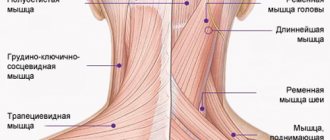
- Acupuncture Quickly relieves inflammation and pain, has an anti-edematous and anti-ischemic effect. The introduction of hair-thin needles reliably eliminates pain attacks.
- Pharmacopuncture Used in combination with acupuncture. This procedure involves the introduction of microdoses of homeopathic medicines, which help achieve the fastest possible analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Acupressure Improves local blood circulation, eliminates spasms of facial muscles, relieves emotional and muscle tension, improves metabolic processes.
- Moxotherapy on bioactive points of the body has a general strengthening effect, improves immunity, and activates the body's protective and regenerative processes.
- Herbal medicine Ideally complements the effects of procedures and consolidates their results, has a sedative effect, improves blood supply to nerve tissue.
Trigeminal neuralgia in Eastern medicine
With regard to trigeminal neuralgia, as with all other diseases, oriental medicine takes a comprehensive approach.
If Western medicine does not go beyond the immediate causes of nerve damage - compression by edema, hypothermia, viral infection, unsuccessful dental treatment or other obvious factors, then Eastern medicine finds and eliminates the root cause of the disease.
Trigeminal neuralgia, like all neuralgia and neuritis, refers to disorders of the Rlung (Wind) regulatory system. This system is responsible for mental activity, psycho-emotional state and nervous regulation of the body. The main reasons why Wind diseases occur are stress, negative emotions, hypothermia, lack of nutrition, sleep, and overwork. It would seem, what is the connection between the trigeminal nerve and the emotional state? However, it exists, and medical science confirms it.
According to official statistics, in 20% of cases, trigeminal neuralgia occurs against a background of negative emotions. In reality, this percentage is much higher if we take into account the long-term consequences of nervous stress, mental trauma, and emotional overload.
Neuralgia is often accompanied by depression and neuroses. Combined with strong cold winds and hypothermia of the face, this is likely to produce symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia.
The question arises: is it enough to simply relieve pain, reduce swelling of soft tissues, and restore normal blood supply to the nerve in order to consider the problem solved? Or does the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia require the same comprehensive approach as the treatment of nervous disorders? Eastern medicine answers this question unequivocally: without restoring the balance of the body, treatment of trigeminal neuralgia cannot be truly effective, successful, and its results cannot be long-lasting and lasting. Only by eliminating all the causes of the disease can the problem of neuralgia be solved so that the patient forgets about it for a long time or forever.
That is why treatment of trigeminal neuralgia at the ITVM clinic includes not only the use of medical procedures - acupuncture, acupressure and others, but also a course of herbal medicine. Tibetan herbal remedies used for neuralgia normalize the psycho-emotional state, increase resistance to stress, improve sleep, help overcome depression, neurosis and have a general strengthening effect. In addition, “ITVM” performs acupuncture on the bioactive points of the body’s meridians in order to restore normal circulation of vital energy and thereby eliminate its overexpenditure, which leads to exhaustion of the nervous system.
Symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
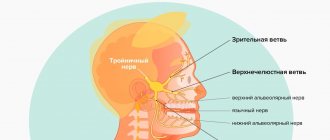
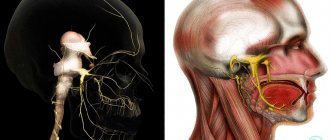
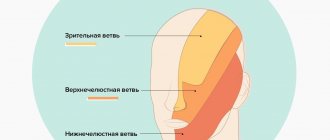
The main thing that causes the greatest discomfort is pain. Unbearable, sharp, reminiscent of an electric shock, pain is imprinted in the mask of suffering. An attack of pain is usually one-sided and short-lived (a few seconds or minutes), repeating once every several hours or months. But there are also cases of almost constant pain. During an attack, a person usually freezes and remains silent, squeezing the affected area of the face with his hand. The localization of pain is determined by the predominant damage to one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve. Sometimes, at the beginning of the disease, acute toothache occurs, but a dental examination does not find its cause.
“Switching on” of pain occurs when the so-called irritation occurs. trigger (trigger) zones: areas of the nasolabial triangle, temple, eyebrows, external auditory canal, tongue, teeth, gums, etc.
Moreover, if a slight impact on them initiates or intensifies pain, then strong pressure, on the contrary, causes relief (hence the reaction of compression of the painful area during an attack). They can “turn on” an attack:
- cold;
- smile;
- sneezing;
- conversation, laughter;
- eating;
- teeth cleaning;
- shaving;
- washing, applying cream, etc.
Knowing this, patients (especially if the attacks are very frequent) try to adhere to a gentle regimen, even to the point of completely refusing to talk, eat, wash, etc.
During an attack, the person on the affected side's face turns red and sweats, tears flow, the secretion of saliva and nasal secretions increases, cramps of the masticatory and facial muscles, and spasms of the eyelids may occur.
Outside of an attack, facial sensitivity may be impaired, either in the direction of loss or significant increase, which is considered a harbinger of a painful attack.
Destruction of the nerve and/or its nuclei leads to deterioration of the trophism of facial tissues, which over time is expressed in:
- dry skin;
- local baldness and graying;
- loss of eyebrows and eyelashes;
- tooth decay and loss;
- asymmetrical tone of the facial muscles, etc.
With a long course and/or very frequent attacks, mental disorders are added: depression, irritability, fear.
Atypical symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia usually manifests itself as an acute attack of pain affecting the right or left (less often) half of the face.
There are also atypical signs of this disease. In particular, trigeminal neuralgia can manifest as pain in the base of the tongue, throat, ear, or sore throat from cold or sour foods. This is the so-called pharyngeal form of trigeminal neuralgia.
If the cause of neuralgia is a herpes virus infection, the symptoms may also be atypical - headache and itching, the appearance of white areas on the skin. The pain may not be paroxysmal, but constant, moderate in nature. In general, any form of the disease in which pain does not occur in attacks, but is constant (pulsating, aching) and accompanied by a burning sensation, is called trigeminal neuralgia type 2, or atypical neuralgia.
When diagnosing the disease, trigeminal neuralgia should be differentiated from symptoms of multiple sclerosis.
With multiple sclerosis, short-term painful attacks covering half the face are also possible, but other symptoms are also present - severe sweating of the forehead, lacrimation, tremors (shaking hands), unilateral blurred vision, dizziness, poor coordination of movements and a number of other neurological symptoms.
Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
Why and how does such severe pain occur? There is no final answer yet, although the search for it has been going on for centuries.
One of the immediate causes of pain is considered to be the destruction of the “insulation” of the nerve - the so-called. myelin sheath, when it is inflamed. In this case, “short circuits” and “leakages” of the electrical signal occur outside the nerve fiber. As a result of the chaotic involvement of a large number of neurons in the process of excitation, pain occurs.
The immediate cause of destruction of the myelin sheath can be:
- viral infection (poliomyelitis, neuro-AIDS, herpes);
- autoimmune process (for example, with multiple sclerosis);
- mechanical compression of the trigeminal nerve fibers inside or outside the skull.
Nerve compression is caused by:
- hemorrhages (stroke);
- dilation and curvature of blood vessels (atherosclerosis, aneurysms);
- facial and head injuries;
- pathology of the maxillary system;
- neoplasms;
- the presence of adhesions (for example, due to meningitis), etc.
Nerve degeneration sooner or later leads to malfunctions in the “remote control” of its control—the sensory and motor nuclei located in the brain. And it even contributes to the formation of areas of increased excitability - the so-called. epileptic foci. Damage to the nuclei can also be primary (its causes are also present in the above list).
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia at home
To relieve pain from trigeminal neuralgia, traditional medicine uses warming - compresses of hot salt or heated buckwheat, a hot hard-boiled egg. Such products must be used with great caution, since exposure to heat can aggravate the inflammatory process. There is also an opposite folk method of treatment - “freezing” the affected area with a piece of ice.
Another folk remedy is fir oil, which is rubbed into the affected half of the face and has a warming effect. In the same way, lavender oil, star balm, garlic oil, radish juice, alcohol tincture of propolis, grated horseradish, tincture of birch buds with vodka and other external remedies are used.
To relieve the symptoms of trigeminal neuralgia, folk medicine uses herbal preparations with calming, sedative and anticonvulsant effects from mint, chamomile, thyme, yarrow and other medicinal herbs.
It should be emphasized that with all the variety of traditional medicine recipes, they only help relieve pain, but are not a means of treating trigeminal neuralgia. They can be used to tide you over for a while before a visit to the doctor, but not as a substitute for such a visit.
Trigeminal neuralgia. Treatment
Pain is a symptom of the disease and at the same time the cause of its worsening. Ordinary, strong analgesics do not relieve pain. Even such radical measures as cutting the branches of the nerve bring only temporary relief, since with the regeneration of the nerve the pain also “regenerates”. In the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, a combination of anticonvulsants (effective for epilepsy), muscle relaxants, antihistamines and sedatives, vitamins, nutritional correction, massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures is now actively used. At the same time, they try to identify and eliminate the cause of central or peripheral nerve damage - acute and chronic diseases of the ENT organs, vascular disorders, pathologies of the dental system, tumors, consequences of head injuries, etc.
The big disadvantage of drug therapy for neuralgia is its duration (sometimes even lifelong) and strong side effects on other organs (for example, on the gastrointestinal tract), which aggravates metabolic disorders and closes a vicious circle.
An alternative option for a comprehensive, or more precisely, holistic impact on the cause-and-effect mechanisms of disease development are holistic methods - acupuncture, homeopathy, osteopathy, herbal medicine, qigong therapy, diet therapy. These methods break the vicious circle, restore the movement of energy and fluids in the body, and release its protective and healing reserves.
At Dr. Sager's clinic in Moscow, these methods are used to treat trigeminal neuralgia, both in combination with each other and with conventional drug therapy (with a course of reducing the dose of medications until they are completely discontinued), and as monotherapy. It all depends on the results of individual diagnostics.
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia
Strengthening the immune system is often recommended as a means of preventing trigeminal neuralgia. However, this advice is too general, and in general is not very suitable for this neuralgia, which is almost never directly associated with reduced immunity. Of course, there is nothing wrong with strengthening your immune system, but your main focus should be elsewhere. From the point of view of Eastern medicine, trigeminal neuralgia is a disease of the Wind.
For the prevention of such diseases, the main importance is the quality of sleep, proper work and rest schedule, good nutrition, avoidance of stress and overwork.
This means that the diet must be complete, contain a sufficient amount of vitamins B, C, A, D and E, fats (including not only vegetable, but also animal fats, for example, butter, and even better, ghee). It is necessary to get enough rest, get enough sleep, monitor your mood, avoid negative emotions and depression. And of course, you need to avoid cold winds and drafts.
For symptoms of neurosis and other nervous disorders, you should undergo a preventive course of herbal medicine. If there are serious signs of a nervous system disorder, it is better to immediately undergo a full treatment course of acupuncture, massage, herbal remedies and other methods of oriental medicine. This will help avoid not only trigeminal neuralgia, but also other neurogenic pain syndromes.