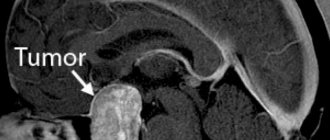
Various types of tumors in the brain account for approximately 6% of all tumor formations in the human body. They occur in approximately 10 - 15 cases per 100 thousand population.
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member of the St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists ALEXANDER SERYAKOV MD, professor, oncologist, hematologist, radiologist (radiation therapist) of the highest category, leading oncologist of the SM-Clinic holding »
What is a brain tumor
“Brain tumors,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov, “are intracranial neoplasms, including both tumor lesions of the brain tissue itself, as well as nerves, membranes, blood vessels, and endocrine structures of the brain.
Such formations can be benign or malignant in nature. Benign tumors put pressure on certain areas of the brain directly adjacent to the tumor and can lead to disruption of the functioning of individual structures in the brain itself.
A malignant tumor is distinguished by very rapid growth and the ability to grow into the surrounding tissues. Glioma is one of the most common types of malignant brain tumor. Its most aggressive type is glioblastoma. It grows quickly and has no clear edges. It is difficult to treat, with a high relapse rate.
Other malignant brain tumors include:
- meningiomas – tumors of the meninges;
- neuroepithelial tumors (gangliomas and astrocytomas);
- Neuromas are special tumors from the membranes of nerve cells.
Treatment of brain cancer
Treatment of brain cancer is a set of measures aimed at getting rid of the disease, improving the patient’s well-being and returning him to a full life.
There are protocol methods for treating brain cancer, such as radiotherapy, surgery, and chemotherapy.
The Russian-Japanese Oncology Center uses only proven and well-proven methods.
The maximum effectiveness of treatment for brain cancer is achieved only if there is a strong desire of the patient for recovery, the support of loved ones, and the trust of the doctor and the patient. Treatment is carried out in accordance with high international standards, using the scientific clinical base and experience of scientists from the Russian Federation and Japan.
Statistics from the Oncology Center show stable results in the treatment and rehabilitation of brain cancer.
Patients who applied at stage I.
Within a year after the discovery of brain cancer, after rehabilitation treatment, 100% of those who applied survive and live a full life for more than 20 years - almost 90% of patients
Patients who applied at stage II.
Within a year after the discovery of brain cancer, after rehabilitation treatment, 100% of those who applied survive and live a full life for more than 15 years - almost 72% of patients
Patients who applied at stage III.
Within a year after the discovery of brain cancer, after rehabilitation treatment, 100% of those who applied survive and live a full life for more than 10 years - almost 48% of patients
Patients who applied at stage IV.
Within a year after the discovery of brain cancer, after rehabilitation treatment, 100% of those who applied survive and live a full life for more than 5 years - almost 28% of patients
Causes of brain tumors in adults
Scientists have not yet determined the exact cause of tumors, but there are assumptions about the connection of their growth with the effects of radioactive radiation, toxins penetrating the body, and environmental pollution.
Children may develop congenital neoplasms - one of the reasons is considered to be intrauterine development disorders. A possible factor may be traumatic brain injury, which can also intensify an already existing process.
There is evidence that some brain tumors can develop after radiation therapy prescribed for the treatment of other pathologies, immunosuppressive treatment, and HIV infection. There is a hereditary predisposition to certain types of brain cancer. But for many people the cause remains unknown.
About 10 - 30% of brain tumors are of metastatic origin - these are cells that are carried by the blood flow (less often lymph) into the brain vessels, tissues, and membranes. About 60% of such tumors are multiple.
Most often it metastasizes to the brain:
- in men – lung damage, colorectal cancer, kidney damage;
- in women - breast cancer, melanoma, colorectal and lung cancer.
Intracerebral metastases occur with cancer of the uterus, digestive tract or prostate.
Can glioblastoma be cured? Doctors talk about the most dangerous brain cancer
The media, citing doctors, claim that actress Anastasia Zavorotnyuk has glioblastoma - brain cancer. In recent years, Zhanna Friske, Dmitry Hvorostovsky, Mikhail Zadornov, and Yves-Saint Laurent have passed away from this disease. Glioblastoma is difficult to recognize in its early stages, and when the tumor becomes aggressive, treatment is not always effective. RIA Novosti talks about the diagnosis of glioblastoma and the most advanced methods of therapy.
"The Silent Killer"
The sad news about Anastasia Zavorotnyuk’s illness coincided with the European Week of Early Diagnosis of Head, Neck and Thyroid Tumors. For the seventh year in a row, in the second half of September, hundreds of oncology clinics in different countries are providing free examinations to everyone. In Moscow, it was possible to get tested at several medical centers at once, including the N. N. Blokhin National Medical Research Center for Oncology and the University Clinical Hospital No. 1 of Sechenov University.
Every morning, several dozen people gathered in the hall of the university clinic. Most came to specialists with tests and head scans, like 60-year-old Muscovite Valentina K. Two years ago, a doctor at a district clinic suspected she had a malignant tumor in her brain. Further examination did not confirm the diagnosis, but Valentina is now carefully monitoring her health.
“Cancer is a silent killer. When the patient exhibits the first symptoms, we are usually talking about the third or fourth stage. Treatment is most effective in the first two stages. Then up to 90 percent of patients recover. Then they are registered all their lives, because cancer is considered a chronic disease,” said oncologist surgeon Alexander Guslyakov
, who examined patients as part of the week of early diagnosis of head, neck and thyroid tumors.
True statistics are hidden
“Unfortunately, there are no accurate data on the prevalence of brain cancer in Russia and the world, because this is a category of tumors of the so-called closed anatomical spaces.
Such neoplasms arise deep in the body and are difficult to diagnose. This is the so-called latent carriage. Let's say a person gets into an accident, and during the autopsy they find a tumor in his brain. The same applies to pancreatic or bile duct cancer. We don’t know specific numbers, we can only extrapolate. For example, Academician Konovalov believes that there are about 35 thousand such tumors in our country per year. But these are selective statistics, it is impossible to completely identify this disease,” explained the head of the department of oncology, radiotherapy and plastic surgery at Sechenov University, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences Igor Reshetov .
Malignant tumors in the human brain are called gliomas. They are distinguished by the degree of aggressiveness, histological characteristics, and the age of the patients. The most common in this group is considered to be glioblastoma multiforme - approximately 12-15 percent of all identified brain tumors (according to researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles). Most often, men suffer from glioblastoma.
The exact causes of this disease are still unknown. Experts speak rather about a combination of factors that cause the disease - heredity, lifestyle, and previous injuries. To date, several genetic mutations have been identified that are, to one degree or another, associated with the risk of developing brain cancer. Scientists estimate the influence of individual genetic damage on the appearance of malignant tumors at 50-60 percent, but they admit that for almost a quarter of tumors biomarkers have not yet been determined.
“We all dream of finding a very specific molecule, marker, metabolite or mutation that would allow one test to identify those who have the highest chance of getting sick.
Unfortunately, this is not yet possible. This method currently only works for rare forms of tumors, such as medullary thyroid cancer. They do have a clear genetic determinant, and for them there is a program of preventive surgical treatment. As for brain tumors, we do not have such tools. Even if we scanned everyone’s head once a year (which is insanely expensive), it would be ineffective. There is such a thing as tumor biology. This is the time of doubling of the tumor mass, the timing of chronobiological growth, etc. So, some types of brain tumors change their characteristics within a month, and this can happen in the interval between examinations,” said Igor Reshetov.
According to the academician, patients themselves can often notice the first signs of a tumor in time; the main thing is to be attentive to your body.
“There is a very simple recipe: if you yourself notice some change in the mucous membrane, if it seems that you have asymmetry in the pupils, some kind of unmotivated headache, if something is constantly inflamed somewhere, do not hesitate, immediately - clarifying further examination. There is no need to wait even two or three weeks and self-medicate. Tumors do not have any special symptoms. They all occur under the masks of other diseases,” the oncologist said.
Zika virus against glioblastoma
Today, the prognosis for those diagnosed with brain cancer is usually disappointing. The lowest chances are in patients with glioblastoma. This type of tumor is considered the most aggressive, and patients treated on average live 15 months. However, now, thanks to progress in medicine, about five percent of patients live up to five years.
Among the innovative treatment methods is virotherapy, when oncolytic viruses are delivered to the tumor. They infect predominantly cancer cells rather than healthy ones. Thus, an international group of researchers has shown that a weakened strain of the Zika virus is effective against glioblastoma. When combined with chemotherapy, it significantly reduces brain tumors in mice. In Russia, scientists from Novosibirsk State University proposed using the smallpox virus for virotherapy of malignant gliomas.
British and American oncologists tried to destroy malignant tumors from the inside. They successfully tested the substance KHS101 on cell cultures and mice. It slowed the growth of glioblastoma cells by damaging their mitochondria. In addition, modified lymphocytes created by American and Italian oncologists also helped sick rodents.
“In my opinion, all research in this area is equally promising.
They all need to be developed. Because treatment of this type of tumor is always combined, it is necessarily a multidisciplinary approach. In Russia, the method has become widespread in the last ten years, when departments for tumors of the central nervous system began to open in the structure of oncology dispensaries and institutes. This made it possible to do the most important thing - to provide combined treatment,” noted Igor Reshetov.
Link to publication: ria.ru
Signs of a brain tumor in adults
Focal symptoms are often among the first to appear.
They arise due to the pressure of the tumor on the surrounding tissues and chemical reactions to foreign cells, hemorrhages, blockage of blood vessels with a tumor embolus, compression of tissues and nerves. As the tumor grows, symptoms from neighboring areas appear, then general brain symptoms. If the tumor is large, a so-called mass effect may occur (the main structures of the brain are displaced, causing the cerebellar region to become wedged into the opening of the skull). One of the early signs is headache. It is usually local and occurs due to irritation of blood vessels, nerves, and meninges. There may be diffuse pain throughout the head, which is typical of meningeal lesions. The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, deep, intense or bursting.
Another sign is vomiting, which is not associated with food intake. It may or may not be at the peak of the headache.
Dizziness occurs in the form of dips, rotation of the body or objects around.
Possible muscle weakness, muscle hypertonicity, uneven on one and the other side of the body, changes in tendon reflexes. Muscle-joint sensations may also suffer - sensations during movement, pressure, vibration.
For many tumors, convulsive syndrome is typical - sometimes it becomes the first sign of brain damage. There may be absence seizures or tonic-clonic seizures, Jacksonian epilepsy. Some people also experience an aura before attacks. As the tumor grows, there may be partial seizures or decreased activity of the lesions.
Some people may have mental disorders. Sloppiness, lack of initiative, aggression, euphoria or causeless gaiety, apathy, complacency can also be signs of brain damage. Tumor growth increases the severity of symptoms. Visual hallucinations, severe memory disturbances, attention problems and thinking problems may occur.
Possible problems with vision, congestion in the area of the optic nerve - these are floaters before the eyes, blurred vision, fog, blurred vision. Fields of vision may be lost.
Additionally possible:
- hearing loss;
- aphasia;
- ataxia;
- eye movement disorders;
- hallucinations (auditory, gustatory);
- autonomic dysfunctions.
If the hypothalamic-pituitary region is affected, hormonal metabolism suffers.
First manifestations and symptoms
The first signs of breast cancer are not highly specific, but their appearance requires an unscheduled consultation with a doctor. Among these symptoms:
- Headache. This malaise is a typical cerebral sign of a progressive tumor.
- Movement disorders. The arm begins to bend poorly, the leg ceases to obey, and hypertonicity of some muscles appears.
- Nausea and vomiting. This general cerebral sign of brain cancer can appear outside of meals, including on an empty stomach. Sometimes a wave of uncontrollable gushing vomiting comes without preliminary nausea, suddenly and reflexively.
- Dizziness. The main reason for this symptom is increased intracranial pressure. The discomfort is complemented by tinnitus and hearing impairment.
- Mental signs. Patients note a feeling of stupefaction, attention weakens, and memory and perception are dulled. There may be a decrease in criticality, deterioration in associative thinking, lethargy and indifference.
The way brain cancer manifests itself also depends on the location of the tumor. Before signs of increased intracranial pressure appear, the patient often experiences an epileptic syndrome. Convulsive tonic-clonic seizures manifest themselves in brain cancer of different locations, but most often such symptoms are typical for damage to the frontal lobes.
Stages of brain tumor in adults
A typical stage for a cancerous lesion determines treatment options, prognosis, and typical signs and symptoms.
There are 4 stages in total - from the mildest to the extremely severe. The first stage is when one of the parts of the brain is affected by a small neoplasm, a nodule, there is no penetration into neighboring tissues, there is no pressure on the surrounding areas of the brain.
The second stage - the tumor grows slowly, but there is penetration into neighboring areas;
The third stage - the tumor changes its structure, cells divide faster, neighboring sections and tissues grow;
Stage four – the tumor is large, grows into neighboring brain structures, and distant metastases are possible.
Diagnostics
The first examination is carried out by a neurologist.
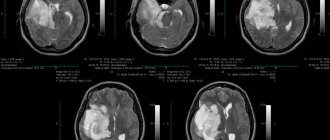
The doctor evaluates general complaints, conducts an examination, examines muscle tone, reflexes, communication, emotions and cognitive functions. EEG and echo-encephalography are also performed. A visit to an ophthalmologist is indicated to assess the condition of the fundus, acuity, and visual fields. Suspicion of a tumor formation is an indication for a CT or MRI of the brain. Angiography of cerebral vessels, PET scan and other complementary examinations may be prescribed. In some cases, a biopsy can help determine the type of cancer, but it is not possible in all cases.
Modern methods of treatment
“The volume of treatment is selected depending on the course of the brain tumor,” says oncologist Alexander Seryakov.
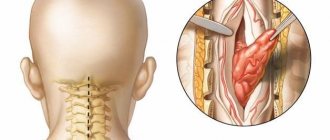
– The most effective is surgical removal of the tumor. The use of surgical microscopy and navigation allows for radical removal of the tumor and minimizes injury to healthy tissue. If the tumor cannot be completely removed, after its partial removal, the patient is prescribed radiation, as well as chemotherapy, targeted (“targeted”) or immunotherapy. For small malignant tumors (up to 3 cm), stereotactic radiosurgery is possible (using Cyber-Knife linear accelerators or Gamma-Knife gamma machines). To remove tumor tissue, many beams of radiation are used at once, which are directed at one point or collected into one beam. Its direction will constantly change during the irradiation session, but the beam necessarily passes through the tumor tissue.
For large tumors, and especially in cases where it is impossible to surgically remove the tumor, classical external beam radiation therapy is used. In some cases, it is used after surgery to reduce the risk of relapse (regrowth).
Chemotherapy is carried out with cytostatic drugs, taking into account the type of tumor. The effectiveness of chemotherapy increases significantly if it is combined with radiation therapy.
Targeted therapy in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy improves survival of patients with aggressive brain tumors. Most often used in the treatment of glioblastomas.
Currently, methods of using immunotherapy for malignant tumors (antitumor vaccines, immunotherapy drugs) and its integration into existing standards of treatment are being considered.
Observation after treatment
Regardless of the type of brain tumor, the patient will undergo regular MRI examinations in the future.
The frequency of MRI procedures depends on the diagnosis.
- If the tumor is characterized by changes and growth , the patient needs to undergo MRI more often - perhaps once every 2 months.
- If the tumor grows slowly or is a benign formation , scanning is prescribed once every 3-4 months.
In the absence of pathologies, examinations are carried out once every six months, then once a year. In any case, the patient should keep in mind that after diagnosis - regardless of whether he underwent surgery or not - he will undergo regular MRI procedures. Magnetic resonance imaging is the best way to monitor the condition of the tumor.
Prevention of brain tumors in adults at home
Prevention of brain tumors, according to oncologist Alexander Seryakov, generally includes:
- healthy lifestyle;
- optimal physical activity (preferably in the fresh air);
- complete rest;
- giving up bad habits (for smokers and alcohol abusers, the likelihood of developing brain tumors increases by almost 30%);
- a diet rich in fruits and vegetables;
- limiting stressful situations (or changing your attitude towards negative circumstances).
Complications after recovery
The more severe the infectious disease, the higher the chance of complications after recovery. Thus, approximately a third of those who have recovered experience complications from the central nervous system and the psyche.
Many survivors talk about fatigue and malaise, difficulty finding words, remembering, and decreased concentration. Some describe their condition as a kind of fog after COVID-19. Researchers report that one in three people regularly experience headaches and dizziness, loss of smell and taste, and muscle weakness.
“Many negative psychological reactions appear after recovery,” Olga Markina shares her experience. “Sometimes symptoms do not appear immediately, but several months after recovery. Patients experience malaise, drowsiness, and decreased stamina. Many people experience anxiety and fear of re-infection, even to the point of hypochondria and phobia.”
A professor of psychiatry at the University of Maryland reports that he believes that in about 30-50% of those who recover, there is an increased risk of future mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety. Also, about half of people who had symptoms of coronavirus suffer from insomnia and depressed mood.
Recent studies say that one in ten coronavirus survivors develop post-traumatic stress disorder, and a third develop depression and anxiety disorders. In addition, 54% of people develop chronic fatigue syndrome within three months of infection.
A new but not yet peer-reviewed study reports that people who recover from coronavirus are more likely to experience intracranial hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, parkinsonism, Guillain-Barré syndrome, dementia and insomnia than those who recover from other common infections, including influenza.