Symptoms of encephalomyelitis
There are several types of encephalomyelitis, depending on which part of the brain is damaged. Therefore, symptoms may also vary, although these differences are more visible in severe forms of the disease. At the initial stage, the differences are minimal. Signs of the disease include:
- fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness, malaise for no apparent reason, depression, which may be replaced by bouts of activity;
- headaches and muscle pain, regular pain in the spine;
- elevated body temperature in the absence of colds;
- symptoms of a cold, for example, nasal congestion, sore throat;
- digestive problems;
- speech disorders;
- convulsions, paresis or paralysis, seizures similar in form to epileptic ones, neuritis of the facial nerve;
- the appearance of rashes on the skin, decreased skin sensitivity;
- urinary incontinence, difficulty urinating or other pathology associated with the functioning of the pelvic organs;
- deterioration of vision, blurred vision, black spots before the eyes, the patient may experience regular pain in the eye area, especially when moving;
- disorders of swallowing function and respiratory function.
Symptoms usually appear abruptly and are pronounced; the disease itself develops very quickly.
Classification of encephalomyelitis
According to international standards for the classification of diseases, encephalomyelitis is divided into the following categories:
- viral encephalomyelitis;
- tropical static paraplegia, expressed by paralysis of the upper limbs;
- bacterial form of diseases;
- myelitis, which is diagnosed in the absence of information about the cause of the disease.
Some materials provide information that the separation can be primary or secondary in nature. In the first case, damage to the tissues of the central nervous system is implied.
In case of secondary damage, they talk about the consequences of injury, the occurrence of a reaction to a vaccine, or infectious encephalomyelitis.
Causes and development factors
The disease is caused by infection or intoxication, but the exact reasons for its development are not fully understood. But there are some risk factors that can affect the patient’s health and provoke encephalomyelitis. These include:
- Traumatic brain injuries, bruises and concussions.
- Viral infections, mainly characterized by the appearance of various rashes on the human body (herpes, chickenpox, rubella, etc.).
- Bacterial infections: toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, etc.
- Colds, ARVI, flu, etc.
- Various types of allergies.
- Introduction of some vaccines, in particular against rabies, measles, diphtheria, etc.
- Reduced immunity, regular stress, overwork, injuries.
The encephalomyelitis virus is believed to be contagious, and a healthy person can become ill after close contact with a sick person. The virus can also enter through the gastrointestinal tract or by droplets. Patients with a hereditary predisposition are also at risk.
Diagnosis of encephalomyelitis
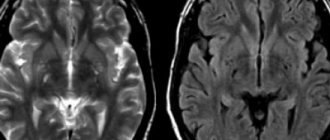
Determining the correct diagnosis is not a difficult task. As a rule, doctors prescribe magnetic resonance imaging of the brain for patients. Pathological changes can be easily visualized on the monitor. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for a lumbar puncture.
When collecting spinal contents (lumbar puncture), attention is paid to how it flows out. If this occurs in the form of a jet, then they speak of the presence of a pathological process.
There are indirect markers that indicate autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Doctors pay attention to the high level of protein content.
Orem is a diagnosis that requires a repeat MRI for encephalomyelitis 6 months after treatment.
Disseminated encephalomyelitis
Multiple or acute encephalomyelitis is similar in its symptoms to multiple sclerosis. But if multiple sclerosis is chronic with periods of remission, then encephalomyelitis is reversible. Therefore, it is important to make a correct diagnosis: only then can effective treatment be selected.
This form of encephalomyelitis is characterized by fever, muscle pain, speech problems, blurred vision, headaches, dizziness and nausea. Patients face various motor disorders: from tremor and hypertonicity to paralysis, problems with coordination and the inability to walk along a given path. In particularly severe situations, the patient cannot even swallow food on his own.
Most changes caused by therapy are reversible and disappear completely with proper treatment.
Causes
The development of acute disseminated disseminated encephalomyelitis is preceded by a viral or infectious disease, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature above 38°C.
Sometimes ADEM occurs as a result of exanthemal diseases: measles, chicken pox, rubella and others. The development of neurological disorders occurs one or several weeks after the first episode of fever. With ADEM, an intense inflammatory process occurs in the brain. As a result, the destruction of myelin, the sheath of nerve fibers, begins. In the initial stages, ADEM is often mistaken for multiple sclerosis, since these neurological diseases have similar symptoms. Modern methods of laboratory and instrumental research allow identifying ADEM.
The causes of acute disseminated disseminated encephalomyelitis are still under study. Research shows that the disease is the result of a pathological reaction of the immune system to infectious or inflammatory processes. ADEM is an abnormal response of the immune system when the defense mechanisms begin to work against the body's own. This pathology is called an autoimmune disease. In this case, the elements that make up the immune system (antibodies, lymphocytes and others) begin to actively fight foreign substances and organisms, while simultaneously attacking healthy cells and tissues (in particular, the myelin sheath). Disruption of the structure of the nervous tissue leads to the appearance of neurological symptoms.
ADEM can occur when the body is infected with the following viruses:
- Herpes;
- Mumps;
- Epstein-Barr;
- Cytomegalovirus.
In rare cases, ADEM develops after vaccination.
The use of active pathogens in a vaccine can provoke an abnormal response of the immune system, leading to autoimmune disorders. Make an appointment
Treatment options for disseminated encephalomyelitis
Fortunately for patients, encephalomyelitis is treatable and in some situations disappears completely. Some of the main conditions are: early start of therapy (literally in the first days after the onset of symptoms), accurate diagnosis (only by accurately identifying the affected area of the brain or spinal cord can the correct rehabilitation program be selected) and inpatient treatment (any attempts to self-medicate can only worsen the situation).
Treatment program:
- Taking medications
. Patients are prescribed antibiotics, hormonal, antipyretic, antihistamine, antiviral and painkillers, a course of vitamins, analgesics, etc. The dosage and schedule of administration are determined by the doctor. A number of medications are aimed at correcting specific disorders: restoring respiratory function, improving blood circulation in the brain, normalizing the functioning of the cardiovascular system, etc. - Physiotherapy.
Good results are obtained by massage, physical therapy, electrical stimulation and other procedures that the doctor selects individually. - Lifestyle correction
. Not only during treatment, but also in later life, the patient should not drink alcohol; overheating and hypothermia, sudden changes in temperature, and overwork should also be avoided.
Doctors know that only with prompt, competent treatment can a patient regain his health, so they select individual therapy taking into account the diagnosis, the general condition of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases, his age, and other factors. A whole team of doctors works with the patient. We monitor patients 24 hours a day, provide wheelchairs for movement disorders, and provide caregivers who are ready to quickly respond to any changes in the patient’s condition. At the same time, we strive to create a comfortable, positive atmosphere so that all our patients feel comfortable and calm, as attitude plays a big role in the success of rehabilitation.
We achieve good results and strive to restore absolute health to all our patients. You can contact us if you have disseminated encephalomyelitis, disseminated myelitis or another form of the disease.
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM, ADEM)
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis ( ADEM , ADEM ) is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the central nervous system thought to be caused by a T-cell hypersensitivity response. This is one of many syndromes that can develop after vaccination or microbial infection, and has a latent period (1-2 weeks) [4,6]. The typical MRI appearance of this demyelinating lesion is predominantly periventricular white matter involvement. The gray matter of the basal ganglia and spinal cord may also be affected, although to a lesser extent.
Epidemiology
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis usually occurs in children or adolescents (usually under 15 years of age). However, the literature describes cases of ADEM in any age groups [12]. Some studies note seasonal peaks in incidence occurring in winter and spring, which is in good agreement with the infectious theory of ADEM [9]. Less than 5% of all reported cases of ADEM occurred after vaccination [8]. Unlike many other demyelinating diseases (eg multiple sclerosis or Devic's disease), no greater predisposition has been identified in women, and even on the contrary, it is slightly predominant in men [12].
Clinical picture
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM, ADEM) usually occurs as a monophasic disease, while individual lesions of the brain may be at different stages of development [4]. In 10% of cases, a relapse develops within the first three months [12]. Unlike multiple sclerosis, the symptoms are more systemic in nature and include fever, headaches, depression in the level of consciousness up to coma, seizures and neurological deficits in the form of hemiparesis, damage to the cranial nerves, motor disorders, behavioral changes in the form of depression, delirium or psychosis [3].
Pathology
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM, ADEM) occurs as a result of a cross-immune response to virus antigens that provokes autoimmune damage to the central nervous system. In half of confirmed cases, IgG antibodies Anti-MOG (myelin-oligodendrogliocytic glycoprotein) are detected[12]. The pathological sign is limited perivenular inflammation (in the English literature - sleeves of demyelination [9]), which is also a characteristic feature of multiple sclerosis. However, MS typically presents as confluent zones of completely demyelinated areas infiltrated by macrophages and reactive astrocytes [9].
Markers
- cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis [12]
- possible increase in myelin basic protein
Diagnostics
Manifestations range from small punctate lesions to tumor-like lesions that have less mass effect than expected for a lesion of similar size and are located in both the infratentorial and supratentorial white matter of the brain. Unlike multiple sclerosis, damage to the corpus callosum is not typical for multiple encephalomyelitis. The lesions are usually bilateral, but asymmetrical. Damage to the cerebral cortex, subcortical gray matter (especially the thalamus and brainstem) is not common, but when present, it allows the lesion to be differentiated from multiple sclerosis [4,12]. In addition to gray matter damage, antibodies to the basal ganglia may form, causing more diffuse lesions [11,12]. Involvement of the spinal cord occurs only in a third of cases and manifests itself in the form of confluent intramedullary lesions of varying size and degree of contrast enhancement [12].
CT scan
Lesions present as poorly demarcated areas of decreased density in the white matter that may have ring-like contrast enhancement.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is more sensitive than CT and demonstrates features of the demyelinating process:
- T2 : manifests as subcortical areas of increased signal surrounded by perifocal edema; possible involvement of the thalamus and brainstem
- T1 with paramagnetic materials : spot or ring-shaped contrast enhancement (open ring enhancement is possible); absence of enhancement does not exclude the diagnosis
- DWI : peripheral diffusion may be limited; the central part of the lesion (which, although high signal on T2 and low signal on T1 weighted images), has neither the diffusion restriction (unlike a brain abscess) nor the lack of signal expected in cysts, which is due to increased intracellular water content in demyelination zone.
Magnetization transfer can be useful in distinguishing between ADEM and RS [3].
Differential diagnosis
- Susac syndrome (retinocochleocerebral vasculopathy)
- acute necrotizing encephalitis of childhood [7]
- multiple sclerosis Marburg variant
- concentric sclerosis Balo
- Schilder's variation
Treatment of orem
The fundamental method of therapy for acute disseminated encephalomyelitis is the use of steroid medications. Over time, it is recommended to minimize the dosage of medications.
This therapeutic technique has its own side reactions, expressed in weakening of the immune system. Therefore, immunoglobulins are prescribed, and sometimes antibodies are removed from the blood.
Treatment is complex and consists of the following measures:
- taking antiviral drugs;
- B vitamins;
- medications to relieve brain swelling;
- nootropics and neuroprotectors.
Due to the fact that acute encephalomyelitis affects the most vital organ, patients may require resuscitation measures: ventilation, connection to a cardiograph, etc.
During the recovery stage, the patient undergoes massage, therapeutic exercises, and stimulation of the cerebral cortex through magnetic impulses.
Treatment of encephalomyelitis with folk remedies is not advisable. It is useful to supplement your therapeutic regimen with tinctures and herbs if your doctor has prescribed them to you. It is unwise to practice independent treatment with folk remedies without adequate therapy; this will lead to a disastrous result - death.
Prevention of encephalomyelitis
Preventing the development of a disease is much easier than curing it. Therefore, follow these simple principles:
- when making vaccines, avoid hypothermia and overheating;
- do not drink alcohol while getting vaccinated;
- do not overload yourself physically;
- play sports and strengthen yourself;
- Do not go to places with large crowds of people during an epidemic.
Orem is a serious diagnosis that requires special attention. You should not delay treatment, otherwise bitter complications cannot be avoided.
Consequences of orem
If you ignore the clinic, unforeseen consequences may arise in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. The majority of patients recover with proper action, but 30% have neurological problems with orem, which can lead to disability and even death.
Consequences of disseminated encephalomyeditis: decreased visual acuity, paresis, difficulty swallowing.
As for the progression of the disease during pregnancy and childbirth, the fair sex significantly increases the risk of exacerbation if they have been ill. It is important to undergo repeated examinations.
It is important to know: encephalomyelitis is a disease that can develop into multiple sclerosis.