VSD is a disease that includes a set of symptoms indicating a malfunction of the vascular system.
In modern medicine, vegetative-vascular dystonia is considered as a combination of various symptoms, and not as a separate disease. The main feature is that its symptoms cause illness throughout the body.
Before diagnosing VSD in a patient, the doctor must rule out other dangerous diseases.
Smoking is especially dangerous for VSD. Why and what this can lead to, we will consider in the article.
A smoker should know that smoking and VSD are incompatible. Nicotine puts a strain on the cardiovascular system, which is already suffering greatly.
Where does VSD come from?
Many experts agree that dystonia is a consequence of a psycho-emotional shock. After this, the general condition of the body deteriorates, which leads to a malfunction of all organs.
Causes:
- Emotional overload.
- Prolonged depression.
- Constant stress.
- Weak immune system.
- Physical overload.
- Insomnia.
- Problems with the spine.
- Smoking, alcohol and drugs.
General
There is no need to talk about how harmful a habit such as smoking is. We have all heard and read many times that smoking leads to lung cancer. In addition, the condition of the skin, hair and teeth deteriorates significantly. With VSD, smoking is especially dangerous, as it significantly undermines the functioning of the entire body. The chances of recovery in this case are practically reduced to zero.
Against the background of dystonia, which negatively affects the functioning of the nervous system, symptoms such as panic attacks, depression, and various phobic reactions may develop.
Smoking only worsens all these manifestations.
Many smokers, in order to calm down, smoke cigarette after cigarette, which saturates the body with harmful substances, which in turn has a detrimental effect on the body.
To summarize, we can say that smoking only worsens VSD, which can lead to irreversible consequences.
The impact of cigarettes on the body and emotional state during VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is manifested by disorders of the nervous system, including insomnia, irritability, depression against the background of a general deterioration of the condition (arrhythmia, osteochondrosis, decreased body defenses, etc.). Due to these physiological and psychological factors, a person experiences constant stress.
After smoking, temporary emotional relief occurs, but the effect of nicotine on the body has long-term negative consequences. Among them are the following:
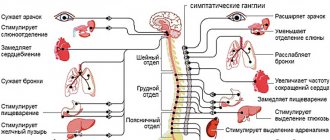
- An increase in heart rate that interferes with the functioning of the circulatory system, resulting in the heart not receiving the required amount of blood.
- Carbon monoxide enters the body with cigarette smoke. It reduces the amount of oxygen needed by all organs, including the heart.
- Nicotine gradually reduces and then replaces the element acetylcholine, which controls cells and tissues with the help of nerve impulses. The lack of this substance leads to irritability and nervousness of a person against the background of general lethargy and weakness of the body. To get into an active state, a person needs to smoke a cigarette again. Thus, physical dependence on nicotine develops.
If a person does not give up the bad habit, the effect of smoking on the course of VSD can result in neurasthenia, panic attacks, the development of phobias and other psychological problems.
VSD after smoking
Despite the fact that many smokers claim that quitting smoking does not improve their condition in any way, but rather the opposite, this is far from true. Of course, one or two days will not change anything in the body. You need to understand that you have been smoking for a long time and have saturated your body with harmful substances. Accordingly, it will take a lot of time to remove them from the body.
Scientists have proven that giving up cigarettes improves the body's protective functions and brings them back to normal over time. Symptoms of VSD after quitting smoking begin to gradually recede.
How does withdrawal symptoms manifest when quitting cigarettes?
Withdrawal symptoms vary among smokers. The main symptom is an irresistible desire to smoke. It is accompanied by:
- Decreased appetite. The patient does not want to eat. He may experience nausea and vomiting after eating. Sometimes intolerance to familiar foods appears. In some cases, appetite, on the contrary, increases. Trying to occupy his hands with something, the patient constantly eats something. Then he quickly gains weight.
- A negative mental symptom complex, which is characterized by nervousness, frequent mood swings, insomnia, and attacks of uncontrolled aggression.
- Physical impairments. Discomfort in the abdomen, diarrhea, flatulence, heart failure, tachycardia, arrhythmia - all these are manifestations of withdrawal syndrome in heavy smokers.
Addicts often complain that after quitting cigarettes, their wounds begin to heal poorly. Any cut takes a long time to heal. Painful cracks form in the corners of the lips and hangnails on the fingers. If you are prone to varicose veins, the veins may become inflamed and existing blood clots may increase.
What is the danger of smoking with vegetative-vascular dystonia?
Smoking with a disease of the nervous system can be not only harmful, but also dangerous. This bad habit significantly worsens the condition of blood vessels, which in turn can lead to various diseases, as well as disrupt the functioning of the cardiac system as a whole.
Unfortunately, not all smokers can immediately pay attention to the symptoms of VSD. They are very similar to the negative manifestations of a heavy smoker. A person, perceiving such manifestations as a consequence of his negative habit, turns a blind eye to them. People consult a doctor, as a rule, in the later stages of the disease, when long-term and intensive treatment is already required and, accordingly, a complete renunciation of their addiction.
Smoking and disorder
A smoker with VSD must take into account a number of factors:
- Nicotine causes tachycardia. A healthy non-smoking person has a resting heart rate of 70 beats per minute. A person who smokes has a heart rate of 80-90 beats per minute. This, in turn, prevents the heart from filling with blood to the fullest extent.
- Carbon monoxide, which enters the body along with smoke, does not allow it to be saturated with oxygen. This negatively affects the functioning of all organs, especially the heart.
- Nicotine deals a large and often irreparable blow to the nervous system.
- A large amount of it affects the reduction of the hormone that is responsible for blood thinning - prostacyclin. Thanks to it, blood pressure decreases, which eliminates the formation of blood clots. The hormone is also responsible for normal vasoconstriction.
- All smokers have high cholesterol. This in turn leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, which cause a heart attack or coronary heart disease.
- Nicotine also replaces acetylcholine. This is a substance that controls the cells and tissues of the body. Nicotine is similar to it in transmitting impulses, which confuses the organs. As a result, the smoker experiences chronic fatigue, feels irritable, begins to complain about memory, and becomes inactive. The body ceases to recognize acetylcholine and already needs nicotine, which, in principle, leads to addiction.
All these negative manifestations have a detrimental effect even on “healthy” smokers. And with vegetative-vascular dystonia, nicotine is not just harmful to health, but dangerous.
Smoking and vegetative-vascular dystonia
VSD and smoking have a double negative effect on the functioning of the heart and blood vessels, provoking the development of coronary heart disease, heart attack, stroke and other anomalies.
First, the presence of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a person already signals problems in the functioning of internal organs, endocrine and exocrine glands, blood and lymphatic vessels. Nicotine, entering the body, deforms blood vessels, impedes the functioning of the heart, provokes oxygen starvation, and causes brain hypoxia.
Thus, both dystonia and the bad habit of smoking enhance the destructive effect of each other, putting a person’s health in serious danger.
Is smoking a cause of VSD?
In many ways, autonomic nervous disorders are formed under the influence of functional or organic lesions.
Undoubtedly, smoking habit is one of these factors.
Each cigarette leads to the compression of blood vessels, increases the pulse rate, increases blood pressure and the intensity of the heart. The regularity of these phenomena causes changes in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which ultimately contributes to the occurrence of vascular dystonia.
Pathology can be determined by the following symptoms:
- rapid heartbeat;
- constant fatigue;
- blood pressure surges;
- systematic headache;
- sudden attacks of dizziness;
- labored breathing;
- slowing down the thinking process;
- weakening memory.
Against the background of frequent vascular spasms that disrupt natural blood circulation, nausea and sometimes vomiting may occur.
Your Narcologist warns: psychological characteristics of smoking and VSD
A person's emotional state affects his physical health. An example of this is smokers.
Their dependence on nicotine is so strong that the absence of a cigarette can cause:
- anxiety;
- causeless fear;
- panic;
- depression.
For many, these reasons make it impossible for them to give up their addiction.
A heavy smoker who also has VSD seriously risks his health. His chronic diseases are aggravated, and new pathologies are formed; this is a fundamental factor not to combine smoking and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Smoking in different forms of VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is defined as a disease, although, according to many, it is only a set of certain signs that allow diagnosing the state of the autonomic nervous system.
There are three main types of VSD.
Hypertensive
The hypertensive variant of dystonia involves increased blood pressure. It can remain constant or increase from time to time.
In this case, the person experiences: headache, nausea, attacks of dizziness.
- stable blood pressure level, significantly exceeding the age norm. It is established under the influence of regular and frequent vascular spasms caused by the intake of nicotine in the body;
- the settling of cigarette smoke inside the vessels in the form of arsenic, formaldehyde, benzene, tar, lead and others, contribute to their damage;
- Excess cholesterol (atherosclerotic plaques) interferes with normal blood flow, creating the preconditions for the development of heart attack and stroke.
The habit of smoking contributes to the formation of cholesterol deposits in blood vessels.
The above factors contribute to the development of dystonia in a more severe form.
Hypotensive
If a hypotensive form occurs, that is, a decrease in pressure, then the person is haunted by a feeling of constant weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, fainting is not excluded, physical activity and ability to work decrease.
Against the background of these signs of ill health, smoking contributes to:
- further depletion of the nervous system;
- decreased functionality of the heart muscle;
- development of cerebral ischemia.
Partial blockage and narrowing of blood vessels makes it difficult to deliver oxygen, which leads to memory loss, insomnia, chronic fatigue, and so on. This usually ends with a stroke, complete loss of memory, and disability.
Cardiac (respiratory)
This form is considered the most common in people diagnosed with dystonia and is characterized by autonomic disorders of the functions of the heart muscle, accompanied by pain.
- worsens tachycardia;
- promotes vasoconstriction, which causes pressing pain in the heart area;
- disrupts the process of natural cleaning of the bronchi;
- suppresses ciliated epithelial cells.
Therefore, smokers suffer from various pathologies of the respiratory system (bronchitis, tracheitis and others) much more severely than other people, and the diseases themselves are complicated.
Reflection of smoking on the nervous system in VSD
Smoking creates a person’s dependence on this habit, which is not easy to get rid of. Over time, nicotine destabilizes the nervous system, first stimulating it and then suppressing it.
This appears as:
- irritability;
- sleep disorders;
- lack of appetite.
Cigarette smoke affects the nerve centers responsible for the digestive, endocrine and cardiovascular systems, as well as those responsible for sexual activity.
Against the background of VSD, smoking leads to:
- prolonged fatigue that does not go away even after a long rest (fatigue syndrome);
- depressed, depressed mental state;
- indifference, indifferent attitude towards life and everything around;
- attacks of severe anxiety, accompanied by fears, in combination with various vegetative (somatic) symptoms.
If the symptoms are not treated, they become uncontrollable and spontaneous.
How to quit smoking with VSD?
Quitting the smoking habit is one of the effective ways to normalize the state of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In the absence of nicotine, the body is fully saturated with oxygen, resulting in:
- the blood supply to all organs and tissues, and, first of all, to the brain, is stabilized;
- the heartbeat is normalized;
- spasms in blood vessels will disappear;
- headaches will go away;
- your overall health will improve.
To cope with such a difficult task as quitting smoking, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
The specialist will prescribe appropriate complex therapy using sedatives, antidepressants, and vitamins.
Treatment must be accompanied by active physical activity, breathing exercises, walks in the fresh air, and proper rest.
If possible, you can take a vacation. It allows you to take a break from the usual rhythm of life, relieve accumulated irritation, and get some sleep.
If you have a desire and your financial situation allows, then the help of a psychologist will not be superfluous. The specialist will advise you on how best to fight the addiction, teach you psychotherapeutic techniques to resist the urge to smoke, and so on.
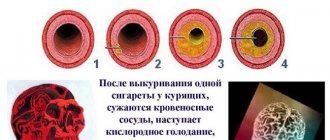
Negative manifestations after smoking one cigarette
One of the dangerous manifestations may be an increase in blood pressure, which can lead to a stroke. Even after one cigarette, the smoker begins to experience tachycardia and vasoconstriction.
Smokers also often experience panic attacks and psycho-emotional agitation.
Even after one puff, arrhythmia and dizziness may occur.
A smoker suffering from dystonia should be aware that the symptoms of VSD are significantly aggravated by smoking.
Subsequently, the smoker finds himself in a vicious circle, which leads to exhaustion of the nervous system. Stress and tension force a person to smoke cigarette after cigarette, which further worsens the course of the disease. Over time, the “snowball” grows, and stopping it becomes simply unrealistic.
Smoking: habit or disease?
There is a very close relationship between smoking and the course of this disease. First, you should consider the consequences of nicotine and other harmful substances entering the body as a result of smoking several cigarettes.
After smoking just a cigarette, the following negative changes appear:
- the pulse and heartbeat quicken, blood pressure rises, which provokes vascular spasm;
- panic attacks or strong psycho-emotional agitation may occur after smoking;
- after puffing, arrhythmia and dizziness may appear;
- the appearance of headaches due to vascular spasms when smoking.
It is worth noting that smoking two or more cigarettes at a time can only aggravate the above symptoms of VSD.
The presence of the disease and smoking leads to a vicious circle. Smoking over time depletes the nervous system, and this several times increases the manifestation of symptoms of VSD. In turn, constant stress and tension, nervousness and depression even more often push the patient to smoke several cigarettes. Thus, a hopeless vicious circle is formed: smoking worsens the course of VSD, and vascular dystonia itself creates situations that encourage smoking. Each time this snowball grows, and it becomes almost impossible to stop.
How does smoking affect the heart in VSD?
As we found out earlier, nicotine affects the walls of blood vessels, and carbon monoxide limits the flow of oxygen into the body. As a result, all resources of the cardiac system gradually begin to deplete.
One of the dangerous symptoms is increased blood clotting, which can inevitably lead to stroke, myocardial infarction or pulmonary infarction. Increased nicotine levels lead to increased cholesterol levels, and this, in turn, leads to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Experts say that the combination of VSD and smoking sooner or later leads the smoker to a hospital bed in the cardiology department.
Recommendations for smokers and quitters
To the question of whether it is possible to smoke with VSD, the answer will be negative. It is necessary to give up the bad habit as soon as possible. Then oxygen will again begin to flow into the body in the required volume, which normalizes cardiovascular activity.
A specialist doctor can help overcome the consequences of nicotine addiction by prescribing sedatives, antidepressants or a course of vitamins.
When quitting smoking, you should follow some general recommendations:
- You need to develop a positive psychological attitude, believe that it is possible to get rid of harmful addiction and regain strength and health.
- Don't put off quitting smoking for another day. The decision made should be implemented immediately.
- You should find a replacement for smoking. Special breathing exercises have a good effect.
- Exercising will help make it easier to quit cigarettes and will help restore and strengthen your health.
If you cannot quit smoking on your own, you should consult a psychologist. There are many techniques that help get rid of nicotine addiction.
Respiratory system diseases
Very often, dystonia leads to breathing problems. A person who smokes feels all the negative symptoms of this disease several times more strongly:
- Lack of oxygen.
- Heavy breathing after smoking a cigarette.
- Dizziness from lack of oxygen.
As a result of nicotine abuse, a disease such as bronchial asthma can develop.
The connection between smoking and panic attacks in VSD
We all know about the negative effects of nicotine on the body. But not all smokers understand how serious the problem can be.
Not many people know that most cases of panic attacks are associated with such a bad habit as smoking.
Smoking during VSD and panic attacks greatly increases the chances of a heart attack and is strictly prohibited.
Without going into the details of psychopharmacology, it can be noted that nicotine increases the level of adrenaline and glutamate. This is what leads to a “narrowing of consciousness.”
This condition is especially aggravated by abrupt cessation of cigarettes. The condition may be similar to when a person smokes a cigarette with narcotic components or, as people call it, “weed.”
Properly selected medications will help you get rid of not only PA, but also a bad habit. Anti-anxiety medications are prescribed first. They will help the smoker not only get rid of the main problem, but also ease the course of VSD. At the next stage, the patient should be prescribed medications aimed at combating smoking. A method of gradually reducing the dosage will be effective and less traumatic for the psyche. Abrupt withdrawal from nicotine will lead to destabilization of the functioning of all organs. To prevent the body from experiencing such stress, you can seek help from a patch, nicotine tablets or electronic cigarettes. These supplements will provide only a small amount of nicotine into the body, gradually reducing its level.
The help of a qualified specialist will not be superfluous. High-quality psychotherapy with the elaboration of all problems will help you quickly and least stressfully cope with the problem of smoking, neurosis, PA and VSD.
Just as with PA, VSD, smoking with neurosis is especially contraindicated. Many smokers are misled into thinking that cigarettes help them cope with stress. Nicotine only masks the main symptoms of the disease, driving them inside.
Interaction between VSD and smoking
Neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD) is a chronic polyetiological functional disease, which is based on disorders of neuroendocrine regulation. It manifests itself as a variety of cardiovascular, respiratory and vegetative disorders, asthenia, disaptation of the body, but has a favorable prognosis.
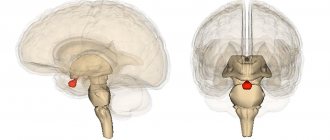
Disturbances of neuroendocrine regulation occur at all levels. The leading role is given to damage to the structures of the hypothalamus, which is the highest center of the autonomic nervous system and the “main” organ of the endocrine system, which controls all others. This determines the dysfunction of the sympathoadrenal and cholinergic systems. Nicotine puts pressure on these same “levers”.
The main chemical that affects the body when smoking is nicotine.
Nicotine in its structure is similar to one of the main mediators of the nervous system - acetylcholine, and therefore is able to bind to nicotinic-type acetylcholine receptors and cause a response.
These receptors are located in the ganglia of the autonomic nervous system and neuromuscular junctions. This determines the effects of nicotine: by binding to one of the most common receptors in the body, it acts on all structural and functional formations, and on the central nervous system, successfully passing through the blood-brain barrier.
The main target of nicotine in the central nervous system is the limbic system (therefore, addiction when smoking is more psychological than physical), but the most important point of application among these structures is the hypothalamus. The one that is responsible for the endocrine and autonomic nervous systems.
Outside the central nervous system, nicotine stimulates the sympathetic system: blood vessels constrict, blood pressure rises, heart rate increases, activity and anxiety levels increase due to the increased release of adrenal hormones.
As a result, the smoker, once again dragging on a cigarette, provokes the activation of already inadequately functioning structures, risking an extraordinary attack of dystonia.
Test for smokers