General information
The nervous system is represented by various nerve plexuses, peripheral nerves, spinal cord and brain.
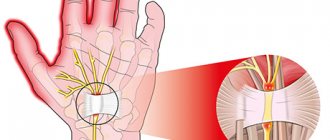
Neuropathy is a non-inflammatory lesion of the nervous system. Peripheral nerves have a very thin structure and are not resistant to damaging factors. According to the level of damage they distinguish:
- Mononeuropathy. Characterized by damage to one single nerve. Mononeuropathy is considered a fairly common option. Most often, mononeuropathy of the upper limb is diagnosed (mononeuritis of the radial or ulnar nerve).
- Multiple neuropathy affecting several nerve endings.
- Polyneuropathy , which is characterized by the involvement of several nerves localized in one area.
Pathogenesis
Neuropathy is usually determined by the nature of the nerve damage and its location. Most often, the pathology forms after a traumatic injury, after suffering from general diseases and during intoxication.
There are 3 main forms of neuropathy:
- Post-traumatic neuropathy. Violation of the integrity of the nerve myelin sheath occurs as a result of acute injury or severe blow. With tissue swelling, improper scar formation and bone fractures, compression of the nerve fibers occurs. Post-traumatic neuropathy is characteristic of the ulnar, sciatic and radial nerves.
- Diabetic neuropathy. Damage to nerve endings is also recorded with high levels of sugar and blood lipids in the blood.
- Toxic neuropathy. As a result of infectious diseases such as herpes , HIV , diphtheria , etc., toxic damage to the nerve plexus occurs. Poisoning with chemical compounds and overdose of certain medications can lead to disruption of the integrity of the nerve trunk.
Neuropathy can develop against the background of a disease of the hepatic system, kidney pathology, osteochondrosis , arthritis , the presence of neoplasms and insufficient levels of thyroid hormones .
Classification
They are classified according to localization:
- Neuropathy of the lower extremities. The most common diabetic neuropathy of the lower extremities is caused by diabetes mellitus . In this form, the peripheral nervous system innervating the lower extremities is affected.
- Peroneal nerve neuropathy. Characteristically, one peroneal nerve is affected, which is manifested by muscle weakness and impaired sensitivity in the innervated area. ICD-10 code: G57 – mononeuropathies of the lower extremities.
- Distal axonal neuropathy after cutting. Post-traumatic or axonal neuropathy develops as a result of damage to nerve endings that arise from certain structures of the spinal cord and are responsible for transmitting nerve impulses to the limbs. If nerve transmission is difficult or completely interrupted, the patient complains of tingling or complete loss of mobility. Distal axonal neuropathy manifests itself differently depending on the nature, type and location of the pathological process.
- Ischemic neuropathy develops when nerve endings are compressed in the area of the musculoskeletal joints and in the spinal column. A violation of not only innervation, but also blood circulation is recorded, which leads to the formation of ischemia. With a chronic course of the process and a long-term disorder, paresthesia and hypotrophic processes develop, which in severe cases can lead to paralysis and necrosis . Ischemic neuropathy has a wide range of symptoms and is not difficult to diagnose.
- The best known form is optic neuropathy. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy . Characterized by damage to the anterior segment of the optic nerve, which leads to very rapid and persistent impairment of visual function, up to complete or partial atrophy of the optic nerve. Anterior optic neuropathy is also known as vascular pseudopanillia . Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy. It is characterized by damage to the retrobulbar posterior part of the optic nerve due to ischemic effects. The posterior form is also fraught with loss of visual perception.
- Ulnar nerve neuropathy. The peripheral nervous system can be affected by several causes. Damage to the ulnar nerve is most often encountered in traumatology. As a result of compression of the nerve trunk, which is located in the area of the elbow joint, the entire upper limb is affected.
- Radial nerve neuropathy. Clinically, it manifests itself as a characteristic symptom of a “dangling hand,” which is caused by the inability to straighten the hand and fingers. Damage to the radial nerve can be associated with trauma, metabolic processes, ischemia, and compression.
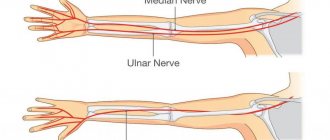
- Median nerve neuropathy. The nervus medianus can be affected in any area, which will inevitably lead to swelling and severe pain in the hand area and impaired sensitivity. The process of flexion of all fingers and opposition of the thumb is disrupted.
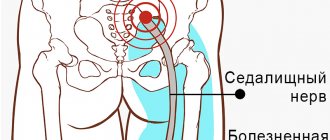
- Pudendal nerve neuropathy. It develops as a result of damage to the pudendal nerve, which is located in the pelvic area. Takes an active part in the act of urination and bowel movement, sending nerve impulses along the nerve trunks that pass through the genitals. Pathology is characterized by severe pain.
- Neuropathy of the tibial nerve. The clinical picture depends on the level of nerve damage. The tibial nerve is responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the foot and lower leg and the sensitivity of the skin in this area. The most common cause of tibial nerve neuropathy is traumatic injury to the nerve trunk.
- Femoral nerve neuropathy. The clinical picture of damage to the femoral nerve depends on the level of damage to the large nerve trunk.
- Neuropathy of the oculomotor nerve. Diagnosis of pathology requires a thorough examination and is complex. The clinical picture is represented by symptoms that occur in many diseases. When the oculomotor nerve is damaged, ptosis, divergent strabismus, etc. are observed.
What is it and the ICD-10 code
When connections between the brain and organ nerves are disrupted and damaged, neuropathy develops. Its most common type is damage to the lower extremities - separately or both at once.
The disease develops as a result of damage to the nerve endings, as a result of which the brain loses control over the functionality of the legs.
Neuritis is an inflammatory process in nerve fibers, which in most cases is of infectious origin.
Damage to the peroneal nerve immediately affects the sensitivity of the leg . It is responsible for extending the leg, toes, and muscles responsible for turning the foot outward.
With neuritis of this nerve, the patient stops using the heel for support, the gait becomes shuffling, and the affected leg is thrown out noticeably higher than the healthy one when walking. The sensitivity of the lower leg is lost, the foot turns inward.
The functionality of the tibial nerve is the opposite of the peroneal nerve . It supplies impulses to the flexor muscles.
Symptoms of the lesion are the opposite of the previous disease: the patient steps on the heel, but cannot transfer the impulse to the toe when moving, the flexion functions of the foot and fingers are lost, the foot turns outward.
Neuritis affects different areas of the lower extremities, but these nerves converge in the lower third of the leg . Both diseases have similar causes, clinical presentation and treatment, so they are usually considered as one nosology.
In ICD-10, NMN neuritis of the tibial and peroneal nerve belongs to class 6 - diseases of the nervous system, namely mononeuropathy, its code is G57.8.
Causes
It is extremely rare that neuropathy develops as a separate independent disease. Most often, nerve endings are affected against the background of a chronic pathology, which acts as a traumatic factor. The development of neuropathy is preceded by the following diseases and conditions:
- hypovitaminosis;
- metabolic disorder ;
- decreased reactivity;
- intoxication , poisoning;
- nerve fiber injury;
- neoplasms (malignant and benign);
- severe hypothermia;
- hereditary pathology;
- diagnosed endocrine diseases.
Causes of inflammation
Neuritis can occur for the following reasons:
- Nerve damage – limb injuries, nerve compression by colloid cords after surgery.
- Nerve compression - tunnel syndrome - prolonged stay in a position that is uncomfortable for the lower extremities, often occurs as a result of professional activity.
- Vascular pathologies and other blood supply disorders - this leads to tissue hypoxia, therefore, metabolic processes are disrupted.
- Toxic lesions - diabetic, kidney.
- Infectious lesions - one of the branches of the nerve fiber is involved in the inflammation process.
- Neuropathy of compression-ischemic etiology develops against the background of the presence of neoplasms - as the tumor increases in size and metastasizes.
Athletes are susceptible to neuropathy, especially runners , people who, due to their professional activities, are forced to lift heavy objects and injure their lower extremities.
It also affects overweight people - in this case, the load on the foot increases significantly, which leads to deformation or damage to the nerve fiber.
Women who wear high-heeled shoes for a long time , especially those with extra pounds and in old age, also risk the development of neuritis. Often the pathology occurs in people who walk barefoot or in shoes without heels at all - with thin soles.
Symptoms of neuropathy
When nerve endings are damaged, muscle fibers become thinner and their reflex function is impaired. In parallel, there is a decrease in contractility and partial loss of sensitivity to stimuli that cause pain.
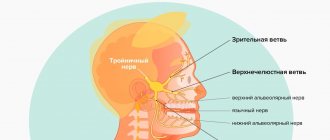
The clinical picture of neuropathy can be very different, and the pathological process can be localized anywhere, causing neuropathy of the peroneal nerve, trigeminal nerve, facial nerve, ulnar and radial nerve. Damage to sensory, motor or autonomic nerve function negatively affects the patient's quality of life. Several forms of neuropathy occur in patients with diabetes
- Peripheral neuropathy. Characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves that are responsible for the innervation of the upper and lower extremities. Symptoms of neuropathy of the upper extremities manifest themselves in the form of impaired sensitivity in the fingers and toes, a tingling sensation, and a feeling of numbness in the upper extremities. The symptoms of neuropathy of the lower extremities are identical: tingling and sensory disturbances in the lower extremities are noted.
- Proximal form. It is characterized by impaired sensitivity mainly in the lower extremities (buttocks, thigh, lower leg).
- Autonomous form. There is a functional disorder of the genitourinary system and digestive tract organs.
Symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy
Most often, alcoholic neuropathy is accompanied not only by sensory disorders, but also by motor ones. In some cases, patients complain of muscle pain of various locations. The pain syndrome may be accompanied by a sensation of “crawling” in the form of paresthesia, tingling, a feeling of numbness and impaired motor activity.
At the initial stage, patients complain of muscle weakness and paresthesia. In every second patient, the disease first affects the lower extremities, and then the upper ones. There are also simultaneous lesions of the upper and lower belts.
Characteristic symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy:
- a sharp decrease, and in the future a complete absence of tendon reflexes;
- diffuse decrease in muscle tone.
Alcoholic neuropathy is characterized by disruption of the facial muscles, and in more advanced cases, urinary retention is noted. In the advanced stage, alcoholic polyneuropathy is characterized by:
- muscle weakness in the limbs: unilateral or symmetrical;
- paresis and paralysis;
- violation of surface sensitivity;
- sharp inhibition of tendon reflexes followed by their complete extinction.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of neuritis of the lower extremities certainly depend on the location of the nerve damage.
The main symptoms are as follows:
- problems with sensitivity;
- severe pain in the area of the affected nerve.
In addition, the disease is accompanied by:
- swelling of the legs;
- periodic sensation of pins and needles and numbness on the surface of the legs;
- convulsions and involuntary spasms may occur;
- patients have difficulty walking, mainly due to pain.
If the tibial nerve is damaged, flexion of the toes is impossible, the movement of the foot is limited - it is abducted outward.
Patients may complain of:
- feeling of coldness in the foot;
- burning;
- pain around the ankle that moves down to the toes;
- difficulty while walking.
Signs of peroneal nerve neuritis:
- loss of temperature, pain and tactile sensitivity of the spot on the back, side-front and in the area of the toes,
- pain in the lateral surface of the foot and lower leg, which intensifies when the limb is flexed,
- difficulty in straightening the toes,
- weakness, to the point of complete impossibility, in the concept of the outer edge of the foot,
- “cock gait” - the leg is bent at the knee and hip joint,
- sagging and turning of the foot inward,
- amyotrophy,
- change in skin color in the affected area - from blanching to a brown or bluish color.
Patients complain that while walking they are forced to step first on their toes and then on their heels.
In addition, it is not possible to straighten the toes and rotate the foot into an anatomically correct position. The patient cannot stand on his heels and walk on them .
Read about the diagnosis of neuritis of the extremities:
- shoulder and elbow;
- median and radial nerves;
- sciatic nerve;
- femoral nerve.
Tests and diagnostics
Neuropathy is considered a rather difficult disease to diagnose, which is why it is so important to correctly and thoroughly collect anamnesis. The difficulty lies in the long-term absence of certain symptoms. The doctor will have to find out: whether medications were taken, whether viral diseases were suffered, or whether there was contact with certain chemicals.
The onset of the disease can occur against the background of alcohol abuse. The diagnosis is pieced together based on many factors. Neuropathy can occur in different ways: progressing over several days or years, and even lightning fast.
Using palpation, the doctor examines the nerve trunks, identifying pain and thickening along their course. A Tinnel test is required . This method is based on tapping the nerve ending and identifying tingling in the zone of sensitive innervation.
A laboratory blood test is performed to determine ESR, and sugar levels are measured. Additionally, an X-ray examination of the chest . Electrophoresis of whey proteins is also performed .
How is the problem diagnosed?
Diagnosis begins with collecting an anamnesis, which can guide a specialist in the right direction to identify the cause of the pathology.
A detailed study of the motor function and sensory sphere of the nerve fibers of the affected limb is also carried out.
To do this, the doctor conducts special tests that give an idea of the muscle strength of different muscle groups of the foot and ankle . The specialist uses a special needle to carry out the tests.
Functional tests are carried out - the doctor asks the patient to bend his toes, stand on his heels, walk on his heels, and rotate his foot.
In addition, it is prescribed:
- Electromyography is an assessment of the movement of an impulse along a nerve fiber.
- Ultrasound – assessment of the choroid plexuses and soft tissues.
- MRI or CT - pictures are taken in different planes, and they display all the structures of the lower extremities. Necessary to clarify the localization of the pathological focus.
- X-ray – prescribed for injuries.
- Laboratory tests - blood tests and so on.
In some cases, thermography of the lower extremities is prescribed - this is a type of medical diagnosis that is based on the use of infrared rays.
During a thermal examination, abnormal areas differ in color from healthy tissues , which gives an idea of the localization and extent of the pathological process.
Neuritis must be differentiated from infectious lesions, injuries, cancer, and toxic effects on the body.
Treatment
Therapy for non-inflammatory damage to nerve endings is individual in nature and requires not only an integrated approach, but also regular prevention.
Treatment methods are selected depending on the form, degree and causes that contributed to the damage to neuromuscular conduction. All therapy is aimed at fully restoring nerve conduction. In case of toxic damage to the nervous system, detoxification measures are carried out (elimination of influencing factors, administration of an antidote ).
Treatment of diabetic neuropathy
In diabetic cases, measures to maintain normal blood sugar levels are recommended. At the same time, it is recommended to get rid of bad habits. Metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus contribute to an increase in the level of free radicals circulating in the bloodstream, with impaired antioxidant activity of one’s own organs and systems. All this leads to disruption of the integrity of the inner lining of the vessel and nerve fiber.
For diabetic neuropathy, the use of medications based on alpha-lipoic acid is indicated:
- Thiogamma;
- Berlition;
- Espa-Lipon.
The traditional neurological set involves the introduction vitamins for the complete restoration of neuromuscular conduction. It is not recommended to resort to treatment with folk remedies.
Forecast and prevention of occurrence
The prognosis of the pathology depends on how soon the patient sought help from a specialist and how correct the treatment was. Irreversible changes significantly worsen the prognosis and lead to disability.
To prevent the occurrence of neuritis, it is recommended:
It is strictly not recommended to delay treatment of the pathology at the first symptoms , as this can aggravate the situation and lead to irreversible consequences. Ignoring the symptoms of pathology leads to incapacity and permanent disability.
Medicines
Treatment of lower extremity neuropathy includes the following medications:
- Neuroprotectors or metabolic accelerators in nerve cells. Drugs for treatment: Mildronate ; Piracetam .
- Anticholinesterase medications , the action of which is aimed at optimizing the sensory functioning of nerve endings. The drugs improve neuromuscular conduction of the lower extremities. These include: Prozerin ; Ipidacrine .
- Antioxidants. Prevent negative consequences from the influence of free radicals on the functioning of the nervous system. A high concentration of free radicals has a destructive effect on the tissues of the peripheral nervous system. Preparations: Cytoflavin ; Mexidol .
- Alpha lipoic acid. The drugs help restore neurocytes and speed up metabolism. High effectiveness is observed in diabetic neuropathy.
- Other medications. The use of B vitamins has a good effect; in particular, B1 , B6 , B12 . Vitamin complexes help restore neuromuscular conduction. There are tablet and injection forms: Milgamma ; Neuromultivitis ; Combilipen .
Self-treatment at home is not recommended.
Treatment of neuropathic pain in adults
Neuropathic pain - what is it?
Neuropathic pain occurs when the transmission of impulse signals along the nerves is disrupted. In adults, neuropathic pain syndrome is described as stabbing, burning, shooting and is often associated with electric shock.
Therapy begins with the simplest painkillers ( Ibuprofen, Ketonal ). If they are ineffective and the pain syndrome is severe, antidepressants and antiepileptic drugs (for example, Tebantin ) are prescribed.
Tricyclic antidepressants
Drugs in this group are often used to relieve neuropathic pain. It is believed that the mechanism of their action is based on preventing the transmission of nerve impulses. The most commonly prescribed medication is Amitriptyline . The effect may occur within a few days, but in some cases, pain therapy is extended for 2-3 weeks. The maximum effect of therapy is recorded at 4-6 weeks of intensive treatment. A side effect of therapy is drowsiness , which is why treatment begins with the smallest doses, gradually increasing the dosage for better tolerability. Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended.
Anticonvulsants, antiepileptic drugs
If it is impossible to use antidepressants, anti-epileptic drugs ( Pregabalin, Gabapentin ) are prescribed. In addition to the treatment of epilepsy, medications are excellent for relieving neuropathic pain syndrome. Treatment begins with the smallest doses, identical to antidepressant therapy.
Diagnostics
Determining peroneal neuropathy begins with questioning.
A neurologist or traumatologist listens to complaints and examines the patient. If you suspect something is wrong, you can immediately use the “heel” test. It is not possible to stand on your heels normally - there is nerve damage.
The doctor tries to turn the foot towards the outside or straighten the toes. This is a simple test to detect neuropathy.
If this type of pathology is present, such an action will be extremely difficult (with effort) or not possible at all. Visually, you can also determine the “birdlike” gait, as well as muscle atrophy.
To determine the presence or absence of sensitivity, take a special needle and touch the desired limb.
After a preliminary diagnosis, the degree of nerve damage is clarified. To do this, electromyography is performed. They may prescribe an ultrasound of the nerve or vessels of the lower extremities, or an MRI.
If the disease arose as a result of grass, then an x-ray of the bone is taken. When the situation is not entirely clear, they resort to novocaine blockade for diagnosis.
It is important to correctly distinguish neuropathy from such pathologies as: polyneuropathy, neuropathy, PMA syndrome, as well as atrophy and tumors of the spine.
Among the problems faced by neurology, neuropathy of the lower extremities occupies a large place. Let us consider in detail the main types of therapy used in modern medicine.
Procedures and operations
In addition to drug therapy, neuropathy of the peroneal nerve also includes physiotherapeutic procedures:
- Magnetotherapy. It is based on the effect of a magnetic field on the human body, which helps relieve pain, restore nerve cells, and reduce the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
- Amplipulse. It is based on the effect of modulated current on the affected area, due to which nerve cells are restored and swelling is reduced. Has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrophoresis with drugs . It is based on the influence of an electric field, due to which medications enter the site of inflammation.
- Ultrasound therapy. When exposed to ultrasound, blood circulation is stimulated and the severity of pain is reduced. Has a tonic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Electrical stimulation. Restoration of neuromuscular conduction occurs under the influence of electric current.
Radial nerve neuropathy is treated in the same way. A course massage is also recommended to restore the radial nerve.
Prevention
Preventive measures include timely treatment of infectious and systemic diseases, normalization of general metabolism. It is important to understand that pathology can become chronic, which is why timely and competent treatment is so important.
In case of a mild course of the disease and a chronic form of neuropathy, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated, where the following is carried out:
- aromatherapy;
- laser and light treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- massage, exercise therapy;
- acupuncture;
- psychotherapy.
Consequences and complications
There are many complications from peripheral neuropathy and they depend primarily on the causative factor that led to damage to the nerve trunk. Main complications:
- Diabetic foot. It is considered one of the most terrible complications of diabetes.
- Gangrene . The cause of the putrefactive process is the complete lack of blood flow in the affected area. The pathology requires emergency surgical treatment: excision of necrotic areas, amputation of a limb.
- Autonomic cardiovascular neuropathy. It is characterized by disturbances in various autonomic nervous functions, including sweating, bladder control, heart rate, and blood pressure .
Symptoms
Neuropathy is accompanied by a clinical picture of severity, which depends on the degree of damage to the nerve fibers.
Nerve dysfunction can be recognized by impaired flexion of the foot and motor ability of the fingers. When walking, the foot is placed incorrectly - the emphasis is on the heel. The muscular system of the lower leg and foot shows signs of obvious atrophy and deformation.
In the case of traumatic origin of neuropathy, swelling forms in the ankle area, blood flow is disrupted, tissue sensitivity increases, and there is severe pain, which intensifies when the damaged areas are touched.
If the cause of nerve neuropathy is endocrine disorders or infectious lesions, the patient loses sensation in the lower extremity area of the leg and foot. The pain syndrome persists and can have a different nature and severity. The pain intensifies with walking and physical activity. The patient may experience involuntary contractions of individual muscles or a convulsive syndrome involving the lower limbs.
In addition, the patient is concerned about neurotrophic disorders, such as dryness of the epidermis in the lower legs and feet, keratinization of the upper layer of the dermis, brittle nails, pallor of the skin and a decrease in local temperature, increased sweating.