Risk factors for ischemic stroke
Stroke in an elderly person is characterized by a severe course, which entails various disorders of neurological and cognitive functions. The main cause of stroke is blockage of blood vessels in the brain by a blood clot. In medicine, there are several types of stroke:
- lacunar;
- atherothromboembolic;
- cardioembolic.
In addition, there are strokes caused by such reasons as a migraine attack, dissection of the arterial wall, and hereditary vascular diseases.
Risk factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology:
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- excess body weight (obesity);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by arrhythmias of various etiologies;
- age over 55 years;
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking).
In most cases, stroke in older people begins suddenly. According to statistics, the peak of hypertensive crises and strokes occurs at night or early in the morning.
Symptoms
Stroke in older women and men is manifested by the following symptoms:
- loss of visual fields;
- high blood pressure, dizziness;
- paresis of a limb or half of the body;
- dysarthria (unintelligible and incoherent speech);
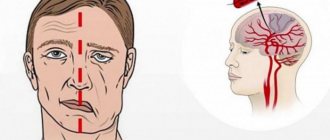
- distorted face;
- confusion;
- loss of coordination of movements (partial, complete).
As a rule, when a stroke occurs, a combination of these symptoms occurs, and to make sure that a person is developing this particular disease, you need to do a simple test before doctors arrive:
- ask to repeat any phrase. If speech is unintelligible, it is a stroke;
- ask to smile. If the patient has a stroke, the smile will be asymmetrical;
- ask to raise your arms, bending them at an angle of 45 degrees, and hold in this position for several seconds. If one arm does not lower, then it is a stroke.
Important! If even one of these signs appears, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is strictly forbidden to give a person any medications, as this can only worsen the situation!
Before the ambulance arrives, you need to lay the patient down, raising his head slightly. Provide him with a flow of air: open the window, unfasten his collar, free him from his belt and tie. If vomiting begins or the victim loses consciousness, carefully turn his head to the side and remove his tongue from the mouth so that it does not fall back.
Diagnosis of hyperthermia
An increase in a patient's body temperature after a stroke can occur for a number of other reasons. In the first place are purulent-inflammatory diseases (PIDs), which could be present in a person before the stroke. To eliminate errors in diagnosing the cause of hyperthermia, it is assessed according to many criteria, for example:
- maximum temperature values;
- cyclicality;
- effectiveness of antipyretic therapy.
In addition, the dynamics of temperature increases are also taken into account, depending on the presence or absence of foci of intravenous insufficiency or complications. For differential diagnosis, thermometry is carried out up to 8 times a day.
Consequences of a stroke
The transferred disease has consequences that, depending on the type and course of the pathology, can remain for many years, or may disappear after a certain period of time.
Manifestations of the disease are divided into several groups:
- speech disorders. A stroke affects different parts of the brain, so the patient may experience changes in articulation or speech production;
- motor disorders. An elderly person may have impaired mobility of the limbs or mobility of the face;
- cognitive disorders. They are characterized by absent-minded attention, decreased intelligence, memory loss;
- emotional-volitional disorders. A person with such manifestations after a stroke becomes “tearful”, as a result of which he can plunge into a prolonged depressive state.
These consequences arise only after the end of the acute period of pathology. In the first weeks after a stroke, the patient has symptoms such as speech impairment, frequent headaches, unstable blood pressure, and arrhythmia. In some cases, high body temperature, tremors, and convulsions are noted.
Complications after a stroke
After a stroke, fever often occurs due to the following complications:
- the damage occurred over a large area of the brain;
- swelling of brain tissue has developed;
- during a stroke, the thermoregulation center in the brain was damaged;
- complication after a stroke – pneumonia;
- an allergic reaction to medications developed.
In cases where the cause of the increase in temperature is its central genesis, doctors perform craniocerebral hypothermia. The brain is cooled through the outer covering of the head using special equipment. This method increases the brain's resistance to oxygen starvation, reduces the risk of developing cerebral edema, relieves existing edema, and reduces tissue temperature.
Brain cooling to reduce temperature is carried out using two methods - non-invasive and invasive. The invasive method involves administering a cooled saline solution intravenously. In this case, it is possible to regulate the temperature, but there are a number of side effects - bleeding, vascular thrombosis.
Treatment
The main goal of emergency physicians is to stabilize the victim’s condition and support the functioning of brain cells before hospitalization. For this purpose, basic therapy is carried out, which includes activities such as:
- control and/or correction of blood pressure;
- temperature control;
- relief of seizures;
- control of heart rate and glucose levels;
- maintaining water-salt balance.
Specific treatment in a hospital setting includes thrombolytic therapy, antiplatelet agents, mechanical thrombus extraction, and elimination of cerebral edema.
Thrombolytic therapy
Indications for such therapy: age from 18 to 80 years and no more than 4.5 hours from the onset of the stroke. The victim is administered an effective drug - tissue-type plasminogen activator, which dissolves blood clots.
Contraindications:
- Blood pressure is higher than 185/110;
- sensitivity to drugs of this type;
- erosion, gastrointestinal ulcer in the last 6 months;
- various brain pathologies;
- recent brain surgery;
- taking anticoagulants, etc.
Taking into account the extensive list of contraindications, thrombolytic therapy is performed in no more than 10% of patients.
Antiplatelet agents
These drugs are prescribed to patients on the second day after thrombolytic therapy. If it is not carried out, then on the first day. Aspirin is prescribed as a preventive measure against recurrent stroke, and its use significantly reduces mortality.
Mechanical thrombus extraction
This technique is the most effective. As a result of its use, blood supply to the brain is restored in the shortest possible period. The principle of mechanical thrombus extraction is the mechanical removal of blood clots using a special high-precision instrument. A stand is immersed in the artery and advanced to the site of blockage, after which it is removed with a catheter. All manipulations are carried out under radiographic control.
One of the main advantages of mechanical thrombus extraction is the ability to perform it within 6–8 hours after the onset of an ischemic stroke and a small number of contraindications. However, the use of this method is not possible in all clinics. This is due to the need to have in the arsenal of a medical institution the most modern equipment and a staff of vascular surgeons capable of performing this manipulation.
Elimination of cerebral edema
In some cases, stroke patients develop brain swelling. Its elimination is carried out with the help of diuretic drugs. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the patient's condition.
Temperature after stroke - causes and methods of treatment
When a person has suffered a serious attack, it is very important to control his body temperature. If the temperature after a stroke does not rise above 37.5 degrees, then serious measures should not be taken. However, it is important to monitor any changes in these indicators. If the temperature rises above 38.6 degrees, then the patient can be given Paracetamol.
It is difficult to calculate the dosage yourself. It is important not to harm the patient further. Experts recommend giving the patient approximately 325-1000 mg of the drug every 5-6 hours. However, the dose of the medicine should not exceed 4 g per day. It is necessary to evaluate not only the patient’s condition, but also his weight and age. If we are talking about an elderly person, then you should not experiment. It's better to call a doctor.
Specialists are taking the necessary measures to lower the temperature. Today there are two methods of such therapy.
Temperature during a stroke is an indicator of cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke. With an ischemic stroke, the temperature in most cases is slightly lowered; with a hemorrhagic stroke, the temperature rises.
An increase in body temperature is a protective reaction, which is the response of the body's immune system to various infections and injuries. With a hemorrhagic stroke, damage to blood vessels occurs, bleeding into the brain tissue occurs - the body reacts with an increase in temperature.
The larger the area of brain damage, the higher the temperature.
Upon admission to the neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital, the patient receives qualified care. A neurologist examines the patient, prescribes tests and treatment.
After a stroke, it is difficult to deal with high fever - antipyretics can aggravate the condition of a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke, and in the case of an ischemic stroke cause hemorrhagic transformation.
Hemorrhagic transformation is the saturation of the brain area with blood, which enters beyond the vessels into the focus of cerebral infarction. Fever and extensive brain damage often lead to the onset of coma in the patient.
Temperature during a stroke is a very important indicator of the patient’s condition. It is most often used to determine the degree of brain damage in a patient. Temperature readings up to 38 degrees are considered to be the maximum permissible.
Stroke studies have shown that the majority of stroke patients had a normal mean temperature upon admission to the clinic. In patients with extensive strokes, the temperature began to rise after a few hours (4-6) to 40 degrees.
In patients with moderate strokes, the temperature rose to 40 degrees 12 hours after the stroke. A mild stroke most often occurs without fever or with a slight rise in temperature.
After a stroke, fever often occurs due to the following complications:
- the damage occurred over a large area of the brain;
- swelling of brain tissue has developed;
- during a stroke, the thermoregulation center in the brain was damaged;
- complication after a stroke – pneumonia;
- an allergic reaction to medications developed.
In cases where the cause of the increase in temperature is its central genesis, doctors perform craniocerebral hypothermia. The brain is cooled through the outer covering of the head using special equipment.
This method increases the brain's resistance to oxygen starvation, reduces the risk of developing cerebral edema, relieves existing edema, and reduces tissue temperature. Brain cooling to reduce temperature is carried out using two methods - non-invasive and invasive.
For cooling, both heating pads with ice and special devices in the form of a helmet for the head are used.
The neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment, which allows you to diagnose a stroke and quickly determine the extent of brain damage.
The hospital team consists of professors and doctors of the highest category, qualified medical personnel. In the hospital, you can undergo studies using ENMG, VEEG, EMG, duplex scanning, neuroimaging and other modern techniques.
The neurological department accepts patients with strokes of all severity, the doctor develops a treatment program based on the patient’s condition.
Elderly people require a lot of attention - after prolonged physical inactivity, decompensation of the vestibular apparatus occurs. A rehabilitation specialist develops a program with an exact balance between the load, the severity of the stroke and the condition of the blood vessels and heart.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist at the Yusupov Hospital by phone.
- ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases)
- Yusupov Hospital
- Clinical neurology with the basics of medical and social expertise. St. Petersburg: Medline-Media LLC, 2006.
- Shirokov, E. A. Stroke, heart attack, sudden death. Theory of vascular accidents / E.A. Shirokov. – M.: Quorum, 2010. – 244 p.
- Vilensky, B.S. Stroke: prevention, diagnosis and treatment / B.S. Vilensky. – Moscow: Higher School, 1999. – 336 p.
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with a neurologist | Price from 3600 rubles |
| Therapeutic massage of 1 anatomical area (up to 15 minutes) | Price: 2000 rubles |
| Lymphatic drainage manual massage (up to 45 minutes) | Price: 5000 rubles |
| Correctional session with a speech therapist-defectologist | Price: 3100 rubles |
| Individual kinesiotherapy session 30 minutes | Price: 2500 rubles |
| Comprehensive rehabilitation program after stroke | Price from 10,830 rubles per day |
Complications that threaten a person's life can develop soon after the onset of a stroke.
Life-threatening complications include, among other things, the patient’s high temperature.
A fever after a stroke may be a sign of infection, such as pneumonia or a urinary tract infection.
Prevention of these complications is one of the main areas of initial stroke treatment.
The appearance of inflammatory processes and elevated body temperature in the acute phase of ischemic stroke is a well-known phenomenon.
Elevated body temperature may occur in cases of infection by exogenous microorganisms or an endogenous inflammatory response to the repair of brain tissue.
The human body's response to the invasion of inflammatory microorganisms, such as bacteria, triggers a process that activates leukocytes and prostaglandins, changing the thermoregulatory setting in the anterior hypothalamus of the brain.
Fever is most common during the first two days after a stroke. However, its true cause is not always easy to establish. Some research suggests that the timing of a fever may indicate its origin.
Normal fever due to stroke-related disease begins within 24 hours of stroke symptoms, while fever due to infection occurs at a later time.
This suggests that if early infection is excluded, early fever in stroke patients may indicate a neurological origin.
It has been suggested that in patients with small stroke infarct volumes, a marked increase in body temperature, C-reactive protein, or white blood cell levels should be taken as an indicator of infection.
When quantifying the inflammatory markers C-reactive protein, fibrinogen and leukocytes, it was found that ischemic stroke does not cause the typical acute phase reaction associated with high temperature in most patients.
However, in severe strokes, massive tissue necrosis can increase body temperature. Another cause of non-infectious fever may be the presence of blood in the brain.
As a result, studies have found that in most cases the identified cause of fever after a stroke is infection.
A study of patients hospitalized after ischemic stroke shows that 25% of patients have a body temperature greater than 38C within 24 hours of stroke onset.
32% had a temperature above 37.5C within 48 hours of stroke onset.
It has been suggested that probable causes of elevated temperature within 48 hours after an ischemic stroke include the presence of pneumococci, streptococci, E. coli, enterococci, parainfluenza virus, or influenza A virus in the patient's body.
The researchers conclude that most cases of fever (about 83%) can be explained by infectious or chemical aspiration pneumonia. Pneumonitis (localized tissue damage in the lungs) is often accompanied by early bacterial infection, even within the first 48 hours after a stroke.
How to overcome it?
Temperature management is considered an important component of stroke care.
It is recommended to treat body temperature above 37.5 C with a search for possible infection and antibiotic therapy:
- To reduce fever, Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) is recommended, with dosages adjusted for specific cases. Approximate dosages of Acetaminophen are 325-1000 mg every 4-6 hours up to 6 times a day (but not more than 4 g/day) at temperatures above 38.6C.
- If the body temperature is high, antipyretics (antipyretics) are recommended for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. The temperature threshold and treatment strategy in this case are selected individually.
Patient care
In most cases, mortality in the first days after the onset of a stroke is caused by impaired blood circulation in the brain. In the subsequent period, patients die from various complications caused by prolonged immobility:
- pneumonia;
- bedsores and/or their infection;
- thromboembolism;
- thrombophlebitis.
That is why patient care must be thorough and regular. It is important to turn the elderly person from one side to the other every 2-3 hours, and also to ensure that the bedding does not bunch up.
Daily care for a person after a stroke includes important elements of rehabilitation, which are recommended to begin immediately after his life is out of danger. Early recovery from this pathology has a beneficial effect on the patient’s condition and contributes to his speedy recovery.
Massage
Passive gymnastics and massage are mandatory activities aimed at preventing the development of bedsores. In addition, these procedures help prevent contracture (limited mobility in the joints) caused by the patient's immobility.
At the initial stage, the patient's muscles are stretched, joints are extended and flexed. Such manipulations should only be carried out by a specially trained person. The time and number of sessions are individual and determined by the attending physician.
Important! The massage must be performed by a specially trained person. The number and time of sessions is determined by the doctor.
If the elderly person is conscious, passive stimulation of the muscle frame and speech gymnastics are prescribed.
The right diet
Caring for an elderly person after an ischemic stroke includes a special diet containing foods rich in potassium. This trace element is found in large quantities in bananas, legumes, fish, seafood, spinach, dried fruits, kefir, and low-fat yogurt. It is recommended to include vegetable salads with vegetable or olive oil and light vegetable soups in the menu.
Coffee, strong tea (all varieties), and alcoholic beverages should be excluded from the diet.
In addition, you should limit your use of:
- red meat dishes (no more than 150 g per day);
- smoked products;
- spicy, salty dishes;
- baking.
Food must be boiled, stewed or baked.
Leisure after a stroke
The patient's time after an ischemic stroke should be devoted to improving mood and returning to an active life.
To improve motor skills and cognitive disorders, it is recommended:
- collect puzzles;
- draw, sew, knit;
- listen to the radio, read books, communicate with people.
Such hobbies promote recovery and significantly increase the chance of returning to a full life.
Doctors are unanimous that a nursing home after a stroke is an excellent opportunity to return to normal life as quickly as possible. The patient is surrounded by care, and qualified staff guarantees proper care, adequate nutrition and round-the-clock supervision.
Preventive actions
Prevention refers to a set of measures aimed at preventing the development of brain strokes, their relapses, and subsequent complications. Necessary:
- Conduct courses of treatment in a timely manner for existing chronic pathologies.
- If you experience frequent pain in the heart area, be sure to check with a cardiologist.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Eat properly.
- To refuse from bad habits
Stroke is one of the most dangerous diseases, often resulting in lifelong disability and even death. A timely, competent response to the first symptoms of the disease, an accurate assessment of the patient’s condition, as well as correctly prescribed treatment will facilitate recovery and improve the prognosis.
Acute cerebrovascular accident is an extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate treatment, especially if a fever occurs during a stroke. After a stroke, people often remain disabled, especially if assistance was provided untimely or unqualified. Currently, the development of new methods of treatment and recovery after stroke continues.
This indicates the high social significance of this problem for our country. Specialists pay no less attention to studying the causes of cerebrovascular accidents. The stroke itself can occur in different ways, and accordingly, the consequences for a person can be very diverse. It is worth noting that a stroke does not always immediately put a person to bed, and the lack of timely treatment makes its further course more difficult.
It is not recommended to use independent or traditional methods for treatment or subsequent recovery after a stroke - they can complement therapy, but only as an adjunct, and if prescribed by a doctor.