- What is brain cancer
- First manifestations and symptoms
- Possible treatment
- Stages of brain cancer
- Prognosis for brain cancer
Malignant brain tumors (BM) are not the most common type of cancer. But such diseases are more life-threatening for patients, as they directly affect a vital organ. Brain cancer is confidently associated in people’s minds with an incurable disease, however, methods for diagnosing and treating malignant neoplasms of this localization have rapidly developed over the last decade, which makes it possible to successfully cope with such a disease.
What is brain cancer?
A malignant tumor or cancer is a disease that begins with a mutation. If a cell begins to grow uncontrollably, a benign or malignant neoplasm occurs in the body. A tumor made from malignant cells is especially dangerous: its components lose the properties of their “native” tissue, multiply non-stop and spread metastases (mutant cells) throughout the body.
There are many types of malignant tumors of the brain, but they can be divided into two groups:
- primary, which initially develop in the brain (from cells of the medulla, meninges, pituitary gland, cranial nerves, embryonic tissue in children, etc.);
- secondary or metastatic, which are brought into the brain from the outside (from a tumor in the lung, breast, etc.).
Breast cancer occurs more often in men than in women. This disease is diagnosed more often in children than in adults. Paying attention to the early signs of brain cancer can save lives and keep you healthy.
Symptoms of brain tumors at different stages
The stages of oncology are not only stages of disease progression, but also stages of change in a person’s overall health. It is very important to recognize the symptoms of brain tumors in a timely manner in order to go for examination.
At first, the disease is quite difficult to recognize. This is due to the slow growth of cells and as yet unexpressed changes that occur in the brain.
Therefore, usually symptoms are either completely absent, or rarely a person may complain of the following:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- headache.
This happens to everyone in life, so few people will pay attention to such deviations and begin to “sound the alarm.”
At the second stage, the “bells” may become more obvious, although many do not pay attention to them.
In addition to the symptoms described above, the following also appear:
- vision suddenly deteriorates;
- convulsions or some kind of epileptic seizures may make themselves felt;
- the feeling of general malaise increases;
- vomiting and nausea are often a concern, which is caused by an increase in pressure inside the skull.
During the oncological process of the third stage, the symptoms are pronounced, but sometimes it is difficult to attribute them to any specific disease, because there are many different nuances.
The patient may complain of:
- Constant headaches that are only temporarily relieved by taking painkillers.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- “Mid flies run before your eyes.”
- It is increasingly difficult for a person to do his usual work without fatigue.
- The temperature rises.
It is not uncommon that at the third stage, lymph nodes are involved in the process and distant metastases appear. And if so, then a person may have pain in different organs, and various types of discomfort may also be felt in them. There were cases when a brain tumor was confused with severe poisoning, since everything pointed to problems with the stomach or intestines, and nausea, vomiting and weakness only complemented this picture.
At the fourth stage, the symptoms are still the same as described above, but sometimes their number increases and they become more obvious:
- Vision deteriorates greatly, sometimes a person goes blind;
- people suffer from vomiting, which does not bring relief;
- in some cases, paralysis is possible;
- a person may have speech impairment or completely lose the ability to speak coherently.
At this stage, treatment of brain cancer abroad is carried out comprehensively and begins immediately after the problem is detected.
First manifestations and symptoms
The first signs of breast cancer are not highly specific, but their appearance requires an unscheduled consultation with a doctor. Among these symptoms:
- Headache. This malaise is a typical cerebral sign of a progressive tumor.
- Movement disorders. The arm begins to bend poorly, the leg ceases to obey, and hypertonicity of some muscles appears.
- Nausea and vomiting. This general cerebral sign of brain cancer can appear outside of meals, including on an empty stomach. Sometimes a wave of uncontrollable gushing vomiting comes without preliminary nausea, suddenly and reflexively.
- Dizziness. The main reason for this symptom is increased intracranial pressure. The discomfort is complemented by tinnitus and hearing impairment.
- Mental signs. Patients note a feeling of stupefaction, attention weakens, and memory and perception are dulled. There may be a decrease in criticality, deterioration in associative thinking, lethargy and indifference.
The way brain cancer manifests itself also depends on the location of the tumor. Before signs of increased intracranial pressure appear, the patient often experiences an epileptic syndrome. Convulsive tonic-clonic seizures manifest themselves in brain cancer of different locations, but most often such symptoms are typical for damage to the frontal lobes.
Causes of the disease
A brain tumor is a difficult to treat disease that can lead to the death of the patient. It can arise for various reasons. If some of them are present in a person’s life, then he can be classified as a risk group.
Brain cancer appears due to the following factors:
- Hereditary gene pathologies. Based on this factor, the disease occurs in 5% of cases. The diseases include: Gorlin syndrome, tuberculous sclerosis, Li-Fraumeni syndrome, APC gene disorder and Bourneville disease.
- Weak immunity. May occur after organ transplant surgery or in AIDS-infected patients.
- Frequent nervous breakdowns, stress, depression and negative influence from others.
- Race and gender. Women and people with white skin are more likely to suffer from this condition.
- Bad ecology.
- Foods eaten with GMOs.
- Long-term exposure to radiation or chemicals on the human body.
- Patient's age. As you age, the likelihood of brain cancer increases and it is more difficult to cure. The tumor also occurs more often in children.
- Secondary tumor. Acquired as a result of metastasis to the skull area.
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs).
Possible treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the type of tumor, its location and size. Doctors analyze the stage of the disease, the patient’s condition and the presence/absence of metastases, conduct tests and diagnostic procedures.
The optimal treatment option is complete removal of cancer cells. Advances in neurosurgery make it possible to perform low-traumatic and highly effective interventions on the brain. But the problem is that removing cancer tissue can be very difficult. GM neoplasms are prone to diffuse growth, they spread to nearby structures and tissues. For imaging, doctors use modern optical medical equipment and contrast agents.
Treatment may also include:
- radiation therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- brachytherapy;
- stereotactic radiosurgery.
Patients are required to be prescribed medications that can reduce symptoms of brain cancer and support the body. Inoperable cancer requires palliative supportive treatment.
Treatment after surgery
After surgical treatment for malignant neoplasms, radiation and chemotherapy are performed. They help reduce the risk of relapse and increase the patient's life expectancy.
After some time, the malignant tumor may reappear in the brain. In many patients, repeat surgery may be performed to remove it. Repeat surgery is generally less successful. However, many patients after such operations can live for several more years, while the lack of treatment would lead to death within a few weeks.
For treatment of malignant brain tumors, contact the NACFF clinic. Call or request a call back to get a consultation with an oncologist or neurosurgeon.
Send documents by email The possibility of treatment will be considered by the chief physician of the clinic Anton Aleksandrovich Ivanov, oncologist-surgeon, kmn
Stages
Doctors distinguish 4 main degrees of brain cancer:
- The neoplasm is small in size, does not affect or compress nearby structures, and does not metastasize.
- The tumor noticeably increases in volume, can disrupt the activity of nearby healthy areas, and also germinate into them; there are no metastases.
- The neoplasm is moderately aggressive, often inoperable, and can produce single metastases.
- The neoplasm reaches a significant size, affects other parts of the organ and gives distant metastases.
The rate of tumor progression depends on the type of cancer. Sometimes cancer develops very slowly, while other tumors are extremely aggressive.
Symptoms
Doctors divide the symptoms of a brain tumor into two types: focal and cerebral. The former depend on the location, and the latter occur in all cases of cancer.
Among the focal symptoms:
- impaired sensitivity or mobility of the limbs;
- sudden change in the patient’s character (temper, calmness, indifference, apathy, irritability, frivolity and various mental disorders);
- problems with urination (involuntary or difficult).
Among the symptoms of malignant brain tumors of all types, the following can be observed:
- Dizziness, imbalance, changes in gait, loss of orientation in space. Dizziness can occur even in a horizontal position.
- Headache. As a rule, they occur in the mornings and evenings and have a dull, bursting character, aggravated by coughing and sneezing. And taking antispasmodics does not give any results.
- Insomnia or constant fatigue.
- Facial distortion (tilt of the mouth, eye or eyelid). Occurs due to compression of the nerves.
- Nausea and vomiting. It can occur uncontrollably, not always after eating, and without taking the proper medications, leading to severe dehydration.
- Deterioration, clouding or complete loss (in the later stages) of vision, “spots” in the eyes.
- The appearance of hearing problems.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Sudden and causeless weight loss.
- Increased body temperature. This happens because cancer cells attack the immune system.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Sudden changes in blood pressure.
- Serious symptoms include breathing, taste, smell and swallowing problems.
- Sound, olfactory, auditory and visual hallucinations, impaired color perception.
- Brief paralysis.
- Sudden surges in intracranial pressure.
Often patients attribute some of the listed symptoms to fatigue that occurs during long work and constant stress. Therefore, a patient often comes for help when stage 1 of a brain tumor has already passed. People prefer to be treated at home and on their own. If they experience pain, they take painkillers, if they have vision problems, they buy lenses, and to eliminate memory problems and hallucinations, it is easier for them to drink sedative herbs. Meanwhile, the disease progresses and the patient loses precious time fighting it. If a brain tumor is not detected and treated in time, the patient will not have long to live with it.
If you have the slightest suspicion or doubt, you should visit a therapist who will prescribe various necessary tests. If it is not possible to visit a specialist, then it is enough to do a biochemical blood test. And if any deviations are detected, you need to undergo a more thorough examination.
Prognosis for brain cancer
If a tumor is detected at an early stage of development, after which the correct complex treatment (surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy) is selected, more than 60% of patients can be saved. Late stages of brain cancer or inoperable tumors allow only 30% of patients to survive more than 5 years. However, some types of tumors are more aggressive - glioblastoma reduces the chance of five-year survival to 5%, but some patients can live with the disease for years. Therefore, it is simply unrealistic to accurately predict how long a patient will live after diagnosis. Even in case of successful treatment, a person after brain cancer remains at risk, because the tumor can recur.
How long do people live with this diagnosis?
On average, life expectancy is up to 2 years. If an advanced pathology is detected (stage 4 brain cancer), there is almost no chance of healing. But there are cases when, after surgery, radiation, chemotherapy with Temodal, the patient turned to experimental treatment methods based on biogenic NK-cell preparations, LAK therapy and lived for quite a long time. Today the record belongs to a 7-year-old boy who, while undergoing this treatment, lived 4.5 years of a full life.
Why is it worth coming to Germany for brain cancer treatment?
In addition to the general reasons and advantages of treatment in Germany, which we described in this section of the site, in Germany doctors never refuse to treat patients who have already come to their clinic for treatment. If the doctors agreed to accept you for treatment, then they will not send anyone home to die, but will fight to the end. When making decisions about the need to use a particular technique, German doctors proceed from the patient’s condition and the appropriateness of treatment, but they never refuse further treatment simply because of the patient’s age, as is often the case in other countries. If it becomes obvious that it is no longer possible to stop the progression of the disease, the patient is offered a well-thought-out palliative program to alleviate suffering and relieve pain as much as possible.
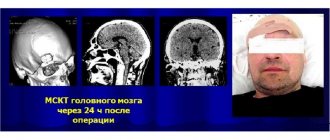
Diagnostics
Symptoms of the disease vary, and a patient with a larger tumor may experience less severe symptoms than a patient with a small tumor. The first thing the patient should do is visit a local physician, who will prescribe further tests.
An ophthalmologist can identify the disease by the condition of the eyeball.
When a patient consults a doctor with symptoms of the disease, he is prescribed:
- neurological examination;
- positive emission tomography;
- CT;
- MRI;
- angiography and other radioisotope techniques;
- magnetoencephalography;
- surgical intervention;
- stereotactic biopsy;
- venticuloscopy;
- Lumbar puncture.
Causes of brain cancer
Only after carrying out all the necessary studies can the doctor draw conclusions about the patient’s health status, determine the stages and possibilities of treatment.
Types of brain oncology
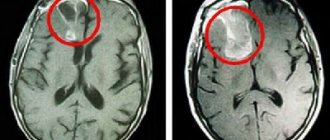
One of the main criteria for the classification of malignant neoplasms is the cellular and tissue composition, that is, the cytological and histological structure of the tumor. There are many types of brain cancer, the main ones are:
- neuroepithelial ─ formed from cerebral tissue (glioblastoma, astrocytoma, ependymoma, neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma);
- neoplasms of the meninges (anaplastic meningioma, hemangiopericytoma, chondrosarcoma);
- choroid plexus tumors (choroid carcinoma);
- malignant formations of the pineal gland - pineal gland (pineoblastoma);
- neoplasms of the pituitary gland (adenocaricinoma).
There are many classifications based on tumor histology. Most specialists use the system developed by WHO experts.
What is cancer and why does it occur? October 30, 20202811 49
Treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain
Removing an astrocytoma is the most rational solution that can increase the patient’s chance of survival. But such removal is possible if the degree of tumor development allows such implantation without causing harm to the brain. If the degree of tumor growth is too significant, then the tumor is treated with radiation and radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
Treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain in modern medicine is based on innovative techniques that make it possible to accurately determine the location and carry out the removal process without causing injury to surrounding healthy tissue. Depending on the degree of tumor development, the patient is injected with a certain amount of contrast agent before surgery; it accumulates in the area of the tumor, which makes it possible to clearly determine the boundaries.
The removal procedure is carried out on the basis of 3D visual diagnostics, which provokes extreme precision of the actions performed. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, but if the formation is located near very important centers, then the patient is certainly left conscious. This allows you to monitor your general condition at the time of surgery.
Treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain today is based on endoscopic surgery. That is, the procedure is carried out through the use of special equipment, which is inserted through small holes in the skull. It is this effect that is considered minimally invasive. But it can be used if the astrocytoma stage is 1-2. At the third stage, the use of this technique is often impossible. In such a situation, an open operation is performed, which involves craniotomy. The procedure lasts at least six hours.