Which doctor should I contact if I have a concussion?
Let's figure out which doctor to go to if you have a concussion. After a concussion, even a mild one, you must see a doctor whose activities are in one way or another related to head injuries.
Surgeon
Sometimes a traumatic brain injury can be accompanied by additional bodily injuries: fractures, dislocations, cracks in the bones of the skull, bleeding. In this case, especially if emergency surgery is required, the traumatologist will send the patient to the general surgery department. In all other cases, consultation with a surgeon is usually not required.
ENT
an otolaryngologist if there is bloody discharge from the ear or tinnitus continues for more than a day .
If you have nosebleeds or suspect a septal injury after a blow or fall, you should also seek advice from an ENT specialist.
Oculist
With a traumatic brain injury, contusion of the eyeball can occur.
If, after a diagnosed injury, you experience pain in the eyes, severe nausea, dizziness, redness of the eye, obvious decreased vision, fog before the eyes, or floaters, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. You should not rely on the fact that everything will go away on its own, since with a concussion and contusion of the eyeballs, swelling of the cornea , hemorrhage, and detachment of the iris can occur. All this requires immediate treatment from a specialist.
Traumatologist
The first doctor you should contact after receiving a traumatic brain injury. A traumatologist will examine the victim, provide first aid, give an initial opinion and send him for further treatment to a neurologist, surgeon or other specialized specialists. The traumatologist can also decide on further hospitalization of the victim.
Neurologist
Primary physician in the treatment of concussion. After discharge from the hospital, the injured person must be observed by a neurologist for a year. If the injury is minor and you have not contacted a traumatologist, you should definitely visit a neurologist. He will prescribe the necessary additional studies to exclude post-traumatic effects on the brain and prescribe treatment.
Where to go if you have a concussion
Mild and moderate concussions are usually accompanied by symptoms that do not prevent the victim from being taken to a medical facility. This could be a clinic, hospital, emergency room. The doctor on duty will examine the patient and then decide on further action. In a situation where a brain injury is accompanied by impaired consciousness, the patient’s inability to move, and a risk of spinal injury, it is better to call an ambulance by phone.
While the team is on the move, it is recommended that a person with a suspected concussion receive basic first aid. If there is bleeding, it must be stopped using bandages or a clean cloth. If a hematoma forms, cold can be applied to the site of impact. The patient is placed on his right side, with his right arm and leg bent at a right angle, and his head slightly raised. If there is a risk of spinal injury, the victim is left on his back, but when vomiting, the head should be placed on the side.
Any traumatic brain injury is a reason to seek medical help. It is not so important which doctor you contact in case of a concussion, the main thing is that this must be done quickly. If possible, it is better not to risk the victim’s health at all, but to immediately call an ambulance, whose employees will understand the situation.
What do they do in the hospital with such patients?
How does a doctor determine a concussion?
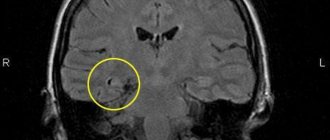
Let's look at how a specialist determines whether a patient has a concussion. The primary goal of the attending physician during a concussion is to rule out the presence of skull fractures, intracranial hematoma, or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Before treatment for a concussion of any severity, a brain examination is performed.
First of all, if cracks or fractures of the skull bones are suspected, bone x-rays are prescribed . Brain tissue damage and possible hematomas are examined using CT and MRI. It is possible to use Doppler ultrasound to examine vascular changes. But first of all, the study is carried out by interviewing the victim and those who were nearby at the time of the injury. Mild and moderate concussions usually have no obvious symptoms.
If there is no fracture of the skull bones, the patient’s blood pressure has returned to normal, then to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor interviews the victim and his relatives in detail about the state of health and the circumstances of the injury.
Concussion is a clinical diagnosis; it is most often established on the basis of complaints and external examination data. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment. If the concussion is mild, he will be sent for treatment at home.
How are they treated?
In the absence of severe symptoms, the doctor will prescribe drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain, nootropic drugs - if there are memory problems, anticonvulsants, non-narcotic painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve headaches.- They will also recommend mild sedatives - teas with mint and lemon balm, valerian tablets.
- He will recommend staying in bed for several days, not reading books or watching TV, categorically prohibiting working at the computer and prescribing additional medications depending on the patient’s complaints.
Diagnosis of concussion
Since doctors determine a concussion after examining and interviewing the patient, it is necessary to pay a visit to a neurologist or traumatologist. To exclude serious damage to the central nervous system, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are prescribed. If skull fractures are suspected, x-rays are taken.
To assess the condition of the cortex, its electrical activity, an echoencephalogram, electroencephalogram, and REG are performed. A complete blood count is done to assess your overall health. Biochemistry is necessary if eclampsia in pregnant women is suspected, which can lead to falls and concussions due to seizures.
Do they put you in hospital?
And if so, in which department are patients with a similar diagnosis located? Moderate or severe concussions require hospital treatment. Such patients are placed in a traumatology, neurosurgical or neurological department.
What are they doing in the hospital? The main task of doctors and nurses is to exclude the presence of severe injuries and provide the patient with strict bed rest for at least the first few days.
Typically, the range of medications prescribed on admission includes painkillers, sedatives and sleeping pills, mainly in the form of injections and tablets. Nursing care means that the nurse brings medications prescribed by the doctor and monitors his compliance with bed rest.
Where to contact?
In case of a severe concussion, you must call an ambulance by calling 03 or 112, or you can also go to the emergency room at your place of residence. In case of minor injury, contact a neurologist at your place of residence. If an injury or bruise was initially treated in a hospital and you want to continue treatment with a good specialist, you can visit a neurologist in a paid clinic.
Clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg
SM-Clinic is a network of clinics in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Appointment with a neurologist - 1500-2000 rubles, radiography of the skull in 2 projections - 1500 rubles. Moscow clinics:
- Medical Center Gritsenko A.G. Consultation with a neurologist by phone is free; radiography of the skull - 950 rubles; In-person consultation with a neurologist at the clinic - 1000 rubles. primary, 800 rub. repeated.
- Network of clinics "Medkvadrat". Initial appointment with a neurologist 1,750 rubles, radiography of the skull bones 1,680 rubles, electroencephalography 2,700 rubles.
- Medline service is a network of medical clinics. An initial appointment with a neurologist costs 1,700 rubles, including laboratory blood tests, ultrasound, radiography, CT, and MRI.
Clinics of St. Petersburg:
- Clinic "Health Workshop". The initial appointment with a neurologist is free by appointment. MRI of the brain and cerebral arteries - 5,500 rubles. Duplex scanning of the main arteries of the head and neck - 2200 rubles.
- Multidisciplinary clinic "Abia". Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a neurologist - 1650 rubles, ultrasound from 900 rubles.
- BaltMed Clinic. Appointment with a neurologist RUR 2,400, duplex scanning of neck and head vessels from RUR 1,000.
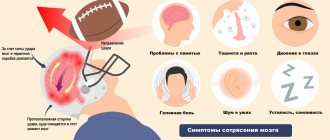
Symptoms
After hitting or falling your head on a hard surface, the brain is shaken inside the skull. This contributes to the temporary separation of the cerebral cortex from the brain stem sections.
A sharp vascular spasm occurs, which goes away after a short time, but cerebral blood flow is temporarily disrupted. What are the main symptoms of a concussion?
Depression of consciousness immediately after a blow or fall. Loss of consciousness is not always present - it may be a state of stupor or disorientation.- Vomiting immediately after an injury, one-time, is usually one of the main symptoms for diagnosing a concussion.
- Increased or slowed heart rate, a sharp jump in blood pressure for a short time.
- The victim turns pale, then turns noticeably red.
- Darkening of the eyes, tinnitus, dilated pupils.
After a short time (from 10 minutes to two hours), the following conditions occur:
- headaches of various types - from local at the point of impact to diffuse;
- severe dizziness;
- unpleasant noise in the ears;
- hot flashes - the face turns very red from time to time;
- mild general weakness, convulsions may occur;
- staggering when walking.
Is hospitalization necessary for this TBI?
If you have all of the above signs, you should definitely see a specialist. A slight concussion in itself is not dangerous, but it can be accompanied by dislocations, cracks in the bones of the skull, and brain contusion. Only a doctor can diagnose all this. Moderate to severe concussions will require hospitalization.
Important! It is necessary to call an ambulance if there is even slight bleeding, loss of consciousness for more than a few minutes, short-term loss of vision, severe vomiting, or a sharp throbbing headache. In case of serious condition, the victim will be left for treatment in a hospital.
Causes and first signs of concussion
The causes of a concussion include a variety of household injuries, as well as a variety of sports or work injuries or road traffic accidents. This disorder is one of the most common: almost everyone who has ever received some kind of traumatic brain injury has experienced a concussion.
Immediately after a concussion, the patient may experience:
- increased breathing;
- one-time vomiting;
- slow or increased heart rate;
- increased blood pressure.
Soon after the injury, these indicators return to normal. Only blood pressure can remain elevated for a long time. It is worth noting that the increase in pressure is due to:
- injury;
- stress factors.
When receiving a traumatic brain injury accompanied by a concussion, the body temperature remains unchanged.
Other symptoms caused by a concussion include:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- pain when moving the eyes;
- noise in ears;
- weakness;
- flushes of blood to the face;
- sweating and discomfort;
- sleep disorders.
In addition, the patient may find it difficult to focus his eyes on anything in the first time after the injury.
Usually the condition of victims improves during the first, or in rare cases, the second week. However, symptoms such as headache or weakness may last longer. Improvement in the condition depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, as well as his age.
In infants, toddlers, and preschool children, for example, it occurs without impairment of consciousness, and the general condition improves already on the third day. Loss of consciousness is also not typical for older people. In older people, instead of loss of consciousness, severe disorientation in place and time is more often observed.