To reduce the risk to the patient's health during the use of this group of psychotropic drugs, a new generation of antipsychotics or atypical antipsychotics, which have a milder effect on the human body, have been developed.
What are neuroleptics
Neuroleptics are psychotropic drugs, the main function of which is to relieve a psychotic disorder, in particular, its productive symptoms. These include delusions, hallucinations, pseudohallucinations, mania, anxiety, aggressiveness, behavioral and thinking disorders.
That is why antipsychotics are prescribed for psychosis and other disorders with behavioral disorders, excitability and aggressiveness:
- schizophrenia;
- bipolar disorder;
- mania;
- phobias;
- affects;
- hysteria;
- severe forms of insomnia;
- senile dementia;
- autism;
- obsessive-compulsive neurosis.
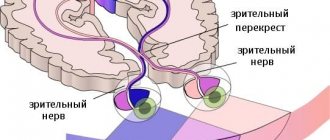
The mechanism of action of antipsychotics is based on blocking D2 receptors of the neurotransmitter dopamine, as well as reducing its transmission in various brain systems.
Antipsychotic, that is, the main effect of these drugs is associated with inhibition of dopamine transmission in the mesolimbic pathway. Thanks to this, positive symptoms are eliminated. But the effect is achieved only with blockade of 65% of the neurotransmitter.
Other effects include:
- hypnotic;
- sedative;
- anti-anxiety;
- antiemetic;
- hypothermic;
- hypotensive;
- stabilizes behavior.
The world first learned about antipsychotics in 1950 with the synthesis of aminazine. Previously, henbane, opiates, bromides, and antihistamines were used to treat psychosis.
Mechanism of action of medications
When using appropriate medications, nerve impulses in the mesocortical and limbic systems of the brain are blocked. The drugs help eliminate anxiety. They help relieve aggression.
Neuroleptics are used for various neurological and mental disorders. The drugs are effective for schizophrenia, senile dementia, mental retardation. In the treatment of various neurological diseases, antipsychotics are used in the form of injection solutions, droppers, and tablets. They are also prescribed for severe insomnia and excessive psychomotor agitation.
Side effects
All the negativity associated with typical antipsychotics and the need to eliminate atypical drugs in this group is caused by their adverse reactions.
By inactivating dopamine transmission in the mesolimbic pathways, they, at the same time, act similarly in the mesocortical, nigrostriatal and tuberoinfundibular pathways.
Being active in the nigrostriatal pathway, neuroleptics cause such complications as neuroleptic extrapyramidal disorders - the most typical for this group of drugs. They manifest themselves as parkinsonism with impaired motor activity in the form of slow movements, muscle stiffness, tremor, and drooling.
Another manifestation is acute dystonia, accompanied by involuntary spastic movements, as well as akathisia - the desire for constant movement to reduce internal discomfort and anxiety.
Neuroleptic extrapyramidal disorders can manifest themselves both at the beginning of antipsychotic therapy and at a later period. They are quite painful for the patient, complicate his life and aggravate the manifestations of the underlying disease.
Blocking dopamine in the mesocortical pathway leads to the development of neuroleptic depression, that is, negative symptoms appear. Among them are depressed mood, decreased physical activity, a feeling of hopelessness, etc. This condition increases the possibility of suicide. Against the background of the action of neuroleptics, cognitive functions also decrease, attention deteriorates, and memory decreases.
Another common complication of antipsychotic drug therapy is hyperprolactinemia (increased prolactin in the blood). It develops against the background of changes in the level of dopamine in the tuberoinfundibular pathway.
The disorder is accompanied by a decrease in the level of sex hormones. This entails changes in the human sexual sphere, for example, frigidity, anorgasmia, and impaired ejaculation. Affects sexual development, causes menstrual irregularities, changes in secondary sexual characteristics. Changes the psycho-emotional background: a person becomes irritable, anxiety and sleep disorders increase.
Other side effects from antipsychotics include anticholinergic disorders (constipation, dry mouth, drowsiness, confusion, changes in heart rate). They have a toxic effect on the liver and change the functioning of the heart, even leading to sudden death.
It should be noted that representatives of this group of drugs do not have the same effect on the human body. Depending on their type, they exhibit side effects to a greater or lesser extent.
Sonapax
When using Sonapax, it is not recommended to drink alcohol or alcohol tinctures. The active component of the antipsychotic is thioridazine. It is a phenothiazine derivative.
Sonapax has a strong effect on the peripheral and central nervous system. The drug has tranquilizing and antipruritic properties. It helps eliminate aggression.
The main indication for the use of Sonapax is complex behavioral disorders that disrupt the patient’s normal life. The product improves cognitive functions. It is used for sleep disorders and various phobias.
Atypical antipsychotics: what are the advantages?
New generation neuroleptics were synthesized in order to reduce the occurrence of side effects and the development of complications during the use of this group of drugs.
Their action is similar to typical representatives, but has fundamental differences. Atypical antipsychotics selectively act on D2 receptors, that is, dopamine. First of all, drugs in this group affect those located in the mesolimbic pathway, and thus suppress the positive symptoms of psychosis.
Some representatives of this class of drugs exhibit a total antipsychotic effect, that is, they stop all productive symptoms, while others act selectively, stopping individual manifestations. These drugs do not affect receptors located, for example, in the nigrostriatal pathway, which significantly reduces the risk of extrapyramidal disorders. This is a fairly significant advantage of atypical antipsychotics. This property made it possible to radically change the attitude towards them. After all, it was previously believed that the antipsychotic effect of neuroleptics is impossible without the manifestation of extrapyramidal disorders. Conclusions about the therapeutic effect of the drug were based on their severity.
The new antipsychotics are called atypical because they do not exhibit the typical side effects of these drugs.
Clozapine, developed back in 1968, is considered the first neuroleptic of the new generation. Its extrapyramidal complications were minimal, but nevertheless its production had to be canceled. This was due to the fact that it caused a severe blood disorder. But subsequently clozapine was reinstated due to its unique functions, and therapy with it required constant monitoring of blood counts.
Since the 1980s, other new generation drugs began to appear.
Due to the selective effect of atypical neuroleptics on dopamine receptors, the degree of manifestation of neuroleptic depression and hyperprolactinemia during treatment with them is reduced. Moreover, they are even prescribed to relieve depression. Although such information is ambiguous. For example, it was found that some drugs from this group are capable, on the contrary, of causing motor neurological complications to an even greater extent. These include Olanzapine, Zeldox. And Risperidone, affecting the hypothalamus, causes hyperprolactinemia.
Atypical antipsychotics have a lesser effect on dopamine receptors. And mostly on serotonin. This allows you to influence the negative symptoms of mental illness, such as emotional coldness, anhedonia, and withdrawal.
In addition to the above properties, new antipsychotics enhance and enhance cognitive function.
Risperidone, Amisulpride, Iloperidone, Clozapine, etc. are considered classic representatives of 2nd generation antipsychotics.
Atypical psychotics are divided into 2 groups:
- The first of them includes drugs that equally block dopamine and serotonin receptors, and also selectively act on norepinephrine synapses - Risperidone, Sertindole. Drugs in this group have pronounced antipsychotic and antidepressant effects;
- Group 2 includes drugs that block serotonin receptors, as well as other mediators - Olanzapine. Their main effect is antipsychotic. Possible risk of hypotension.
Teraligen
According to many patients, Teraligen is an antipsychotic, the best for neuroses. It is also used for neurosis-like conditions.
The active component of the drug is alimemazine tartrate. The tablets have a rather complex composition. The auxiliary components of Teraligen include: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose, talc, wheat starch. The medicine has antispasmodic, hypnotic, and antipsychotic effects. The tablets help with sleep problems, somatic diseases, and depression. An antipsychotic that eliminates psychoasthenic symptoms is the safest drug for psychopathy.
Negative properties
Despite the undeniable advantages of these drugs over classical ones, they nevertheless have several negative effects on the body.
First of all, this is the risk of weight gain, which can lead to obesity. The consequences include diabetes mellitus, heart disease, pancreatitis, and atherosclerosis. Atypical drugs are more likely to cause obesity than typical drugs.
Pathological absorption of fluid appears. A person can drink about 20 liters of water per day. It causes headaches, visual disturbances, digestive disorders and even coma.
All antipsychotics exhibit cardiotoxicity to varying degrees. These include rhythm disturbances, myocardial conduction, hypotension, and inflammation of the heart muscle. In severe cases in patients with cardiac pathology, antipsychotics cause myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, and cause sudden death.
Other side effects of atypical antipsychotics include drowsiness and sedation. At the beginning of therapy, such manifestations are even useful, especially in cases where the patient is overcome by insomnia. However, subsequently they lead to disruption of thinking, consciousness, motor activity, and interfere with daily work and professional activities.
Such effects, when they go beyond what is permitted, are often mistaken for new symptoms of the disease. This introduces certain difficulties in clearly understanding the picture of the disorder.
It is worth repeating that the effects of different representatives of atypical psychotics differ from each other. Among them there are drugs with minimal side effects. On the other hand, there are drugs whose effects are more pronounced, but also have more negative consequences.
Haloperidol
The active substance of the drug is a butyrophenone derivative with a characteristic antipsychotic effect and moderate sedative properties. Haloperidol helps with persistent vomiting. The drug eliminates stuttering and psychoses of various natures. Haloperidol helps with acute mental disorders. The drug eliminates confusion. Haloperidol is also effective against hallucinations.
Some representatives of the group
Risperidone is probably the most prominent representative of the 2nd generation antipsychotics. Being a powerful dopamine receptor blocker, it exhibits a strong, effective antipsychotic effect. But, along with this, the list of its side effects is quite wide. Compared to other “atypists,” it causes depression, increased prolactin and extrapyramidal disorders to a greater extent, provokes nausea and vomiting, weight gain, drowsiness and other undesirable reactions. But no one writes him off, since he most effectively fights psychotic agitation.
Quetiapine . One of the safest atypical antipsychotics. Shows a pronounced anti-anxiety effect and normalizes mood. It has a weak effect on serotonin and dopamine receptors, and has a greater effect on adrenergic receptors. Used for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Fluphenazine . The drug is for injection use. It has a moderate effect on the noradrenergic system, and a pronounced effect on the dopamine system. Eliminates irritability and has a psychoactivating effect. Used for hallucinations and to treat neuroses.
The drug is administered intramuscularly in a dose of 0.25 or 0.5 ml with further consideration of the administration regimen. It can enhance the effects of other psychotropic drugs and alcohol, so their simultaneous use is undesirable. When used in parallel with narcotic analgesics, it causes depression of the central nervous system and respiration.
Clopixol was developed more than 20 years ago. It is actively used abroad, but in Russia it was introduced into practice relatively recently. The drug acts on 3 types of receptors: serotonin, dopamine and adrenergic. Available in two forms: injections and tablets.
Injectable forms are Acufase and Depo.
Clopixol-Acupaz is used for acute psychosis, exacerbations of its chronic forms, as well as for mania. It eliminates the nuclear symptoms of schizophrenia: hallucinations, mania, disturbances in mental activity, relieves anxiety, aggressiveness, and reduces manifestations of hostility.
One injection of the drug is enough to relieve acute symptoms. The effect lasts up to three days. After this, they will probably appear again, so it is advisable to prescribe Clopixol in the form of depot or tablets.
Clopixol-Depot provides a prolonged sedative effect. The maximum effect is achieved after the first week after administration of the drug. A single injection of 1 ml of Clopixol-Depot for two weeks or 2 ml for four weeks replaces the daily intake of tablets of the same name for 14 days.
Aminazine and Levopromazine
A relatively safe drug belongs to phenothiazine derivatives. The drug helps eliminate psychomotor agitation. Aminazine reduces the severity of symptoms such as delusions and hallucinations.
Aminazine enhances the effect of tranquilizers and antidepressants.
The drug is effective for obsessive-compulsive disorder. Aminazine is used for alcoholic psychosis. One of the indications for the use of the drug is persistent sleep disturbance.
Levopromazine is characterized by sedative, hypotensive and antidepressant properties. The drug, which does not have a negative effect on brain activity, is prescribed for dementia. Levopromazine is also used for mental and motor disorders.
Dosage regimens
The prescription of atypical antipsychotics must be strictly justified, and their administration requires strict adherence to the regimen. They are prescribed in several ways.
The most reliable and proven is a gradual increase in dose .
In contrast to the previous method, the fast : the dose is increased to an acceptable one within a few days, and all subsequent treatment is maintained at this level.
The zigzag method involves periodically changing high and low doses throughout the entire therapy.
The shock method involves administering the drug in the maximum dosage several times a week. Thus, the body experiences a kind of chemical shock, and psychosis recedes under its influence.
Combination therapy is also used , in which several groups of antipsychotics are used. These can be exclusively atypical antipsychotics or a combination of both generations.
Fluphenazine
Fluphenazine belongs to a broad-spectrum drug with a large list of indications. The drug is prepared in the form of an injection suspension. Fluphenazine is used in the treatment of schizophrenia.
The drug helps with restlessness and increased nervous excitability.
The antipsychotic, which causes side effects relatively rarely, helps improve mental activity.
Fluphenazine is not used in combination with antispasmodics. The active component of the drug is fluphenazine decanoate.
Restoring the body after taking pills
As you know, it is quite difficult to “get off” antipsychotics after many years of using the pills. The drugs inhibit the production of dopamine. After stopping taking antipsychotics, emotions often become dulled.
In most cases, it is possible to restore the normal state of the emotional sphere with the help of special medications. The production of dopamine is also activated when walking in the fresh air. Regular physical exercise also contributes to the patient’s recovery.
Some of the most effective drugs for improving dopamine production include:
- Tyrosine;
- Dopamine.
In order not to leave the path of recovery and not fall into depression again, you need to watch your diet. Foods rich in tyrosine are beneficial. The diet should include seafood, green tea, bananas, and chicken eggs.
Ginkgo biloba after taking antipsychotics
Taking care of your health too late can lead to unwanted complications. Therefore, after completing the course of taking antipsychotics, it is recommended to take ginkgo biloba. The medicinal plant helps improve peripheral and cerebral circulation.
In this simple way you can achieve changes such as:
- improved sleep;
- restoration of normal blood circulation in the lower extremities;
- memory improvement.
Ginkgo biloba is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to its components. A plant with this name should not be used for severe diseases of the digestive tract. The use of ginkgo biloba is not recommended for those with reduced blood clotting.