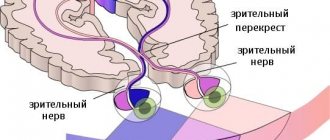
Ependymoma is a pressing problem in oncology, neurology and neurosurgery. The most complex organ of the human body is the brain, which consists of tissue called ependyma. All the internal cavities of the brain are filled with this tissue. Under the influence of various factors, ependyma can change - grow, transform into a tumor of ependymocytes (epithelial-like cells). The location of emendioma is usually the posterior cranial fossa. People of all ages are susceptible to the disease. Mostly the neoplasm is benign. It is more common in pediatric patients: 60% of patients with ependymoma are children under 5 years of age. Moreover, unlike adults, in children the tumor is in most cases malignant. Low-grade ependymoma can metastasize and treatment should begin immediately. Removal of the ependymoma is generally recommended.
Causes of ependymoma formation
What serves as the driving force for tumor development is not known exactly. Oncologists identify only factors that precede the appearance of a tumor of this type:
- heredity: if close relatives have a history of cancer, the person is at increased risk;
- harmful working conditions: regular exposure of the body to carcinogenic, chemical, nuclear substances contributes to the occurrence of various kinds of diseases, including central nervous system tumors;
- radioactive radiation;
- infection with oncogenic viruses such as herpes, papilloma, etc.;
- poor ecological environment;
- bad habits.
People with reduced immunity and survivors of cancer are also at risk of developing ependymoma.
Why do patients prefer to undergo ependymoma treatment abroad?
Over the past thirty years, survival rates for patients with tumors of the central nervous system, including ependymomas, have increased markedly. All this became possible thanks to modern diagnostic methods, modernization of neurosurgical equipment, improvement of neuroanesthesiology, and resuscitation.
The development of high-quality microsurgical technology, the availability of the latest generation of operating optics, the use of intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring when removing ependymoma, and good clinical results are fundamental arguments in favor of treating this disease abroad.
Scientists abroad are constantly looking for new therapeutic approaches to the treatment of ependymoma. Thus, in the course of research by American and Canadian specialists, a strategy was developed using specific biomolecular agents that help slow down the growth of the tumor structure and lead to its destruction.
During surgical interventions on the brain in foreign clinics, they try to use organ-preserving operations in order to preserve the important functional activity of the central nervous system structures. But tumors of this type have relapses, so Israeli and German doctors prescribe a course of radiotherapy after surgery. Among the techniques used, the following should be mentioned: linear accelerators, Cyber Knife, Gamma Knife. After the treatment course, patients are offered rehabilitation.
Despite the fact that treatment of brain tumors, including malignant ependymomas, abroad is expensive, most patients from different countries prefer to be treated in Israeli specialized centers. And one of the main reasons is that the cost of cancer treatment in Israel is much lower compared to Europe and the USA.
Classification of ependymomas
Today, doctors distinguish four types of tumors of this type according to their etiology and degree of malignancy:
- Mixopapillary type.
A benign neoplasm is located in the lower parts of the spinal cord. It occurs more in adult patients. The prognosis after treatment is favorable. - Sudappendymoma.
A benign formation is located inside the ventricles of the brain, grows slowly, and there are practically no symptoms. Relapses are rare. - Classic type ependymoma.
The most common type of pathology. Recurs frequently and progresses to the next stage. - Anaplastic type - ependymoblastoma.
This type is diagnosed in a quarter of all cases of ependymoma. The malignant tumor grows rapidly and metastasizes in all cases.
In most cases, removal of brain ependymoma is performed.
What is ependymoma and its types?
Ependymomas are fairly rare tumors that arise as a result of mutations in cellular structures (ependymocytes) of the brain or spinal cord. They are classified as primary tumors of the central nervous system (CNS). Formations of this kind can be benign or malignant. The main difference between ependymoma and other tumor-like growths in the brain is its ability to metastasize. As a result of this process, tumor cells circulate through the cerebrospinal fluid and can travel to other organs. Low-grade ependymomas account for approximately 25% of the total number of diseases of this type.
This type of tumor can be found in men and women of any age category. It is noteworthy that ependymoma is one of the most common intracranial pathologies of the brain in children. Neoplasia of this type mainly occurs in the lower posterior region of the head, in the region of the posterior cranial fossa.
Ependymoma is classified according to type as follows:
- classic or typical (II degree of malignancy);
- myxopapillary (benign, I degree of malignancy);
- anaplastic (malignant, III degree of malignancy);
- subependymoma (grade I malignancy);
- ependymoblastoma (malignant, very rare form).
Regardless of the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant), when it is detected, treatment must be started immediately, since further growth affects the vital functions of the brain and spinal cord.
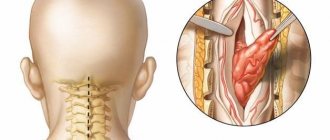
Spinal cord ependymoma
A tumor of this kind is localized in the terminal part of the spinal cord, in the spinal region. Ependymoma of the spinal cord
most often found in children of six years of age and very rarely in patients who have crossed the forty-year mark. As a rule, it is benign in nature; according to statistics, only 15% of such tumors are malignant. Ependymoma, located in the spinal cord area, is a rather rare phenomenon; it usually forms in the cranial fossa and spreads by metastases.
Ependymoma of the cervical spinal cord
Tumors in the cervical spinal cord manifest as sensory disturbances in the arms, or paralysis of the upper limbs with elements of atrophy. Treatment is usually surgical. Its results directly depend on the timely operation and changes in the spinal cord. It is possible to carry out conservative treatment using rehabilitation measures to restore physiological functions.
Based on their histological nature, ependymomas are distinguished: cellular, papillary, clear cell, tanycytic.
- Clear cell ependymoma grade II
Clear cell ependymoma consists of tumor cells with swollen transparent cytoplasm and a clearly defined cell membrane. The tumor is usually gray-pink in color with a dense consistency with multiple blood vessels.
Surgical treatment makes it possible to remove neoplasia and restore normal movement of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Ependymoma Grade II
Grade II ependymomas are slowly developing tumor-like growths from the walls of the ventricles or the spinal cord canal. They consist of ependymal cellular structures and are often diagnosed in childhood or young adulthood. This type of tumor-like formation is most often located in the lumbar or thoracolumbar parts of the spinal column; they belong to the II degree of malignancy.
- Anaplastic ependymoma Grade III
This type of ependymoma is a malignant tumor. Neoplasia grows rapidly, is characterized by an aggressive course and a tendency to metastasize.
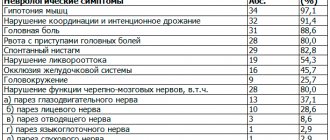
The complex of symptoms inherent in the disease
The following signs of pathology are distinguished:
- severe and chronic headaches;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- unsteadiness of walking;
- difficulty swallowing;
- impairment of auditory and visual functions;
- epilepsy attacks;
- mental retardation (in a child);
- increased intracranial pressure;
- irritability;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- impaired fine motor skills;
- decreased concentration.
If the tumor has involved nearby tissues, the following symptoms appear:
- sharp and severe back pain;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- urinary incontinence.
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the tumor.
Ependymoma
Ependymoma, treatment in German clinics.
Ependymomas are glial tumors that arise from the ependymal cells of the inner chambers of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
They make up about 5 to 10% of all gliomas. Ependymoma most often occurs in the posterior fossa in children and in the spinal cord in adulthood. The first peak of the disease is at the age of 5 years. The second peak occurs in adulthood: from 30 to 40 years. Ependymoma is the third most common brain tumor in children. Treatment of ependymoma in Germany from the world's leading specialists. According to the WHO classification, ependymoma subtypes are distinguished:
- Myxopapillary ependymoma (WHO grade I) is a benign tumor that occurs almost exclusively in adults in the lower part of the spinal cord and cauda equina.
- Subependymoma (WHO grade I) is a benign tumor, often accidentally discovered in the region of the ventricles of the brain.
- True ependymoma (WHO class II) is a slow-growing, localized tumor in the inner ventricles of the brain or spinal cord.
- Anaplastic ependymoma (WHO grade III) is a rapidly growing tumor, especially in children. Anaplastic ependymoma quickly grows into the surrounding brain tissue and causes an increase in intracranial pressure (formation of hydrocephalus).
Symptoms:
Symptoms of ependymoma directly depend on the location of the tumor in the central nervous system.
Nonspecific constitutional symptoms appear regardless of the location of the tumor. Such symptoms include headaches and back pain, dizziness, anorexia, nausea, weight loss, fatigue, decreased productivity, poor concentration, personality changes and developmental delays. The cause of these symptoms is usually gradually increasing pressure inside the skull and problems with the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid.
Specific signs of ependymoma can indicate the location of the tumor in the central nervous system. Ependymomas in the cerebellum, for example, cause problems with balance and gait, while tumors in the central regions of the brain can cause epileptic seizures. Ependymoma in the spinal cord can cause paralysis of the lower limbs.
Diagnostics:
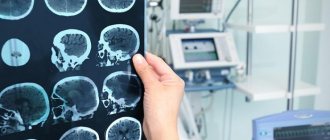
After a thorough history, physical and neurological examination, imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are used to detect ependymoma. Using these methods, the exact location and size of a tumor in the central nervous system can be determined. But in order to definitively establish a diagnosis, a sample of tumor tissue must be subjected to histological analysis. A tumor biopsy is done through minimally invasive surgery.
Therapy:
Treatment of children with ependymoma must be carried out in the pediatric neuro-oncology department. The department's highly qualified staff is familiar with the most advanced therapeutic procedures. Doctors work closely with each other and constantly improve treatment plans. Treatment of ependymoma of the brain and spinal cord in Germany.
Surgery is the first therapeutic step for both ependymomas in the head and tumors of the spinal canal. Some ependymomas cannot be completely removed due to their location. In particular, an ependymoma in the area of the cerebellopontine angle or a tumor in the 4th ventricle of the brain can only be partially removed due to the risk of damaging vital brain tissue.
WHO class I ependymoma: If the tumor has been completely removed, no further therapy is usually indicated. However, it is necessary to carry out follow-up inspections at certain intervals.
Ependymoma WHO class II-III: surgical treatment of visible tumor is not sufficient. Even if the tumor was completely removed during surgery, there is a high probability of local recurrence. Less commonly, there is a risk of recurrence to distant sites in the brain or spinal cord.
If the tumor cannot be completely removed, subsequent local radiotherapy is necessary, regardless of tumor location and histological subgroup. Radiation to the residual tumor and tumor bed is intended to help prevent recurrence in this area.
The question of the advisability of additional chemotherapy is open.
The prognosis for patients with ependymoma depends on the type, location, and spread of the tumor. In addition, the age and health of the patient play an important role.
German specialists always use intraoperative ultrasound technology and neuro-monitoring during brain or spinal cord surgery. These navigation aids provide minimally invasive access and intraoperative control. Preservation of vital cranial functions and intracranial nerves are critical when deciding on the extent of surgery.
Quality of life and maximum patient life expectancy are at the forefront for German neurosurgeons.
Regarding the choice of the best German clinic and neurosurgeon for the treatment of ependymoma, patients and their families can contact us for advice at any time. It is advisable to have the results of studies already conducted with you at the time of application. This will reduce the time it takes to draw up an official proposal for the treatment of ependymoma in a German clinic.
Diagnosis of the disease
In order to determine the history of the origin of the pathology, the stage of the disease, the size of the tumor, the neurologist prescribes:
- Computed tomography.
— Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Puncture of cerebrospinal fluid to confirm the diagnosis.
These methods allow you to examine the tumor as accurately as possible. After making a preliminary diagnosis, it is recommended to:
- angiography;
- stereotactic biopsy;
- ultrasonography;
- ventriculoscopy;
- electroencephalography.
MRI and CT are the most modern and effective methods for diagnosing tumors.
Treatment method for ependymoma
Today, the following methods of treating the disease are used:
- Operation
. Surgical removal of brain ependymoma is the main method of treating the pathology. If the formation is malignant, then even complete excision gives a survival rate of no more than five years. The most disappointing prognosis for epindymoblastoma. In our clinic, neurosurgical operations are performed by experienced doctors using new generation equipment and technology.
If the tumor is localized in the posterior cranial fossa, access to it is limited and complete excision is impossible. After surgery, radiation therapy is performed. If the patient is a child, radiation exposure is minimized or replaced with chemotherapy.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
. Used as an alternative to surgery to treat patients over 14 years of age. Irradiation of the tumor is performed using a CyberKnife. The radiosurgery method is effective for the treatment of myxopapillary tumor and subepindymoma. Impairment of neurological processes may persist after treatment.
- Radiation therapy
. The technique involves influencing the formation of radiological radiation. The main indication for use is localization of the tumor in a hard-to-reach place, and also as an addition to a set of measures after surgery. The advantage of the method is that the radiation is directed strictly to the affected tissues, without the risk of damaging healthy cells, unlike surgery.
You can make an appointment at our clinic using the contact number. Diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of the patient’s condition are carried out by qualified doctors.
Treatment
Neoplasms of the brain and spinal cord, regardless of the nature of the tumor, require immediate treatment, since as the tumor grows it can lead to serious disruptions in the functioning of this vital organ.
As a rule, effective treatment of oncology can be achieved by using various methods of cancer therapy in combination, where in addition to surgery, radiosurgery on CyberKnife, it is also possible to use various combinations of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. If the spinal cord tumor is small enough, treatment is carried out using the most innovative method of cancer treatment - CyberKnife radiosurgery.
Treatment using the CyberKnife system
Treatment of spinal cord ependymoma with the CyberKnife system
Preliminary diagnostics (CT and MRI studies) carried out at the stage of diagnosis and confirmation become the basis for treatment planning. Based on the images obtained, the required shape and location of the volume is determined, in which a zone of uniformly high dose of ionizing radiation will be formed - it will completely coincide with the contours of the tumor lesion indicated by the attending physician.
The finished 3D model indicating the zones (and the minimum/maximum radiation dose in them) is loaded into the CyberKnife software package to calculate the number and trajectory of thin rays of ionizing radiation that form a dose that is destructive to the tumor. After this, the patient can begin treatment of ependymoma with CyberKnife.
Radiosurgical treatment using CyberKnife does not require special patient preparation, including the administration of anesthesia. During the treatment session, the patient is conscious, and the robotic “arm”-manipulator of the complex sequentially takes the positions specified in the treatment plan, in each of which a separate thin beam of ionizing radiation is supplied. After completing the fraction (15-30 minutes), the patient can return to their usual daily routine. The number of fractions (and, accordingly, the cost of treatment) depends on many individual factors, therefore the duration, composition of therapy and the cost of treatment are determined for each patient by his attending physician.
The use of a high-precision robotic system makes it possible to remove the main focus of a pathological neoplasm using high doses of ionizing radiation, without resorting to traditional surgery, which can lead to serious consequences for the patient’s health in the postoperative period.
However, when the volume of the spinal cord tumor is large enough to require the use of CyberKnife, the main treatment for spinal cord ependymoma is surgery , which can be supplemented by a course of radiation therapy using a high-precision IMRT linear accelerator and chemotherapy treatment.
The traditional surgical treatment of spinal ependymoma has many limitations due to the location of the tumor and the volume of healthy tissue damaged during access, primarily the nervous system. Unfortunately, spinal ependymoma is most often diagnosed at the stage when the tumor exceeds the permissible size for radiosurgical treatment on CyberKnife. Given that surgery rarely removes the entire tumor, radiation therapy delivered using a high-precision linear accelerator (IMRT) is an effective alternative for curative treatment.
Radiation therapy
The principle of IMRT radiation therapy for this tumor largely corresponds to the principle of tumor radiosurgery using CyberKnife. Just like when using the CyberKnife system, the precision of radiation therapy is ensured by the controlled delivery of a high dose of ionizing radiation into the tumor volume. The spatial contours of the tumor and the required dose in it are determined by the radiation therapist and medical physicist. CT and MRI images obtained during preliminary diagnostics to confirm the diagnosis are loaded into a computer planning system. Next, with the participation of a radiologist, a three-dimensional model of the relative position of tumor and healthy tissues is simulated in the software package.
As a rule, special preparation of the patient (including anesthesia) is not required - the patient is conscious during the fraction (session) of treatment of ependymoma, and the moving part of the linear accelerator sequentially occupies the positions indicated in the treatment plan, in each of which radiation is administered required field. After completing the fraction (30-40 minutes), the patient can immediately return to his normal daily routine. The number of fractions depends on many individual factors, so the duration, composition of therapy and cost of treatment are determined for each patient by his attending physician.
Radiation treatment of tumors
For each zone specified in the virtual model, the values of the minimum and maximum doses that need to be administered during the treatment process are determined and entered into the planning system. Thus, the doctor sets a high dose within the boundaries of the tumor and the paths of its metastasis and a zero dose in the area where critical structures of the body are located (brain stem, salivary glands, lens, etc.). According to these data, the program determines the points and shapes of the fields, arranging them in such a way as to achieve the required distribution of doses delivered to the body at their intersections.
After approval of the plan, treatment begins: it is carried out on an outpatient basis, during the treatment session (fractions) the patient is comfortably positioned on the couch while the moving part of the linear accelerator occupies successive positions from which beams of the required shape are supplied. The configuration of each beam of the beam shape is formed by a multi-leaf collimator, controlled by the system according to a given plan; during treatment, all parameters are monitored by the responsible specialist.
The high dose, destructive for the tumor, will be composed of the volume of intersection of each of the individual radiation fields. In this case, healthy tissues receive a tolerable dose of radiation (does not affect biological tissues), and the most important structures of the body (such as the brain stem, aorta, salivary glands, etc.) are absolutely protected - a zero-exposure zone is set for them at the treatment planning stage , the so-called “cold zone”.