Erythrophobia – a condition in which a person is afraid that his face will turn red or become covered with red spots in public. Found in 0.2% of the population. Often seriously complicates communication with others and business partners. It is especially significant for patients whose profession involves publicity or active communication with people.
Specialists at the Leto clinic provide qualified treatment for erythrophobia using medicinal and non-medicinal techniques. You can make an appointment by phone 8(969)060-93-93.
Causes
The face is actively supplied with blood. A huge number of small vessels pass through the subcutaneous tissue and muscles. The muscles are located superficially and are fixed at one end directly to the skin. Because of these features, even a small rush of blood is enough to change complexion.
From time to time, noticeable redness of the face occurs in all people. Provoking factors are high or low ambient temperature, significant physical activity, strong emotions (excitement, embarrassment, shame). In patients with erythrophobia, the face turns red even with minor experiences or at rest.
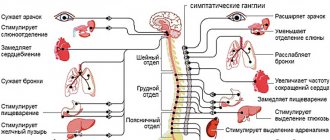
The reason for the vivid physiological reaction is the individual characteristics of autonomic regulation - increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system. Repeated, untimely or inappropriate episodes of facial flushing provoke anxiety and anticipation.
Emotions cause increased production of adrenaline, which stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. The patient blushes. Negative emotions are “fixed” and repeated, which causes an increase in episodes of hyperemia and generalization, that is, the spread of a pathological reaction to an increasing number of life situations.
Do not be shy
Many, speaking about this peculiarity of theirs, admit that I am almost always embarrassed, even because of the fleeting glance of a random passerby.
What can we say about situations when you have to speak in public, have an important conversation, look your boss in the eye... Some may blush because of someone else’s mistake, and then the person thinks that his reddened face “screams” about guilt or misconduct. And sometimes, to blush, it’s enough just to remember your natural inclination. But you can learn to live with this feature. And psychologists are unanimous: you just need to allow yourself to blush without feeling shame! — The fear of blushing manifests itself in a public place when a person is not alone, —
says
psychotherapist Ekaterina Averkova.
“
Moreover, this condition can develop from fear itself, that is, without any serious preconditions. A person is afraid to blush and blushes even more: because others will see it and can somehow evaluate and interpret it. Anxiety increases, and over time the situation can worsen: people fall into a stupor when an interlocutor approaches them, this can lead to anxiety disorders, fear of visiting public places, speaking, and depression.
Where does erythrophobia come from? As psychotherapists like to say, everything comes from childhood.
“Most likely, the child didn’t even notice that he was blushing,”
says Ekaterina Averkova.
“We all blush, but not everyone attaches such great importance to it.” But if someone told the child about this, laughed and gave some kind of social assessment, then next time he may be afraid of repeating the situation. The reaction is consolidated, this will be accompanied by an excessive feeling of shame, the fear of being a laughing stock, hurt or weak.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of erythrophobia is considered to be facial hyperemia or the appearance of spots on the face. In some cases, redness spreads to the neck and décolleté. Some patients feel hot during an attack. External changes cause significant mental suffering and negatively affect self-esteem and social adaptation.
Not knowing how to get rid of erythrophobia, patients avoid crowded places and choose specialties that do not involve communication with other people. Choosing a partner for them is associated with enormous difficulties, since first personal meetings are always accompanied by excitement, which causes severe facial hyperemia.
Any contacts can present difficulties : traveling on public transport, talking with a salesperson in a store, meeting friends in a cafe or on the street.
Restrictions in all areas of life cause the development of secondary mental disorders: depression, social phobia. Patients with erythrophobia may experience suicidal thoughts and intentions due to a feeling of hopelessness and hopelessness.
What does it represent?
Redness of the skin is inherent in absolutely every person. It just manifests itself differently.
Some people have a slightly noticeable slight blush as a reaction to some experience, spicy food or, say, physical activity. And for some, not only their cheeks turn red, but also their ears and neck.
And if an ordinary person does not attach any importance to this feature of the body, then erythrophobe is not able to control the horror that arises even at the thought that his skin will even slightly change its usual color.
And it doesn’t matter whether he “blushes” in front of one person or in front of a large audience. He is equally scared and ashamed.
According to statistics, mainly women are susceptible to this phobia. Most likely, this is due to the fact that they are more emotional and sensitive.
It’s rare to meet a man who is embarrassed by any kind of attention paid to him, isn’t it? But among the strong half of humanity there are also erythrophobes.
Despite the fact that this disorder does not pose a particular threat to a person’s physical health, it does affect his social life. And, as you understand, not for the better.
The fear of blushing in public can lead to the fact that the phobe simply begins to avoid communication. Therefore, he will choose a job where contacts are excluded, abandoning his own ambitions and prospects.
And his life will resemble a vicious circle. Since the worry is that if only the excitement does not make itself felt in the form of a blush (in medicine, blushing syndrome), the person still blushes, which is why he begins to worry even more, and so on.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is determined by a psychologist or psychotherapist and is based on information obtained during a survey and external examination. During the diagnostic process, it is important to distinguish erythrophobia from other conditions accompanied by similar symptoms: hot flashes during menopause, carcinoid syndrome, manifestation of rosacea, the body’s reaction to certain medications.
To exclude other causes of hyperemia, patients' faces are examined by an endocrinologist, dermatologist, oncologist and gynecologist. The scope of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic procedures is determined taking into account the identified violations.
Causes
Low self-esteem
The face is equipped with a large number of blood vessels. When a person is nervous, his blood pressure rises, which speeds up the blood circulation process.
In some people, these vessels are located too close to the surface of the skin, so that even a completely minor experience is noticeable.
So, individuals with low self-esteem may not accept their appearance, believing that they are already ugly, plus their cheeks are red, like a baby’s.
They are embarrassed by the fact that any emotion becomes known to everyone with whom they communicate. Sometimes you really want to hide sympathy or other feelings, but your face always betrays treacherously that there is no question of any indifference.
Psychological trauma
If a child in childhood was teased by his peers because he immediately blushes, this could provoke the development of complexes in him, which gradually led to erythrophobia.
It is not uncommon for anchoring to occur. This is a method in NLP (neurolinguistic programming), which consists of creating a conditioned reflex. That is, a certain reaction to a stimulus.
Specialists usually strive to consciously form a positive anchor in the client to help him cope with certain problems. But this process often occurs unconsciously without the participation of a psychotherapist.
For example, a person was once caught in a lie. And if in connection with this he experienced intense, toxic, that is, destructive shame, then subsequently, every time he tries to hide the truth, he will experience this feeling again. Because it became entrenched in his subconscious as a negative experience.
It may even get to the point where he worries every time he needs to communicate with someone. After all, what if you have to lie again?
Upbringing
If parents did something that constantly criticized their child and pointed out his shortcomings, this has an extremely negative effect on his psyche and self-esteem.
Plus, if they did it publicly, and also by punishing them, the development of any kind of phobias will be ensured.
Since such behavior forms an incorrect perception of one’s personality, as well as a lot of fears. The little man becomes anxious, unsure of himself, fearful and overly shy.
The child, experiencing not only resentment, but also shame, will try to hide his emotions so as not to show his vulnerability. For which he runs the full risk of getting hit on the head, being ridiculed, blushing, and being scared.
Erythrophobia also manifests itself if the baby did not receive support in fairly tense moments that he was unable to cope with on his own.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
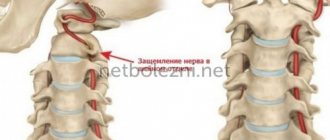
Sympathectomy
The operation lasts about 25 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia. Under endoscopic control, a special clip is applied to a small section of the sympathetic nerve to compress the nerve.
After surgery, the patient spends the night in the hospital; in addition, it is advisable to have another 2-3 days of rest and recovery, after which you can return to work. The first few days there may be pain at the puncture sites, as well as behind the sternum and shoulder blades. Serious physical activity in the first 10-12 days is undesirable.
It is important to note that the decision on the need for surgical intervention can only be made by a doctor. Only he can determine whether substellar sympathectomy will be the solution to the problem.
Possible complications
If the patient’s face has areas of skin with persistent redness, the skin is damaged, or thermoregulation is impaired, the operation may not give the desired results. In addition, surgery is effective only on the face area and will not help eliminate redness of the neck and décolleté.
In the operation of substellar sympathectomy
There are also some side effects, one of them is
compensatory hyperhidrosis
or increased body sweating. However, its manifestations are very individual: in some cases they are noticeable only during special diagnostics, in others - sweating of the back and abdomen noticeably increases.
Contraindications to sympathectomy
Contraindications to surgery include excessive sweating, excess weight, and bradycardia (slow pulse). The operation is also contraindicated for professional athletes due to the possible decrease in heart rate, which may interfere with their athletic achievements.
MORE MATERIALS ON THE TAG “SYMPATECTOMY”
What kind of disease is this
Fear of blushing is often confused with blushing syndrome. In contrast, erythrophobia is accompanied by fear.
It is
a reaction of the nervous system to stimuli.
A person can no longer independently control the processes in the body. He is afraid of making a bad impression on his interlocutor and is convinced that a red face repels others. The fear of turning purple in the presence of people is psychological in nature.
There are two types of erythrophobia:
1. Classic . The whole face turns red. 2. Geographical . Certain areas turn purple.
This phobia gives rise to self-doubt, and, as a result, a person experiences neuroses and stress, and tries to avoid crowds of people.
There are other unpleasant consequences of this pathology:
• lack of desire to move forward; • complete withdrawal from interaction with society; • development of depression; • fear of expressing one's opinion; • constant dissatisfaction with oneself.
In rare cases, the patient experiences a feeling of hopelessness and begins to think about suicide.
Diagnosis of blushing syndrome
You can suspect erythrophobia based on the signs that we have already discussed. However, only a psychologist can make an accurate diagnosis. The specialist studies the client’s complaints and life history, analyzes situations when redness appears. It is important to distinguish erythrophobia from similar fears, for example, from the fear of public speaking. In this case, redness is a symptom of another problem. It is important to determine the root cause as it will determine the treatment plan.
Causes of acrophobia
They are divided into two groups: physiological and psychological.
Physiological include all types of complications after inflammatory diseases and injuries that lead to disruption of brain function.
- Genetic predisposition and signs of mental disorders transmitted hereditarily.
- Mental overload of the body caused by frequent stress and emotional experiences.
- Diseases associated with disruption of the vestibular apparatus, which is responsible for the ability to maintain balance, connecting the functions of the cerebellum and vision.
- The emergence of a psychological crisis caused by regular alcohol poisoning.
Psychological reasons include: Improper upbringing of a child, with a lack of affection, tenderness, praise, constant underestimation of the child, his actions and deeds, which forms low self-esteem in the child.
Predisposition of children to increased levels of anxiety and suspiciousness, uncertainty or shyness.
The child's tendency to fantasize and great impressionability often lead to panic and screams after a dream or mental image of falling from a height.
Psychologists believe that any fear originates from stress or psychological trauma. The fear of heights has a slightly different reason. It occurs due to a violation of the self-preservation system, which is activated in situations that do not pose a danger.
For such people, any situation that tears him away from the surface of the floor or ground provokes a panic mood. Such a person is afraid to even stand on a chair or go out onto the balcony.
Panic arises not because of a fear of heights, but because of the imagination of upcoming pictures of falling, pain, death... In children, such manifestations are more often observed after a negative experience of falling or injury, fixed on a subconscious level.
Incidents that happened in childhood are often forgotten and as an adult, a person cannot find a connection between the present state and past events. Psychology describes many cases of crisis situations when patients with acrophobia show suicidal tendencies, explaining that when they experience a fear of heights, it attracts them, causes the heart to tremble and activates the brain.
At such moments, a person may experience a displacement of feelings of anxiety and panic into indifference to oneself, which paints pictures of falling from a height.
The literature describes an interesting experiment conducted with young children. They were invited to play on a high platform, divided into two halves, one of which was transparent and everything that was happening below was visible through it.
The children played calmly on one half and did not give in to any persuasion to move to the transparent surface. Scientists have concluded that the reasons for the fear of heights are inherent in a person at the subconscious level. After all, these children did not have a traumatic experience or fall.
They found that the feeling of fear is characteristic not only of humans, but also of animals with vision.
Symptoms of acrophobia
Experts suggest that almost 10% of the world's population suffers from panic disease, but not everyone seeks help. Men are susceptible to this disease much less frequently than women.
But the symptoms of the disease are described and knowing them, you can always identify this disease and get help. These include the following signs:
- Out of fear, a person loses control, cannot assess the current situation and perceives everything inadequately;
- It seems to him that the earth is disappearing from under his feet and a passionate desire appears to find support and cling to it;
- Dizziness and shortness of breath appear;
- Palpitations, tremors of arms and legs;
- The body becomes covered with red spots, the pupils dilate;
- If a person breaks into a sweat, then a decrease in body temperature follows (cold sweat);
- The condition may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- The mouth becomes dry or, on the contrary, there is severe sweating;
Watch a video on how to deal with acrophobia:
In each situation, symptoms are expressed differently, sometimes stronger, sometimes weaker. It depends:
- on the condition of the person himself (fatigue, severity of signs of anxiety),
- from the height that is in the human viewing area.
In a state of overwhelming horror, people most often press themselves to the ground, crawling away from the place of visibility to the side.
Signs and symptoms of erythrophobia
Some erythrophobes have a reddened entire face, other erythrophobes become covered in spots, while others have a red face, neck, chest, and arms. One way or another, a change in the color of the skin is noticeable, and the person himself feels awkward. Therefore, erythrophobes try to avoid such situations. This is the main symptom of erythrophobia.
If an awkward situation cannot be avoided, then redness is complemented by other somatic reactions:
- nausea,
- vomit,
- headache,
- dizziness,
- chills,
- tremor,
- tachycardia,
- arrhythmia,
- feeling of suffocation
- feeling of a lump in the throat,
- confused consciousness.
In this state, a person may faint or panic. He tries to run away, hide, avoid contact. At these moments, erythrophobe is capable of aggression and rudeness.
What happens if erythrophobia is not treated?
With regular manifestations of erythrophobia, individual patients often become victims of their psychological complexes, which leads to undesirable consequences, worsens the quality of social life and the ability to adapt to society:
- Both men and women can feel insecure and inferior, especially if they begin to compare themselves to other people.
- A person is on the verge of completely refusing to overcome life’s difficulties, the desire to move forward and self-development is lost.
- One’s own opinion is no longer expressed even when the patient is completely confident that he is right.
- Low-skilled professions are chosen that do not require constant contact with visiting people or colleagues. All extraneous social connections cease in their infancy.
- A person is in a state of constant dissatisfaction, as he does not have the opportunity to implement the accumulated knowledge and skills. The scope of application of skills is reduced only to professional interests.
- An offer to advance up the career ladder is perceived as a negative promise.
- New social phobias develop, which lead to a complete refusal of contact with other people. A person is constantly in a state of stress, he is diagnosed with autonomic neuroses and other severe somatic disorders.
- In particularly advanced situations, a feeling of doom arises and the patient begins to incline toward suicidal thoughts.
With the right approach, erythrophobia will recede, and all attacks that have happened to a person previously will be considered only as a life experience. Constant diligence and the ability to extinguish the psycho-emotional reactions of your own body help to achieve a sustainable withdrawal effect.
What is erythrophobia
The name is derived from two Greek words: ἐρυθρός, which translates as “red”, and φόβος, which translates as “fear”. Erythrophobia is an irrational, panicky fear of blushing in public. For example, during a public speech or during one-on-one communication, at the dinner table, etc. The more often this happened, the greater the fear, complexes, and uncertainty of the individual.
Interesting! Erythrophobia is sometimes called stress flushing. And in medicine, the redness itself is called hyperemia. In medicine, this is called blushing syndrome.
How to get rid of erythrophobia
Treatment of erythrophobia can be surgical and psychotherapeutic.
As we have already determined, erythrophobia has medical background. From this point of view, surgery helps in treating blushing syndrome: doctors use a special clip to compress the bundle of nerves responsible for the redness reaction. The operation is called sympathectomy. However, this cannot be called a panacea; it is important to work out the psychological foundations: shyness, increased anxiety, low self-esteem, etc.
On these forums (, ,) you can see real reviews about surgery for erythrophobia (blushing syndrome). This helped some people get rid of redness forever, while others encountered complications. There you will also find a discussion of the treatment of erythrophobia using tablets and read reviews and doctors’ opinions.
Interesting! Botox is sometimes used to treat erythrophobia (blushing syndrome).
To work through the psychological causes of nervous redness, you need to learn how to conduct autogenic training. An erythrophobe must realize that his anxiety and anticipation of redness only intensifies the reaction. A person can control this, because it is just a somatic reaction. It is important to accept this as a normal reaction of any organism and as its own peculiarity.
In addition to auto-training, psychological correction uses cognitive-behavioral psychotherapy, hypnosis, and group psychotherapy. In advanced cases, medication is indicated: antidepressants, tranquilizers, sedatives.
Note! To understand all the components of redness, you need to contact not only a psychologist, but also doctors (endocrinologist, therapist, dermatologist, gynecologist). Perhaps in your case there are no medical reasons and the redness is associated solely with psychological problems.