What does a neurologist treat?
A neurologist deals with many diseases and syndromes. Let's take a closer look at them.
General diseases
Back and neck pain
These could be injuries to the spine and spinal cord (sprains) or conditions caused by overloads, intervertebral hernia, osteochondrosis, protrusion, etc. However, most often pain appears due to diseases of the spine - against the background of compression of the spinal cord roots.
Headaches and facial pains
A cephalologist and a neurologist deal with the problem of headaches and facial pain.
Most of these pains are primary, that is, they arise on their own and are not associated with pathological processes - migraine, tension headache, cranial neuralgia. However, there are many secondary pains that occur against the background of other diseases - infections, lesions of the cervical spine and skull, injuries. Separately, they talk about pain that appears in response to the withdrawal of a drug after a long course of use.
Dizziness
When walking, a person loses balance, may lose consciousness or simply fall. Often the cause of this phenomenon is damage to the vestibular apparatus or blood flow through the vertebral arteries.
Weakness in the legs or arms
Muscle weakness can be in some individual muscles or in many at once, and develops gradually or suddenly. Depending on the cause, the patient may experience other symptoms.
Most often, muscle weakness is associated with compression of the spinal cord or spinal roots due to intervertebral hernia or other pathologies.
Diseases of internal organs
This is also the area of competence of a neurologist, because often back pain is not at all a consequence of osteochondrosis or a hernia, but rather a manifestation of the pathology of some internal organ. A good neurologist will definitely distinguish one from the other and prescribe competent treatment and consultation with a specialized specialist.
Pathologies of the nervous system
A neurologist monitors the normal functioning of the nervous system and deals with its diseases. It is very important to see a doctor as early as possible, because some diseases in the later stages lead to disability, are extremely difficult to stop and may not be cured completely.
Diseases associated with brain pathologies
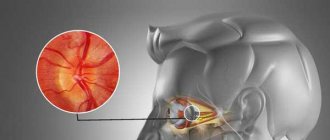
Stroke
This is a sudden and rapid disruption of blood circulation in the brain with damage to certain parts of it. As a result, those functions for which the affected area was responsible are lost.
Symptoms can vary from decreased vision to complete paralysis.
When a stroke occurs, the clock literally counts, and the patient must be immediately taken to the hospital to diagnose the type of stroke and prescribe therapy. It is treatment carried out in the first hours after an attack that increases the chances of recovery.
Epilepsy
This disease is dealt with by an epileptologist - a neurologist who is an expert in this field.
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disease that develops due to the presence of pathological foci in the brain. These lesions excite neurons, causing involuntary seizures to occur in a person. The patient becomes detached from reality during an attack and may harm himself. This distinguishes epilepsy from ordinary seizures.
In most cases, epilepsy is curable, and a good neurologist will definitely help.
Alzheimer's disease
It is also called “senile dementia”. It is a neurodegenerative process in the brain that begins in people over 65 years of age. In rare cases - earlier. Accompanied by apathy, impaired memory, motor functions, speech, coordination, perception of the outside world and people, gradual exhaustion and loss of everyday skills.
Parkinson's disease
A neurologist who specializes in this disease is a parkinsologist.
The disease progresses slowly and is a degenerative process in the brain, namely its structures responsible for maintaining muscle tone, controlling movements, and posture.
It manifests itself as a limitation in the pace and range of movements, muscle stiffness, trembling of the limbs, and instability of posture. Accompanied by mental and autonomic disorders.
Consequences of psycho-emotional stress
Insomnia and sleep disorders
Delay in falling asleep, disturbance in the duration and depth of sleep, etc. The main causes are psychotrauma, nervous overstrain, neurological diseases.
Arterial hypertension
With this disease, blood pressure is persistently above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. As a result, concomitant changes in the blood vessels and heart develop.
The main doctor who treats arterial hypertension is a cardiologist. However, the cause of the disease is psycho-emotional stress, so an examination by a neurologist is mandatory.
Congenital diseases
Tourette's syndrome
Symptoms of this disease include vocal (words, sounds) and motor (periodic uncontrolled body movements) tics. They can occur many times a day, be simple or complex.
Another symptom is coprolalia, that is, shouting obscene and offensive words.
Life expectancy and level of intelligence in patients are normal. Typically, by adolescence, the severity of tics decreases. Before a tic, most people with this syndrome experience a strong urge, such as the urge to sneeze or scratch an itchy area.
Leukodystrophy
A group of hereditary diseases in which degeneration of the white matter of the spinal cord and brain progresses.
The main clinical signs are increasing cerebellar, pyramidal and extrapyramidal disorders, pseudobulbar and bulbar syndromes, deterioration of hearing and vision, seizures similar to epileptic, developing dementia. In rare cases, sensory disturbances are observed.
The first disorders appear in preschool age, these are central paresis and paralysis. Then dysphonia, dysphagia, dysarthria, coordination disorders, and optic nerve atrophy appear.
Syringomyelia
Severe and progressive disease of the central nervous system. With it, a cavity is formed inside the spinal cord and medulla oblongata. If the cavity enlarges and a gap appears in the lower parts of the brain, the prognosis becomes much worse.
The disease often disables young and middle-aged people.
Crouzon syndrome
A rare genetic disease that manifests itself as premature fusion of the cranial bones, which causes deformation of the facial and brain parts of the skull. As a result, the shape of the head changes, the nose becomes hooked, hearing and vision are impaired, and the middle third of the face is underdeveloped.
Dandy-Walker syndrome
A disease in which abnormalities occur in the development of the cerebellum and the cerebrospinal fluid spaces surrounding it. It has a genetic nature. It is manifested by the expansion of the 4th ventricle and the formation of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst in the back of the skull, the absence or underdevelopment of the cerebellar vermis. May develop quickly or gradually.
With this syndrome, there is a slow development of motor skills in the baby and a continuous expansion of the skull. At an older age, intracranial hypertension and its corresponding symptoms appear, as well as cerebellar symptoms - loss of coordination, static ataxia.
Neurofibromatosis
One of the most common hereditary diseases, in which the patient develops benign and malignant tumors. Tumors affect the nerves, causing pigment spots to appear. There is no specific treatment. Benign tumors are removed surgically, while malignant tumors are treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
Wilson-Konovalov disease
One of the most severe hereditary diseases of the central nervous system and internal organs. May be acquired. When it occurs, the copper metabolism process in the body is disrupted and a large pool of free copper is formed. If you do not start removing copper in time, then death occurs within 5-7 years from the onset of the disease.
When copper damages the liver, cirrhosis occurs, and the brain develops severe neurological symptoms (increased muscle tone, trembling of the body and limbs, impaired swallowing, speech, and intellect). A characteristic symptom is the Kayser-Fleischer ring - a brown-green pigment along the edge of the cornea.
Spina bifida
This is a congenital anomaly that occurs when there are disturbances in the development of the fetus, often leading to disability of the child.
Spina bifida is caused by the fact that at the stage of intrauterine development the neural tube does not heal and the spinal cord is not fully formed. Where there is a cleft, the spine splits, and its arches do not close tightly enough. As a result, a section of the spinal cord comes out and a hernial sac is formed.
Symptoms of a hernia are weakness and impaired movement in the limbs, disruption of the pelvic organs, lack of sensitivity below the hernial sac, paralysis of the legs, urinary incontinence, cerebral edema.
Also within the scope of competence of a neurologist are:
Vascular diseases
They are dealt with by an angioneurologist. These may be: vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine, atherosclerosis, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, arterial aneurysm, cerebral vascular injury.
Complications of the perinatal period
The result of these complications is various diseases in infants, which are dealt with by a pediatric neurologist. The most common of them is cerebral palsy (CP).
Cerebral palsy is a violation of motor skills and the ability to maintain a posture, motor defects. All this is due to the fact that when the child was in the womb, his brain was damaged. This can also happen during childbirth due to complications, the use of obstetric instruments, and other things.
In addition to cerebral palsy, a pediatric neurologist is consulted with muscular dystonia syndrome, perinatal encephalopathy, and consequences of perinatal damage to the central nervous system. Children should be shown to a neurologist as planned at 1, 3, 6 months and 1 year.
How does the consultation work?
The neurologist usually takes your medical history and performs a neurological examination. Sometimes the doctor will also examine the heart, skin, and other parts of the body. Neurologists often seek help from MRI or CT scans of the brain, EEG (tracking of brain activity), or testing of nerves (nerve conduction tests). Sometimes more comprehensive tests are considered. If these tests are necessary, your neurologist will explain to you in detail why they will be useful.
Assessing and diagnosing damage to the nervous system can be very difficult. Many of the same symptoms occur in different combinations across different disorders. To further complicate the diagnostic process, many disorders have no definitive causes, markers, or tests.
Neurological tests to evaluate children may include:
- Electroencephalogram (EEG). A procedure that records continuous electrical activity in the brain using electrodes attached to the scalp.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
- Electrodiagnostic tests (eg, electromyography and nerve conduction velocity). Tests that evaluate and diagnose nerve, muscle, and motor neuron disorders. Electrodes are inserted into a muscle or placed on the skin over a nerve, muscle, or group of muscles, and the electrical activity and response of the muscle is recorded.
- Positron emission tomography (PET). A computer-based imaging technique that provides a picture of brain activity rather than brain structure by measuring levels of an administered tracer molecule, most often glucose.
- Arteriogram (also called an angiogram). A procedure that produces images of the arteries and/or veins leading to and through the brain. CT angiography, a newer and less invasive technique, is sometimes used.
- Cerebrospinal fluid test (also called a spinal tap or lumbar puncture). A procedure used to evaluate or make a diagnosis by examining fluid taken from the thecal sac, a sac of fluid located below where the spinal column ends.
- Evoked potentials. Procedures that record the brain's electrical response to visual, auditory, and sensory stimuli.
- Myelogram. A procedure in which dye is injected into the spinal canal so that the structure appears clearly on x-rays. Although this was once common, it is rarely used.
- Ultrasound (also called sonography). A diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves and a computer to create images of blood vessels, tissues, and organs. Ultrasound is used to monitor the functioning of internal organs and to assess blood flow through various vessels.
- Neurosonography. A procedure that uses ultra-high frequency sound waves to allow the doctor to evaluate the structures of the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and other structures.
At the Renovazio Medical Center, an appointment with a neurologist is made online (by filling out the feedback form) or by calling the numbers listed in the “Contacts” section.
Symptoms for which you should consult a neurologist
- Headaches are sudden, sharp, increasing.
- Dizziness, fainting, presyncope.
- Pain in the limbs, back, neck, body.
- Shooting facial pain - with gusts of wind, touch, while talking or chewing food.
- Muscle weakness.
- Unsteadiness of gait, general lack of coordination of movements.
- Sleep disorders, including insomnia.
- Visual impairment – double vision, loss of parts of the visual field, blurred contours of objects and people, “islands” of blindness.
- Speech disorders - inability to control the tongue and lips, inability to form competent phrases, lack of speech, altered voice volume.
- Uncontrolled movements of the arms or head, speech tics, uncontrollable coughing or sniffling during a conversation.
- Drooping eyelid.
- Memory impairment.
What does a neurologist do during an examination?
The appointment begins with a conversation with the patient and collection of anamnesis. It is imperative to inform the neurologist that there were diseases of his profile in the family, tell in detail about the symptoms, say when and how they began, etc. You must bring all available medical documentation to the appointment - examination results, an outpatient card, if you have it on hand. If it is impossible to speak clearly with the patient, a relative or accompanying person should come to the appointment and answer questions. Based on the results of the initial conversation, the doctor will understand whether there are any speech or consciousness disorders.
Then an external examination of the patient is carried out. The neurologist pays attention to the symmetry of the shoulders and limbs, posture, motor activity, and notes trembling of the hands or body. The doctor will ask you to squeeze their arm to test muscle strength. With neurological pathology, it can be different in different hands.
The neurologist examines reflexes - cutaneous, periosteal, pupillary, tendon, meningeal. Tendon reflexes are tested by lightly hitting the tendon of the target muscle with a hammer. Pupillary - by moving the hammer in front of the patient's face, who must follow it with only his eyes.
Types of mucosal reflexes and ways to test them:
- pharyngeal - if you act on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, swallowing will occur;
- palatal - the palate tightens when you touch it;
- corneal - when the doctor touches the cornea of the eye, the eyelids close;
- anal - the sphincter contracts when there is tingling around the anus.
Skin reflexes are tested by irritating the skin with a specific object. As a result, the muscles contract locally. There are the following skin reflexes:
- plantar – the toes bend when the skin of the foot is applied;
- cremasteric - if you act on the skin of the thigh from the inside, the testicle is tightened;
- abdominal - the doctor quickly moves the handle of the hammer along the skin of the abdomen, in response to which the oblique and rectus muscles contract.
Temperature sensitivity of the skin is tested by applying test tubes with liquid of different temperatures to the body.
Pain sensitivity is tested by lightly pricking the skin with a needle. Tactile sensitivity is assessed using a piece of fabric or a brush.
All these tests are tests of surface sensitivity. Next, the neurologist checks the deep. To test the sensation of pressure, objects of different weights are placed on the skin. Normally, a person feels a pressure of up to 0.02 g with the palm and inner side of the forearm. To study the deep muscle-articular feeling, the doctor makes passive movements in different joints of the patient.
Then combined sensitivity, or complex sensitivity, is checked. This includes testing: coordination, the ability to reproduce graphic patterns “drawn” with a blunt object on the skin, a sense of localization - the ability to correctly assess one’s spatial position.
Cerebellar function must be examined. The neurologist checks stability in the Romberg position (the patient stands, feet shifted, eyes closed, arms extended straight in front of him), asks to touch the tip of the nose with one finger with eyes closed.
A test for diadochokinesis is also performed: the patient stands with his eyes closed and rotates his hands in different directions; if the cerebellum is damaged, the amplitudes of movements on different hands will vary.
Another test is the heel-knee test: the patient lies on his back and touches the knee of the other with the heel of one leg.
The doctor also performs a pointing test - you need to touch the hammer with your index finger.
Types of diagnostics prescribed by a neurologist
Based on the results of the examination and tests, the doctor may refer the patient for some examinations from this list:
- MRI – regular or with contrast, in the second case the accuracy of visualization of nerve structures is higher;
- CT head;
- echoencephalography;
- PET (positron emission tomography);
- cerebral angiography;
- lumbar puncture;
- Ultrasound Doppler scanning;
- myelography;
- Ultrasound of the spine;
- electroneuromyography;
- gammaencephalography;
- laboratory tests - clinical and biochemical blood tests, general urine analysis, etc.
How is treatment done by a neurologist, what methods are used?
The choice of treatment method depends on the disease, its stage, age and general health of the patient. Basic techniques:
- manual therapy;
- different types of therapeutic massage;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- biofeedback therapy;
- traction therapy (spinal traction with rings, blocks, belts);
- kinesitherapy;
- osteopathy;
- drug therapy;
- blockades
To relieve muscle-tonic syndromes and pain, periarticular and joint blockades are prescribed.
In the treatment of neuroses and sleep disorders, special medications and psychotherapy are prescribed. In this case, a neuropsychiatrist or psychotherapist is involved in treatment.
For vascular disorders, epilepsy, concussion, consequences of surgery, etc., a medicinal method of treatment is used, that is, based on the patient taking medications prescribed by a neurologist.
Treatment is always individual, and many factors are taken into account when developing a treatment plan. And only with this approach can patients count on the effectiveness of therapy and its minimum duration.
The most commonly used techniques from the above:
- Manual therapy
is a treatment method based on manual manipulation. It is used mainly for the treatment of internal organs and the musculoskeletal system. - Physiotherapy
– individual selection of physiotherapeutic techniques for each patient – temperature, ultrasound, electromagnetic, electric current, vibration and other types. - Osteopathy
is a gentle influence on the patient’s body to restore biomechanics. Neurology uses craniosacral and structural osteopathy, which regulate bone relationships and affect the musculoskeletal system. - Acupuncture
is the effect of ultra-thin needles on biologically active points of the human body. Simply reflexology can also be used - acupressure, laser techniques, cold treatment, etc. - Kinesitherapy
– the patient works on special decompression machines, which reduce the load on the joints and allow you to do exercises without pain.
Additional neurological studies
After clarifying complaints, anamnesis of illness and life, general and neurological examination, doctors at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital draw up a comprehensive examination scheme, which includes:
- computed tomography - reveals areas of hemorrhage, malformations of arteries or veins, allows you to see changes in tissue, their softening or swelling in case of traumatic brain injury or cerebral infarction;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern diagnostic method that provides more detailed information due to the greater resolution of the device;
- angiography - a contrast radiographic study that reveals changes in the blood vessels of the brain;
- multislice tomography is a non-invasive method for visualizing cerebral vessels;
- Ultrasound examination - allows you to obtain a detailed image of the large vessels of the neck.
Lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis are performed for meningitis, hemorrhages, and neoplasms of the meninges.
X-ray examination uses contrast. On X-rays, a radiologist can see intervertebral disc herniations, proliferation of vertebral bodies, and tumor processes. The study gives a clear picture of the state of the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord. Electroencephalography allows you to record the biopotentials of the brain. Using electroneuromyography, the condition of peripheral nerves, muscles, the localization of the pathological process and the degree of damage to nerve fibers are determined. In neurology, diagnostic methods such as biopsy of muscles and nerve tissue, genetic studies, clinical and biochemical blood tests are used.
Prevention of neurological diseases
There are only four rules, if followed, you will not encounter neurological problems:
- Exercise regularly or at least do daily exercises.
- Get proper rest - sleep at least 8 hours a day, but at night, and not during the day or evening.
- Eat right so that your diet contains all the necessary vitamins and minerals, avoid junk food, alcohol, and fast food.
- Walk in the fresh air as often as possible, at least 20-30 minutes a day, and preferably 1 hour.
Recommendations from experts
The nervous system can and should be strengthened. It is not difficult and anyone can do it. Here's what neurologists advise to strengthen the cardiovascular system and prevent neurological diseases:
1. Move! Physical exercise has a beneficial effect on the health of the entire body. Experts especially recommend Pilates classes. They strengthen the back muscles and joints.
2. Swim! Swimming helps relieve back pain and relax the nervous system, and also strengthens the muscle corset.
3. Get enough sleep! Normal functioning of the nervous system is possible only with full sleep (at least 8 hours).
4. Take a walk! Walking in the fresh air is a great way to relieve stress.
5. Form a positive perception of life! The ability to rejoice and find positive aspects in everything allows you to maintain your nerves and overall health.
6. Follow the regime! An optimal daily routine also has a positive effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
7. Do not self-medicate or ignore symptoms! For any neurological manifestations, make an appointment with a doctor. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and protect against serious consequences of the disease.
FAQ
How to make an appointment with a neurologist?
You can sign up for Dr. Gruzdev’s Clinic in two ways: call us by phone or click the “Sign up” button in the upper right corner of the site and fill out a simple form.
If you want to go to a neurologist at a municipal clinic, then first you need to get a coupon to see a therapist, who, if indicated, will give a referral to this specialist.
Who treats neuroses, a neurologist or a psychotherapist?
Neuroses are treated by both of these specialists at the same time.
Who treats shingles, a neurologist or a dermatologist?
Shingles is treated by either a dermatologist or a neurologist.
Who treats depression and prescribes antidepressants, a neurologist or a psychiatrist?
Depression often accompanies neurological diseases; it may be a symptom of organic brain damage. It always worsens the clinical picture of a neurological disease and reduces the patient’s recovery options.
Depression is detected after a stroke, in Parkinson's disease, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer's disease. And, conversely, with long-term depression without treatment, changes occur in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and amygdala.
Therefore, a neurologist treats depression. However, he must redirect the patient to a psychiatrist if:
- there is a severe form of depression;
- the patient has suicidal thoughts;
- bipolar depressive disorder is present.
A neurologist can independently treat minor and subsyndromal depression.
The neurologist also prescribes antidepressants, but he prioritizes the minimum of side effects and negative interactions with other medications over the clinical effectiveness of the drugs. The antidepressant should not adversely affect a neurological disease, cause an increase in blood pressure, impair cognitive function, or cause hypotension.
Who diagnoses “dysarthria” and treats the disease, a speech therapist or a neurologist?
Both of these specialists treat dysarthria and can make this diagnosis.
Who treats Alzheimer's disease, a psychiatrist or a neurologist?
It is best if both of these specialists are involved in maintaining the normal condition of the patient, each in his own profile. This will help you adapt better and improve your quality of life.
Principles of treatment
What does a neurologist do when there is already a diagnosis? Begins to treat the disease using different methods.
Medicines
To relieve acute pain and inflammation, medications are prescribed, and maintenance therapy is provided if necessary. Problems with blood vessels, concussions, epilepsy, and conditions after surgery almost always require medication.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy is a treatment with hands (from the Latin manus - hand), which helps eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasticity, normalize microcirculation and range of motion. Widely used for diseases of the joints and spine, neuroses.
Massotherapy
One of the most effective methods of treating neurological diseases, along with therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy. Using special techniques, the specialist gently influences the patient’s body to stimulate the body’s natural recovery processes.
Physiotherapy
Through physical techniques, it is possible to accelerate tissue regeneration processes, improve nerve conduction, thereby reducing the intensity of pain and inflammation.
Reflexology
The essence of the method is the impact on bioactive points to restore the disturbed balance. It is based on the idea of the body as an integral system, when one of its elements fails, others suffer.
Traction traction
Used to stretch limbs and muscles in case of bone fractures and diseases of the spine.
Kinesitherapy
“Movement treatment” is how this term is translated from scientific language. This is a type of physical therapy that combines medical, physiological, and biochemical aspects.
Osteopathy
This is a method similar in effectiveness to massage and manual techniques. But, unlike them, it affects the very cause of the disease, helping to restore the well-coordinated functioning of the body.
Therapeutic blockades
For severe pain that cannot be relieved with conventional medications, the sore spot is injected. Injections are made directly into the painful area, hitting the nerve endings. The procedure relieves a person from pain in a matter of minutes for a period of half an hour to several days.