Our clinic diagnoses and treats the nerves of the hands (radial, ulnar, median). To treat neuropathy of the ulnar, radial, and median nerves, you will need to be examined by a neurologist; if any studies have been previously performed, be sure to take their results for consultation, incl. the x-rays themselves . If the studies have not been performed, we will do everything necessary in our clinic or with our colleagues in other clinics.
- What are the causes of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves?
- Ulnar nerve neuropathies: symptoms
- Radial nerve neuropathy: symptoms
- Median nerve neuropathies: symptoms
- Diagnosis of neuropathies of the ulnar, radial and median nerves
- Treatment of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves at the Echinacea clinic
- When is surgery necessary?
How can we help you:
- We will establish a diagnosis, find the point of damage or the cause of nerve inflammation. We perform a wide range of electromyography and ultrasound of nerves and have accumulated considerable experience. According to needle myography data, it is possible to predict the prospects of non-surgical treatment or determine clear indications for surgery (the risk of complete loss of the nerve).
- We will find out and discuss with you the prospects and chances of non-surgical treatment. Medicines can be used here, incl. administration of anti-inflammatory and absorbable drugs directly to the point of compression or damage to the nerve. In terms of rehabilitation treatment, magnetic stimulation of the nerves of the hands has proven itself well: the effect is visible several days after stimulation.
- If the chances of restoring the radial, ulnar or median nerve without surgery are low, we recommend surgical treatment . We perform most of the operations on an outpatient basis. You will be able to go home on the day of surgery. In addition, surgery without hospitalization is significantly cheaper. After surgical treatment, we will offer a course of rehabilitation treatment.
What are the causes of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves?
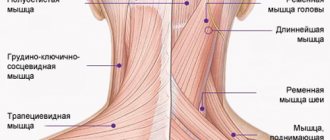
The radial, ulnar and median nerves pass through narrow canals formed by bones, ligaments, tendons and muscles. Nerve tissue is very delicate and vulnerable. Often we detect nerve suffering even with slight narrowing or deformation of the nerve canal. Narrowing or deformation of the canals of the radial, ulnar and median nerves occurs:
- In case of injury (bone fracture, bruise, hemorrhage, sprain or wound); Often, when injured, the nerve is pulled into scarred tissue or compressed by a bone fragment; nerve injury can also be represented by a nerve bruise, partial or complete interruption.
- When squeezed in an uncomfortable position (tucked or pinned hand while unconscious or intoxicated, under anesthesia);
- With thickening and deformation of the elbow or wrist joints and ligaments , with chronic injury and overload of the joints, often associated with the type of activity (athletes, musicians, drivers, cooks, dentists, working with vibration and metalworking tools). Very often, such changes are facilitated by diseases of the cervical spine. These types of neuropathy are called tunnel syndromes of the ulnar, radial and median nerves (cubital tunnel syndrome, carpal tunnel syndrome) .
Stimulation electromyography of the upper extremities, electroneuromyography (ENMG) of the upper extremities / EMG of the arms
The function of the nerves is to conduct electrical impulses from the brain to the muscles and organs, and to the brain from the sensory receptors of the body. Any damage to the nerve leads to disruption of the conduction of excitation along the nerve, which means disconnection of the affected part of the body from the brain.
Therefore, if the radial, ulnar or median nerve suffers, the following are possible:
- Decreased strength and weight loss of arm muscles
- Decreased sensitivity (numbness).
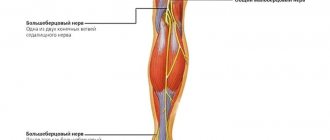
What is neuritis of the radial nerve of the hand
The radial nerve is one of the mixed type nerves, responsible for the motor functions of the hand and communication with the central nervous system. Radial neuritis is characterized as inflammation of the upper extremities of a person, in which dysfunction of the extensor ability of the elbow and wrist joints is observed.
Post-traumatic neuritis of the radial nerve
This disease occurs as a result of injuries to the nervous tissue of the hand (doctors call it one of the most common types of damage). Treatment of post-traumatic neuritis of the radial nerve depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, the type of injury and characteristic signs.
Since the very name of the disease “post-traumatic neuritis” speaks for itself, with this pathology, first of all, the limb is immobilized using a plaster cast. Doctors of modern medicine also use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which relieve pain and eliminate inflammatory processes.
It is imperative to consult a doctor in case of traumatic neuritis of the radial nerve to avoid loss of skeletal muscle activity or loss of mobility of the connected ends of bones. Radial neuritis (ICD 10 code: G56.3) can develop not only due to hand injury, but also due to other reasons.
Diagnosis of neuropathies of the ulnar, radial and median nerves
The most successful treatment for neuropathy is treatment directly at the point of nerve damage. For successful treatment, your treating doctor will find out:
- At what exact point is the nerve damaged (compressed); this helps us provide targeted treatment;
- What exactly led to the nerve suffering (trauma, scar, compression);
- The degree of nerve suffering (complete or partial damage, the presence of a recovery process, the presence of complete death of the nerve, etc.).
Often, to establish the cause of nerve pain, a detailed neurological examination is sufficient , during which the strength of the muscles controlled by the nerve, the possibility of certain movements, sensitivity, the presence of pain points and seals along the nerve are assessed. Auxiliary diagnostic methods are electroneuromyography, radiography and computed tomography.
Electroneuromyography allows you to assess the speed and volume of impulses along the nerve, detect the location of damage/compression, and determine the prognosis for recovery. Electromyography helps us evaluate the effect of certain types of treatment and choose the most suitable ones. The Echinacea clinic uses a modern computer electroneuromyograph.
X-ray and computed tomography of the joints will provide complete information about the deformation of the joints and bone canals of the nerves, the causes and points of nerve compression.
Arm pain
Gout
Arthritis
Rheumatism
Ulcer
26724 March 26
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain in the hand: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Pain can be accompanied by various pathological processes of the upper extremities - injuries, degenerative and inflammatory lesions, neurological syndromes. Pain in the arm can be one of the symptoms of diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive systems of the body.
Types of hand pain
The variety of pain syndromes is determined not only by the complexity of the structure of the upper limbs, but also by the variety of functional loads. By its nature, the pain can be pulling, shooting, aching. It may bother you when there is strain on the arm, or it may occur at night and disturb sleep. In addition, irradiation (return) of pain to the arm is possible due to myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, colic, cholecystitis, and stomach ulcers.
Possible causes of arm pain
Arm pain can be physiological in nature and be caused by muscle fatigue
after heavy or unusual stress.
It occurs due to the accumulation of anaerobic metabolic products (lactate) in muscle tissue and resolves within two to three days.
After significant physical activity exceeding the muscle endurance threshold, delayed pain may occur (1–2 days after physical activity). Experts believe that they are caused by damage to muscle cells, their membranes, and connections between microfibrils. Such pain is usually long-lasting.
Injuries
– bruises, fractures, tendon sprains, muscle tears – are characterized by a sharp onset of pain and its intensity. Bruises and fractures are accompanied by severe pain, swelling, and hemorrhage from small or large vessels.
A sprain occurs when there is a sudden movement in the joint, lifting significant weights, or a fall with emphasis on the arm and is characterized by varying degrees of damage to the connective tissue fibers. This injury is accompanied by severe pain, swelling and limited mobility in the joint. Often, sprains occur in the area of the wrist and elbow joints after heavy loads or monotonous movements repeated many times.
Muscle ruptures and tears occur when overused. In addition to severe pain, there is hemorrhage in the area of injury and the inability to tense the muscle.
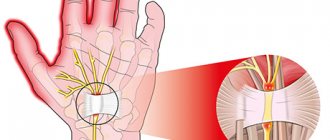
One of the largest groups of diseases that causes severe pain in the arm is tunnel syndromes
caused by compression and inflammation of the nerve in a narrow space (tunnel) formed by the muscles, ligaments and bones of the arm.
Additional factors that increase the risk of such inflammation are endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism), impaired joint mobility due to arthritis or rheumatism, tumor formations in the nerve area (neurofibroma, schwannoma) or beyond it (hemangioma, lipoma). As a rule, tunnel syndromes develop during prolonged similar movements (when working at a computer, playing tennis) or injuries. This is facilitated by incorrect posture, scoliosis, and osteochondrosis.
Inflammation of tendons and joint ligaments
also develops with significant physical stress and injury, especially in cases where the tendons are attached to powerful muscles. Stretching and microtrauma at the attachment site are accompanied by aching, aching pain, which can become unbearable during physical activity. Inflammation leads to swelling and limited mobility in the joint. A common pathology of the hand is epicondylitis, in which inflammation affects the junction of the muscle and ligament of the elbow joint. In this case, the pain is localized in the elbow area and accompanies movement in the elbow, hand and fingers.
Joint damage due to arthritis
causes not only pain, but also stiffness of movement. The causes of such damage may be osteoarthritis, gout, etc.
In any case, all signs of inflammation are present: pain, swelling, local increase in temperature, redness of the skin in the projection of the joint, impaired movement in the joint.
Rheumatoid
arthritis
is characterized by damage to first the small and then large joints of the hand, which is accompanied by stiffness of movement in the morning. In addition to increased pain, joint deformation and limited mobility, the disease is also characterized by general manifestations of the disease - fatigue, sweating of the palms and feet, weight loss.
Deposition of uric acid salts (urates) in the joints is the main manifestation of gout
– leads to severe pain. Its intensity is so great that even simply touching the sore joints causes discomfort. The basis of the disease is a metabolic disorder.
With inflammation of the ulnar periarticular synovial bursa - bursitis
– pain occurs in the elbow and is accompanied by swelling of the joint. In addition to severe pain in the arm, which limits movement, local redness of the skin and increased temperature over the joint area may be observed.
Arm pain may be due to anterior scalene syndrome
and be accompanied by muscle spasm and compression of the nerves and vessels of the shoulder girdle. The disease may be based on degenerative changes in the vertebrae (osteochondrosis) of the cervical spine or trauma.
The patient is bothered by pain in the neck and shoulders, which prevents him from raising his arms up and to the sides, taking a deep breath, or tilting his head.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and its complications
(disc protrusion, intervertebral hernia) cause pain in the arm due to pinching of the nerve that innervates it. In this case, not only sharp pain may occur, but also numbness of the hand and impaired sensitivity.
There is another reason that should always be kept in mind when pain in the arm occurs - myocardial infarction
. The patient feels severe pain behind the sternum, which can radiate to the neck, back and left arm. Such pain is not the only sign of this dangerous condition. As a rule, shortness of breath, cold sweat, and difficulty breathing are present.
Diagnosis and examinations for arm pain
To diagnose a condition that may be causing arm pain, it is necessary to consider how acute the pain is and the events that precede its onset. With severe injuries, making a diagnosis is usually not difficult, but to distinguish a bruise from a fracture, radiography is necessary.
Treatment of damage to the radial, ulnar and median nerves at the Echinacea clinic
When it is clear where, how and why nerve compression occurs, local treatment in the form of physiotherapy, therapeutic blockades, massage, and manual therapy becomes much more effective. Therefore, treatment in our clinic begins with finding out the cause and location of nerve damage .
The main goals of treatment for nerve compression:
- Remove nerve compression. To do this, we use powerful resorption therapy: we use enzymes that resolve and soften scar tissue, bone and cartilage growths (Karipazim enzyme, etc.), massage, and injecting medications directly into the site of nerve compression. Sometimes, to release the nerve, manual therapy and massage of the areas of compression of the ulnar, median and radial nerves (cervical spine, elbow, wrist joints, etc.) are sufficient.
- Accelerate healing and restoration of the nerve. To do this, we use modern medications that help restore the nerve freed from compression and scarring.
- Restore muscle function and volume. Special exercises, electrical stimulation of muscles, and physiotherapy are used here. The rehabilitator will tell you in detail and show you how to perform rehabilitation procedures at home.
When is surgery necessary?
In case of nerve injury, it is very important to decide in a timely manner whether conservative or surgical treatment is advisable. The answer to this question can be obtained after conducting needle myography, which will answer the question of what is the degree of damage to the nerve and whether it has a tendency to recover. If during this study it turns out that at least partially the nerve is preserved, we carry out active conservative treatment, after which we must repeat the study to make sure that the treatment had an effect . If, during needle myography, it turns out that the nerve is completely damaged and its restoration is impossible, we resort to the help of a neurosurgeon who suturing the nerve or releasing it from significantly narrowed canals. Then we perform the entire range of restoration procedures.