Parkinson's disease is a severe degenerative disease. It is diagnosed in 60–140 people out of 100 thousand patients. Mostly elderly people are affected. The onset of the disease is diagnosed at the age of 55–58 years. Refers to incurable pathologies. Men are more often affected. The juvenile form also occurs in twenty-year-old patients.
The pathology is chronic, accompanied by motor disorders. But drugs have been developed that can slow the progression of Parkinson’s disease, relieve symptoms, and improve the patient’s quality of life and care.
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease have been known for more than a millennium, but J. Parkinson described and systematized them at the beginning of the 19th century. Pathology was named after him. The biochemistry of destructive processes in the extrapyramidal system began to be studied in detail in the 50s. last century.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease was carried out using belladonna alkaloids, surgical therapy was developed - destruction of the basal ganglia was carried out. Currently, the gold standard of treatment is the use of Levodopa.
Definition of disease, cause of disease
Parkinson's disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease of the extrapyramidal motor system. Develops slowly. The main cause of the pathology is the destruction of neurons that produce dopamine in the substantia nigra and other parts of the brain.
The causes of Parkinson's disease have not been determined. Factors contributing to the development of the pathological process:
- Aging is accompanied by a decrease in the number of neurons and an increase in Lewy bodies.
- Heredity - 15% of patients have a family history of Parkinson's disease. But the gene responsible for its development has not been identified.
- Intoxication, living in disadvantaged areas - the influence of pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, FOS, heavy metal salts has been proven.
- The use of medications that have extrapyramidal disorders as a side effect.
Smoking is not a provoking factor. Parkinson's disease is diagnosed less often in patients with bad habits than in non-smokers. This is associated with the dopamine-stimulating effect of nicotine.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
There are true Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism syndrome - a complex of symptoms that develop after head injuries and severe intoxication.
Characteristic signs of the disease:
- Tremors in the arms and legs - in Parkinson's disease, they occur at rest. Frequency of up to 6 involuntary movements per second. Occurs at an early stage of the disease. Starts with one arm, then spreads to the other side of the body. A “yes-no” symptom may be observed. During sleep and at rest, the tremor stops, but intensifies during emotional shocks.
- Hypokinesia – decrease in motor activity. This symptom manifests itself as a change in handwriting, speech, and the disappearance of characteristic facial expressions.
- Muscle rigidity – increased muscle tone. The limb freezes in a bent or straightened state. A typical symptom is the “supplicant pose.”
- Postural instability - this symptom occurs in the later stages of the pathological process. Patients have difficulty starting and finishing movement. The body may begin to move faster than the legs. In this case, the center of gravity shifts and the patient falls.
In addition to the main diagnostic signs, Parkinson's disease is accompanied by autonomic and mental symptoms. They are individual. Both obesity and exhaustion, sweating, drooling, psychosis, and hallucinations are observed.
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a slowly progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system, manifested mainly by motor disorders in the form of hypokinesia, muscle rigidity, resting tremor and postural disorders, as well as autonomic, cognitive, affective and other disorders.
CLINICAL PICTURE
Motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease are manifested by the well-known neurological tetrad of symptoms (hypokinesia, rigidity, tremor and postural dysregulation).
SYMPTOMS
• The most obvious and easily identified symptom is shaking. Resting tremor is typical for parkinsonism, but other types of tremor are also possible. Postural and even intention tremor are very often detected. In typical cases, these types of tremor are inferior in severity to resting tremor. Sometimes postural tremor is not inferior in intensity to the three resting tremors or is even the only type of tremor; in such cases, diagnosing Parkinson's disease becomes extremely difficult (if other symptoms of parkinsonism have not yet appeared).
• Muscle rigidity is obvious in severe parkinsonism, but may be almost invisible in the initial stages, especially in the trembling form of the disease. It is very important to identify at least minimal asymmetry of tone in the limbs (asymmetry of symptoms is a characteristic feature of all stages of Parkinson’s disease).
• Hypokinesia is an obligate symptom of parkinsonism of any etiology. However, in the initial stages of Parkinson’s disease it may be invisible to the doctor, so simple but very demonstrative techniques are used to identify it (for example, clenching and unclenching your fingers as quickly as possible). First of all, hypokinesia manifests itself in some basic actions related to the patient’s self-care (brushing teeth, shaving in men, fastening small buttons, lacing shoes, etc.). Hypokinesia is understood not only as slowness of movements, but also as a decrease in their number, as well as in the speed, amplitude and degree of variety of motor acts. Individual “body language” and expressive style as a whole suffer, including speech, facial expressions, and motor flexibility.
• Postural disturbances often appear very early (for example, the characteristic asymmetry of arms extended forward), but begin to attract the attention of the doctor when they reach such a degree that they become maladaptive (stage III). In general, postural abnormalities are less specific to Parkinson's disease compared to other components of the parkinsonian tetrad.
TREATMENT
Treatment should be carried out exclusively by a neurologist. Self-medication is unacceptable.
The main directions of treatment for Parkinson's disease include the following measures: • Drug therapy (symptomatic and neuroprotective). • Non-drug treatment methods. • Medical and social rehabilitation. • Neurosurgical treatment. Regardless of the stage of the disease, the modern concept of treating Parkinson's disease involves two strategic approaches: the search for drugs that can slow down, delay or stop its progression (the so-called neuroprotection) and the creation of new, more effective drugs for symptomatic therapy. The latter approach is currently considered the main one.
NUTRITION FOR PARKINSON'S DISEASE...
Pathogenesis
The target organ for Parkinson's disease is the brain, the structures of the extrapyramidal system. With the development of the pathological process, the death of nerve cells in the substantia nigra occurs. Overt symptoms occur when 60% of neurons are lost.
In parallel, an increase in Lewy bodies is detected. The latter are also formed during natural aging, but in Parkinson's disease their number is several times higher.
The death of glial cells and an increase in phages are observed. Although Lewy bodies are not considered a characteristic symptom of the disease, as the disease progresses they are found in all structures of the brain. In later stages - and in the cerebral cortex.
The components of the extrapyramidal system are responsible for the automation of movements - walking, running, emotional reactions. Normally, this part of the brain sends impulses to peripheral motor nerve cells and ensures that the muscles are ready for movement. The ability to take the intended posture depends on the coordinated work of the extrapyramidal system.
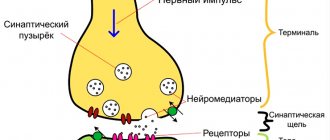
The identification of dopamine helped explain the functions of this part of the brain and explain the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. A characteristic sign of the disease is a sharp decrease in neurotransmitter in all parts of the brain. Symptoms of Parkinson's disease depend on which part of the extrapyramidal system is affected.
Secondary parkinsonism
The main clinical manifestations of parkinsonism are bradykinesia, muscle rigidity and postural tremor. Bradykinesia is a decrease in the number and speed of movements; patients become slow, their gesticulation gradually disappears, their facial expressions become poorer, and walking is no longer accompanied by accompanying hand movements. Muscle rigidity is a constant muscle tension that is first detected when attempting passive movements in a limb, and then becomes noticeable by constantly bending the limbs at the elbows and knees. Postural tremor is usually expressed in the hands and head, a fine tremor of which occurs at rest and disappears during motor acts. Over time, these symptoms lead to significant immobility of the patient and are accompanied by postural disorders (impaired coordination of movements, the ability to hold a certain position); characteristic personality changes occur, mnestic disturbances occur.
A distinctive feature of the clinic of secondary parkinsonism is the more rapid development of symptoms during the manifestation of the disease and their accelerated progression in the future. Symmetry of manifestations is typical, while in Parkinson's disease symptoms initially appear on one side and become bilateral only after some time. With the secondary nature of parkinsonism, its manifestations are combined with other symptoms of cerebral damage: pyramidal syndrome, cerebellar ataxia, early intellectual impairment, etc. In the patient's history, as a rule, there is an indication of the action of one or another etiofactor that preceded the appearance of parkinsonian syndrome (TBI, stroke, drug use). neuroleptics, encephalitis, etc.). In treatment, dopaminergic drugs are insignificantly effective, and elimination of the etiofactor sometimes contributes to a significant regression of parkinsonian manifestations.
Various etiological variants of parkinsonism are characterized by their own clinical features. Thus, parkinsonism after encephalitis is characterized by strong rigidity, the presence of pronounced vegetative manifestations and oculogyric crises; tremor is often absent. In posthypoxic parkinsonism, tremor, on the contrary, is pronounced. Vascular parkinsonism is accompanied by cognitive disorders and early formation of postural disorders; tremor is slightly expressed. Secondary parkinsonism in hydrocephalus is characterized by the dominance of the Hakim triad - dementia, ataxia, urinary incontinence; with corticobasal degeneration it is combined with cortical symptoms - apraxia, disorder of complex types of sensitivity, “alien” limb syndrome; in dementia with Lewy bodies, along with parkinsonism, cognitive impairment and mental disorders - psychosis, hallucinatory syndrome.
Classification and stages of disease development
Doctors distinguish 5 stages of Parkinson's disease. The basis is the progression of symptoms.
Classification according to Hoehn and Yahr:
- Stage zero – there are no signs of the disease.
- The first is that motor symptoms appear. One side of the body is affected.
- The second is a bilateral defeat. Symptoms intensify and new areas of the body are affected.
- Third, postural instability is diagnosed, but the patient can care for himself.
- Fourth, the symptoms of the movement disorder progress, the patient can only move short distances.
- The fifth stage of the pathological process - the patient is completely incapacitated. Symptoms of mental disorders and autonomic disorders intensify.
There are 3 main forms of the disease. The classification is based on the severity of one or another group of characteristics:
- Rigid-bradykinetic – increased muscle tone, contractures. The patient freezes in one position for a long time. For example, "petitioner" or "mannequin".
- Trembling-rigid form - the main symptom is trembling of the limbs, general stiffness of movements.
- Trembling - tremor of the limbs, tongue, jaw, tongue. Muscle tone is normal, the patient can control motor activity.
Neurorehabilitation for Prakinson's disease
The article was prepared by neurologist-parkinsonologist P.V. Smirnov.
Hello! Very little attention is paid to the rehabilitation of Parkinson's disease in our country. While the main manifestations of the disease, such as slowness of movements (hypokinesia), stiffness, impaired ability to maintain balance, and low patient motivation to move, lead to stiffness, musculoskeletal pain and worsening symptoms of Parkinsonism, thereby forming a vicious circle of the disease!
How can we break the vicious circle of Parkinson's disease and slow down the progression of the disease?
Of course, adequate antiparkinsonian therapy comes first.
Properly selected therapy creates conditions for maintaining motor activity at a normal level.
Worldwide research has demonstrated that regular physical activity leads to neuroplastic changes in the brain and can slow down the degenerative process in Parkinson's disease.
Recommendations for any patient should include:
- Regular walking
- Stretching exercises
- Flexion/extension and rotation in joints
- Balance and posture exercises
Also don't forget about:
- memory training (use mnemonic techniques, diary entries, etc.). — development of fine motor skills (drawing, embroidery, playing instruments).
All exercises are best done to rhythmic music!
In complex treatment to relieve increased muscle tone and pain in the extremities, massage, physiotherapy (high-intensity magnet, transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation, etc.), practicing exercises with an instructor with the obligatory continuation of exercises at home can help.
At home, you need to create devices to facilitate movement and reduce the fear of burning (handrails, rugs, etc.)
Rehabilitation for Parkinson's disease in St. Petersburg
On the basis of our Smart Clinic, it is possible to draw up and undergo an individual rehabilitation program for patients with Parkinson’s disease
The standard rehabilitation program includes:
Consultation with specialists
— Appointment (examination, consultation) with a parkinsonologist before and after the rehabilitation program
— Appointment (examination, consultation) with a rehabilitation specialist before and after the rehabilitation program
— Appointment (examination, consultation) with a psychotherapist
Physical rehabilitation
— Classes with an instructor in specialized physical therapy
- Massotherapy
Physiotherapy:
– High-intensity magnet (SIS – Super Inductive System)
— Electrical stimulation and ultrasound
— High intensity laser
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease
It is almost impossible to recognize Parkinson's disease at an early stage. Initial symptoms - trembling fingers, fatigue - are attributed to stress and fatigue. But early diagnosis improves the patient’s prognosis, increases the duration of socially active life, and reduces the rate of destruction of brain cells. As symptoms progress, one can even assume Parkinson's disease in absentia.
The initial diagnosis is established based on an analysis of the patient’s complaints and the results of a neurological examination. It is also recommended to obtain an opinion from 2 doctors, since in a quarter of cases the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is made incorrectly.
Physiotherapy techniques for Parkinson's disease
Manifestations of the disease decrease with the following procedures.
TES therapy. Involves the impact of pulsed current on certain areas of the brain. Provides regulation of nervous activity, restores normal functioning of the nervous system, helps relieve pain. The technique helps restore motor function and control over movements. It additionally relieves accompanying symptoms of Parkinson's disease: increases resistance to stress, restores normal sleep and a stable emotional state. Courses of TES therapy as part of a rehabilitation program slow down the development of the disease and improve the general condition of the patient.
Acupuncture. Helps stimulate the production of dopamine, improves the transmission of nerve impulses, relieves pain, and regulates the functioning of the nervous system. Restores normal emotional background, relieves neurological symptoms (spasms, tics, tremors). In Parkinson's disease, acupuncture is carried out in such a way as to provide a combination of inhibitory and stimulating effects and restore the normal level of neurotransmitters.
Electrosleep. A relaxing procedure in which low-frequency pulsed current stimulates the production of serotonin, has a calming effect, and provides deep relaxation. For patients with Parkinson's disease, electrosleep sessions provide pain relief, a decrease in neurological symptoms, and an increase in overall tone, activity, and performance. A course of such procedures helps to normalize the functioning of the central nervous system and launch restoration processes in brain cells.
Differential diagnosis
If there are 4 characteristic symptoms, an error in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease is unlikely. But in any case, other similar diseases should be excluded. The following are not typical for the pathology:
- early postural instability, dementia, impotence, urinary incontinence, difficulty swallowing and speaking;
- lack of any response to Levodopa;
- rapid progression of brain disorders;
- cerebellar damage;
- visual disturbances not caused by drugs.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is an incurable destructive disease. Therapy is aimed at eliminating symptoms, reducing the rate of patient degradation, improving quality and increasing the active period of life.
In the conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease, the following drugs are used:
- Drugs that increase the amount of dopamine in the brain - Levodopa. To stabilize the active substance in tissues, Tasmar (Tolcapone) is prescribed.
Tasmar is prescribed as part of combination therapy for Alzheimer's disease - in parallel with the main therapeutic agents. The drug reduces the activity of the enzyme that converts levodopa into one of the phenylalanine derivatives. Levodopa is an effective drug used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
- Dopamine receptor agonists - to stimulate this area, mimic the action of the neurotransmitter.
- MAO inhibitors – inhibit enzymes that break down dopamine. For example, such as Segan (Yumex, Selegiline, analog Deprenil, Eldepril).
One of the effective anti-Parkinsonian medications is the drug Segan (Yumex). Its main active substance, Seleginine, reduces the destruction of dopamine in the brain, and also enhances the effect of another substance - levodopa, which, when it enters neurons, is converted into dopamine. The use of selegiline improves brain function and also has a positive effect on mood and overall well-being.
- Dopamine reuptake inhibitors - increase the sensitivity of receptors to the neurotransmitter.
- Anticholinergics - to relieve symptoms of the disease such as hypersalivation, hyperhidrosis and excessive activity of the sebaceous glands.
If conservative treatment of Parkinson's disease is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated. Destructive operations and stimulation of brain areas are used.
Methods of surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease:
- Thalamotomy - indicated when the main symptom is tremor and only one side of the body is affected.
- Pallidotomy - such an intervention for Parkinson's disease is performed when the main symptom is movement disorders.
- Neurostimulation – if conservative treatment of Parkinson’s disease is ineffective or if there is intolerance to medications. This procedure involves implanting electrodes into brain structures. The patient can independently regulate the intensity of stimulation.
The intervention is permitted for Parkinson's disease with bilateral involvement. This operation is reversible and easily tolerated. The downside is its high cost.
Prognosis, prevention of Parkinson's disease
The prognosis is unfavorable. Without treatment, after 8 years the patient becomes completely dependent on relatives and cannot care for himself. When using Levodopa, the active life expectancy for Parkinson's disease is 15 years. But the speed of its development is individual.
Prevention is as follows:
- high-quality treatment of brain pathologies and head injuries;
- avoid stress;
- take vitamins and supplements such as phenylalanine (L-Phenylalanine);
- Observe safety precautions when working with pesticides and chemicals.
Parkinson's disease is an incurable pathology. But scientists are conducting research and developing new therapy methods. At the first signs of Parkinson's disease, you should consult a doctor and begin drug treatment.
Bibliography
- Vasiliev Yu.N. Parkinson's disease: pathogenetic significance of stress. Irkutsk, 2009, “Imprint”. – 128 p.
- Samii A., Nutt JG, Ransom BR Parkinson's disease (English) // The Lancet. – Elsevier, 2004. – Vol. 363. – P. 1783 – 1793. – PMID 15172778.
- Levin O.S., Fedorova N.V. Parkinson's disease. – M.: 2006. – 256 p.
- Sayutina S.B., Shprakh V.V. Parkinson's disease (in questions and answers). Irkutsk: RIO IGIUVA, 2010. – 124 p.
- Yakhno N.N.. General neurology: textbook. allowance / N. N. Yakhno, V. A. Parfenov. – 2nd ed., rev. and additional – M.: MIA, 2009. – 208 p.
- Zhukova N.G., Zhukova I.A., Gashilova F.F. Diagnostic criteria and treatment algorithms for Parkinson's disease: Textbook. – Tomsk: Publishing House “Printed Manufactory”, 2007. – 122 p.
- Fahn S. The medical treatment of Parkinson disease from James Parkinson to George Cotzias. Mov Disord. 2015; 30(1):4–18.
- Mak MK, Wong-Yu IS, Shen X, Chung CL.Long-term effects of exercise and physical therapy in people with Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021 Nov;13(11):689–703.
- https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parkinson's_Disease#Pathogenesis