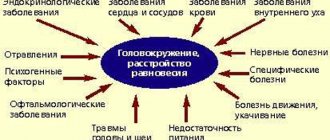
Why does dizziness occur during pregnancy?
In addition to changes in the body, there may be other causes of dizziness.
The most common:
- rapid change of body position or turn of the head;
- motion sickness in transport;
- being at a significant altitude;
- lack of fresh air in the room;
- heat - both outside and in the room;
- decreased blood sugar levels due to a long break between meals or constant consumption of low-calorie foods;
- toxicosis, especially in the 1st trimester;
- changes in weather and atmospheric pressure;
- when the expectant mother stands on her feet for a long time or does not change her position.
There are a number of factors that can confidently predict dizziness in an upcoming pregnancy. As a rule, they are associated with diseases the woman has suffered, such as:
- diabetes;
- anemia;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- micro-strokes;
- initial stage of multiple sclerosis;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- brain tumors;
- problems of the vestibular apparatus;
- inflammation of the inner ear;
- weather sensitivity;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- head injuries;
- epilepsy;
- increased intracranial pressure.
All these conditions and diseases are accompanied by dizziness. If a pregnant woman does not have the above reasons, then dizziness is a consequence of pregnancy. And here it is important to know the reasons for this condition, which depend on the duration of pregnancy.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
Dizziness and fainting during pregnancy
In the first trimester of pregnancy, which lasts up to 12 weeks, important changes occur in a woman’s body, such as the formation and development of all organs of the future fetus. A woman’s body is being rebuilt to a new level of work. Nausea, dizziness and weakness worry almost all expectant mothers. And it is very important at this stage to avoid overwork, fasting, and lack of sleep, otherwise the body may react by “switching off” and loss of consciousness, the so-called fainting, that is, a violation of cerebral circulation.
When blood pressure drops, the brain begins to experience oxygen starvation and fainting - this is a compensatory reaction to the lack of oxygen.
Fainting and pre-fainting conditions in a pregnant woman can occur under the following circumstances:
- stuffy room, cramped
- fatigue during physical activity
- sudden change in body position
- taking a hot bath (causes a sharp dilation of blood vessels)
- hunger (causes low blood glucose levels)
- decreased hemoglobin levels
- viral infections
- emotional stress
- physiological problems (osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, vegetative-vascular dystonia, heart and vascular diseases, brain tumors, anemia)
For any person, a short-term loss of consciousness can be dangerous, and doubly so for a pregnant woman. Regardless of the duration of pregnancy, the mother-placenta-fetus system suffers. This can lead to complications such as weakness during labor, an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage, and poor uterine contractions after childbirth.
First aid for fainting:
Call a doctor. The woman must be laid on a horizontal surface , it is important that her legs are at head level, unfasten tight clothes, open the windows, give ammonia (wet a cotton swab with alcohol and let it breathe for a few seconds).
If dizziness and fainting recur repeatedly, then it is necessary to find out the cause of such conditions. Treatment means eliminating the cause.
As you know, pregnancy is not considered a disease, therefore, the more active the pregnant woman’s lifestyle, the easier the pregnancy is tolerable. Properly selected physical exercises well tone the body, blood vessels and heart. Walking and swimming are necessary to eliminate these problems. Moderate physical activity helps eliminate dizziness, fainting, and also promotes easier childbirth.
Prevention and precautions:
- Avoid places with large crowds of people, ventilate the room more often.
- relax more, walk,
- moderate physical activity, swimming.
Not recommended:
- stand up abruptly
- in the second half of pregnancy, lie on your back for a long time.
Frequent small meals are very important.
If you experience dizziness, weakness, tinnitus and first self-aid, you must take a horizontal position, unfasten your collar and belt to make breathing easier. In the room you need to open the window, you can wash your face with cold water, inhale the vapors of ammonia and vinegar. You can also take tincture of valerian, valocardine or carvalol. Drink strong sweet tea and lie down quietly.
Be healthy and take care of yourself!
about the author
- Sytova Valentina Ivanovna
- Obstetrician-gynecologist of the first category
- All publications by the author
Causes of dizziness during pregnancy by trimester
At any time, if dizziness is short-lived and rare, then you should not worry.
1st trimester
In the early stages of pregnancy, the main cause of dizziness is the body’s adaptation to the changes occurring in it. In addition, there is intense hormonal changes, which can also cause dizziness.
Causes of dizziness:
- being in a stuffy, hot room;
- travel in transport;
- sudden change in body position.
Often dizzy due to toxicosis in the early stages of pregnancy.
Dizziness in the 1st trimester, as a rule, does not require treatment, but you should definitely inform your doctor about it.
If in the 1st trimester dizziness is pronounced, occurs frequently and is accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain and bleeding - go to the hospital immediately! Perhaps these are signs of a threatened miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy!
2nd trimester
The body went through an adaptation period and adapted to the new state. But the uterus still continues to grow and is already beginning to put pressure on the arterial vessels and nearby organs. This can cause dizziness in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
Other causes of dizziness:
- long periods of inactivity (hypodynamia);
- long stay in a stuffy or hot room;
- oxygen starvation (during this period of pregnancy, the blood flow of the uterus is already 1/3 of the total blood circulation, because of this, some organs, including the brain, may lack oxygen);
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- anemia (low level of hemoglobin in the blood);
- gestational diabetes (the pancreas of the expectant mother cannot cope with increased insulin production, the disease goes away after childbirth).
If you experience constant dizziness in the 2nd trimester, especially at week 24, be sure to tell your doctor about it.
3rd trimester
In late pregnancy, in the absence of any diseases, the main cause of dizziness may be sleeping or resting in the wrong position. From the 27th week you can only lie on your side. When lying on your back, the significantly enlarged uterus compresses the general blood flow, which can lead to dizziness.
And although dizziness in the last trimester is quite common, its duration should not exceed 30 minutes.
Other reasons:
- the expectant mother stands on her feet for a long time;
- walks a lot;
- blood sugar levels decreased.
After the 38th week, the body begins to prepare for childbirth, there is a flow of blood to the pelvic organs, which, in turn, can also cause dizziness.
If your eyes become dark and your blood pressure rises during dizziness, this is a sign of impending fainting! We need to go to the hospital urgently!
Degree of toxicosis during pregnancy
Toxicosis during early pregnancy most often has moderate manifestations and does not affect the health of the expectant mother and baby. But it is important to monitor changes in your well-being, as this condition can transform into a more unpleasant one. How often and severely toxicosis occurs determines the severity of this condition.
1st degree.
The expectant mother experiences no more than five attacks of nausea during the day. They may end in vomiting or not, but in general, neither the quality of life nor the health status of the expectant mother is affected. Outside of such attacks, she can eat a nutritious and varied diet, drink enough fluids, and all pregnancy indicators are normal.
2nd degree.
With the second severity of toxicosis, the pregnant woman experiences up to ten attacks of nausea and/or vomiting per day. At the same time, she feels a pronounced deterioration in health when consuming certain foods, from strong odors, or when traveling by car or public transport. With such toxicosis, medical supervision and assessment of the body weight of the expectant mother are important. In cases where instead of weight gain, weight loss is observed, we are talking about nutrient deficiency. They are missed not only by the mother, but also by the baby. One of the manifestations of grade 2 toxicosis may be the appearance of an unpleasant odor when breathing. It indicates that the woman’s body does not have enough glucose and water, and to replenish the water and energy balance, it began to use up reserves.
3rd degree.
The number of vomiting attacks reaches 25 times a day or more. The condition of the pregnant woman is assessed from severe to critical - it depends on how long the severe toxicosis lasts and how much of an impact it has had on the woman’s body. A pregnant woman experiences severe weakness, rapid pulse, and a loss of body weight of 5-10 kg in a short period of time. And the results of laboratory tests indicate that the mother’s kidneys are already having difficulty coping with the load.
How does dizziness manifest?
Dizziness is an insecure feeling of oneself and a feeling of instability of one’s own body, when it seems that everything around is moving, floating in a circle, balance is lost, the floor disappears from under one’s feet.
Manifestations of dizziness:
- weakness;
- it gets dark in the eyes;
- nausea;
- noise and/or ringing in the ears;
- fingers and toes go numb;
- feeling of coolness throughout the body;
- impaired coordination of movements.
If dizziness is accompanied by weakness, tinnitus and nausea, fainting is possible! Call an ambulance immediately! Lean on the support and don't move.
Photo source: shutterstock.com
Diagnostics
The set of diagnostic measures for dizziness includes:
- MRI of the brain – exclusion of organic lesions.
- MRI of intracranial arteries - detection of signs of intracerebral blood flow disturbances.
- MRI of the cervical spine - detection of dystrophic changes complicated by herniation.
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck - determination of the intensity of blood movement.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
- Complete blood count - assessment of hemoglobin level.
- Consultations with a neurologist, otorhinolaryngologist, cardiologist. Sometimes diseases of the inner ear, heart defects, and neurological disorders that worsen during pregnancy provoke dizziness.
Interesting: What kind of pain reliever can you use while breastfeeding?
X-ray methods (classical X-ray, computed tomography) are contraindicated during pregnancy due to the teratogenic effect of ionizing radiation.
Treatment methods and first aid
First aid for dizziness
To avoid falling and injuring yourself and your unborn child, you should know the rules of behavior when dealing with dizziness:
- immediately try to sit or lean against a vertical surface;
- Self-massage of the head, neck and ears using circular movements without pressure helps;
- you should immediately provide access to fresh air (ask to open the window, loosen the belts and waistbands on your clothes, unfasten the top button);
- You can put a cold compress on your forehead;
- It will be useful to have either smelling salts, ammonia, or essential oil with you - inhaling pungent odors helps with dizziness.
Treatment of dizziness during pregnancy
During normal pregnancy, dizziness is not treated. Only three cases require medical intervention:
- anemia;
- gestational diabetes;
- low or high blood pressure.
You can alleviate your condition with these diseases yourself:
- for anemia, introduce iron-rich foods into the diet and take iron-containing medications;
- for low blood pressure - drink sweet tea, you can (but without abusing) weak sweet coffee, tincture of ginseng or eleutherococcus;
- If you have high blood pressure, drink ginger tea or warm milk.
Gestational diabetes should be treated under the supervision of a doctor. Do not self-medicate under any circumstances!
Changes in the body in the second trimester of pregnancy
The second trimester according to the obstetric calendar begins at week 13 and continues until week 26. Physiological changes in the female body are manifested:
- Increased breast volume. The reason for this restructuring is the intensive production of sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone) in the 2nd trimester. The pain that occurred at the beginning of pregnancy disappears. Increased sensitivity of the nipples appears.
- False contractions. Weak in intensity, short-lived cramp-like sensations are training the uterus before childbirth. If they become more frequent and painful, contact your supervising obstetrician-gynecologist.
- Rounded belly. The baby’s weight increases, the uterus, and therefore the abdomen, grows. The gained kilograms reduce a woman’s mobility. Actions that were previously easy to perform now require effort.
- Change in skin color. Active subcutaneous microcirculation provokes a change in shade. It becomes darker, which is most noticeable around the nipples, in separate areas on the face, and linearly on the stomach. Prolonged sun exposure aggravates the situation, so it is recommended to use sunscreen.
- Stretch marks. A growing belly, enlarged breasts, and weight gain lead to stretching of the skin and the appearance of pink stripes. Another reason is progesterone, which blocks collagen synthesis. The dermis loses moisture and is more easily injured.
- Deterioration of nasal breathing, increased bleeding of gums. Increased blood flow thickens the mucous membranes of the nasal passages, causing snoring. Your gums become sensitive, so it is recommended to use a soft toothbrush.
Interesting: Why do you get headaches during pregnancy? Causes, treatment and prevention of pain
Prevention of dizziness
You can prevent dizziness by following these recommendations:
- control your diet (up to 5 meals in small portions);
- create a balanced diet that takes into account the needs of a woman and a growing child;
- avoid long stays in stuffy, closed rooms;
- to walk outside;
- worry less;
- do gymnastics (in the absence of contraindications);
- take a contrast shower in the morning to improve the tone of the vascular wall.
Interesting: Why do you get dizzy during pregnancy?
Preventive measures are based on the rules of a healthy lifestyle, adhering to which pregnancy will pass without complications.