Diseases of the nervous system, incl. neuroinfections, brain cysts and arachnoiditis are the specialization of our clinic. We will clarify the reason for the formation of the cyst in your case, conduct an examination for neuroinfections and the necessary treatment of the brain cyst, etc. We will be happy to help you.
- Brain cyst is a consequence of the disease
- Do brain cysts grow?
- Symptoms
- Examination and diagnosis
- Brain cyst: treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
Brain cyst is a consequence of the disease
There are two main types of cysts:
1. An arachnoid cyst is a bubble of fluid accumulated between the adherent layers of the meninges. Such cysts remain after inflammation of the meninges , hemorrhage or injury. Arachnoid cyst of the brain is not a completely correct redundant expression, since the name “arachnoid” comes from the name of the arachnoid membrane of the brain (arachna - spider). If the fluid pressure in the arachnoid cyst is higher than the general intracranial pressure, it can compress the cerebral cortex and cause unpleasant symptoms.
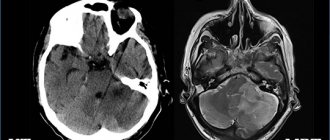
MRI scan of the brain. The brain is shown in grey, the fluid in black. 1 – normal slit-like fluid space between the temporal and parietal lobes of the brain. 2 – arachnoid cyst of the brain, an accumulation of fluid is visible in the substance of the brain.
2. Cerebral or intracerebral cyst (corpus callosum, subcortical nuclei, hemispheres, cerebellum, brain stem, etc.) is an accumulation of fluid at the site of a dead area of the brain. Thus, the fluid replaces the lost volume of brain matter. The cause of death should be clarified, and further destruction of the brain should be prevented. Common causes of cysts are cerebrovascular insufficiency, stroke, trauma, inflammation (encephalitis), and surgery in the cranial cavity.
MRI scan of the brain. 1 – normal fluid cavities (ventricles of the brain). 2 – Intracerebral fluid cyst at the site of a dead area of the brain.
An arachnoid cyst of the brain is always located on the surface of the brain, in the area of the membranes. Cerebral intracerebral cyst - in the thickness of the brain substance.
Arachnoid cyst - what is it?
An arachnoid cyst is a neoplasm limited to the arachnoid or collagen membrane. Cerebrospinal fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid, accumulates inside it. The cyst is located between the duplicating arachnoid membrane. It is precisely due to the location of its localization that this neoplasm received the appropriate name. In the place where the cyst is formed, the arachnoid membrane of the brain is thickened and has a duplication, that is, it is divided into 2 sheets. It is between them that cerebrospinal fluid can begin to accumulate.
Cysts are most often small in size, although when they are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, they can swell. Such bubbles put pressure on the cerebral cortex and cause corresponding symptoms.
The location of the cyst formation may vary. Its favorite localization is the cerebellopontine angle, the Sylvian fissure or the area above the sella turcica. As practice shows, about 4% of the population are carriers of such cysts, but most people do not know about their existence, since there are simply no symptoms. More often, arachnoid cysts are diagnosed in men. No explanation has been found for this, but scientists believe that there is a relationship between the frequency of traumatic brain injuries, which occur much less frequently in women. Arachnoid cysts account for about 1% of all brain tumors.
Do brain cysts grow?
A brain cyst is not a cancer. The size of the cyst can be easily monitored using MRI or CT scanning. If the size of the cyst has become larger over time, it means that some damaging factor continues to act on the brain. In this case, we look for and treat the causes of cysts.
The main reasons for the growth of arachnoid cysts in the brain:
- The fluid pressure in the cyst increases;
- Inflammation of the meninges continues (arachnoiditis, infection);
- Concussion in a patient with a previously formed cyst.
The main reasons for the growth of intracerebral cysts (and/or the appearance of new cysts):
- Cerebrovascular accidents continue, new foci of micro-strokes appear;
- The infectious or autoimmune process of destruction of brain matter continues (multiple sclerosis, multiple encephalomyelitis, neuroinfection).
The causes of the appearance or growth of brain cysts can usually be determined by the results of MRI, blood tests, and studies of blood flow through the vessels of the brain. Treatment is based on research results.
Causes
There are a number of factors that cause the formation of an arachnoid cyst of the left temporal lobe. As already mentioned, pathology can be primary or secondary. Depending on the type, the reasons that can trigger the appearance of the disease also change. It is worth considering in general what leads to the formation of a neoplasm.
Negative factors:
- Abnormal development of the fetus inside the womb.
- Pathological formation of vital body systems in the embryo.
- Deviations in the development of the nervous system in the fetus.
- Injuries sustained during birth. Difficult childbirth, hematoma in a newborn.
- Various bruises, concussions and injuries received at any age.
- Bleeding in the brain due to a stroke or rupture of a blood clot.
- Various inflammatory processes, for example, meningitis or arachnoiditis.
- Surgical interventions and their complications.
These factors increase the likelihood of a cerebrospinal fluid cyst in the left temporal lobe. The same reasons can be identified for those cases when the deviation is formed in the right region.
Localization must be determined, because it is important for further treatment. Doctors also find out the reasons why the disease appeared, because they may need to be eliminated.
Symptoms of a brain cyst
Symptoms are determined by the underlying disease that caused the cyst to appear. Therefore, they are diverse and nonspecific.
One or more of the following symptoms may occur:
- Headache;
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the head;
- Sensation of pulsation in the head;
- Noise in the ear with intact hearing;
- Hearing impairment (sensorineural hearing loss);
- Visual disturbances (double vision, spots before the eyes, etc.);
- Symptomatic epilepsy;
- Paresis (partial paralysis) of an arm and/or leg, permanent or transient;
- Episodes of loss of consciousness;
- Balance imbalance;
- Numbness of any part of the body, permanent or transient.
If the brain cyst is a trace of a long-term illness, there may be a complete absence of any symptoms.
Examination and diagnosis
MRI or CT will provide unambiguous information about the presence, size and location of the cyst. A study with intravenous contrast helps to distinguish a cyst from a tumor You can perform such a study at the Clinic of the Academy of Sciences .
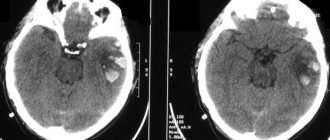
MRI scans of the brain. 1. Cyst after cerebral hemorrhage 2. Cerebellar cysts after ischemic stroke (blockage of cerebral arteries) 3. Cystic adhesive arachnoiditis
To avoid the enlargement and appearance of new cysts , we must clearly understand and treat the root cause of their occurrence. Therefore, we carefully examine you for circulatory disorders, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Doppler ultrasound of the head and neck vessels (USDG) will help detect narrowing of the vessels that supply the brain with arterial blood. Lack of blood supply can lead to focal death of the brain matter and the appearance of cysts.
Heart studies (ECG, Echo-CG) . The brain may not have enough blood supply due to rhythm disturbances or heart failure.
Blood test for clotting and cholesterol. An increase in cholesterol concentration in the blood and increased clotting are the main causes of blockage of brain vessels with subsequent formation of cysts. This problem is easily solved with the help of modern medications.
Blood pressure monitoring. Episodic increases in pressure are a common cause of strokes and post-stroke cysts. A monitor is a small device that is constantly with you for 1 day and records your blood pressure on a memory card. The data is then read by a computer and gives the doctor a complete picture of the pressure for the day.
blood tests for infections and autoimmune diseases of the nervous system in cases of suspected neuroinfections, arachnoiditis, and multiple sclerosis.
How to detect?
An examination by a neurologist allows one to suspect the presence of a tumor in the brain only if the cyst reaches a significant size. Only in this case does it give certain neurological symptoms.
Therefore, if the doctor suspects the presence of a cyst, he will refer the patient for the following studies:
- EEG.
- REG.
- Echo-EG.
- MRI or CT have the maximum information content and allow you to clarify the diagnosis. The use of MRI with contrast is especially important. This method makes it possible to distinguish a cyst from a brain tumor.
Brain cyst: treatment at the Echinacea Clinic
The first thing we will do is find out whether your cyst needs treatment and whether your poor health is associated with it. More than half of all cysts do not require treatment at all. Treatment is necessary if the cyst causes any symptoms, increases in size, or is at risk of developing new cysts. Treatment of a brain cyst is carried out regarding the underlying disease that caused its formation.
Resorption of adhesions of the meninges in arachnoid cysts - more details on the page of our website about arachnoiditis. For this purpose, we use two powerful absorbable drugs: Karipain (Karipazim) or Longidaza.
If we are talking about an infectious or autoimmune process , it is necessary to find and eliminate chronic foci of inflammation in the body. Treatment with antibiotics alone is practically useless. If arachnoiditis occurs, it means there is a gap in the immune defense, and first of all it is necessary to restore the body’s immune shield and reduce autoimmune aggression. All of our neurologists have specialized training in immunology. Based on the results of a blood test for immune status and infections, we will offer you a consistent and safe course of anti-infective and immunomodulatory treatment.
Treatment of cerebrovascular accidents requires the fulfillment of three conditions: reduction of coagulation, reduction of blood cholesterol concentration, normalization of blood pressure. Nootropics ( improve the supply of brain cells with oxygen and glucose) and Antioxidants (increase the resistance of brain cells to increased intracranial pressure) are used
In our clinic you can contact any neurologist. Be sure to take with you all the medical documents available to you, even those that, at first glance, are not related to the brain .