The name of the disease comes from the Greek word, which means drowsiness when translated into Russian. This is due to the fact that during sleep a person experiences rapid, uncontrolled eye movements.
Pathological changes in the motor functions of the eyeball, expressed by involuntary very frequent movements, are called nystagmus. Typically, nystagmus is accompanied by a decrease in visual function. The reasons for development determine the physiological and pathological nature of this condition.
Causes of nystagmus
When pathological nystagmus occurs, the eyes deviate from the object in question and abruptly return to it. This happens with a certain cyclicity. Physiological nystagmus usually manifests itself as small jumps of the eyeballs that occur when observing a very fast moving object. Decreased vision is observed with both forms of nystagmus.
The causes of the development of congenital nystagmus can be abnormal intrauterine processes, sometimes leading to various disorders in the visual organs. The causative factor may be birth trauma during a difficult birth, leading to damage to the nervous system. Overstrain of the central nervous system sometimes also provokes the development of the disease.
Myopia, farsightedness, strabismus and other visual deviations can cause nystagmus. A special role in this is played by clouding of the optical spheres, atrophy of the optic nerve and dystrophic changes in the retina.
In addition, infectious diseases and brain injuries associated with damage to the pituitary gland, labyrinth or cerebellum sometimes lead to the development of nystagmus. A favorable background for the onset of the disease is created by narcotic drugs, side effects of certain medications, multiple sclerosis and residual effects of a previous stroke. Stress and prolonged negative emotional stress are often provoking factors in the development of the disease.
Types of nystagmus
Movements of the eyeballs during nystagmus can be in the vertical or horizontal direction. Depending on this, there are two types of this symptom:
- Jerky
- when the eyes move slowly to one side and quickly return back - Pendulum-shaped
- with uniform oscillatory movements of the eyes from side to side.
With nystagmus, the eyeballs move involuntarily, and the movements sometimes change their direction depending on the direction of gaze, the position of the head or the general condition of the Patient - when tired or overexerted.
In this case, the gaze does not concentrate on a specific object and does not linger in a strictly specified direction, so the image that is formed in the brain turns out to be unclear, and the level of visual acuity decreases.
Symptoms of nystagmus
Symptoms of nystagmus also determine its classification. With horizontal nystagmus, eye movements occur along a horizontal line from right to left and vice versa. This is the more common type of nystagmus. Vertical nystagmus is characterized by deviation of eye movement up and down. Accordingly, diagonal nystagmus is determined by moving the eyes diagonally. A rarer case of nystagmus is rotational, in which the eyes rotate in a circle. In addition, there are differences in the nature of the movements. Pendulum and jerk-like nystagmus are determined. It is possible to combine different forms, which is defined as a mixed type of nystagmus.
The congenital form of the disease is accompanied by jerky nystagmus, manifests itself in early infancy and is not corrected. Acquired forms have subtypes: vestibular, installation optokinetic.
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a disease that is accompanied by constant, severe and uncontrollable twitching of the eyes and, as a result, a noticeable decrease in visual acuity.
What does it mean to cure nystagmus?
Nystagmus is always a consequence of one or another disease that reduces visual acuity. Therefore, we have developed a treatment system that, on the one hand, blocks eye twitching, and on the other hand, increases visual acuity.
We block nystagmus using a surgical intervention system that we have specially developed. This system reliably allows us to completely block nystagmus with direct gaze in 78% of cases, and to significantly reduce the amplitude and frequency of eye twitches in 22% of cases.
But this is not enough. It is necessary to maximize the patient's visual acuity. We achieve this through special therapeutic measures. In almost all cases, it is possible to increase the patient’s visual acuity, and in some cases even obtain subnormal visual acuity.
The system we have developed represents an alternative to the widespread opinion and treatment tactics in Russia for managing patients with nystagmus, which suggests the impossibility of curing it.
If modern, correct, comprehensive and timely treatment is carried out, nystagmus can be cured. The sooner it is started, the faster the child can be rehabilitated. And the achieved result will be sustainable!
Treatment of nystagmus in children
When treating this disease, Yasny Vzor specialists use an integrated approach, which includes:
- surgical intervention;
- spectacle correction;
- therapeutic treatment.
Surgical stage in the treatment of nystagmus
The task of the ophthalmic surgeon is to block the oscillatory movements of the eyes (or significantly reduce them) with a direct gaze position and remove the forced position of the head, which often occurs in patients with nystagmus. Surgery is the only way to block these movements. You should start with surgery. This is the foundation for further rehabilitation. The modern “knifeless” technologies we have introduced allow us to perform operations while preserving the vessels and nerve elements of the eye, this is a huge achievement!
For nystagmus, at Yasny Vzor we perform unique surgical operations that block and stop the development of the disease. We were the first to develop a three-stage rehabilitation system for patients with nystagmus, the essence of which is the most accurate diagnosis of the state of the visual system with nystagmus in combination with surgery and therapy to improve visual acuity.
The surgical technique depends on the type of nystagmus, so accurate diagnosis is extremely important - it is important to determine the cause. It is for this purpose that we apply diagnostic standards that allow us to see the most minimal disturbances at any level of the visual system - from the transparency of the media and visual cells of the eye to the cells of the visual cortex of the brain.
After the operation, it will be possible to carry out measures to improve vision.
In parallel with the surgical intervention, an ophthalmological examination is carried out, which allows you to determine the exact refraction of the child and examine the fundus. If there is a refractive pathology (astigmatism, myopia, etc.), the child is prescribed spectacle correction.
Therapeutic treatment involves a special set of measures to improve visual acuity.
Diagnosis of nystagmus
The child’s parents can also identify the primary symptoms of nystagmus, since uncontrolled movements of the eyeballs are visible to the naked eye. Only a specialist can conduct a thorough examination and determine the cause. To avoid complications and prevent further decline in visual acuity, it is necessary to diagnose the disease as early as possible and begin treatment for nystagmus in children.
An examination by an ophthalmologist may additionally include electrophysiological studies (visually evoked potentials, electroretinogram) and optical coherence tomography, which allows you to take an image of the retina, determine possible changes in the structure of cells and the thickness of the layers, which may be the cause of low vision with nystagmus. To identify and treat congenital nystagmus, it is first necessary to conduct genetic studies.
To choose the right treatment method, it is necessary to find out the cause of the disease.
For this purpose, the doctor may prescribe additional studies:
- MRI of the brain and orbits;
- Echo-EG;
- CT scan of the brain;
- EEG.
Also, for diagnosing nystagmus and strabismus, our clinic has a unique Gazelab device - currently the only one in Russia and the CIS countries. This compact and proven device can be used to test vision in children from 2 years of age. It allows you to accurately identify the affected muscle out of the twelve eye muscles, which directly affects the tactics of future surgery. No other diagnostic device has such accuracy and such capabilities.
You should not delay diagnosis, since the process of vision loss depends on the age of the child. It worsens most quickly in young children. That is why most patients with congenital nystagmus have rather low visual acuity.
Reasons for the development of nystagmus in a child
Nystagmus can be caused by various disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system. It is congenital or acquired. In the first case we are talking about nystagmus in newborns. Often acquired nystagmus is combined with partial or complete atrophy of the optic nerve, refractive pathology (myopia, astigmatism), and also occurs in children with genetic diseases (Leber's disease, albinism).
The reasons for the appearance of acquired nystagmus in adults and children are similar:
- encephalitis;
- eyeball injury;
- stroke;
- brain diseases;
- inflammation of the inner ear;
- multiple sclerosis;
- exposure to drugs or toxins;
- traumatic brain injury;
- Meniere's disease.
Symptoms of nystagmus
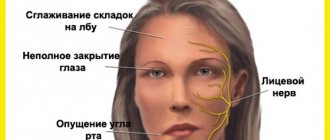
With nystagmus, the child’s head can often take an unnatural position. This condition is called ocular torticollis. It arises due to the fact that with nystagmus there is always a position of the head in which the oscillatory movements appear much less or disappear completely. The child unconsciously finds this position of the head and begins to look in this position, since due to the smaller number of oscillatory movements, the quality and acuity of vision in this position is much better. It is difficult for a child at any age to determine the presence of a health problem. Moreover, nystagmus often develops against the background of another disease.
Features of the development of nystagmus in children
A newborn over 3-4 weeks of age should begin to focus on objects. In the absence of fixation and the presence of oscillatory movements, you need to contact a specialist as soon as possible in order to determine the cause of the disease and begin treatment measures as early as possible. If this does not occur, he should be tested for congenital nystagmus. It is more difficult for a child, especially at a young age, to communicate the discomfort caused by the onset of the disease. Regular dizziness, a feeling of instability and twitching of visual images lead to a distorted vision of the surrounding world and deterioration of vision.
Types of nystagmus
The disease is classified according to various parameters. Nystagmus can be congenital (detected after birth) and acquired (detected at any age if there is a disorder in the functioning of the nervous system). In addition, according to the nature of the disease, nystagmus can be:
- pathological (provoked by various diseases and pathological processes in the body);
- physiological (manifests itself in the presence of irritation of the nervous system).
In the latter case, the disease also has 3 varieties - vestibular, attitudinal and optokinetic. Vestibular nystagmus is manifested by jerky movements and occurs in people who have had an infectious disease of the inner ear or have had Meniere's disease. Optokinetic nystagmus is characterized by spasmodic movements of the eye. Installation nystagmus is visible with extreme gaze abduction.
Classification of the disease according to the direction of vibrations
Based on the type of repetitive movements of the eyeball, the disease is divided into horizontal, rotatory (otherwise rotational), diagonal and vertical nystagmus. In the latter case, the eyes move up and down, that is, vertically. The diagonal shape can be determined if the oscillations are carried out diagonally, rotatory nystagmus - when the eye moves in a circle. With nystagmus, oscillations are divided into jerk-like, pendulum-like and mixed. In practice, horizontal nystagmus is most often encountered, in which eye movements are directed along the horizontal axis, that is, to the left and to the right. Other forms are observed less frequently. Based on the amplitude of oscillations of the eyeball, medium-, large- and small-swing nystagmus is also distinguished.
Treatment of nystagmus
Due to the fact that it is not possible to completely cure the disease, treatment is aimed at reducing the progression of the disease and improving visual functions. The treatment regimen is based on therapy of the underlying disease that provoked the appearance of nystagmus. To improve visual functions, vision correction is performed. Contact lenses and glasses are used for myopia and farsightedness. Correcting astigmatism has a very significant effect on inhibiting further progression of the pathological process.
Vitamin therapy, drugs that support the immune system and vasodilators are used. For special indications, surgery is performed to correct the oculomotor system to reduce eye fluctuations.
Disease prevention
In the prevention of nystagmus, adherence to a correct lifestyle plays a significant role, especially for expectant mothers, because Nystagmus is a serious disease, and in its congenital form it promises big problems for the future person. Currently, there are many medications that improve metabolic processes in the tissues of the eyeball. Many of them can be purchased at pharmacies without a doctor's prescription. However, before using them, you must carefully study the instructions so that the use of the drug does not bring any complications. Treatment of nystagmus is a long, painstaking process, so you need to be persistent and patient.
Team of doctors Ochkov.Net