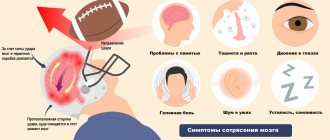
Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
3. Signs of a concussion and its types
What are the signs of a concussion?
Concussions are often difficult to diagnose. There may well be a bruise or cut on the head, but it is impossible to see the concussion itself. The effects of a concussion may not become apparent until days or even weeks after the injury occurs. Some concussion symptoms may last seconds, while others may last much longer.
Concussions happen very often. Therefore, it is very important to be able to recognize the signs of a concussion.
to take all necessary measures in a timely manner.
Here are some common physical, mental and emotional symptoms of a concussion. Any of these may be evidence that a person has suffered a traumatic brain injury:
- confusion of consciousness;
- slurred speech;
- nausea or vomiting;
- headache;
- problems with balance or dizziness;
- blurred vision;
- increased sensitivity to light and noise;
- slowness;
- tinnitus;
- changes in behavior;
- difficulty concentrating;
- memory loss.
Types of concussion
Concussions are classified based on key features
– loss of consciousness and duration of concussion symptoms.
With a mild concussion,
a person does not lose consciousness, and the symptoms themselves last less than a minute.
With a moderate concussion,
consciousness is also not lost, but symptoms persist for longer than 15 minutes.
A severe concussion
is characterized by loss of consciousness, even if it lasts only a few seconds.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
First aid for concussion
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Brain contusion
Brain contusion. There are mild, moderate and severe brain contusions. Mild brain contusion is observed in 10-15% of patients with traumatic brain injury. It is characterized by a loss of consciousness after an injury lasting from several to tens of minutes. After restoration of consciousness, typical complaints are headache, dizziness, nausea, etc. As a rule, retro-, con-, and anterograde amnesia is noted. Vomiting, sometimes repeated. Moderate bradycardia or tachycardia may be observed, and sometimes systemic arterial hypertension. Breathing and body temperature without significant deviations. Neurological symptoms are usually mild (clonic nystagmus, slight anisocoria, signs of pyramidal insufficiency, meningeal symptoms, etc.), often regressing within 2-3 weeks. after injury. Fractures of the calvarial bones and subarachnoid hemorrhage are possible.
Moderate brain contusion is observed in 8-10% of victims. It is characterized by a loss of consciousness after an injury lasting from several tens of minutes to several hours. Amnesia is pronounced (retro-, con-, anterograde). The headache is often severe. Repeated vomiting may occur. Mental disorders are sometimes observed. Transient disorders of vital functions are possible: bradycardia or tachycardia, increased blood pressure, tachypnea without disturbing the rhythm of breathing and airway patency, low-grade fever. Often, meningeal and brainstem symptoms, dissociation of muscle tone and tendon reflexes along the body axis, bilateral pathological signs, etc. are detected. Focal symptoms are clearly manifested, the nature of which is determined by the localization of the brain contusion; pupillary and oculomotor disorders, paresis of the limbs, disorders of sensitivity, speech, etc. These symptoms gradually (within 3-5 weeks) smooth out, but can persist for a long time. With moderate brain contusion, fractures of the bones of the vault and base of the skull, as well as significant subarachnoid hemorrhage, are often observed.
Severe brain contusion is observed in 5-7% of victims. Characterized by loss of consciousness after injury lasting from several hours to several weeks. Motor agitation is often pronounced. Severe disturbances in vital functions are observed: arterial hypertension (sometimes hypotension), bradycardia or tachycardia, disorders of the frequency and rhythm of breathing, which may be accompanied by disturbances in the patency of the upper respiratory tract. Hyperthermia is pronounced. Primary brainstem neurological symptoms often dominate (floating movements of the eyeballs, gaze paresis, tonic nystagmus, swallowing disorders, bilateral mydriasis or ptosis, divergence of the eyes along the vertical or horizontal axis, changing muscle tone, decerebrate rigidity, suppression or increase in tendon reflexes, reflexes with mucous membranes and skin, bilateral pathological foot signs, etc.), which obscures focal hemispheric symptoms in the first hours and days after injury. Paresis of the limbs (up to paralysis), subcortical disorders of muscle tone, reflexes of oral automatism, etc. can be detected. Generalized or focal epileptic seizures are sometimes observed. Focal symptoms regress slowly; gross residual effects are frequent, primarily in the motor and mental spheres. Severe brain contusion is often accompanied by fractures of the vault and base of the skull, as well as massive subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Moderate brain contusion
Moderate brain contusion occurs in 8-10% of victims with TBI.
CLINICAL PICTURE
In case of moderate brain contusion, CT in most cases reveals focal changes in the form of non-compactly located zones of low density with areas of high-density inclusions or a moderate homogeneous increase in density in a small area. In case of moderate brain contusion, fractures of the bones of the vault and base of the skull, as well as significant subarachnoid hemorrhage, are often diagnosed.
SYMPTOMS
It is characterized by loss of consciousness after injury from several tens of minutes to several hours. Retrograde, congrade and anterograde amnesia is expressed. The headache is often severe. Repeated vomiting is possible. Mental disorders occur. Transient disorders of vital functions are often noted: bradycardia or tachycardia, increased blood pressure, tachypnea without disturbing the rhythm of breathing and patency of the tracheobronchial tree, low-grade body temperature. Shell signs are often pronounced. Brainstem symptoms are detected: nystagmus, dissociation of meningeal symptoms along the body axis, bilateral pyramidal signs, etc. Focal symptoms (depending on the location of the brain contusion) are clearly manifested: pupillary and oculomotor disorders, paresis of the limbs, sensitivity disorders, speech disorders, etc. These focal signs gradually (within 3-5 weeks) smooth out, but can persist for a long time.
TREATMENT
Treatment should be carried out exclusively by a neurologist. Self-medication is unacceptable. Due to the variety of damage to the brain, bone structures and soft tissues of the head during TBI, the treatment of victims requires a strictly differentiated approach, taking into account all the characteristics of the injury, the most important of which are the clinical form of brain damage and the severity of this damage. There is a certain correspondence between the clinical form of the injury and the degree of its severity. At the same time, it must be pointed out that there is no complete coincidence between these characteristics. Medical practice and numerous studies, including those based on the principles of evidence-based medicine, have shown that the most important criterion for treatment is the severity of TBI. In this regard, modern principles of patient management, the choice of methods of conservative and surgical treatment depend mainly on the severity of the injury suffered, taking into account all its other characteristics.
Brain contusion. Symptoms Diagnostics. First aid
Home / Useful information
A brain contusion is a traumatic brain injury, which is accompanied by loss of consciousness for a short or fairly long time (which determines the severity of the injury) and the obligatory development of structural changes in the substance of the brain.
The presence of structural changes distinguishes a brain contusion from a concussion, in which only functional changes occur. Thus, a brain contusion, which is characterized by the appearance of a focus of tissue necrosis in the brain substance, the development of multiple small hemorrhages into the substance or large hematomas in the intrathecal space, is a life-threatening condition.
If a person receives a traumatic brain injury and loses consciousness for several minutes or longer, it is necessary not only to provide first aid, but also to immediately call an ambulance.
The sooner an ambulance arrives and the sooner assistance is provided, the greater the chance of saving the victim’s life! That is why it is better to choose a private ambulance, which will arrive at the scene in a matter of minutes and provide full assistance!
Causes of brain contusion
The most common cause of brain contusion is trauma, with household and work-related injuries predominating in some countries and regions, and road traffic injuries in others.
However, it should be borne in mind that the cause of a brain contusion can be not only the actual injury received by a healthy person. Often, brain contusion can occur in people suffering from epilepsy, diseases of the musculoskeletal system, pathology of the cerebellum, and so on, i.e. people who fall frequently and may be injured.
Whatever the cause of a brain contusion, you should always call an ambulance as early as possible, since the complications of a brain contusion can be varied and often threaten the life of the victim!
Symptoms of brain contusion
The clinical picture of a brain contusion may or may not have some specific signs.
One of the main signs is loss of consciousness, which lasts from several minutes to several tens of minutes or even hours. An important criterion is the trauma that preceded the loss of consciousness.
If there was no injury, then the cause of loss of consciousness can be either simple fainting or serious vascular problems (stroke).
It is important to understand that the symptoms of a concussion consist solely in a violation of higher nervous activity, i.e. loss of consciousness, and then impairment of speech functions, vision, hearing, sensitivity or motor activity, depending on the area of the brain that was affected.
At the same time, a brain contusion itself may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the bones; a fracture of the bones of the base of the skull can lead to the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (a special fluid contained between the meninges) from the nose and ears. Bleeding from the ear can also be a sign of a fracture and damage to the middle and inner ear.
Both a skull fracture itself and a brain contusion can become life-threatening conditions due to possible complications. It is believed that bleeding and the formation of small hemorrhages or large hematomas during brain contusion triggers the process of aseptic inflammation. As is known, the inflammatory reaction is accompanied by tissue swelling, so one of the dangerous complications of a brain contusion, especially if it is severe, may be cerebral edema - a condition that requires specialized and emergency care.
That is why emergency medical assistance should be called for any victim with loss of consciousness. And the sooner the team arrives, the greater the likelihood that assistance will be provided in a timely manner, and the threat to the patient’s life will be minimal!
Our emergency medical services partners include the best equipment, highly qualified specialists and new vehicles. This is a guarantee of quick arrival at the place of call, provision of timely assistance and rapid hospitalization in the department, where the patient will be provided with highly specialized care, including surgical intervention!
Diagnosis of brain contusion
At the scene of injury, after a general medical examination, our emergency medical services doctors will be able to make a preliminary diagnosis and determine further tactics for managing the patient.
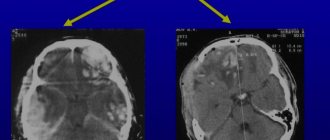
As a rule, without the use of modern research methods, it is only possible to distinguish traumatic brain injury from other diseases and pathological conditions that require radically different care. After making a preliminary diagnosis of a brain contusion, our specialists transport the patient as soon as possible to perform an extremely necessary study - computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
These research methods make it possible to visualize changes in the brain substance and membranes and, accordingly, determine further treatment tactics. In any case, patients are advised to be hospitalized for at least 7 days. However, the decision on the need for surgical treatment is usually made only after a CT or MRI scan.
First aid for brain contusion
First aid for a brain contusion should consist of clearing the airways, providing access to oxygen, placing the person in an elevated position, and in the absence of consciousness, a position on the right side with the head down.
An ambulance should also be called immediately.
We advise you to contact our company, and we will organize:
— arrival of an ambulance within a few minutes
— we can quickly organize or transport the patient to the nearest specialized department.
Lack of delay is the main thing for any patient with a traumatic brain injury, which is why you should not save money and it is better to use the services of real specialists in their field who will provide proper assistance in the shortest possible time!
Brain concussion
Bruise and concussion
Statistically, concussion is considered the most common head injury. It is a mild form, so victims often ignore contacting neurologists.
This condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- amnesia (memory loss) for events that occurred before the injury;
- short-term loss of consciousness is possible (up to 15 minutes);
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache;
- increased sweating, feeling of heat;
- temporary deafness (tinnitus);
- dizziness.
The main sign of a concussion is the absence of damage to the bone tissue of the skull. It takes about 10 days for complete recovery. If the victim was or is unconscious, examination by a doctor is mandatory.
On this topic ▼
Cervical spine injuries
Before medical assistance arrives, you should adhere to the following rules for providing assistance:
- The victim who is unconscious should be placed on his side. The surface must be hard and level. Legs and arms are bent. It is recommended to turn your head towards the floor. This position provides the necessary flow of oxygen and is also safe in case of vomiting.
- If the skin is damaged or bleeding, apply a clean bandage.
- in the case when the victim is in clear consciousness, lay him down with his head slightly raised. Remove the constricting elements of clothing (tie, belt), unbutton the top buttons on the shirt. Keep him awake until the doctor arrives or for an hour after the injury.
You should know that the distinguishing feature of a concussion from other head injuries is the absence of internal pathological changes. If the examination revealed even minor damage to brain structures, then we need to talk about a more serious type of TBI – brain contusion.