One of the types of ischemic stroke is lacunar, localized in the pontomesencephalic region or cerebral hemispheres. This is the most common form of pathology diagnosed at the Yusupov Hospital in many patients with ischemic stroke. Early diagnosis will avoid complications and can be performed in a modern hospital clinic equipped with high-precision medical equipment. Yusupov Hospital, rightfully considered a leading clinic for the treatment of strokes.
Overview of Lacunar Ischemic Stroke
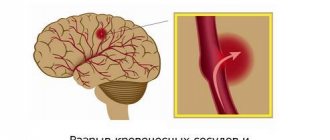
Lacunar ischemic stroke leads to pathological disorders in the deep layers of the brain and the formation of so-called lacunae (cavities), the diameter of which ranges from one to fifteen millimeters. Sometimes the lacunae merge, resulting in the formation of large cavities filled with blood or plasma and fibrin.
With this pathology, the patient’s consciousness, vision, speech, and other functions of the cerebral cortex are practically not impaired. In addition, symptoms of brain stem damage are also completely absent. Thanks to these distinctive features, lacunar stroke can be differentiated from other types of this pathology.
In the absence of qualified neurological assistance, this type of brain catastrophe threatens the development of severe complications, including death. According to statistics, after patients have suffered a lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain, the survival prognosis is: in the first month - 70-80%, within a year - about 50%. Therefore, early diagnosis of pathology plays a vital role.
Pathophysiology of lacunar disease
The trunk of the middle cerebral artery, as well as the arteries forming the circle of Willis (segment A1 of the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and posterior communicating arteries, precommunal segments of the posterior cerebral arteries), the main and vertebral arteries together give off branches with a diameter of 100-400 µm, piercing the deep gray and white matter of the cerebrum and brainstem. Each of these small branches can undergo thrombosis, either as a result of an atherothrombotic lesion at its onset (damage to the branches of the basilar artery or the trunk of the middle cerebral artery) or with lipohyalinous thinning of its walls at a location more distant from the beginning. With thrombosis of these branches, small infarcts (less than 2 cm) develop, which are designated as lacunae. In many cases they are even smaller - 3-4 mm. There is no doubt that arterial hypertension is a risk factor for such small vessel damage. Lacunar cerebral infarctions account for 10% of ischemic stroke cases.
Causes of lacunar ischemic stroke
The main cause of lacunar stroke is considered to be arterial hypertension, which leads to brain damage and depends on blood pressure, the degree of damage to the arterial walls and their condition. In order to prevent the development of a cerebral catastrophe, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital monitor surges that occur during the day, since lacunar stroke occurs against the background of sharp changes in arterial pressure.
The risk group consists of persons suffering from the following pathologies:
- hyaline dystrophy AG;
- atherosclerosis;
- infectious inflammation of arterioles localized in the brain (previously suffered);
- diabetes mellitus
Along with the above, lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain can be caused by vasculitis, the form of which can be either specific or nonspecific.
Identification of the disease
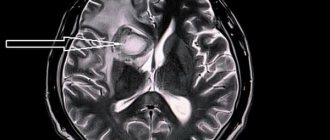
Modern medicine makes it possible to identify lacunar pathology. The pictures taken later clearly show the location of the tumor. They will also indicate the areas of the brain that are affected by the disease and will help determine the shape and size of the cyst. Methods used by specialists:
- head biopsy;
- blood tests for the presence of pathogenic microbes;
- blood tests for coagulation and cholesterol;
- blood pressure monitoring for 24 hours;
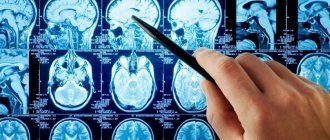
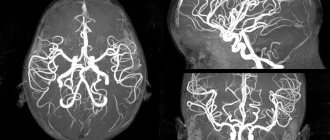
- MRI;
- electrocardiography;
- spiral CT;
- Dopplerography.
The principle of Doppler ultrasound
CT and MRI show the location of the tumor, the volume and affected area of the brain. Electrocardiography and Dopplerography will reflect the condition of blood vessels, arteries, the presence of heart failure and blood circulation speed. Using a biopsy, specialists will determine the type of tumor. All kinds of tests will show the condition of the blood vessels and the presence of infection. Blood pressure monitoring will also confirm pathology in the brain.
Diagnosis of lacunar ischemic stroke
In order to determine lacunar ischemic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, which are the most informative in this situation. Using these studies, the location, number and volume of formed lacunae are revealed. With lacunae of small diameter, fixation of lesions is difficult. To make a final diagnosis, along with the results of the studies, the neurologist takes into account the patient’s medical history, especially if he is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension or alcoholism.
Treatment of lacunar ischemic stroke
Treatment of lacunar stroke at the Neurology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is based, first of all, on the use of drugs whose action is aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as having a neuroprotective effect. The development of collateral blood flow is promoted by drugs such as cinnarizine and Cavinton.
The Yusupov Hospital attaches great importance to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused vascular damage. Blood pressure is constantly monitored. If its levels are high, the patient is prescribed antihypertensive drugs. High cholesterol levels, determined by laboratory tests, are corrected by taking lipid-lowering drugs - statins, the action of which is aimed at blocking enzymes that help the synthesis of cholesterol compounds in the liver.
Specialists at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital constantly monitor the function of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If necessary, the patient is prescribed medications that correct the water-electrolyte balance in the body and reduce swelling of brain tissue.
To prevent relapse, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet agents. For arterial thromboembolism, warfarin is used. In some cases, a course of anticonvulsant drugs is recommended.
To prevent dementia, patients are prescribed a course of drugs Neuromidin or Gliatilin. In the presence of pseudobulbar syndrome, fluoxetine is used.
For patients with lacunar ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use an individual approach, resulting in high treatment results.
Treatment
If the cystic neoplasm is small in volume and does not bother the patient, treatment is not required. You can maintain your condition with trips to a sanatorium and preventive treatment. But you need to monitor the size and condition of the tumor, its position and shape, so as not to develop new symptoms. Scientists have concluded that even a small cyst can accelerate the aging of the body.
Basically, such formations are treated by influencing the causes. They use antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and antihypertensive drugs. All medications are prescribed taking into account the person’s medical history. These drugs are commonly used by doctors:
- antioxidants;
- medications that help restore blood circulation;
- anti-adhesion drugs;
- nootropics;
- immunomodulators.
Treatment with medications is prescribed to improve blood clotting in lacunar tumors to control cholesterol and blood pressure. It is not possible to completely get rid of the disease in this way; medications only support the patient’s life. For a complete cure, surgery is necessary.
Sometimes pills don't do the job. Symptoms become more severe and life becomes worse. In this case, the patient needs to decide on surgery. This method is the only possible treatment option that completely rids a person of the tumor. Treatment methods:
- trepanation;
- endoscopy;
- shunting.
In the latter case, a drainage tube is inserted into the brain to remove fluid from the lacuna. This operation must be repeated for a long time, and the risk is enormous. The method is used only in extreme cases. In the second method, the skull is pierced with an endoscope and the tumor is removed through the puncture. It is the most painful, but safe. In the case of trepanation, there is a risk of damaging the brain, but the operation is the most effective.
Experts' prognosis for lacunar ischemic stroke
If a patient is diagnosed with a single lacunar stroke of the brain, the prognosis is favorable. As a rule, after rehabilitation, the patient experiences restoration of all functions, although the presence of sensory residual and motor symptoms may sometimes be observed.
During a relapse, a lacunar state of the brain may develop, and the risk of this complication is very high: according to statistics, after a repeated lesion, this occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Despite the restoration of all impaired functions, lacunar ischemic stroke negatively affects the mental state of the patient, in which gradual changes occur. There is the appearance of memory loss, disorientation and difficulty communicating, tearfulness, frequent hysterics, a feeling of helplessness and a state of passion.
Rehabilitation after lacunar ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital involves a whole range of measures: medical, social and psychological. They are aimed at restoring functions lost after a stroke. The hospital’s highly qualified doctors: neurologists, physiotherapists, psychotherapists have extensive practical experience in the field of rehabilitation medicine; they have in their arsenal the world’s leading techniques, modern medical equipment and the latest drugs for treating the consequences of brain accidents, thanks to which they can achieve high results. The clinic provides services for transporting patients to the hospital. Call and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Complex of therapeutic measures
For small lacunar cysts, when clinical manifestations do not bother the patient and there are no disturbances in brain function, then supportive treatment and rehabilitation are carried out in sanatorium institutions. However, it is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of the cyst, changes in its position, shape and size, since scientists believe that even a small formation accelerates the aging process of the body.
The main treatment is aimed at the pathologies that caused the cyst to appear. Depending on the etiology, antiviral drugs or antibiotics, antihypertensive and immunomodulatory drugs are used.
Medicines used by neurologists for drug therapy of cysts:
- anti-adhesion agents;
- medicines to restore blood circulation;
- immunomodulators;
- antioxidants;
- nootropic drugs.
During drug treatment, cholesterol levels, blood clotting, and blood pressure are constantly monitored. To completely get rid of a lacunar cyst today means to undergo surgery, to agree to surgical intervention. Patients whose quality of life sharply decreases take this risk.
Methods offered by modern medicine for removing lacunar cysts:
- bypass;
- endoscopy;
- craniotomy.
Today, the use of an endoscope is considered less invasive. Such equipment is used when the cyst is in an easily accessible place. But there are contraindications for endoscopy. When shunting, a drainage tube is inserted into the cyst cavity by puncturing the skull, through which the fluid contained inside the formation flows out, and the walls of the cyst gradually grow together. This method has a risk of infection. Craniotomy today is the most highly effective operation, although the most difficult. It makes it possible to remove cysts of any size, located anywhere. However, trepanation carries a high risk of damage to brain tissue.
Still, the most effective treatment for a lacunar cyst is to get rid of it surgically. It is selected by doctors solely for health reasons and is performed only if the prognosis is favorable.