Circadian rhythm regulator
Biological rhythms are genetically programmed processes.
They are an important mechanism for the body’s adaptation to the environment and indicate its condition, well-being and performance. Among the many biological rhythms, circadian rhythms are important for the functioning of the body. Circadian rhythms - the human internal clock
The usual period of fluctuation in circadian rhythm functions is 24 hours.
The periods of sleep and wakefulness in living organisms alternate cyclically. Scientists have proven the influence of light on human biological rhythms. Melanopsin receptor
, present in the retina of the eye, is not involved in image formation, but is involved in circadian rhythms. Experiments were carried out, and in the absence of light, the subjects still went to bed and woke up at normal times. And this period was equal to 24 hours. After some time it increased to 36 hours. But upon returning to normal life, the 24-hour sleep-wake period was restored.
This confirms that a person has an “internal clock” that operates despite the absence of external signals. One of the external signals is light, which, as mentioned above, affects the functioning of pineal gland hormones.
Considering the periodicity of circadian rhythms, it is possible to draw conclusions about the mechanisms of many diseases. As is known, the results of diagnostic studies also depend on the time of day.
Features of a person's circadian rhythms affect his activity. There are morning, afternoon and evening types of circadian rhythms (chronotypes) - the so-called “larks”, “pigeons” and “owls”. "Larks" are adapted to morning activities, "pigeons" - to daytime activities, and "owls" - to evening activities.
Do you suspect yourself or someone close to you has signs of insomnia? Take the innovative CogniFit neuropsychological test for insomnia and find out in less than 30-40 minutes whether you have cognitive symptoms that may indicate a sleep disorder. Receive a detailed report in pdf format with personal recommendations!
Innovative neuropsychological test CogniFit for insomnia
Genetic mediation of circadian rhythms is demonstrated by 50%, the rest of the data relates to psychological and environmental factors. If a person often has to travel and this is associated with a change in time zones, then negative consequences arise - the so-called “jet lag” effect. This is a violation of circadian rhythms during the transition from one rhythm of life to another.
The pineal gland is a regulator of the body's circadian rhythms. All biological rhythms are subordinate to the body’s rhythm driver - the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which is located in the hypothalamus. This is the control center of the body's biological clock.
Melatonin, located in the pineal gland, is a messenger hormone that conveys signals to organs and tissues. Its work depends not only on concentration, but also on the duration of its production
The pineal gland is an important link in the implementation of circadian signals, because brain activity is dependent on lighting
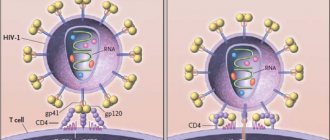
Information about light comes in a complex way: retina – SCN – superior cervical ganglion – pineal gland.
Disturbances in the interaction of the SCN with the pineal gland due to impaired melatonin production leads to depression. The circadian and seasonal rhythmicity of the pineal gland is clearly organized. The presence of many biologically active compounds in this gland and the complexity of its work indicate its exceptional position and influence on the physiological processes of the body.
Treatment of pineal gland diseases
Treatment for circadian rhythm disorder includes:
- restoration of sleep-wake rhythms (go to bed and get up at the same time),
- avoidance of activities that excite the nervous system before bedtime (workouts, active games, watching action movies),
- avoiding the use of digital devices at night,
- taking sedatives and, in severe cases, artificial melatonin preparations (Melaxen).
Cystic transformation of the epiphysis usually does not require any treatment (if the ductal system is blocked); observation by a neurosurgeon and regular MRI of the brain are required. Surgery is indicated for cyst growth, increased headaches and brain symptoms (nausea, vomiting, disorientation, vision, fainting, etc.).
Echinococcosis undoubtedly requires specific treatment for the parasitic disease. In the absence of cyst growth and severe brain symptoms, the prognosis is favorable.
Treatment of secondary lesions of the pineal gland (inflammatory processes, atrophy, impaired blood supply) should be aimed at eliminating the cause that caused them. Direct impact on the organ itself is usually not required.
Persons with diseases of the pineal gland should be under the supervision of a neurosurgeon.
It is interesting that it is the pineal gland, according to many esotericists, that is the organ - the seat of the soul. This judgment is probably due to the fact that this is the last of the open endocrine glands and its functions are multifaceted and not fully understood.
Functions and hormones
Neuropathologists and neurosurgeons who study the pineal gland of the brain have long studied what it is and why it is needed.
The main function of the pineal gland is the regulation of circadian (otherwise known as cycadal) rhythms, metabolism, and other endocrine functions. It secretes vital hormones melatonin, serotonin and some others. They are most actively released at night, in the dark, when a person has been sleeping for several hours - this is from midnight until dawn. Artificial lighting deceives the pineal gland, blocking the release of hormones. Therefore, absolute darkness is necessary for night sleep.
Melatonin hormone
Melatonin is produced in the blood only at night; light blocks its release. With the onset of dawn, another hormone begins to be produced. During the day, there is significantly less melatonin in the body; the pineal gland does not produce iron at this time.
A supply of melatonin can be obtained from food, although in quantities that are completely insufficient for health.
Melatonin is also called the “hormone of youth”, which prevents early aging of the body. If there is lighting, it is practically not produced. This is why it is not recommended to sleep with light on. During the polar day, doctors recommend tightly curtaining the windows in the bedrooms.
Melatonin is also directly related to sexual function; it is also responsible for the cyclicity of menstrual function in women.
The lack of this hormone leads to psychosomatic diseases, metabolic disorders, and sleep disorders. Because of this, general health worsens, insomnia occurs, and women may experience ovarian dysfunction. Its high level gives healthy longevity and good physical fitness, vision and memory.
Now a synthetic melatonin has been created, which is similar in structure to natural one. It is prescribed to people with severe insomnia.
Hormone serotonin
This hormone of the pineal gland regulates the psycho-emotional state of a person, relieves stress, and regulates smooth muscle tension. Helps cope with various states of anxiety, obsessive thoughts, aggressiveness, and so on. Its popular name is “happiness hormone”. Unlike melatonin, it is produced during the daytime.
Additional positive emotions also promote the production of serotonin.
Excess light interferes with the conversion of serotonin to melatonin.
With a lack of this hormone, depression and various phobias develop. Alcoholism and drug addiction can also be caused by a lack of this hormone. More complex mental illnesses are also possible.
Editor's note: Are brain metastases treatable?
Harmonizes the rhythm of wakefulness and sleep
To maintain life, the body needs to regulate the rhythm of rest and wakefulness. At night, it reduces nervous tension and produces substances that have a hypnotic effect on the body. If at this time you prevent this blockage and take substances that, on the contrary, invigorate, you can disrupt this function. Which will subsequently require drug treatment.
Suppression of sexual desire
Pineal gland hormones suppress sexual desire in childhood. In children and adolescents, the epithalamus is larger relative to the size of the brain than in adults, and more melatonin is produced per unit of weight. Accordingly, attraction does not arise at this age. With the onset of puberty, the suppression gradually ceases.
Inhibits the development of tumors
Pineal gland hormones prevent the uncontrolled production of growth hormone. This helps the body recognize pathological cancer cells in time and prevents them from developing. We have the pineal gland to thank for this obstacle.
Helps to navigate in space
Thanks to the hormones of the pineal gland, a person can determine his location.
It also stimulates the immune system, and in general all metabolic processes of the body. With age, the pineal gland begins to decrease in size and atrophy. This inevitably leads to the occurrence of oncology.
Pineal hormones
Pineal hormones have a very strong influence and regulate the lifestyle of every person. An analysis of the functions of the individual hormones secreted by this gland in everyday life provides convincing support for the assertion that the pineal gland is the place where the soul interacts with the body, and the body with the soul. What hormones does this “secret” gland secrete?
The two most important hormones produced directly by the pineal gland are:
- Serotonin
– this hormone is released throughout the day. First of all, it has a calming effect, but too low its level causes depression, anger and even aggression. Serotonin additionally provides a signal to prepare for sleep. - Melatonin
– produced by the pineal gland at night. It makes people feel sleepy. But the light that reaches melatonin definitely lowers its levels. So, this is the information that you need to get up after the night. - DMT (dimethyltryptamine)
– this hormone is produced by the cells of the pineal gland. It is a type of psychedelic psychoactive substance. May cause hallucinations and strong visual effects.
By producing these hormones, the pineal gland is entirely responsible for regulating each person's circadian system. The effect of the hormones of this gland is most strongly felt when changing time zones (the famous “jet lag syndrome”). Their deficiency additionally causes appetite or metabolic disorders.
Jet lag syndrome
The pineal gland not only produces its own hormones, but also participates in the production of others. These include:
- Vasopressin
– stimulates growth levels. It also regulates the density of urine. The largest amount of this hormone is produced during sleep. Vasopressin also stimulates the production of cortisol, and the pineal gland secretes this hormone from the pituitary gland. - Somatropin
is the name of growth hormone. The pineal gland is involved in its production, and the highest levels of this hormone occur during puberty. - Thyroid hormones
- the small pineal gland secretes melatonin and also regulates the thyroid gland by stimulating thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). - Gonadotropins
- these hormones stimulate the activity of the human gonads (ovaries and testes). The pineal gland plays a very important role in the process of puberty and supports the functioning of these organs, - ACTH
, also known as the stress hormone, the pineal gland is involved in the production of this hormone. As a result of its action, more cortisol is released, and the pineal gland regulates this process. Thanks to these actions, the body properly prepares for awakening.
What is the pineal gland
The pineal gland, or pineal gland, shaped like a pine cone, is a small formation deep in the brain. The organ belongs to the type of internal secretion, perceives light, and is activated when illuminated. The pineal gland develops from the epithalamus, located in the posterior part of the forebrain. Animals also have this organ and serve as their “third eye”—it distinguishes the level of illumination, but not visual images.
The work of the pineal gland in humans is associated with the production of melatonin, the establishment of biological rhythms, the determination of the frequency of sleep and changes in body temperature. The pineal gland is complex anatomically and physiologically, affecting the disruption of the body’s circadian rhythms during flights, decreased melatonin synthesis, diabetes mellitus, depression, insomnia and oncology.
Where is
The pineal gland is located under the scalp, inside the brain. The pineal shape is due to the growth impulse of the network of capillaries inside the gland, growing into segments as the organ grows. Increasing in size with age, the pineal gland penetrates the region of the midbrain and is fixed in the groove between the upper colliculi of its roof. The mass of the formation is no more than 0.2 g, the length is 15 mm, and the width of the gland does not exceed 10 millimeters.
Structure
When studying the functions and operation of the gland, it is necessary to know the structure of the pineal gland. On the outside, the pineal body is surrounded by a soft connective tissue membrane of the brain and interconnected blood vessels. It consists of specialized cells - pinealocytes and gliocytes. During the development of the embryo, the pineal gland appears in the second month in the form of a choroid plexus; as it grows, its walls thicken, two lobes become visible, between which vessels grow, gradually merging into one pineal organ.
Hormones
An intensive exchange of proteins, nucleides, lipids and phosphorus occurs in the organ. Additionally, pineal gland hormones can be distinguished: peptide and biogenic amines. The pineal gland produces:
- Serotonin - turns into melatonin inside the gland when there is a lack of light. Serves as a “happiness hormone”, improves mood, is responsible for a person’s psychological state, and regulates vascular tone.
- Melatonin - determines the rhythm of gonadotropic effects, including the menstrual cycles of women. It inhibits the function of the genital organs and inhibits growth hormone produced by the pituitary gland. When the epiphysis is removed, premature puberty occurs, increased spermatogenesis and enlargement of the uterus. Hormone production increases in the dark.
- Norepinephrine is a “mediator” of wakefulness, released in daylight.
- Histamine – protects the body from the effects of unwanted substances.
Functions
Until now, doctors have not sufficiently studied the functions of the pineal gland, but they attribute the following:
- melatonin production to synchronize circadian rhythms (sleep-wake);
- influence on immunity;
- stimulation of aldosterone production due to adrenoglomerulotropin;
- inhibition of excessive secretion of growth hormone;
- support for the timing of sexual development and behavior;
- inhibition of tumor development;
- fine regulation of metabolism.
Activation
The pineal gland is activated by light. Along with it, when illuminated, the hypothalamus, which is responsible for thirst, hunger, sexual desire and the biological clock of aging, begins to work. When the pineal gland awakens, a person feels pressure at the base of the brain. According to Indian teachings, the pineal gland is considered a powerful source of etheric prana energy, which a person needs to enter his inner world or the spheres of higher consciousness.
Followers of yoga practice its activation in order to open the “third eye.” To do this, they raise the vibration frequency, which forces the pineal gland to work more actively. The third eye, hidden inside, helps to see the world beyond the physical shell, travel out of body and connect the physical world with the soul. There are teachings on clairvoyance.
- Hormones of the female body - names, where they are produced and what they are responsible for, the norm and treatment of abnormalities
- Thyroid puncture - analysis results. How to puncture a thyroid node
- Thyroid cyst: symptoms and treatment
https://youtube.com/watch?v=W2eUSdROI9c%250D
When is treatment required?
If damage to the pineal gland provokes negative symptoms, the doctor considers treatment options - medication or surgery. Drug therapy is symptomatic, and surgery is resorted to in cases of life-threatening complications.
Conservative therapy for a large epiphysis cyst includes:
- Diuretics (furosemide, mannitol, diacarb) - to reduce intracranial hypertension and relieve symptoms of cerebral edema;
- Anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, finlepsin, etc.) – for convulsive syndrome, especially often accompanying parasitic infestation;
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, naproxen, ketorol) - for severe headaches;
- Tranquilizers and antipsychotics - for severe psychotic disorders.
The described treatment is extremely rarely indicated for true cysts, since they usually do not reach such a size as to provoke seizures, but analgesics and diuretics are prescribed to many. In addition, the doctor may recommend adaptogens and the drug melatonin for disturbances in sleep and wakefulness, daytime drowsiness and insomnia at night.
Surgical treatment of a pineal gland cyst in the brain has a number of indications:
- A cyst larger than 1 cm causing neurological disorders;
- Rapid increase in the volume of the formation with compression of the brain;
- Acute occlusive hydrocephalus;
- Echinococcosis.
Removal of an epiphysis cyst is possible through craniotomy, but one must remember that such an operation is extremely complex and fraught with serious complications, because the organ is located quite deep, and in the process of accessing it, damage to brain tissue cannot be ruled out. After trephination, there will be no cyst left, but the side effects are quite real, so this treatment is carried out only for health reasons.
Surgeries aimed at alleviating the symptoms of hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension include endoscopic drainage of the cystic cavity and shunting techniques.
endoscopic drainage of the cyst cavity
Drainage using endoscopy is a minimally invasive operation that removes the contents of the cyst, reducing the pressure of its walls on the brain and reducing intracranial pressure. This intervention is considered relatively safe.
From the editor: How to easily learn the textShunting is indicated for severe hydrocephalus. During this operation, bypass routes for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid into other body cavities are created, thereby reducing its pressure in the ventricles of the brain and improving the general condition of the patient.
It is clear that any intervention inside the skull is risky, so neurosurgeons take a very balanced approach to the need for surgical treatment of a true pineal cyst, however, the echinococcal cavity does not provide a chance not only for cure, but also for improving the patient’s condition in a conservative way, so surgery is often the only option for saving the patient's life.
Many patients and their relatives, concerned about the problem of epiphysis cysts, try to resort to traditional methods of treatment, of which there are quite a few on the Internet. It is worth noting that neither decoctions of burdock, nor hemlock, nor any other plants can reduce the cyst, much less get rid of it, so it is better to abandon them immediately.
Treatment with non-traditional methods of any intracranial neoplasm will, at best, have no effect, at worst, it will cause intoxication, and in case of large formations, it will lead to a loss of time during which it is possible to examine the patient and draw up a plan for the most rational treatment.
Children with a cyst that causes symptoms should change their regime in favor of rest and walks, canceling additional activities if the child becomes very tired after them. When a cyst and other brain malformations are combined, rehabilitation in a neurological department and transfer to home schooling may be required.
If your health suddenly deteriorates, you should immediately contact a neurologist, especially if this happens to a child. With asymptomatic cystic transformation of the pineal gland, you can live your normal life, but not forgetting about timely visits to a specialist and MRI control.
Brain pineal cyst
Cystic transformation of the pineal gland occurs in rare cases, and is often discovered accidentally during diagnostic procedures for other reasons. A pineal gland cyst is a rounded cavity in the tissues of the organ with a dense shell and fluid inside. This is a benign formation that is formed due to blockage of the excretory duct of the gland and the accumulation of secreted substances. The reasons may be the following factors:
- neuroinfections;
- cerebral stroke;
- congenital abnormalities of the structure of brain tissue;
- thick consistency of secretory fluid;
- traumatic brain injuries, operations.
Cysts of helminthic origin are even less common - when they are infected with echinococcus, penetrating into the gland through the bloodstream. This parasite forms a capsule, protecting itself from the body’s immune factors, and the cyst is gradually filled with its waste products, increasing in size. Other reasons for the development of cysts cannot be excluded, but they have not yet been established.
Pineal gland of the brain, cyst - symptoms
In most cases, an epiphysis cyst does not cause any symptoms. If its dimensions exceed 10 mm in diameter, then the following symptoms are possible:
- causeless headaches, noise in the head;
- nausea, vomiting;
- visual disturbances;
- violation of coordination, orientation in space;
- sleep disorders;
- pain in the eyes when rotating the eyeballs.
What are the dangers of a pineal gland cyst in the brain?
A cerebral epiphysis cyst can be a completely harmless formation if it is up to 10 mm in size and does not cause symptoms. It is only necessary to regularly monitor it (via MRI) in order to track a possible increase in time.
When the cyst grows:
- The development of hydrocephalus is dangerous - a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Sometimes neurotic disorders, epilepsy, and decreased mental activity are provoked.
- The threat is posed by a cyst of parasitic origin, causing inflammation and hemorrhage in nearby tissues.
Pineal gland cyst of the brain - treatment
In cases where the pineal gland cyst is parasitic, has a size of more than 10 mm, and provokes severe symptoms, it is subject to surgical treatment - removal. Often the operation is performed endoscopically, less often open craniotomy is performed. Conservative treatment, including taking a number of medications (diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipsychotics) is prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure and eliminate mild symptoms.
Cyst
Epiphysis cyst of the brain is a very common pathology. A pineal cyst is a benign neoplasm. Scientists have not yet precisely figured out the cause of its occurrence. A cyst in the pineal region is most often small in size; the appearance of such a microcyst is asymptomatic. Such a tumor is found by chance during an MRI. In this case, its size and location can be easily determined.
A tumor of the pineal gland with a diameter of more than 5 mm is rare and can cause serious problems. It is accompanied by a number of symptoms.
Doctors believe that there are the following reasons for the appearance of a cyst:
- The excretory duct is blocked. Because of this, melatonin does not flow out, it accumulates.
- The parasitic disease echinococcosis develops. It causes the formation of cysts filled with parasites.
It is possible that there are other reasons. They have so far been little studied, since the appearance of a cystic growth most often occurs without symptoms.
Even such a modern hardware method as MRI cannot always tell you exactly how a cyst develops. It is often supplemented with other studies, such as a biopsy. It is the biopsy that helps to obtain comprehensive information about the nature of the tumor and the cells that make it up.
The purpose of the biopsy is to determine whether there are cancer cells in the tumor. It also helps to find out what the nature of education is and how it develops.
It is extremely important to differentiate benign neoplasms from possible cancerous brain tumors.
The appearance of a cyst can be accompanied by symptoms that are characteristic of many other diseases (double vision, headache, impaired gait, coordination, a person sways in different directions, nausea, vomiting).
If a cyst in the pineal gland of the brain compresses the duct, hydrocephalus may develop (the outflow of fluid from the brain is impaired).
The severity of cystic symptoms directly depends on the size to which the cyst or other neoplasm has grown. If the dimensions are critical, it can completely block the outflow of fluid. This is fraught with serious disorders of brain activity. A person may develop depression, dementia, delirium, and epilepsy.
As the cyst grows, the symptoms also increase, and the condition worsens sharply. As practice has shown, this rarely happens. Cysts in this area usually grow slowly.
When a cyst develops, surgical treatment is not always indicated. If it is small and weakly growing, the patient is recommended conservative treatment and regular monitoring.
Melatonin secretion
The function of pineal melatonin is extremely important for human health. This substance is formed through a complex chemical transformation of the neurotransmitter serotonin. Indirectly, the concentration of secretion in the blood affects the level of melatonin. But this dependence can be traced only in the dark. During the day, significantly less melatonin is produced in the brain. If the total amount of hormone per day is considered 100%, then during daylight hours only 25% is produced.
It is known that the nights are longer in winter, so in the natural environment the level of melatonin is higher in the cold season.
But modern man lives in conditions far from natural. The presence of artificial lighting allows you to rest and work at night. Of course, by extending daylight hours, a person exposes his health to a certain risk.
Daily shifts, staying awake after midnight, and getting up late help suppress the secretion of melatonin in the pineal gland of the brain.
Ultimately, these changes can lead to the development of diseases associated with the function of the pineal gland.
It is believed that insomnia, depression, hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and other serious pathologies may be the result of malfunctioning of the pineal gland.
Functions
The main function is braking. The pineal gland produces hormones that inhibit the functioning of the gonads and reduce the amount of secretion they secrete. It also slows down the functioning of the thyroid gland and takes part in the metabolism of minerals.
To ensure its functions, the pineal gland produces the hormone melatonin, as well as serotonin and adrenoglomerulotropin.
It is curious that the process of serotonin production is activated during the day, under the influence of sunlight, but melatonin is produced during sleep, around midnight. Despite the tiny size of the pineal gland, it produces enough hormones that are so important for the proper functioning of the body.
Melatonin is produced in varying amounts throughout the day. The hormone is most actively produced at midnight. This affects the change in a person’s body weight throughout the day, as well as the functioning of his organs. The pineal gland is activated at night. If a person sleeps little, goes to bed late, or even works in the dark, the consequence may be a failure in the production of these hormones. Working at night can cause serious problems with the pineal gland. The entire body will suffer from this, in particular the immune system, genitourinary system, brain, etc.
If a tumor appears on the pineal gland, the child goes through puberty much faster than usual. It is precisely because of this sign that parents may suspect that the baby is experiencing malfunctions of the pineal gland. The causes of disorders are tumors of the pineal gland, cysts, etc. In order to have objective information, you need to contact an endocrinologist at the first signs of the disease. For a long time, symptoms may be hidden.
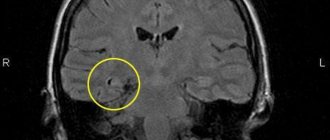
What does a pineal gland cyst look like on CT and MRI?
Computed tomography visualizes a fluid-dense mass with well-defined edges and peripheral calcifications found in 25% of patients. In many cases, there is also a peripheral accumulation of contrast in the cyst in the form of a thin and smooth “rim”. The cyst disrupts the course of the internal veins of the brain, displacing them upward.
Pineal cyst with a typical hyperintense signal on MRI (T2 WI) (marked with a blue arrow). Left: axial tomogram, right – sagittal
The following signs are observed on MRI:
- T1 VI
- Typical iso- or hypointense signal compared to brain parenchyma
- The signal is usually uniform
In 55–60% of cases, the signal is hyperintense compared to the cerebrospinal fluid
- High intensity signal
High intensity signal that is often not completely suppressed
There is no diffusion restriction
- Approximately 60% of cysts accumulate contrast
Pineal cyst
A pineal cyst is quite often diagnosed as a disease.
A pineal cyst is a very benign tumor lesion that does not spread to other organs. This cyst is filled with inflammatory cells (leukocytes, lymphocytes and macrophages). Usually surrounded by delicate epithelium. It is difficult to identify clear reasons for its formation. Most often it occurs in young people when the pineal gland undergoes many transformations. This causes some changes in the organ.
A pineal cyst is asymptomatic, but when it puts too much pressure on the brain structures, the following symptoms may appear:
- long-term migraines (up to 72 hours);
- problems with proper vision, squint;
- sleep disturbance;
- disturbances of wakefulness.
Prolonged migraine
This disease is very often detected only by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, carried out in the diagnosis of other diseases. Treatment for pineal cysts mainly involves eliminating symptoms and pain. This condition should be regularly monitored by a doctor. Very often the cyst resolves or significantly decreases in size, but if the lesion grows, surgical intervention is required.
Organ pathologies, their symptoms and treatment
In addition to disruption of daylight hours, other negative factors affect the functioning of the endocrine gland:
- congenital abnormalities of brain development;
- severe neuroendocrine pathologies;
- damage to brain cells.
Editor's note: Are brain metastases treatable?
Hypoplasia of the pineal gland is indicated by the early onset of puberty. Doctors rarely diagnose congenital malformations of the pineal gland.
Functional disorders can be eliminated quite easily - you need to review your daily routine and treat background pathologies. For the proper production of melatonin and other important substances in the pineal gland, you need to include foods of various categories in your diet. Balancing nutrition is a prerequisite for the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
On a note! Pineal gland diseases occur in men and women. The more provoking factors, the higher the risk of damage to the pineal gland. Lack of attention to the signs of pathological changes can cause severe damage to the nervous system, ischemic stroke, and hypertensive crisis. If problems with the pineal gland occur in children, then against the background of active growth of the tumor, the functioning of the adrenal cortex is disrupted, which provokes a shift in the timing of puberty to an earlier period.
Hemorrhage into the pineal gland tissue
A dangerous process develops in adults against the background of vascular atherosclerosis. In children, a serious condition rarely occurs. Sometimes a stroke occurs due to an aneurysm (congenital abnormality).
Against the background of hemorrhage in the brain, various parts of the nervous system are often affected. An MRI is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. A neurologist, neurosurgeon, cardiologist, and other specialists are involved in treatment.
Parasitic diseases
Most often, this type of pathological process is detected in residents of regions where livestock farming is developed. In most cases, echinococci penetrate the pineal body. The size of parasites is from 2 to 8 mm. Waste products poison the body, the movement of dangerous tapeworms disrupts the functioning of the pineal gland and provokes the development of tumor-like formations.
With echinococcosis, cysts are prone to active growth. The cavity with a dense capsule must be removed: non-surgical methods and medications do not have any effect. A cyst in the pineal gland is diagnosed using immunological tests and tomography. To eliminate the pathological process, you need the help of a qualified infectious disease specialist and neurosurgeon;
Pineal tumors
Volumetric neoplasms in the tissues of the pineal gland are benign and malignant. Often the cause of development is the influence of ionizing or X-ray radiation.
While the tumor is small, the patient does not suspect the existence of a pathological focus in the pineal gland. If the neoplasm grows, reaches 3 cm, and cell malignancy actively occurs, then negative symptoms appear. Patients complain of headaches that cannot be controlled, and blurred vision.
After examination with a tomograph, the doctor confirms or denies the suspicion of tumor development. Treatment is strictly surgical. If tissue histology shows the presence of atypical cells, then the patient, under the guidance of an oncologist, receives chemotherapy or undergoes a course of radiation to suppress the growth of cancerous structures.
Modern problems with the pineal gland
Calcification is the biggest problem for the pineal gland. Fluoride accumulates in the pineal gland more than in any other organ and leads to the formation of phosphate crystals. As your pineal gland hardens due to crystal production, less melatonin is produced and your sleep-wake cycle becomes dysregulated [1].
Research also shows that fluoride curing accelerates sexual development in children, especially girls [2]. And this is a serious problem, since a study conducted 30 years ago reported that 40% of American children under the age of 17 had active pineal calcification. Since then, we have seen children, especially girls, experience early onset of puberty [3].
In addition to fluoride, halides such as chlorine and bromine also accumulate and damage the pineal gland. Calcium supplements can also cause problems. Without enough vitamin D—64% of Americans are vitamin D deficient—calcium does not become bioavailable and calcifies human tissue, including the pineal gland [4].
Eliminating fluoride may be the best first step to reduce health problems. Use fluoride-free toothpaste, avoid tap water, and drink filtered water. For better water filtration, use a reverse osmosis filter. Eat calcium-rich foods rather than take calcium supplements if you can get plenty of vitamin D.
YOUTH AND AGING. A CURE FOR CANCER?
Russian scientist V.N. Anisimov believes that “melatonin has a circadian rhythm, i.e. its unit of measurement is the chronological metronome - the daily rotation of the Earth around its axis. If the pineal gland is the body's sundial, then, obviously, any changes in the length of daylight hours should significantly affect its functions and, ultimately, the rate of its aging. Changing the length of daylight hours significantly modifies the body’s functions, in particular reproductive and immune, the development of age-related pathologies and, therefore, can affect life expectancy.”
In addition, both Anisimov and Reuter, conducting numerous studies, came to the conclusion that melatonin and epithalamin stimulate the cells of the body’s immune system, slow down the aging of the immune system, normalize a number of age-related disorders of fat-carbohydrate metabolism, and also inhibit free radical processes in the body. What does this tell the reader uninitiated in medical terminology? And the most important property of melatonin and epithalamin is their ability to prevent the development of both spontaneous and induced by various chemical carcinogens and ionizing radiation of neoplasms. Think about these words.
If the production of these substances is most active at night (as science shows), then, in fact, any treatment for cancer should be carried out at night, and during the day, sleep and meditation treatments should be used to the maximum.
Physiology, effect on the body
The influence of the pineal gland is currently poorly studied. It is very small and located in a rather inconvenient area of the brain for research.
It is known that melatonin provides daily rhythms of the body's activity.
Endocrine functions are as follows:
- slows down the aging of the immune system;
- normalizes the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats;
- inhibits the activity of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland at night.
Melatonin has a very good effect on brain activity, vision and other systems:
- protects against cataracts;
- prevents pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- protects against headaches;
- prevents pathologies of the central nervous system;
- protects against tumors;
- regulates wakefulness and sleep;
- reduces cholesterol levels;
- strengthens the immune system;
- tones blood vessels, normalizes blood pressure;
- reduces blood sugar;
- protects against depression.
Melatonin is very important for teenagers. It improves memory, therefore promoting quality learning.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine recipes can be used to treat pineal cysts only after consulting a doctor. Benign neoplasms are treated:
- Tincture based on hemlock. To prepare the medicine, the flowering caps of the plant or dry seeds are used. The raw materials are filled with vegetable oil and infused for three weeks. The resulting solution is filtered through gauze. The medicine must be dripped into the nose, two drops, twice a day. The course of treatment is long, up to two months.
- Tincture based on Caucasian dioscorea. Dry raw materials are infused with vodka. Used to improve cerebral circulation and normalize blood pressure.
- Rosemary decoction. A tablespoon of dry herb is brewed with a glass of boiling water. The solution is drunk in four doses, before meals. You can only take freshly prepared medicine. Rosemary decoction can be drunk until the symptoms of the disease pass.
- Burdock juice. The juice squeezed from the leaves of the plant is infused for five days in a cold place. Morning and evening every day you should drink two tablespoons of the medicine on an empty stomach. The treatment is long - two sessions of 20 days each with a break of a month.
- Herbal infusions. To improve brain function, a general strengthening complex is taken. You can prepare a decoction from a mixture of herbs, flowers, fruits: linden, rose hips, elderberry, calendula, viburnum.