Home care for people with dementia
Caring for older people with dementia is based on the constant presence of a caregiver next to the patient. Considering that a loved one is losing most life skills, the support of a caregiver is required throughout the day in all activities.
Care for mild dementia
The patient is helped to perform morning hygiene procedures, get dressed, and get himself in order. Food is prepared for him and he is fed 5 times a day. Correlate diet and medication schedule. Physiological functions are monitored. If the elderly person does not maintain control of the toilet, a diaper is put on him and changed when he is full.
If motor skills are preserved, the ward is taken for a walk. Fresh air stimulates the functioning of the whole body, filling the lungs with oxygen.
It is advisable to conduct classes on the development of cognitive abilities in the first half of the day. At this time, the brain is more active. The materials used for classes are:
- Crosswords;
- Board games;
- collections of exercises.
Physical exercise is also beneficial for the patient. It is recommended to do gymnastics in the morning, breathing exercises, and accustom the ward to Nordic walking.
Treatment of the disease should be under the supervision of a physician. Periodically, a psychiatrist is called to the patient’s home so that the doctor can assess the elderly person’s condition and make timely adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Care for severe dementia
When a patient with dementia loses the ability to move, it is necessary to care for him as for a bedridden patient. Much attention during care is paid to preventing the occurrence of bedsores. The patient's position is regularly changed: they are turned over on the right and left side, on the back, placing the limbs comfortably. They massage those places where the patient has been lying for a long time, avoiding tissue atrophy. The bedding is changed frequently, even if there are small areas of soiling.
For an elderly person, choose comfortable clothes without rough seams made from natural cotton. The lower part of the kit must be securely fastened so that the patient cannot tear off the diapers on his own. In an unconscious state, the patient can stain himself and the bed with the contents, scratch his skin, and cause an infection.
You may also be interested in the article: Proper care for bedridden patients
Food for an elderly person with dementia should be of a liquid consistency: problems arise with chewing and swallowing food. When feeding, the patient is seated, placing pillows under his back. For drinks, closed sippy cups are used. The food is served at a warm temperature. People with senile dementia will not be able to cool it down on their own. And cold dishes cause aversion in a seriously ill person.
Drug treatment for dementia
There are many types of dementia, so treatment can vary greatly depending on the cause of the disease. Such causes may include vascular pathologies, neuroinfections, trauma, poisoning, and metabolic disorders. Hypertension, obesity, and bad habits are risk factors for the development of dementia and aggravate its course. That is why before therapy it is important to assess the patient’s health status and existing somatic diseases. Metabolic disorders, for example, are the cause of cognitive impairment in five percent of cases, and in twenty percent they are an aggravating factor. It is also important to treat diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory systems, thyroid gland, kidneys and liver. It is necessary to monitor the patient's diet, which should be balanced, contain the necessary vitamins and enough fluid.
The most important step before prescribing medications is diagnosis . In diagnosis, various research methods must be used to exclude the possibility of making an incorrect diagnosis and to correctly determine the type of dementia. Methods include clinical and psychological examination, laboratory and electrophysiological research methods. Neuroimaging methods are usually especially informative. For the most accurate diagnosis, a combination of these methods is recommended.
| Find out more about diagnosing dementia |
Treatment for dementia may vary depending on the extent of the impairment and its origin. For Alzheimer's, Pick's and Parkinson's diseases, especially with severe cognitive impairment, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors . The acetylcholinergic system plays an important role in processes such as concentrating or learning new information. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors help increase the transport of acetylcholine in the brain. Clinical trials of such drugs have shown that their use reduces the severity of cognitive disorders and increases the patient’s ability to self-care.
So, for Alzheimer's disease, the following drugs are prescribed: Donepizil (Aricept), Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl), Ipidacrine (Neuromidine). The latter has relatively recently begun to be used in the treatment of dementia, but has shown good results, especially in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. These drugs are acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, but there is also a drug that is not included in this group - Memantine. The drug affects the glutamate transmission system in synapses. In case of severe impairment of cognitive functions, the activity of the glutamanergic system increases, the drug normalizes neurotransmitter transmission and improves the patient’s mental abilities. The drug can be prescribed either as monotherapy or in combination with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
For Parkinson's disease with signs of dementia, Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl) and Memantine are recommended. The therapeutic potential of Reminyl increases the nicotinergic effect, which increases concentration. For dementia with Lewy bodies, Memantine is recommended.
Rivastigmine (Exilon) has advantages in the treatment of rapidly progressing and presenile forms The drug inhibits two types of cholinesterases, which makes it possible to increase the duration of the therapeutic effect. Exilon is also used in the form of a patch, which ensures a constant supply of the drug into the blood, eliminating fluctuations in drug concentrations and reducing side effects.
For vascular forms of dementia, treatment also includes drugs from the class of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, but they are also supplemented with therapy aimed at the cause of the disorder - that is, vascular pathology. The goals of therapy are to improve cognitive functions, symptomatic treatment and prevention. Due to the large number of causes of vascular dementia, there is no single standard treatment method. Depending on the vascular disease and the characteristics of cognitive and mental disorders, the treatment strategy is chosen.
In diseases where the main risk factor is high blood pressure , it is important to gradually normalize it. To do this, drugs such as ACE inhibitors are used, preferably in combination with diuretics. ACE inhibitors are Parindopril and Lisinopril. Lisinopril will be preferred in cases of combination of high blood pressure and diabetes mellitus.
To prevent cerebrovascular accidents and other complications associated with the cardiovascular system, antiplatelet drugs are recommended. Among these drugs, the most famous is acetylsalicylic acid. These disorders contribute to the emergence and development of vascular dementia. , Donepizil (Arisept), Galantamine hydrobromide (Reminyl), and Ipidacryl are most often used for vascular dementia Mematin is also used for vascular dementia
Pharmacotherapy for dementia is usually long-term and continuous. The therapeutic effect manifests itself within 2–6 weeks of treatment and lasts for six months to a year. Then, unfortunately, during the natural progression of the disease, a decrease in cognitive functions and the appearance of signs of behavioral disorders are possible. However, if therapy is not carried out, deterioration will occur much faster. Drugs can be combined depending on the general physical health of the patient.
Doctors at the Mental Health Clinic have extensive experience working with various mental illnesses, including dementia. With us you can receive inpatient and outpatient treatment, with the possibility of a specialist visiting your home. In the case of a severe form of the disease, hospital treatment is used; for mild and moderate forms, outpatient and home treatment is prescribed.
Do you need a consultation? We know how to help! Call us
Tips for relatives of people with dementia
Caring for a loved one who suffers from dementia is hard work. Psychological burnout inevitably occurs. Watching your ward lose his mind every day has a negative impact on the condition of loved ones.
We recommend following expert advice when caring for an elderly person with dementia:
- Try to accept the disease and its manifestations in behavior. Remember that the patient’s negative statements about you, accusations of theft and deception are not his true thoughts and feelings, but symptoms of the disease.
- Create a warm emotional environment for the ward. You need him to be able to trust you. Then the seriously ill person will not experience anxiety and despair.
- Maintain a clear daily routine. A patient with dementia should develop a sleep-wake pattern to avoid confusion.
- Control your emotions, do not scream, no matter what actions the patient performs. Such reactions can often provoke him to run away from home.
- Do not demand a quick answer to a question from a sick person. He forgets the meaning of words and thinking occurs at a slow pace.
- Try to talk with the patient on different topics: this will help him maintain his speech. An elderly person remembers events of the past clearly; focus on this. In this way, you solve two problems: you support the patient in trying to remember information and evoke pleasant feelings in him. The elderly enjoy reminiscing about their childhood and youth.
- If you feel like you are on the verge of a breakdown, give yourself a social break: ask for help from loved ones, hire a nurse, find a good boarding house for an elderly person.
A patient with dementia is often placed in a boarding house for the elderly when it is not possible to care for him at home.
Caring for a patient with dementia in a boarding house
Boarding houses are divided into two types: public and private. People are admitted to public institutions based on referrals from social service centers. No special voucher is required for a private boarding house. The establishments provide similar services. Differences may relate to the quality and cost of service.
The advantages of a private boarding house are:
- small number of residents;
- modern rehabilitation equipment and technical equipment;
- personal care for seriously ill patients.
At home, care falls on the shoulders of one family member; in a boarding house, care services are provided by different employees. The staff not only have experience in caring for older people with chronic diseases, but also undergo regular training. A patient with dementia receives:
- medical care for illness;
- psychological assistance;
- hygiene care;
- fractional dietary meals.
Patients do not feel lonely. The elderly live surrounded by peers; leisure programs and hobby classes are organized for them.
You may also be interested in the article: How to choose a private facility for the elderly
Prevention of dementia
Eliminating the causes of dementia should begin at a young age.
- Quit smoking and alcohol. Abuse of bad habits causes cerebral infarctions and strokes.
- Play sports and exercise. Movement improves the exchange of oxygen in the blood, the cells receive constant fresh nutrition. Walking improves thinking and attention.
- Remove spicy, fatty foods with excess carbohydrates from the menu. Include fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts, cereals, fish and seafood in your diet.
- Avoid intoxication of the body. Do not choose work associated with hazardous production.
- Get tested regularly for blood sugar and cholesterol levels, and do an ultrasound of your internal organs.
- Train your intellect constantly: learn new information, a foreign language, a profession.
It is important to undergo a medical examination every year from a general practitioner, independently or from a labor organization.
Causes of dementia
1. Diseases of the nervous system:
- Alzheimer's disease;
- Dementia with Lewy bodies;
- Primary progressive aphasia;
- Corticobasal degeneration;
- Parkinson's disease.
2. Poor blood circulation in the brain:
- Stroke in a “strategic” area;
- Chronic cerebral ischemia;
- Binswanger's disease.
3. Metabolic disorders:
- Somatogenic disorders (respiratory/hepatic/renal failure, hypoglycemia);
- Hypothyroidism (thyroid disease);
- Deficiency states (deficiency of B1, B12, folic acid, proteins).
4. Poisoning:
- Metal salts (aluminum, zinc, copper);
- Medicines (anticholinergics, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, antipsychotics, lithium salts, etc.)
5. Brain infections:
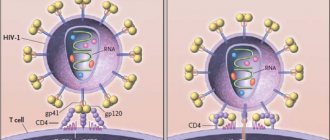
- HIV;
- Spongiform encephalitis (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease);
- Meningoencephalitis.
6. Multiple sclerosis.
7. Traumatic brain injury.
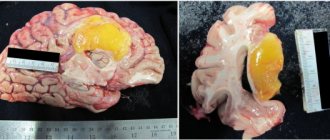
8. Brain tumors.
9. Liquorodynamic disorders (normotensive hydrocephalus).
10. Alcoholism.
Thus, the causes of dementia can be very diverse. In some cases, these are incurable diseases; in others, they are diseases and conditions that can be corrected. Therefore, the opinion that dementia is completely incurable is erroneous, and the results of therapy will depend on the causes of dementia. Also, the symptoms accompanying the pathology largely depend on the causes of dementia.