
There are several diseases that are often detected when diagnosing long-term cephalalgia:
- osteochondrosis is a chronic disorder in which there is a decrease in the cartilage layer between adjacent vertebrae, pathological growth of the articular surfaces of bones and the formation of osteophytes (bone growths);
- protrusion and hernia - protrusion of an intervertebral disc of different sizes, which leads to compression of blood vessels and nerves, chronic pain in the neck and head;
- spondylosis is a pathological condition in which fusion and immobility of adjacent segments of the cervical spine are observed;
- curvature of the neck - scoliosis and kyphosis also cause chronic cephalgia.
In advanced stages of spinal diseases, as well as in cases of progressive congenital anomalies, surgical treatment is recommended. Headaches go away if you eliminate their main cause - compression of nerves and blood vessels. In the initial stages, the doctor prescribes painkillers, medications for blood supply and nutrition of the intervertebral discs. At home, you need to do neck exercises; it is also useful to go swimming and carry light loads in the fresh air.
Vascular diseases
Chronic vascular diseases are one of the reasons why your head may hurt for several days or weeks in a row. They lead to deterioration of blood supply to brain tissue, prolonged ischemia and lack of nutrients for the functioning of brain structures. During the diagnostic process, several common diseases are discovered that can cause headaches.
- Atherosclerosis is a chronic metabolic disorder in which there is an increase in the level of various fractions of lipoproteins and cholesterol in the blood. These substances accumulate on the inner wall of blood vessels and form plaques over time. With atherosclerosis, it is important to pay attention to any changes in well-being and consult a doctor at the first sign of a headache.
- Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure. The disease manifests itself as attacks of headache, which is accompanied by nausea, general weakness, and dizziness. Typical signs also include redness of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure. This condition is no less dangerous, as it can provoke an ischemic stroke. During an attack, a pressing pain in the head begins, tinnitus and dizziness, rapid heartbeat, paleness of the skin and mucous membranes.
If you suspect vascular disease, it is important to undergo an examination and take into account all the recommendations of doctors. A special diet with a low content of animal fats, moderate exercise, and medications to strengthen the walls of blood vessels and stabilize blood pressure are recommended. In advanced cases and without treatment, there is a high probability of ischemia (oxygen starvation) of brain cells, which leads to an increased risk of stroke.
Other reasons
Headache is not an independent disease, but one of the symptoms of a number of disorders. It should not be ignored, especially if it does not go away for a long time. It can occur against a background of stress and fatigue, intense mental and physical stress without sufficient rest. However, more dangerous conditions may also be detected:
- neoplasms – chronic pain is one of the first signs;
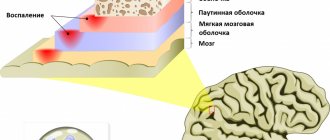
- meningitis, encephalitis - infectious diseases of the brain and its membranes;
- sinusitis - purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which can manifest itself as a complication of colds and acute respiratory viral infections;
- parasitic infestations – headaches occur due to intoxication with toxic waste products of helminths.
If the headache is long-lasting and bothers a person for a week or two weeks in a row, you should not try to find a treatment on your own. In the event of a severe attack, doctors recommend seeking help within two hours. It is this period that is most important for providing first aid if a person has a stroke.
Headache
Encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis
Polio
Hypercholesterolemia
18295 31 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Headache - causes, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods. The basis of headaches is irritation of pain receptors located in:
- dura mater and cerebral vessels;
- periosteum of the skull, vessels of the soft tissues of the head, muscles.
The brain tissue itself does not contain pain receptors.
Types of headaches (cephalgia)
Headaches are divided into primary and secondary. A headache is considered primary if it is the main manifestation of a brain disease, such as in migraines and tension headaches.
Secondary headache is a symptom of other disorders, for example, head trauma, chronic cerebral ischemia, viral diseases, diseases of the cervical spine, etc.
Let's look at the four most common types of headaches.
Possible causes
Tension headache
Tension headache is the most common form of primary headache. Psycho-emotional stress, depression, anxiety and various phobias, overstrain of the muscles of the shoulder girdle - these are the main causes of tension headaches. Migraine headache
Migraines occur in women about three times more often than in men, and about 60-70% of all migraine cases in women are so-called menstrual migraines. However, the causes and mechanism of development of migraine attacks are not completely clear. At any age, in both men and women, migraine attacks can be provoked by emotional and physical overload, eating disorders, drinking alcohol, changes in weather conditions, sharp noise, strong odors, etc. Headache with colds
Headaches from colds are caused by hyperthermia and the damaging effects of microorganism toxins on brain cells. Headache in chronic cerebral ischemia
The cause of this pain, which is the most common secondary headache in elderly patients, is cerebral vascular pathology, in which blood circulation is disrupted and blood supply to brain tissue deteriorates.
The result is progressive brain dysfunction.
What diseases cause
tension headaches?
Tension headaches are caused by irritation of structures in the central nervous system (CNS) called the nociceptive system. Myogenic, stress, and psychogenic headaches are tension headaches.
Most often, tension headaches occur at a young and working age.
In cases of tension headaches, a person experiences bilateral, usually not strong, pressing and squeezing, monotonous and dull headaches. Attacks of such pain are accompanied by fatigue, nervousness, impaired appetite and sleep, and decreased performance. The duration of the attack is from 30 minutes to several days.
Migraine headache
Indicates only one disease - migraine, since attacks of such cephalgia have a peculiar character. Migraine pain is paroxysmal, throbbing, of moderate or severe intensity. It covers half of the head.
The pain may intensify with physical activity, tilting the head, and is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Bright light, sharp sound, strong smell increase the pain. A migraine attack may be preceded by an aura, a collection of visual, auditory, olfactory or other neurological symptoms that lasts up to one hour.
Headache due to colds
Occurs in most acute and chronic diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract caused by bacteria or viruses. In some cases, the intensity of such cephalgia correlates with the severity of fever, severity of cough, sore throat and other symptoms. The pain most often spreads throughout the head. Headache in chronic cerebral ischemia
The concept of chronic cerebral ischemia includes: discirculatory or vascular encephalopathy (slowly progressive cerebrovascular accident), cerebrovascular insufficiency (pathology of cerebral vessels), vascular dementia (a disorder that causes organic damage to the brain). In the clinical picture of chronic cerebral ischemia, dizziness, decreased cognitive function, emotional lability (unstable mood), motor-coordination disorders, and perception disorders (tinnitus, “floaters” before the eyes) become indispensable companions of headaches. Headaches are usually not severe, spread over the entire head, and last for a long time. Diagnostics and examinations
Tension headache and migraine headache, headache with colds
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist based on anamnesis and assessment of the patient’s complaints. Headache in chronic cerebral ischemia
Radiation examination is key for chronic cerebral ischemia (ultrasound Dopplerography of cerebral vessels)
Diagnostic methods
If a person has had a headache for a week, it is important to determine why the symptom is occurring. To do this, the doctor prescribes a set of examinations, depending on the results of the examination. These include:
- EEG (electroencephalography) – examination of the brain, which will identify various diseases;
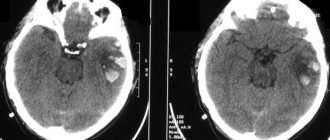
- MRI is a modern, informative technique, prescribed for suspected tumors, cerebrovascular accident, stroke;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head with the addition of a contrast agent (Dopplerography) - allows you to determine areas where blood circulation is impaired;
- laboratory blood tests are prescribed to determine inflammatory processes, the concentration of cholesterol and other substances, and disruption of the functioning of individual organs and systems.
Determining the cause of the headache is the first stage of successful treatment. The Clinical Brain Institute has high-quality equipment that allows you to visualize the full picture of the disease. All examinations can be completed in our center, including complex modern techniques.
Headache treatment
Treatment for a person who has had a headache for a week or more can only be determined by a doctor. Rest, a cold compress on the forehead, and a light massage of the neck and head are recommended as first aid. If the pain is severe, you can take painkillers from your home medicine cabinet. The doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment based on the diagnostic results, which may include the following steps:
- drug therapy - taking analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, drugs to improve nutrition and blood supply to brain cells, intervertebral cartilage;
- surgical treatment – surgery is necessary for neoplasms and advanced diseases of the cervical spine;
- additional techniques that include physiotherapy, gymnastics and therapeutic massage, swimming.
A short-term headache after a hard day at work indicates that you need to normalize your work and rest schedule. However, if it does not go away either today or on the second and third days, it is important to consult a doctor. There is a high probability of detecting chronic diseases, which can progress as they progress.
When you can and when you can’t tolerate pain after filling
My tooth hurts under a filling, what should I do? First of all, do not panic, but calmly understand the situation. If a tooth hurts after a filling, the nature of the pain and the appearance of some other symptoms matter.
Tooth hurts under temporary filling
The intensity of pain under the temporary filling should gradually decrease
Can a tooth hurt under a temporary filling? Of course, it can, but natural pain is not severe, and its intensity gradually decreases. The tooth hurts after filling, mainly during the day, when it is subjected to one or another impact - pressure (chewing hard food), drinking hot, cold or sour drinks.
- Possible reasons : most often, this is normal, the tooth begins to hurt for natural reasons. Painful sensations can also occur due to overheating of tissues during preparation, light-curing of fillings, problems with drying the dental cavity after preparation, or fillings that are excessive in height.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : for natural pain and pain associated with minor violations of the therapeutic process, it is enough to rinse your mouth with an infusion of chamomile flowers and take an anesthetic (Analgin, Pentalgin, Nise).
Acute pain after filling
Very often, a tooth hurts after root canal cleaning and filling. The acute nature of the pain syndrome is associated with injury or inflammation of sensitive tissues - pulp or periodontium. Much also depends on the pain sensitivity of the patient himself.
- Possible reasons : incomplete removal of pulp from the tooth cavity.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : take a painkiller and see a dentist.
Read more about the causes and methods of eliminating acute pain in the teeth in this article.
Throbbing pain after filling
If the tooth hurts severely after filling, the pain has become throbbing, then this is a sign of inflammation of the pulp - pulpitis. A sharp headache often appears.
- Possible causes : the cause of pulsating pain syndrome may be poor-quality treatment of the dental cavity and root canals, possibly perforation of the walls.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : take any painkiller orally and immediately consult a dentist.
Only a dentist can relieve throbbing pain
Aching pain after filling
When a tooth aches after a filling is placed, this is normal. How long a tooth hurts after canal filling depends on the complexity of the manipulations performed. The intensity of the pain is important: if it increases, the pain intensifies sharply when pressed, then this is a symptom of incipient inflammation. A decrease in intensity is a favorable sign.
- Possible reasons : this is natural pain in a filled tooth.
- What is the best way to relieve pain : rinse with a decoction of oak bark or an infusion of chamomile flowers. If the pain seems too severe, take a pain reliever.
Read about how to eliminate aching toothache here.
Tooth hurts after filling when pressing
If a tooth hurts after a filling when you bite it, then most often it has natural causes and goes away in five to seven days.
- Possible reasons : if after filling a tooth hurts when pressed, then most often this is a consequence of treatment and injury to dental tissues.
- How best to relieve pain : temporarily avoid chewing food on the side of the filling, rinse your mouth with light antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
Prevention methods
According to statistics, adults often have headaches due to acquired disorders. Common causes are poor diet, stress and lack of rest, and excess weight. Today, many people, including young people, lead a sedentary lifestyle, which also negatively affects the general condition of the body. Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain have several tips on how to provide timely prevention of headaches at home:
- regularly measure blood pressure, especially at the age of 40 years or more;
- perform simple exercises for the neck and head every day, including during the working day;
- consume sufficient amounts of vitamins and microelements;
- give up bad habits, smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as fatty foods high in cholesterol.
If a person has a headache for several days or even weeks, it is worth contacting the Clinical Brain Institute. Doctors will develop an individual program for diagnosing and treating chronic pain. The scheme will include only the necessary informative techniques that will allow you to quickly make an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective course of treatment, including at home.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 3/5 — 7 votes
Share article on social networks