Many people do not regard involuntary muscle twitching as a nervous tic and believe that it will go away on its own. It is almost impossible to find information on the Internet that would systematize all the symptoms and at the same time describe the characteristics of a nervous tic or spasms of individual parts of the body.
In our article you can find information about twitching of various parts of the body, their causes and the symptoms of diseases that can cause such phenomena, as well as familiarize yourself with treatment methods.
If you have muscle twitching throughout your body or in certain parts of your body, you should definitely consult a doctor. He will be able to determine whether it is a nervous tic or a seizure. Considering that all human movements must be conscious and coordinated, a nervous tic not only brings discomfort to the perception of one’s body, but can also signal mental, vegetative-vascular and immune diseases. It is worth considering that self-medication will not always be effective, and will often cause irreparable harm; you should consult a doctor. Let's look at individual types of nervous tics and hyperkinesis of various parts of the body in more detail.
Nervous tic
A nervous tic is a muscle contraction that is arrhythmic and involuntary. It can be temporary or permanent. The temporary effect can be caused by strong feelings, fear or a pinched nerve. And a permanent tic is formed due to a lack of microelements after illnesses. Types of nervous tics and hyperkinesis: – Teeth grinding. - Twitching of the wings of the nose. – Brief twitching of the muscles of the limbs. - Shaking head. – Nervous tic from hyperkinesis in sleep.
Ticks are also divided depending on their location: – Local tics manifest themselves in the contraction of one muscle group. – A generalized tic combines the simultaneous contraction of several groups at once, and at the same time they begin and stop simultaneously.
Muscle twitching as a symptom of osteochondrosis
The appearance of muscle spasms is not the only sign of osteochondrosis. The destruction of cartilage tissue between the vertebrae causes the following disorders:
- Static. Destruction of the discs leads to the fact that the load on the spine becomes uneven, bone displacement appears and the load on some muscle groups increases. This leads to pain and limited mobility.
- Vascular. Compression of the veins and arteries by the displaced vertebrae occurs, and with prolonged disruption of blood flow, signs of ischemia of the internal organs become noticeable. Partial or complete compression of blood vessels is characteristic of cervical osteochondrosis.
- Neurological. Irritation of the root by the spinous processes or a decrease in the size of the nerve canal disrupts complete innervation. Patients note changes in skin sensitivity (the appearance of goosebumps, decreased sensitivity), weakness in the limbs and involuntary muscle contractions.
Twitching can occur in different ways:
- Nervous tic or tremor. Under the influence of frequent nerve impulses, the muscle periodically contracts reflexively.
- Myospasm. Patients feel a cramp that cramps a part of the body, severe pain appears and mobility is sharply limited.
More often, with osteochondrosis, spastic muscle contractions appear in a small area of the body. The appearance of muscle twitching throughout the body is a dangerous syndrome, indicating compression of the cervical artery or other large vessels, the compression of which causes acute cerebral ischemia.
Consequences of muscle twitching
The causes of nervous tics can be:
– lack of vitamins and microelements such as potassium or iron;
- head injury;
– prolonged emotional and mental stress;
– strong feelings;
– pinched nerve;
– neuralgia or vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Consequences that can result from lack of treatment for nervous tics:
– pinched nerve and increased muscle tension;
– if the cause of a nervous tic is vegetative-vascular dystonia, then the result may be a circulatory disorder;
– a nervous tic caused by excessive physical exertion can lead to convulsions or partial loss of limb mobility.
Cramps and muscle spasms in osteochondrosis: causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Cramps and spasms of muscle tissue occur due to overexertion, which develops due to changes in the structure of muscles and bones. The appearance of a symptom means the progression of osteochondrosis. The development of the disease is accompanied by spinal dysfunction. The disease requires contacting a doctor to prescribe a set of therapeutic measures.
Causes
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative process that results in complete or partial deformation of the intervertebral discs. Damage to the spine provokes involuntary contractions of muscle tissue. However, there are other factors that contribute to the progression of symptoms during the course of the disease. There are several secondary reasons:
What do cramps mean in osteochondrosis?
As the disease progresses, the spine may perform less of its functions. A share of the load from bones is transferred to muscle tissue.
Toxins accumulate in the muscles, and venous outflow is disrupted due to problems in the circulatory system.
Cramps and muscle spasms that occur as a result of degenerative changes indicate the active progression of osteochondrosis, an increase in the area affected by degenerative tissue changes.
What can be confused with
The causes of cramps and muscle spasms can be dysfunction of metabolic processes and physical activity. When diagnosing the disease, it is important to distinguish the degenerative process in the spine from other factors:
- pregnancy provokes cramps in the legs;
- a lack of B vitamins, magnesium, potassium and calcium or their excess provokes severe muscle tension;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- thyroid hormone imbalances, diabetes, cause seizures;
- neurotic conditions, such as hysterical neurosis, contribute to the occurrence of convulsive attacks.
- a sharp decrease in the amount of fluid, characteristic of vomiting, diarrhea, the use of diuretics, increased sweating, blood purification in renal failure;
- high physical activity can cause microtraumas, the healing of which is characterized by muscle pain and cramps;
- circulatory disorders, for example, uncomfortable position during sleep. Due to the body being in an incorrect position for a long time, blood circulation in the muscles slows down. As a result, pain, weakness and muscle cramps occur;
- static muscle strain, for example due to incorrect posture, causes muscle spasms;
- Constant stressful situations cause an increase in the amount of hormones produced, such as adrenaline, cortisol, which provokes an increase in heart rate and increased muscle tone.
How to get rid of cramps with osteochondrosis
If a convulsive spasm occurs, you cannot tolerate discomfort and wait until everything goes away on its own. To make you feel better, you need to take the following measures:
- in case of cramps during sleep, it is recommended to take a sitting position, lower your legs to the floor, and rise slowly;
- to relieve muscle spasms, you can use warming ointments and compresses;
- for severe cramps, massage and stretching of the affected muscle will help;
- If other methods do not help, you can use acupuncture.
Which doctor should I contact?
Depending on the individual signs of osteochondrosis development, treatment is carried out by doctors of different profiles. The first doctor you need to contact is a therapist. After collecting anamnesis, he will refer the patient to a specialized doctor. For neurological disorders, treatment is carried out by a neurologist. Most often, osteochondrosis is treated by a traumatologist.
Treatment of osteochondrosis and seizures
The course of treatment depends on the stage of progression of osteochondrosis, concomitant diseases, and the patient’s well-being.
Drug treatment
Treatment with medications involves the use of muscle relaxants - drugs that act on muscle tissue and help relieve spasms. It is possible to use analgesics and antispasmodics.
If the cause of the disease is severe emotional stress, medications are prescribed that affect the state of the patient’s central nervous system.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used.
Surgery
At the last stage of osteochondrosis progression, when therapeutic methods do not have the required effect, doctors prescribe surgical treatment. It implies:
- removal of hernia, tumors and bone processes;
- installation of an implant instead of a removed disc;
- normalization of the position of the intervertebral disc;
- laser reconstruction of the damaged element.
Conservative treatment
To reduce the risk of complications and normalize the patient’s condition, the following methods are used:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- yoga;
- swimming;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- acupuncture.
Source: https://cmrt.ru/simptomy/sudorogi-i-myshechnye-spazmy-pri-osteokhondroze/
Why does involuntary twitching of the muscles of the arms and legs occur?
Considering that the muscles of these parts of the body are most involved in everyday life, their twitching can be caused not only by psycho-emotional, but also by strong physical stress. For example, after a long workout with weights, a phenomenon such as twitching of the muscles of the arms and legs may be observed. As a rule, such phenomena go away on their own within a few days. However, if the twitching continues for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor, first of all, a therapist, who will determine the need to consult a neurologist, psychologist or neurosurgeon.
Why does the shoulder muscle twitch?
Spontaneous twitching of the muscles of the shoulder joint can be caused by physical activity. This phenomenon is usually observed in athletes or people whose profession is related to loading and unloading. If the twitching is constant, then it may be due to a lack of potassium in the body. In this case, after consulting a doctor, drug treatment, including vitamin therapy, will be prescribed. In addition, twitching of the left shoulder may be associated with heart disease, so if such a symptom occurs, it is recommended to consult a physician or cardiologist.
Why does my nose twitch?
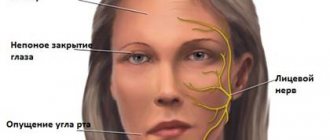
Twitching of the nose and involuntary sniffing are quite often caused by psychological experiences. This type of twitching requires a mandatory visit to a neurologist. If such a tic is one-time in nature, it would be advisable to take sedatives and perform calming breathing exercises. Facial massage will also help eliminate nervous tics if they are associated with overstrain of facial muscles.
Why does my head twitch involuntarily?
Head tremors can be caused by various serious diseases:
- multiple sclerosis;
– neuralgia;
– cerebellar disease;
– abuse of alcohol and drugs;
– severe stress;
– side effects from taking various medications.
Such twitchings are divided into benign and malignant.
Benign ones, as a rule, are not associated with any serious diseases and do not cause serious discomfort to the patient. As a rule, this type of tremor occurs in adolescence due to insufficient functioning of the thyroid gland.
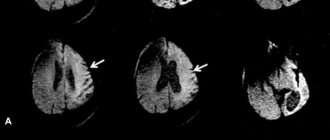
Diagnosis of causes:
– special studies of head tremor;
– electromagnetic radiation from the brain;
– tomography and MRI of the brain.
Why do spontaneous leg tremors occur during sleep?
As you know, brain activity does not stop during sleep. Spontaneous muscle twitching during sleep even received a scientific name - Simmonds' nocturnal myoclonus. Such shudders do not pose any danger to human health; they are directly related to brain activity during sleep. If involuntary shaking of the legs leads to awakening, then we may be talking about Okbom's restless legs syndrome. The main reason why these syndromes arise is neuroses and improper functioning of the subcortical part of the brain. In order to determine what causes such twitching, it is necessary to study the functioning of the blood vessels, as well as the psychological state of the patient. After identifying the cause, we can talk about prescribing treatment. This may include:
– taking sedative and epileptic drugs;
– rest and lack of psychological stress may be indicated;
– massage and muscle relaxation;
– following a diet and taking vitamins.
Muscle spasm due to osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis is considered the main root cause, which provokes spasm and muscle twitching. First of all, this condition is associated with a violation of venous outflow and the accumulation of breakdown products in the muscles.
Normally, tissues receive important elements and oxygen through the bloodstream, and also remove waste and toxins.
With the development of degenerative processes, the established system is disrupted, which is associated with a change in the anatomical position of the vertebrae.
With venous stagnation, tissue swelling develops, which puts pressure on the base of the cerebral vessels, causing hypoxia.
With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, which is considered the most common pathology, spasms of the neck muscles are a natural reaction to stagnation of venous blood.
The muscle fibers contract pathologically and cannot relax, trying to push it through the vessels.
The inability of muscle tissue to relax causes the accumulation of lactic acid, which causes pain in the shoulder, neck and head.
Minor causative factors
Cervical osteochondrosis is not the only root cause of muscle spasms. There are factors that provoke the occurrence of a negative symptom against the background of spinal degeneration:
- back injuries;
- statistical body position;
- stress;
- pinched nerves;
- disturbance of calcium-magnesium metabolism;
- systematic impact on muscles;
- physical inactivity;
- intervertebral hernia;
- curvature of posture.
Associated symptoms
Pathological muscle tone in osteochondrosis is observed at all stages of pathology development and is especially pronounced under the influence of external and internal stimuli. The pathology is accompanied not only by muscle spasms, but also by a number of other negative symptoms, the manifestation of which depends on the localization of the degenerative process:
- Cervical chondrosis. Muscle twitching is observed in the neck and back of the head; in advanced cases, the disturbance of innervation spreads to the upper extremities. The disease is characterized by aching pain, dizziness, hand tremors, impaired swallowing function, changes in hearing, and painful sensations in the occipital region of the head. There are cases of neuralgic symptoms in which the eyelids twitch.
- Thoracic chondrosis. The pathology is accompanied by pain in the chest region, which simulates an attack of angina and tachycardia. Spasms affect the intercostal space.
- Lumbar chondrosis. Severe pain accompanies leg cramps. Sometimes there is chills all over the body. In this case, mobility is impaired and swelling of the lower extremities is noted, which periodically twitch involuntarily.
What to do if muscles twitch on their own
If this problem occurs, first of all, it is worth analyzing the previous few days, if such twitching is of a one-time nature. If a few days before the onset of such a symptom there was severe stress, nervous tension, or a psycho-emotional state, then you need to rest well, do breathing exercises, and such twitching will disappear on its own.
If there are chronic diseases, such twitching may be associated with their exacerbations or the general course of the disease. In this case, it is necessary to contact, first of all, a therapist, who will identify a specialist who is competent to answer the question of why twitching occurs and how to eliminate it.
After consulting a therapist, the cause of twitching can be determined as vitamin deficiency, namely, insufficient levels of potassium and iron in the blood. In this case, the most effective treatment will be vitamin therapy and taking special medications.
If there is a constant or prolonged twitching of a muscle, you should definitely examine the vascular system: do an electro- or tomographic study of the brain, which will give answers to the questions: what is it - a pinched nerve or insufficient blood circulation to the brain, which in turn can cause involuntary twitching muscles of various parts of the body.
If twitching of the muscles of the arms and legs occurs after prolonged strength exercises, first of all, you need to eliminate physical activity and give the muscles a rest. Twitching of this type, as a rule, goes away on its own within a few days and does not recur.
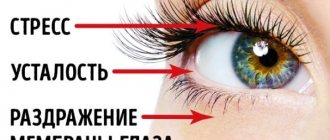
Nerve twitches under the eye: diagnosis and treatment
In order for the doctor to prescribe optimal therapy, you should resort to diagnostics, including information:
- about the spread of the disease;
- about the examination of the patient;
- about conducting research.
The examination is carried out by a neurologist. Consultation with an ophthalmologist and neurologist is also recommended. To be sure that there are no tumors in the skull, an X-ray examination or MRI should be performed. A psychiatrist’s opinion is also important in diagnosis, in order to exclude possible organic diseases in the brain.
Therapy should eliminate the main etiological factor. For example, a nervous tic was triggered by a viral infection. In this case, antiviral drugs are prescribed. If the eye twitches due to emotional stress, the patient is advised to rest completely.
If such a process is observed in a child, the doctor must give his parents an explanation that it is necessary to eliminate all conflicts in the family, as well as normalize the home environment and visit a psychotherapist. To eliminate the manifestations of nervous tics, sedatives and muscle relaxants are prescribed. A good effect is achieved with the help of herbal preparations (valerian or motherwort). In certain cases, Botox injections are used.
Twitching under the eye, what should I do? If you experience systematic twitching, you should consult an ophthalmologist and a neurologist. If no pain is observed during twitching, the following measures are taken:
- Factors that have a negative impact on the patient’s psychological state are eliminated.
- The patient is advised to increase sleep duration.
- Minimize the amount of time you spend in front of the computer and TV.
- Special gymnastics are prescribed: with your eyes closed, you need to count to 65, and then open your eyes wide. Repeat 5 times.
- You should take natural sedatives: decoctions of chamomile, lemon balm, and valerian extract.