Paresthesia is numbness of the limbs or other areas, which is accompanied by subjective symptoms such as burning or tingling. In many cases, the disease is curable - medications and physiotherapeutic procedures are used for therapy. If necessary, surgery may be prescribed.
Paresthesia: what is it?
This term refers to a sensitivity disorder in which a person feels a burning, tingling or “crawling” sensation. These are subjective sensations associated with objective reasons. As a rule, they are associated with irritation of a nerve that lies close to the surface of the skin. This may be the result of a shock, mechanical pressure, or due to a temporary interruption of the blood supply.
The main factors leading to paresthesia:
- prolonged compression, for example, of a limb;
- osteochondrosis of any part of the spine;
- tumors of different nature (benign, oncological);
- tourniquets that are applied to stop bleeding;
- nerve ending injuries;
- burns, exposure to high temperature (this may cause problems with the sensitivity of the tongue and lips);
- inflammation in the vascular tissues that supply nerve cells with blood;
- diabetes mellitus and other hormonal disorders;
- poisoning with chemical poisons, biological toxic substances;
- deficiency of certain B vitamins;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- intermittent claudication;
- atherosclerosis;
- incorrect position at night (during sleep);
- mechanical shocks.
Before treating limb paresthesia
It is very important, before starting to treat paresthesia of the extremities, to conduct a differential diagnosis and exclude the possibility of developing dangerous infections and malignant neoplasms that compress the nerve fiber. To diagnose a disease that causes paresthesia of the limbs as a clinical symptom of its course, the following examination methods are used:
- X-ray image of the spine (in case of paresthesia of the upper extremities, you need to take an image of the cervical and cervicothoracic region, in case of damage to the lower extremities - lumbar and lumbosacral);
- angiography and neuromyography - allow you to evaluate the conductivity of the nerve impulse and the condition of sensory axons;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels allows us to exclude atherosclerosis, narrowing of the lumen due to diabetes mellitus and the development of varicose veins;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues to exclude the risk of developing focal infections and tumors;
- MRI and CT if it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis.
You can start diagnosing by visiting a neurologist. In Moscow, this doctor conducts initial free consultations with patients in our manual therapy clinic. Make an appointment at a time convenient for your visit.
Types of paresthesia
There are 2 main forms of the disease – transient and chronic. In the first case, tingling, burning and other unpleasant sensations go away on their own, without the use of drugs or surgical intervention. For example, if a person has been in an uncomfortable position for a long time, it is enough to change position, perform an exercise, and the paresthesia will go away without additional treatment.
However, there are also chronic paresthesias. They are associated with damage to different parts of the nervous system. In turn, they are divided into several types:
- Primary – against the background of infection, for example, HIV, tumor or autoimmune.
- Secondary - against the background of alcoholism, lack of B vitamins, metabolic disorders, for example, in the case of diabetes.
Rarely, paresthesia manifests itself as numbness of the lips, tongue or chin. Moreover, similar phenomena occur due to dental intervention (removal of wisdom teeth).
Another type is acroparesthesia. These are severe pains in the arms or legs associated with Fabry disease or calcium deficiency, or disturbances in the functioning of peripheral nerves. The main symptoms are tingling, numbness, burning, and numbness in the extremities, especially the fingers.
WHY DO YOUR LIMBS GO NUMB?
Parasthesia - why and from what?
Does it ever happen that your hands suddenly go numb or your leg cramps? Perhaps you slept in an uncomfortable position, for example, curled up in the Sapsan St. Petersburg - Moscow, or sat for a long time, without moving, holding a small child in your arms and realizing that one awkward movement and he would wake up. The unpleasant feeling and feeling of helplessness at such moments is both painful and quite annoying. Many believe that the cause of temporary "loss" of a limb is an obstruction of blood flow to the leg or arm, which can cause, for example, tingling and inability to control that part of the body for a minute or several minutes. However, the causes of numbness in the limbs are much more complex, and in some cases may indicate serious health problems.
Paresthesia is a type of sensitivity disorder characterized by spontaneously occurring sensations of burning, tingling, crawling, and numbness.
WE SEPARATE TROUBLE FROM THREAT.
Numbness of the limbs can be divided into:
- Dangerous;
- Safe.
By safe numbness or passing paresthesia , osteopaths and neurologists mean numbness as a result of prolonged stay in one position, “tight” and tightened clothing, shoes or accessories (for example, the narrow top of expensive Italian boots, a tightly tightened strap from an elite wristwatch, etc. .). This type of numbness is not caused by internal diseases and is accompanied by unpleasant tingling sensations. But where do they come from?
As a result of prolonged compression (imagine that you were dozing with your hand under your head and woke up with a numb hand), the nerve pathways are pinched, the superficial nerves are mechanically irritated and temporarily do not send “messages” in full, the brain loses “connection” for a certain period "with a limb. The limb seems to be “sleeping,” and when we change the position of the body and the pressure disappears, it begins to wake up. This process is accompanied by a tingling sensation, as the nerves of the limbs resume communication with the brain, and as soon as normal communication is established and impulses are transmitted as usual, the tingling sensation disappears. Discomfort and painful sensations are an unpleasant, but very effective way, given to us by nature, with the help of which the body warns the brain that something is wrong. If one limb's connection to the brain is interrupted for too long, nerve damage can occur.
Now let’s look at “dangerous” numbness, which occurs regularly and on its own, regardless of external factors, body position, posture or compression. If you often or periodically feel numbness in your limbs (arms or legs) or in any other area of the body, this may indicate a variety of diseases. This type of numbness of the limbs is called chronic paresthesia. Chronic paresthesias often occur as symptoms of lesions in various parts of the nervous system. These may be primary disorders: infectious, tumor lesions of the nervous system, neurodegenerative or autoimmune processes and a number of others. Paresthesia can also occur with secondary lesions of the nervous system, developing as complications of existing diseases.
While the most common way to temporarily experience paresthesia is to sit for long periods of time with your arms or legs crossed, there are other forms of paresthesia that can have long-term effects or last only a few seconds. You can suffer from various neuropathies, for example, carpal tunnel syndrome, for years, but you can experience pain, unpleasant tingling and numbness when you hit your elbow, very intensely, but briefly. Moreover, a love of chili peppers can lead to paresthesia, as they can cause a tingling sensation in the mouth due to the pain receptor that responds to capsaicin. Paresthesia is also called numbness of the tongue, cheek, and chin due to the removal of a wisdom tooth.
WHAT CANNOT BE LEAVED WITHOUT ATTENTION.
Neuropathies (neuropathies) are lesions of one or more nerves, usually arising as a result of their damage, compression or intoxication, as well as disturbances in the nutrition of nerve tissue. Find out more on the website of the EVO Specialized Medical Center.
Peripheral neuropathy is damage outside the brain and spinal cord. Depending on which fibers (sensory, motor or receptor) are damaged, the symptoms are accompanied by a decrease in sensitivity (up to its complete absence) and activity of the muscular system, and in severe cases - limited mobility of the limb and disruption of the functioning of internal organs. The first alarm signal in this case is precisely parasthesia : a sensation of goosebumps, sudden awkwardness, numbness and tingling, involuntary muscle contractions (tics). In more serious cases, there is difficulty bending and straightening the joints.
Thus, if you did not just “rest” the leg or sit in another charming place, but began to notice a constantly recurring problem in the limbs, then you should not ignore the consultation of a neurologist and osteopath with further diagnosis and treatment. In our EVO clinics, we use complex treatment methods that are aimed at eliminating the root cause, reducing pain, restoring the functions of the damaged nerve and preventing relapse of the disease. The basis of our approach to neurological pathology is not only pharmacotherapy, but primarily osteopathic and manual therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, apitherapy, hiruotherapy, biopuncture, massage, exercise therapy, etc.
Accompanying illnesses
Paresthesia often develops against the background of such pathologies:
- sciatica;
- cervical spondylosis;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- transverse myelitis;
- restless legs syndrome (tingling and burning in the legs).
If complications occur, the disease can progress rapidly. Therefore, patients with these diseases should undergo periodic medical examination.
Hyperesthesia (increased tooth sensitivity) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of hyperesthesia is aimed at reducing the speed of fluid flow in the dentinal tubules. This can be achieved in the following ways:
- blockage of enamel micropores with the help of desensitizers - drugs that reduce tooth sensitivity;
- reducing the size of micropores using mineralizing agents, for example, gels with a high content of fluoride and calcium. These include gels ROCS Medical Minerals, GC Tooth Mousse;
- closing or narrowing of dentinal tubules using a laser [14];
- preparation and filling of teeth for carious lesions;
- surgery on the gum when it recedes as a result of periodontal disease;
- correction of the bite.
In 1935, dentist L. Grossman identified the main properties of an ideal remedy for combating hyperesthesia [12]. In his opinion, it should act quickly and be effective for a long time, not irritate the pulp, not provoke pain and not change the color of the teeth. There are quite a lot of such drugs now. Desensitizing agents (reducing tooth sensitivity) are produced in the form of gel, toothpaste, rinse, varnish, etc. Toothpastes are most often used.
For mild hyperesthesia , as a rule, applications of various solutions are sufficient.
The drug Remodent in the form of a 3% aqueous solution for applications is applied to areas of hyperesthesia for 15-20 minutes. For the course of treatment to be effective, it is necessary to make 8-28 such applications (one 2 times a week) until a positive result is achieved. Sometimes a 3% solution of remodent is used as a rinse (4 times a week). The full course includes about 40 procedures.
Strontium chloride is used in the form of a 25% aqueous solution and 75% paste. When rubbing the paste, stable compounds of strontium appear with the hard tissue of the tooth. This remedy is a good prevention of hyperesthesia after tooth preparation and removal of dental plaque.
To eliminate hyperesthesia, a 30% aqueous solution of zinc chloride is also used. After this, an application is carried out with a 10% solution of potassium ferrocyanide. It seals the tubules with the resulting sediment. The duration of the applications is one minute. The use of a paste containing alkalis is also indicated: sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, potassium, magnesium. It attracts dentinal fluid, which is contained in the micropores of the enamel, and reduces tooth sensitivity.
A modern treatment for hyperesthesia is bifluoride-12, a special colorless varnish containing fluoride, and fluocal, a dental gel containing sodium fluoride. They are carefully applied to the teeth with a brush or foam swab. Both products create a coating that saturates the enamel and dentin with fluoride ions, which leads to a decrease in sensitivity. Fluocal can also be used in the form of an application solution. Typically, a course of treatment with such applications includes only 2-3 procedures. Varnish is usually used as an auxiliary method that enhances the effect of the main drug [15].
Treatment of hyperesthesia with laser has been shown to be the preferred treatment method. It is aimed at narrowing the dentin tubules by combining the proteins of the dentin fluid, partially melting the hard tissues and relaxing the internal nerve receptors. Laser therapy has no side effects [15].
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, so it not only relieves symptoms, but also affects the course of the disease. Treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to treating the main cause of hyperesthesia, it is necessary to restore the mineral composition of enamel and dentin, and normalize the content of phosphorus and calcium in the body. For this purpose, calcium glycerophosphate, clamine or phytolon, as well as multivitamin preparations are prescribed. Taking phosphorus-calcium drugs throughout the course of treatment provides a good prognosis. Otherwise, restoration of normal sensitivity will take a long time.
To eliminate pain at the beginning of treatment, in addition to using toothpaste with phosphate, electrophoresis with a 2.5% solution of calcium glycerophosphate is required. The course of such physiotherapy is 10 sessions. In case of hyperesthesia against the background of impaired neurological status, the use of a galvanic collar according to Shcherbak is indicated (also at least 10 sessions).
Studies have shown that the effect of complex treatment of hyperesthesia occurs quickly and lasts for quite a long time. The content of phosphate and calcium in the dental tissues increases, the level of calcium and phosphate in the blood normalizes.
During the treatment of hyperesthesia of any degree it is necessary:
- select personal hygiene products;
- control bad habits (do not bite nails, pencils);
- adjust your diet (exclude soda, sticky sweets, consume vegetables, fruits and dairy products more often);
- wear a mouth guard at night (for bruxism) [14].
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of the disease, regardless of the type, include:
- numbness – weak and strong;
- tingling;
- burning sensation;
- the feeling that goosebumps are crawling all over the body.
Indirect signs are:
- pale skin;
- previously unexperienced hair loss;
- decrease in temperature (only in the affected area).
Often these symptoms occur in the feet, in the neck, especially on the side, on the hands, and in the head area. Normally, such sensations gradually disappear without treatment. But if they are repeated again and again and become pronounced and long-lasting, this clearly indicates the development of the disease. In such cases, you need to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
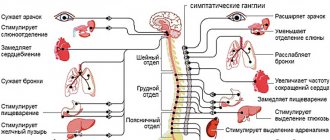
This symptom can occur as part of damage to the nervous and cardiovascular systems of various etiologies. Among the most well-known causes of numbness in the hands are osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, tunnel syndromes, Raynaud's syndrome, neuritis, diabetic, toxic and other neuropathies, neurocirculatory dystonia, as well as more rare conditions - multiple sclerosis, atherosclerosis of the vessels of the upper extremities, brain tumors and others diseases. In some cases, numbness and other unpleasant sensations can lead to a significant decrease in the quality of life, in others it can lead to complications such as necrotic changes in tissue (for example, in atherosclerosis), the addition of other symptoms in tumors of the nervous system - serve as a poor prognostic sign.
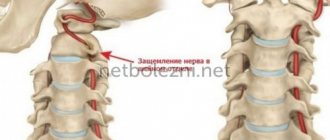
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a chronic degenerative disease that affects the intervertebral discs with their gradual destruction (formation of prolapse, hernial protrusions) and the appearance of a clinical picture of compression, stretching of the spinal roots, spinal cord, as well as reflex irritation of the muscles and ligaments. Numbness in this case is usually observed only on one side (can be provoked by an incorrect position during sleep), as well as other symptoms: headaches, neck muscle tension, radicular pain syndrome. The main diagnostic methods include visualization methods of the cervical spine - radiography, CT and MRI, which make it possible to identify characteristic changes (instability of the affected segment, decreased height of the intervertebral disc, hernias, damage to ligaments and muscles). Treatment is usually symptomatic and includes physical activity, exercise therapy, manual therapy, physiotherapy, painkillers and muscle relaxants during exacerbations; in severe cases, surgical treatment methods are used.
One of the most common tunnel syndromes is compression of the median nerve (carpal tunnel syndrome). The reasons for the development of this neuropathy include factors that lead to a narrowing of the carpal tunnel, in which the median nerve passes. Numbness and unpleasant sensations in the form of tingling and burning are localized in this case in the area of the thumb and index finger on the palm side. The main diagnostic methods include clinical (Tinel test) and electroneuromyography. Treatment can be conservative (using glucocorticosteroids, wearing an orthosis) or surgical - excision of the ligament limiting the canal.
Raynaud's syndrome is a condition that occurs as a result of dysregulation of vascular tone and is accompanied by spastic reactions of the small vessels of the hand in response to physical or emotional influence. The clinical picture is represented by attacks of vascular spasm in the area of 1-4 fingers with a characteristic change in the color of the skin (pallor, blueness and redness) with a feeling of numbness and burning. There is both primary Raynaud's syndrome and secondary - against the background of other diseases (scleroderma, SLE, dermatomyositis). Diagnosis is usually based on the characteristic clinical picture. For treatment, drugs are used - calcium antagonists, inhibitors of specific enzymes, prostaglandin analogues, vasodilators.
Late-stage diabetes mellitus can damage nerve fibers, leading to the development of both distal (lower limb) and proximal (upper limb) neuropathy. At the same time, sensitivity decreases, burning sensations, numbness and pain appear, especially at night, and in the future, damage to the motor nerves may occur with a decrease in strength in the limbs and deformation. Diagnosis in the later stages of the disease is usually not difficult and the diagnosis is usually already known to patients. In other cases, to make a diagnosis it is necessary to determine the glucose level, determine the function of internal organs that may be affected by diabetes (kidneys, retina, cardiovascular system), and also conduct electroneuromyography to confirm nerve damage and its severity.
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the upper extremities at the first stage is manifested by cramps, numbness, burning and coldness of the extremities against the background of exercise, however, as the disease progresses (an increase in the atherosclerotic plaque and an increasing restriction of blood flow through the affected vessel), the symptoms persist at rest, and later without appropriate treatment Necrosis and gangrene of the fingers may occur. In addition to clinical examination, diagnostics includes visualization of blood flow disorders (contrast angiography, ultrasound examination methods). Radical treatment is carried out only by surgical methods (plaque removal, vessel plastic surgery, bypass surgery).
To diagnose and treat numbness in the hands, at the first stage you need to consult a general practitioner, who will help identify additional symptoms and prescribe the necessary examination methods and consultation with other specialists.
Diagnosis of the disease
To determine the disease, the doctor conducts a visual examination, studies the patient’s history and complaints. For example, the condition of the skin, its color and temperature are checked. Laboratory diagnostic procedures are also carried out:
- blood analysis;
- toxicological analysis;
- MRI of the spine, head;
- Ultrasound of cervical vessels;
- X-ray of legs;
- diagnosis of the thyroid gland.