Oligophrenia is a syndrome of congenital mental defect. This disease is expressed in the form of mental retardation, formed due to pathologies of the brain. The main manifestations of this syndrome are in the form of disturbances in the thought process, will, speech, motor skills and emotions. This disease is characterized by defective mental development in a fully formed adult.
Mental retardation oligophrenia
This deviation causes mental retardation, which is expressed in:
- a decrease in skills acquired as a person grows up;
- delays in the general development of intelligence.
In fact, in medicine there is a general term that refers to all deviations in human development - mental retardation. Oligophrenia can be distinguished from other pathologies by the following characteristics:
- very difficult to train;
- repeated mastery of the same task practically does not increase the chances of mastering it;
- complete destruction of brain functions;
- intellectual dysontogenesis;
- with very rare exceptions, the inability to become a full-fledged member of society.
MODERATE AND SEVERE FORM OR IMBECILITY
With moderate brain damage, imbecility develops. This diagnosis implies that the child is able to understand speech addressed to him, has relatively developed speech skills, and can learn to perform simple automatic actions after long training.
Imbeciles have impaired behavioral sphere, their attention is quite unstable. Such children are very difficult to teach because they do not understand the meaning of their work and are completely indifferent to its results. They are usually very attached to their caregivers.
Timely correction of imbecility will allow children to master the following skills:
- Simple labor operations.
- The ability to self-care, but to the best of the individual child’s abilities.
- Orientation in everyday life.
- Basics of correct behavior.
In the process of correctional work with such children, special attention is paid to the development of their mental functions and cognitive activity. Imbeciles are recognized as incompetent, and their education is carried out in specialized orphanages.
Diagnosis of oligophrenia
At the current stage of development of medicine, some of the diseases that are associated with mental retardation can be detected even at an early stage of pregnancy. One such disease is Down syndrome. If it is detected, the doctor must tell the parents in detail about oligophrenia and how this pathology may be accompanied. They should know how a child who develops this disorder can grow up. This is necessary so that parents can decide for themselves whether they should terminate the pregnancy or not.
Another stage of the diagnostic study begins immediately after the birth of the baby and consists of a blood test for the presence of hypotherosis and phenylketonuria. These diseases often cause mental retardation.
When symptoms of oligophrenia appear in a child who was considered completely healthy until that time, a fairly wide range of studies are carried out to search for its causes. To begin with, the history of his life and the presence of various diseases, mainly mental, along the family line are examined. The pregnancy history is also checked for asphyxia or hypoxia. The postpartum period is also important in this case, especially regarding possible injuries to the child at this time.
After all this, the child is examined to identify neurological and mental abnormalities, as well as to determine the severity of the disease if it is detected. This is followed by other studies that are designed to determine diseases of the internal organs, dysfunction of the enzyme system and the presence of congenital diseases. Depending on the results obtained, subsequent actions are determined.
Causes of mental retardation
All causes of this syndrome are usually divided into two types: congenital and acquired. The first include:
- prematurity of the child;
- genetic abnormalities;
- chemical or infectious damage to the fetus;
- exposure to ionizing radiation while inside the womb;
- birth injury;
- asphyxia.
Acquired causes of the development of oligophrenia include:
- central nervous system infections;
- head injuries;
- hypoxia of the brain.
Often mental retardation is caused by pedagogical neglect, characteristic of dysfunctional families. In addition, there have been cases of oligophrenia, the causes of which have not been fully elucidated.
Approximately 50% of cases of this disease are the result of genetic changes. These are mainly chromosomal abnormalities, which include Down syndrome and other similar manifestations. Sometimes mental retardation is caused by a dysfunction of certain genes or their mutation, the degree of which exceeds a thousand. In addition, oligophrenia can accompany diseases such as:
- Toxoplasmosis. Caused by parasites that accompany domestic animals. When ingested by a pregnant woman, they also penetrate into the fetus, causing many malformations.
- Phenylketonuria. Caused by a disorder of phenylalanine metabolism. As a result, a large number of toxic products of its breakdown are formed. If you start treatment in a timely manner, you can avoid the formation of oligophrenia.
- Microcephaly. It represents the formation of a skull that is too small relative to the size of the brain. Accordingly, the brain also slows down its growth.
- Hydrocephalus. It consists of the accumulation of too much fluid in the brain area due to obstructed outflow or too rapid formation.
TRAINING AND EDUCATION
Children with such a form of delayed intellectual development as debility are capable of learning. Such children can attend regular schools, but their education is carried out in auxiliary programs. But you should not evaluate them by the amount of knowledge acquired; it is much more important to teach the lagging child skills that will help him in the future. If he grows up in love with the support of loved ones, then he will be able to learn to perform the simplest labor operations, and he will perform them with pleasure.
Mental retardation cannot be cured; such people will remain good-natured children who do not know how to lie for the rest of their lives. They are good at handicrafts and are happy to help with housework. If loved ones constantly talk to them, read educational books to them and show educational television programs, then a person with mental retardation will develop. The lack of such support leads to inevitable degradation and loss of acquired skills.
Features of oligophrenia
This phenomenon belongs to a wide group of diseases that are associated with developmental disorders. It is considered to be an abnormal underdevelopment of a person’s mental state, his personality and even the whole organism. Every hundredth person in industrialized countries suffers from this disease. Moreover, more than 3/4 of this number have mild mental retardation. There are twice as many men with oligophrenia as women.
It is not possible to conduct more accurate statistical studies because there are differences in the diagnosis of this disease, in the degree of society's tolerance for mental disorders, and in the availability of medical care.
Oligophrenia is not a progressive disease. This is most likely a consequence of a previous serious illness. The degree of mental retardation of patients with this disease is assessed by a special coefficient, which is derived on the basis of psychological tests. It is extremely rare for oligophrenics to be recognized as incapable of adapting to life in society.
Oligophrenia symptoms and signs
In fact, it is not entirely correct to call oligophrenia a disease, because it is actually a pathological condition caused by various kinds of diseases. Symptoms of oligophrenia appear in combination with somatic manifestations, as well as disturbances in the emotional, motor and speech spheres. Some of the most common manifestations of this condition are:
- Delay in physical development. Depending on the form of this disease, it can be almost invisible or very severe. For example, an adult may look like a teenager of 15-16 years old.
- Slowing down of personal development. Most often it manifests itself in everyday situations, such as choosing clothes or buying groceries. Such oligophrenics are easily suggestible, unable to make adequate decisions on their own.
- Weakened memory. Most often, such a person remembers numbers, names or numbers very selectively. And he does it completely mechanically.
- Distracted attention. A person simply cannot concentrate on one thing. They are constantly distracted.
- Poor vocabulary and illiterate speech. With a mild form of the disease, a person can even be taught meaningful reading. If a person is diagnosed with a severe form, then the maximum that can be achieved even after many years of training is mechanical spelling. In this case, the mental retard will not even understand the meaning of what he just read.
- Comprehensive mental retardation. The difference from ordinary mental retardation is that it affects not only personality characteristics and intelligence, but also all other traits of human character. These include the ability to perceive, emotions, speech, memory, motor abilities, willpower, the ability to think and concentrate.
- Abstract thinking disorder. This symptom can be called the most characteristic. A person suffering from oligophrenia completely lacks imaginative thinking. It is more based on a specific situation, which is typical for two or three year olds.
The most vivid and detailed symptoms appear only at school age. In children under one year of age, mental retardation is almost impossible to determine, except perhaps in the most severe cases. As for younger children, such deviations can be identified by a lag in speech and mental development, as well as a lack of interest in the world around them.
SIGNS
First of all, it is worth noting that mental retardation is not a disease from which one can be cured. This condition is caused by irreversible changes in the cerebral cortex during the formation of the nervous system in the perinatal period. The main actions of doctors and other specialists will be aimed at socializing such a child in society and teaching him the simplest skills.
Signs of mental retardation in children:
- low level of cognitive activity. The child simply does not understand why he needs to learn something, and therefore does not want to make efforts in this direction;
- motor skills practically do not develop;
- significant delay in speech development, small vocabulary. The child cannot form sentences and pronounces words incorrectly;
- lack of abstract thinking, inability to perform even the simplest logical operations, thought processes are slow or completely absent;
- the child plays the simplest games because he can only imitate those around him. Such a child chooses work that is very easy, since it does not require volitional effort;
- mood can fluctuate sharply for no particular reason, excitability can be both quite high and low;
- the child perceives the world around him with significant difficulties; he is not able to navigate in space. Such children are not able to understand the process of forming a whole from individual parts and cannot determine the main thing;
- concentration of attention is short, switching from one type of activity to another occurs very slowly.
Children with such deviations are characterized by voluntary memory; they usually focus on the external features of an object rather than on its internal features.
Signs of mental retardation in children can appear immediately after birth, but most often this pathology is detected after 3 years. The time of diagnosis largely depends on the severity of the condition: the more significant the damage to the central nervous system, the earlier the symptoms of mental retardation will be noticeable.
Forms of oligophrenia
In total, there are three forms of oligophrenia:
- First. Caused by hereditary factors. These include diseases such as Crouzon syndrome, Marfan syndrome, true microcephaly and others.
- Second. It is characterized by the fact that the development of oligophrenia is caused by damage to the fetus inside the womb. This is usually caused by various viral infections, toxoplasmosis, congenital syphilis, hormonal disorders or listeriosis.
- Third. Usually occurs during fetal development when exposed to factors such as Rh factor conflict. The afterbirth period is affected by birth trauma or asphyxia. And the transmission of infections, traumatic brain injuries, congenital hydrocephalus, as well as poor development of brain systems.
There are also true and false forms of oligophrenia, which do not belong to any of the above.
Causes of dementia in children
About 70% of all cases of acquired dementia are due to Alzheimer's disease, which primarily affects older people over 65 years of age. For this reason, dementia in young people is rare and is mainly due to hereditary factors. Gene mutations in chromosomes provoke increased production of abnormal amyloid plaques, which affect nerve cells and destroy established interneuron synoptic connections. Degradation of brain activity in people under 40 years of age can also occur as a result of mechanical head injuries, drug, alcohol or radiation intoxication, as a complication of chronic cardiovascular pathology.
Childhood organic dementia is usually a complication of some serious diseases. Secondary residual dementia occurs with stable residual disorders of the brain, without further deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Main causes of dementia in children and older people
| Causes of dementia in children | Causes of dementia in adults |
|
|
Hereditary degenerative dementia in children develops against the background of such genetic diseases as Newman-Pick, Batten, Huntington or Lafora disease, Rett and Sanfilippo syndrome, leukodystrophy. Hereditary forms of dementia progress rapidly as children grow and the clinical manifestations of the underlying genetic disease manifest. An intense increase in symptoms can lead to death already in adolescence.
Important. Organic dementia in children, and especially in adolescents, is often aggravated by psychological trauma. The obvious loss of acquired skills has a painful impact on the child’s emotional state and can deprive him of his motivation for rehabilitation.
Degrees of mental retardation
Oligophrenia has several stages, which differ in the nature of manifestation and the different level of mental abilities of people suffering from it. There are three stages in total: mild, moderate, severe.
Mild mental retardation or mental retardation
This stage also bears the definition of “moronism.” If it manifests itself in a child, he begins to develop cognitive functions, motor skills and articulation much later than his peers. Speech defects are observed. The stage of debility is typical for the age period from 8 to 12 years.
Such children should be educated in specialized institutions. At the same time, a program is studied that corresponds to four grades of high school. During this time, they can master mechanical reading, writing and counting skills. These people can serve themselves, make simple purchases, and they are also able to help with housework.
There are cases, although not too often, that oligophrenics, despite a low general level of development, can be gifted with one developed ability. This could be artistic talent, memory, or the ability to perform complex mathematical calculations.
The intelligence level of such patients is in the range of 50-69 points. This allows them to master some simple professions.
Average degree
Defined as imbecility. A person can normally navigate in a familiar environment and independently satisfy all the needs of the body. There is promiscuity in sexual behavior and an increased level of sexual desire. Behavior is often aggressive.
People in such a state fully understand what is being said to them and can even memorize several simple phrases and even learn to count elementary examples. They can also learn how to take care of themselves and even perform simple tasks if there is a specially equipped work area.
Imbeciles are very attached to their loved ones and react very strongly to both praise and blame. Their thinking is greatly inhibited, which is why they completely lack initiative. They get lost in a new environment and have great difficulty adapting to new circumstances.
It has two forms: unexpressed and expressed. The first corresponds to psychological age up to 9 years and intellectual level ranging from 35 to 49 points. The second corresponds to an age of up to 6 years and an IQ from 20 to 34 points.
Severe mental retardation
It is called "idiocy". Represents the most severe degree of this disease. It is characterized by very severe impairments of intellectual development, which correspond to the psychological age of 1 to 3 years. At the same time, the level of intellectual development is below 30 points.
These patients are deeply disabled and require serious care. Their thinking and speech are in their infancy. All emotions are limited to the pleasure of satisfying physiological needs. If this fails, then these emotions are replaced by displeasure, accompanied by anger and aggression.
Such people are not subject to any training. At best, they can only understand individual words; most often, even this does not happen. They are unable to recognize close relatives. The severe consequences caused by such profound developmental deviations lead to the fact that they very rarely live to be 30 years old. And then only if they are properly cared for, because they are completely incapable of even caring for themselves.
What you need to know about dementia? Memo for relatives
Dementia is an acquired dementia, characterized by a persistent decline in memory and intelligence, impaired orientation in time and space, with the loss of previously acquired knowledge and practical skills, as well as with the difficulty or impossibility of acquiring new knowledge.
Dementia affects mainly older people, but can also appear in youth due to injuries, inflammatory diseases of the brain, strokes, and the toxic effects of alcohol and drugs.
Gradually, every year more and more, a person with dementia loses touch with the present and moves further back into the past. What was perceived later is recorded in memory weaker and is forgotten first. But the memories of youth, on the contrary, are preserved.
For example, a 70-year-old man, remembering nothing about the last 40 years of his life, feels like a 30-year-old man. And a situation easily arises when he, no longer recognizing his loved ones, wonders: how can this elderly lady be his wife if he himself is only 30 years old.
Either he recognizes his 50-year-old daughter as a mother, or, having been retired for many years, he is convinced that he needs to get up early every morning and go to work, etc.
It is this phase of the disease, when motor activity is preserved, but memory and orientation in place and time are significantly lost, that is the most difficult for everyone affected by this situation.
Patients react irritably, and often aggressively, when someone “wants to mislead them with incorrect information” (as it seems to them).
Relatives are forced to watch helplessly as their relative gradually loses mental abilities, no longer recognizes them, swears for no reason, fussily gets ready to go somewhere, becomes awkward and unkempt, begins to get lost in his own apartment, etc.
But at the same time, the patient retains a “plan” of his previous environment in his head. For example, if previously you had to turn right around the corner twice, and there was your parent’s house. Today, the patient, getting up from his chair, turning the corner to the right twice, opening the closet door, thinks that he is entering his parents’ house, and will try to break through the shelves.
To treat with great sympathy this unfair, in the opinion of relatives, irritability and aggression of a patient with dementia requires such a huge degree of understanding and patience that not everyone can do it.
The lack of understanding and patient attitude of relatives towards the painful condition of a person suffering from dementia aggravates both the severity of the disease and the situation in the family.
What are the severity levels of dementia?
Mild degree: professional activity and social activity are clearly limited; the ability to live independently, maintain personal hygiene is preserved, mental abilities are not affected.
Medium degree: difficulties living independently; some control is required;
Severe: activities of daily living are impaired; failure to maintain minimal personal hygiene; motor abilities weaken; no more control over the body; the need for constant maintenance and care from others.
What is most common in patients with dementia?
- severe impairment of short-term and long-term memory, for example, the patient does not remember names or does not recognize people; difficulties with understanding and recognition; speech disorders; disturbances in orientation in time and space; inability to perform personal hygiene up to complete loss of ability, for example, to go to the toilet independently; disturbance of motor processes during daily activities and even during simple movements such as walking;
- apathy (indifference);
- disturbance of social behavior, irritability and aggressiveness; lack of motivation or ability to manage a home.
How does the behavior of people with dementia change and how should relatives behave with them?
Patients become distrustful of their surroundings. They are in continuous movement all day long, often fiddling with their clothes and, it seems,... Many patients may scream for no apparent reason. They especially often experience excruciating anxiety. Patients often resemble small children in that they suddenly experience mood changes for no apparent reason. The resemblance to the child encourages relatives to address them in the same way, which is correct from the emotional side. You should always react very positively to patients. Refuse once and for all from any types of punishment. Punishment is completely meaningless and will lead nowhere. A person with dementia is unable to learn anything, even if he really wants and tries. The patient does not have the opportunity to behave differently, that is, correctly.
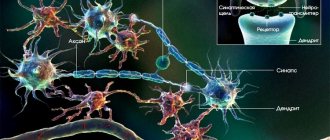
How does complete forgetfulness develop?
Any type of dementia is caused by the death of nerve cells in the brain. In dementia, harmful proteins called amyloids are deposited in certain areas of the brain. It is still not possible to find a treatment to prevent the occurrence of such plaques. It is also known that the interaction of nerve cells in the brain occurs with the help of special substances, so-called transmitters. These substances pass through the gap between the cells and attach to a specific receptor site. Each receptor fits a specific transmitter like a key to a lock. If “the key fits the lock,” then “the cells speak to each other,” i.e., information is transmitted correctly. When there are too few or too many substances transmitting information, the interaction of nerve cells is disrupted, which leads to the occurrence of nervous and mental diseases. In dementia, two transmitters primarily play a role: glutamate and acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is involved in learning processes and therefore its deficiency leads to the impossibility of effective learning. Important control centers of the brain depend on glutamate and 70% of all neurons in the cerebral cortex are affected by it.
Modern methods of treating dementia.
Treatment is carried out in two directions:
- drug therapy
- optimal care that supports mental initiative and a sense of security.
Classification of oligophrenia
There are several types of classification of this pathology. The first divides it into:
- primary, which includes genetic mutations;
- secondary, which arises due to other factors.
There is also a classification created by M.S. Pevzener and modified in 1979. She divides oligophrenia into:
- light;
- having disturbances in the processes of inhibition and excitation;
- having disturbances in the functioning of the analyzing system;
- with a predominance of psychopathic forms of behavior;
- with severe underdevelopment of the frontal lobes of the brain.
Oligophrenia in children
This pathology in children manifests itself in the form of a lack of interest in understanding the world around them, the absence of most emotions from things that worry other children, as well as in the deep originality of their inner world. In childhood, mental retardation still allows development, but this process occurs much more slowly than in peers and is accompanied by certain deviations.
After the child has developed speech, the risk of developing oligophrenia is significantly reduced, but another form of it, dementia, may begin to progress. In this case, the violation of intellectual development becomes irreversible, because as it progresses, the human psyche completely disintegrates.
There is only one exception to this rule. It lies in the fact that mental retardation is accompanied by a mental illness, which only lulls this effect. The development of such children most often moves in a completely unfavorable direction.
Signs of mental retardation in children include weak interest in the objects around them. For example, babies do not try to reach for toys or do not want to play with them. This interest appears only at the age of 3 years. Children who have been diagnosed with oligophrenia, if they do not study with speech pathologists, even at the end of the preschool period, instead of drawing, can only chaotically and aimlessly scribble with a pencil.
Oligophrenic children are usually characterized by involuntary memorization of any objects or events. The more impression they made, the more strongly they will be etched in the child’s memory. Voluntary memorization begins to form only at the beginning of school age. Mental retardation is characterized by instability of feelings, emotional immaturity, a limited range of experiences, extremes in the manifestation of emotions such as fun, joy or grief. They are dependent, lack initiative and impulsive.
DEEP DEGREE OR IDIOTY
Idiocy is the most severe form of pathology. The child is not able to comprehend the world around him, speech functions are very limited. Coordination of movements, behavioral and emotional disorders are severely impaired, and motor skills are also impaired. All the desires of such children are aimed only at satisfying the needs determined by human physiology.
In turn, idiocy is divided into three types:
- deep idiots, they can also be called overweight and recumbent. Such children lack sensations, their behavior is similar to the behavior of animals, and stimuli can cause an inappropriate reaction. Incapable of self-care;
- typical idiots have more pronounced instincts. In order to be able to satisfy their needs, such children can even utter a few sounds, but speech does not develop beyond this;
- speech idiots are able to pronounce some words, they have a reaction to the people around them and the world, but they have no cognitive activity. A feature of this condition is low coordination and uncertain movements.
Children with this diagnosis are considered incompetent and cannot learn. The efforts of specialists are usually aimed at ensuring that idiots can acquire the simplest self-service skills. The process of correcting this condition is carried out in specialized children's boarding schools.
Qualified help for oligophrenia
The Salvation Clinic provides treatment for debility and imbecility in inpatient and outpatient settings. Specially trained, highly qualified personnel (speech therapists, psychologists, psychiatrists, psychotherapists) work with patients. The clinic fully complies with international standards. There is a modern renovation, good diagnostic capabilities, and conditions for healing the psyche and body. We offer:
- European health care service;
- high quality of psychotherapeutic assistance;
- progressive correctional methods for the development of social skills, speech, thinking, attention;
- moral support of relatives;
- 24-hour counseling;
- a real chance to socialize, return to normal life without restrictions;
- courteous attitude towards patients;
- affordable prices for the treatment of mental retardation.
In case of idiocy, hospitalization in a specialized hospital is provided. We provide accommodation in separate rooms with all amenities. The rooms are equipped with orthopedic furniture, television, private bathroom, and air conditioning. You can install an individual nursing station. Patients are under constant supervision of responsible staff. Adequate fortified nutrition, rest, and a variety of leisure activities are provided. Outdoor walking tours are offered daily. The clinic is located in a park area, we have a landscaped area. There is specialized security. Isolation from the external environment is ensured, which is especially important in severe mental retardation, in which the following complications may occur:
- attempts to commit murder/suicide;
- socially dangerous behavior;
- excessive aggressiveness.
In a calm environment with proper care, the patient can relax and live a happy life. We provide a report on the patient’s condition at the first request of relatives, and we carry out our work conscientiously. Contacting our center is a real opportunity to improve the quality of life of a loved one with mental disabilities and allow themselves a break. It is difficult to come to terms with the idea that a loved one is not like everyone else. We will be able to share the burden of responsibility with you and provide proper care to the patient. Contact us, there is no need to be alone with your problem!