One of the types of ischemic stroke is lacunar, localized in the pontomesencephalic region or cerebral hemispheres. This is the most common form of pathology diagnosed at the Yusupov Hospital in many patients with ischemic stroke. Early diagnosis will avoid complications and can be performed in a modern hospital clinic equipped with high-precision medical equipment. Yusupov Hospital, rightfully considered a leading clinic for the treatment of strokes.
Overview of Lacunar Ischemic Stroke
Lacunar ischemic stroke leads to pathological disorders in the deep layers of the brain and the formation of so-called lacunae (cavities), the diameter of which ranges from one to fifteen millimeters. Sometimes the lacunae merge, resulting in the formation of large cavities filled with blood or plasma and fibrin.
With this pathology, the patient’s consciousness, vision, speech, and other functions of the cerebral cortex are practically not impaired. In addition, symptoms of brain stem damage are also completely absent. Thanks to these distinctive features, lacunar stroke can be differentiated from other types of this pathology.
In the absence of qualified neurological assistance, this type of brain catastrophe threatens the development of severe complications, including death. According to statistics, after patients have suffered a lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain, the survival prognosis is: in the first month - 70-80%, within a year - about 50%. Therefore, early diagnosis of pathology plays a vital role.
Lacunar cerebral infarction - what is it?
Pathogenetic mechanisms of lacunae formation are associated with acute disruption of cerebral blood supply. The death of brain parenchyma at the site of impaired microcirculation with the formation of lacunae is an irreversible condition. For the first time, lesions were identified in patients with hypertension. The autopsy material made it possible to identify lesions up to 150 mm in size located in different segments of the brain. Cognitive deficit in nosology leads to mental disorders, secondary parkinsonism.
Scientific literature describes the nosology in fifteen percent of patients against the background of various types of strokes. Russian neurologists (Skvortsov, Schmidt, Gusev) established the probability of the formation of pathology in the working population is about 0.3%.
Causes of lacunar ischemic stroke
The main cause of lacunar stroke is considered to be arterial hypertension, which leads to brain damage and depends on blood pressure, the degree of damage to the arterial walls and their condition. In order to prevent the development of a cerebral catastrophe, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital monitor surges that occur during the day, since lacunar stroke occurs against the background of sharp changes in arterial pressure.
The risk group consists of persons suffering from the following pathologies:
- hyaline dystrophy AG;
- atherosclerosis;
- infectious inflammation of arterioles localized in the brain (previously suffered);
- diabetes mellitus
Along with the above, lacunar ischemic stroke of the brain can be caused by vasculitis, the form of which can be either specific or nonspecific.
General information
One of the types of cerebral infarction (ischemic stroke) is lacunar infarction, which is a small (up to 15 mm in diameter) brain damage that occurs when local blood circulation and gas exchange are disrupted. The reasons for this situation are varied and not fully understood, but most often it is blockage of supply vessels as a result of changes in their walls (atherosclerosis, inflammation), emboli (blood clots, fat droplets, bacterial colonies, etc.). Most of them are found in the periventricular region, basal ganglia, and thalamus - the central, deep structures of the brain. Lacunar infarctions account for 20-30% of all strokes.
Diagnosis of lacunar ischemic stroke
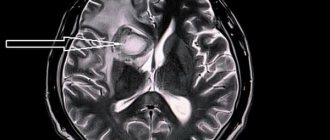
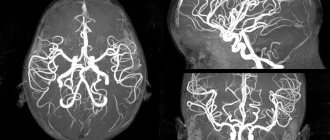
In order to determine lacunar ischemic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern diagnostic methods such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, which are the most informative in this situation. Using these studies, the location, number and volume of formed lacunae are revealed. With lacunae of small diameter, fixation of lesions is difficult. To make a final diagnosis, along with the results of the studies, the neurologist takes into account the patient’s medical history, especially if he is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension or alcoholism.
Clinical picture
In most cases, the attack can be sudden, very quickly leading to blockage of the arteries, but it can last up to five days. Precursors may include ischemic attacks that cause disruption of cerebral circulation in small cerebral arteries.
During an attack, you may experience high blood pressure and an irregular heart rhythm. Single cysts - lacunae do not lead to paralysis of the body. Detection of the lacunar form of cerebral infarction is complicated by the implicit manifestation of symptoms:
- Impaired motor skills are expressed in the inability to move the limbs; they become less sensitive.
- Loss of coordination. The patient may complain that everything is floating before his eyes, there is an unsteady gait and disorientation.
- The lacunar form of the disease is characterized by neurological disorders, expressed in the deterioration of memory, the ability to analyze, there is no logic of reasoning, and other processes of the brain are disrupted.
To immediately contact a doctor, one of the following symptoms of a stroke is sufficient:
- A sharp manifestation of weakness in the legs, fainting, loss of consciousness;
- Distortion of the face, numbness of half the body, limbs, impaired skin sensitivity;
- Difficulty in speech and impairment of its perception;
- The patient begins to feel dizzy and finds it difficult to maintain coordination of movements;
- Severe pain in the head appears;
- Cramps, increased muscle tone.
The disease can occur in the form of a micro-stroke or without clinical manifestations at all. It can develop at any age. Cases of the disease have been described in patients who have just turned 25 years old.
Features of the pathology:
- stroke develops only against the background of hypertension;
- there are no headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, loss of consciousness or disturbances thereof;
- neural symptoms increase gradually over 2-48 hours (usually the patient’s disturbances develop during night sleep, and in the morning he wakes up with symptoms of a stroke);
- the prognosis for this disease is favorable; after an attack, complete or partial restoration of brain function is observed;
- examination of cerebral vessels using contrast agents does not show any abnormalities; computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can reveal small foci of low density, but not always, especially if the infarction is small.
Doctors describe about 20 clinical syndromes that can be observed with the development of lacunar stroke. The following are most often diagnosed:
- The isolated motor variant is the most common and occurs in 60% of patients. Lacunae form within the capsule and pons. The patient develops paralysis of one half of the body, usually the limbs, sometimes the face. Plegia is observed on the side opposite to the lacuna. No further neurological symptoms develop.
- The isolated sensitive variant is observed in almost 20% of patients. The lacunae in this case are localized in the ventral thalamic nerve ganglion. Disturbances of all types of sensitivity develop: temperature, nociceptive, tactile, muscle-articular. Manifestations of the disease can involve the head, arms, legs and torso. Typically, after what period sensitivity is fully or partially restored.
- Atactic hemiplegia develops when pathological foci appear in the capsule and pons of the brain. Occurs in 12% of patients. The patient experiences muscle hypotonia in the arms or legs, pyramidal disorders, and impaired coordination of movement on the side of the injury.
- Dysarthria and clumsiness of the hands when moving are observed in 6% of patients; pathological foci form in the pons of the brain. The patient has a speech impairment; on the one hand, paralysis of the limbs and head may develop.
Editorial: Symptoms, causes and treatment of endogenous depression
The following syndromes are also often diagnosed:
- dyskinesia;
- false bulbar syndrome;
- parkinsonism syndrome;
- forced gait in small steps;
- urgency to urinate, incontinence;
- hemiparesis and loss of sensation of one half of the body.
With the development of a lacunar stroke, there is no disorder of consciousness or vision, systemic impairment of formed speech (aphasia), or other symptoms of damage to the cerebral cortex.
Treatment of lacunar ischemic stroke
Treatment of lacunar stroke at the Neurology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is based, first of all, on the use of drugs whose action is aimed at improving cerebral circulation, as well as having a neuroprotective effect. The development of collateral blood flow is promoted by drugs such as cinnarizine and Cavinton.
The Yusupov Hospital attaches great importance to the treatment of the underlying disease that caused vascular damage. Blood pressure is constantly monitored. If its levels are high, the patient is prescribed antihypertensive drugs. High cholesterol levels, determined by laboratory tests, are corrected by taking lipid-lowering drugs - statins, the action of which is aimed at blocking enzymes that help the synthesis of cholesterol compounds in the liver.
Specialists at the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital constantly monitor the function of the patient’s cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If necessary, the patient is prescribed medications that correct the water-electrolyte balance in the body and reduce swelling of brain tissue.
To prevent relapse, the patient is prescribed antiplatelet agents. For arterial thromboembolism, warfarin is used. In some cases, a course of anticonvulsant drugs is recommended.
To prevent dementia, patients are prescribed a course of drugs Neuromidin or Gliatilin. In the presence of pseudobulbar syndrome, fluoxetine is used.
For patients with lacunar ischemic stroke, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital use an individual approach, resulting in high treatment results.
Treatment
In the hospital!
This condition, despite its milder course compared to other types of IS, requires hospitalization in the neurological department for inpatient treatment.
Monitoring of physiological parameters is mandatory: blood pressure, heart rate, ECG, respiratory rate, body temperature, blood glucose, hemoglobin oxygen saturation in arterial blood.
It is also necessary to protect GM from oxidative stress, or neuroprotection using neurometabolic drugs.
To enhance regenerative and reparative processes, nootropics (GABA or choline derivatives), vascular and metabolic nootropics are used.
In order to improve the rheological properties of blood (reduce its viscosity), an appropriate drug group is used. Treatment is complemented by the appointment of vitamin therapy, especially vitamins E (antioxidant effect), group B (regulation of nervous system functions), RR (redox processes).
Micro-stroke “on your feet” and treatment at home
It must be said that sometimes minor symptoms (for example, numbness of the face and arm, slight weakness in an arm or leg, difficulty speaking, which went away within 1-2 days) could be signs of a minor stroke.
You can assume a micro-stroke in the legs based on the results of an MRI (tomograms show small single cysts in the substance of the brain) and an episode of the appearance of the above complaints in the past, according to the patient.
When finding out the reasons for the appearance of such complaints in the past, the patient may associate them with severe psycho-emotional stress and experiences, or they may be causeless.
Treatment at home is unacceptable for any type of stroke
It may be fraught with the fact that, under the “mask” of a micro-stroke, the onset of a more serious brain disease may be missed, which requires timely identification and prescription of targeted therapy aimed at eliminating the immediate cause.
When assuming a previous vascular episode, the main task is not to miss a more serious recurrent vascular accident, especially since the risk of its occurrence is higher in those who have already had this happen.
Get examined, take preventive treatment (if required) and see a doctor.
Experts' prognosis for lacunar ischemic stroke
If a patient is diagnosed with a single lacunar stroke of the brain, the prognosis is favorable. As a rule, after rehabilitation, the patient experiences restoration of all functions, although the presence of sensory residual and motor symptoms may sometimes be observed.
During a relapse, a lacunar state of the brain may develop, and the risk of this complication is very high: according to statistics, after a repeated lesion, this occurs in almost 70% of cases.
Despite the restoration of all impaired functions, lacunar ischemic stroke negatively affects the mental state of the patient, in which gradual changes occur. There is the appearance of memory loss, disorientation and difficulty communicating, tearfulness, frequent hysterics, a feeling of helplessness and a state of passion.
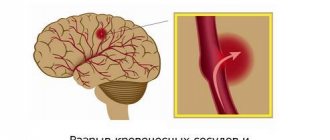
Strokes
The definition of “stroke” means a violation of the integrity of the arterial wall with blood entering nearby tissues. This disease has serious consequences - disruption of the neural network in the cortex due to hematoma, which leads to loss of physical and cognitive abilities.
In the ICD 10 scale, strokes occupy 3 gradations.
- I 60 is a subarachnoid hemorrhage when a vessel ruptures between the arachnoid and pia mater. This code has 5 subtypes of the disease, which are determined by the location of the damaged artery. Additional encoding is indicated using a dot.
- I 61 – parenchymal (intracerebral) hemorrhage. A rupture of a blood vessel in the inner region of the brain, where the gray and white matter is located. This code also contains 5 additional subtypes that define a specific break area.
- I 62 – the location of the hemorrhage is unknown. The doctor identified the fact of a stroke, but the specific area of damage was not found. This code has 3 additional subtypes.
The consequences of the hemorrhagic type of stroke are included in the headings of the ICD 10 scale. These deviations develop against the background of a stroke and can cause lifelong disability for the patient. Such pathologies need to be treated urgently in order to exclude a very likely fatal outcome (about 30% of patients die within five years due to subsequent complications).
insult
Rehabilitation after lacunar ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation at the Yusupov Hospital involves a whole range of measures: medical, social and psychological. They are aimed at restoring functions lost after a stroke. The hospital’s highly qualified doctors: neurologists, physiotherapists, psychotherapists have extensive practical experience in the field of rehabilitation medicine; they have in their arsenal the world’s leading techniques, modern medical equipment and the latest drugs for treating the consequences of brain accidents, thanks to which they can achieve high results. The clinic provides services for transporting patients to the hospital. Call and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.