3 January 2021
21181
0
4 out of 5
Some diseases of the spine, vascular disorders and even endocrine pathologies can provoke the occurrence of such an unpleasant and very detrimental condition as cervical myelopathy. It is accompanied by disturbances in sensitivity and mobility, and can also lead to serious complications. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it in the early stages of development, establish the cause of its occurrence and effectively influence it in order to avoid worsening the condition.
Myelopathy concept
Myelopathy is a comprehensive definition of spinal cord disorders of a dystopic nature and any etiology. It can be a complication against the background of diseases of the spine and joints, vascular degenerative processes, injuries, metabolic or infectious processes, and therefore the final diagnosis should be clarified by explaining the nature of the origin of the disease - ischemic, compression, etc.
The vast majority of myelopathies have an onset outside the spinal substance, as developed against the background of:
- osteochondrosis;
- vertebral fractures;
- spondylosis;
- intoxication (toxins, radiation, etc.);
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes mellitus and other pathologies of the spine, blood vessels and endocrine system.
The following most common cases of myelopathy are caused by direct damage to the spinal substance:
- injuries;
- infections;
- tumor;
- heredity.
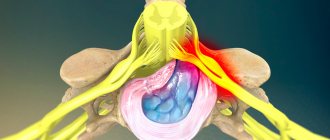
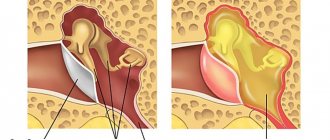
As an exception, the disease may develop after a lumbar puncture. The compression type (with compression of the spinal cord) predominates over all others.
Myelopathy
Some of them are associated with atrophy of the nervous tissue of the spine due to a neoplasm, others arise as a consequence of compression of the spinal substance resulting from mechanical damage, and others may arise due to the effect of radiation on the spine. If the cause of spinal damage is any concomitant disease, then myelopathy will be called this disease. For example, if the cause of myelopathy is diabetes mellitus, then the myelopathy will be called diabetic.
In addition, the cause of this chronic disease of the spinal cord can also be damage to the vertebrae, for example, their dislocation, a herniated disc. Sometimes myelopathy appears as a symptomatic manifestation of infections or inflammatory diseases in the spinal cord or appears due to insufficient blood supply to the spinal cord. A type of myelopathy, Brown-Sequard syndrome, occurs due to compression of nerve fibers at the level of the tenth segment of the spine and is accompanied by impaired muscle mobility on the side of the spinal cord injury, as well as impaired sensitivity on the opposite side of the body. In addition, the onset of this chronic disease can be viral infections. This disease can also appear as a complication after vaccinations given to a person (for example, vaccinations against smallpox, measles).
Who is most susceptible to myelopathy?
Men and women are equally susceptible to this disease, and it has no age restrictions. The severity of changes in the spinal cord directly depends on the degree of damage to it by the disease that caused myelopathy. If middle-aged people are most susceptible to spinal cancer, spinal injuries most often occur in young men. Myelopathy, which occurs as a result of osteoarthritis of the spine, most often occurs in people of retirement age. People who participated in gymnastics at a younger age are at risk for spondylogenic myelopathy. Persons with vascular disorders of varying severity are more susceptible to the occurrence of impaired blood flow in the arteries of the spine.
What is the prevalence and incidence of myelopathy? To date, accurate information does not exist. However, here are some numbers: it is believed that approximately ten percent of people with cancer are likely to develop myelopathies due to tumor growth in the spine, most of which will be localized in the upper spine, and a minority in the lumbar region. Men over the age of 60 are most susceptible to cervical osteoarthritis of the spine.
How does myelopathy manifest itself, and what methods of recognizing it exist?
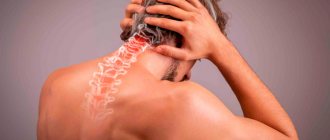
Symptoms of myelopathy vary depending on the causes of its occurrence and the severity of the patient's condition. If this disease arose due to an oncological process in the spine, spinal injuries, then myelopathy may be accompanied by pain, sometimes radiating to nearby parts of the body (arm or leg), impaired coordination of movements or loss of sensitivity in individual parts of the body.
If the cause of myelopathy is osteoarthritis, then pain in the spine in the affected area, weakness, and limited mobility of the spine are possible. In addition, one of the complications of myelopathy may be disturbances in the functioning of the intestines or bladder, and loss of sensation in the perineal area. If myelopathy occurs as a result of an infectious process, then the patient’s body temperature may increase. If the patient suffers from Brown-Sequard syndrome, then it is likely that muscle mobility and sensitivity of individual parts of the body will be impaired.
During an examination of the patient by a neurologist, various diseases caused by compression of the cervical spine can be detected. Rapid, rhythmic muscle contractions may result from motor neuron dysfunction in the spine. Some medical tests can also detect changes in reflex activity, loss and changes in sensation in certain parts of the body.
To determine the depth of the lesion, it is sometimes necessary to check the patient’s sensitivity and adequacy of response to external stimuli of the body from the legs to the face. It is also useful to determine the degree of activity of the abdominal reflexes. It is necessary to determine whether the patient has paralysis or decreased sensitivity in certain areas of the body. Assessing the functioning of the rectum is also of great importance in making the diagnosis.
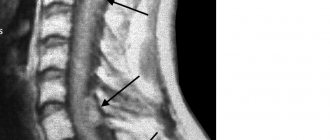
Modern methods for diagnosing myelopathy include: X-ray examination, computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the spine. These methods will allow us to identify and assess the degree of damage to both the spine itself and surrounding tissues. Sometimes laboratory tests are also prescribed to rule out the cause of the disease such as vitamin deficiency (it is known that vitamin B 12 plays an important role in the transmission of nerve impulses, and its deficiency can lead to anemia and irreversible damage to the nervous system).
The patient may be prescribed a general blood test to determine the level of leukocytes in the blood and ESR. An increased level of leukocytes may indicate the presence of an infectious process in the spinal cord, and an increase in ESR may be observed during inflammatory processes in the body or signal the presence of cancer. Sometimes the patient has to have cerebrospinal fluid analyzed to rule out inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord or brain and other diseases. Sometimes a biopsy of nerve tissue from the spine or nearby muscles is performed.
Modern methods of treating myelopathy
Treatment methods for myelopathy directly depend on the factors that caused it. For injuries of the spine of a mechanical nature (fractures, dislocations of the vertebrae), if they are accompanied by pain, painkillers, non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed, a procedure for temporary immobilization of the spine is carried out, and then restorative treatment is prescribed (physical therapy, massage). Sometimes the damaged segments of the spine must be surgically removed or the fractured vertebrae must be reassembled and fixed.
If the cause of myelopathy is multiple sclerosis, then first of all treatment is aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition with this disease with the help of modern medications. Bacterial and viral diseases of the spinal cord require the use of antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs. If myelopathy arose due to an oncological formation in the spine or nearby tissues, and this led to compression of the nervous tissue, then surgical removal of the tumor is necessary.
What is the prognosis for recovery from myelopathy?
With myelopathy, the prognosis of the patient's future condition after treatment depends, first of all, on the severity of damage to the nerve fibers. If there was no damage to the spinal cord, then a complete cure is possible. Full recovery of the patient is also possible after timely and adequate treatment for an infectious disease of the spine. With osteoporosis, arthritis and other chronic diseases, a temporary permanent improvement in the patient’s condition is possible; in this case, the main goal of treatment is to prevent the progression of the disease.
If, despite everything, the disease develops, then disability may occur. Severe spinal injury sometimes does not go away without leaving a trace and can lead to persistent and incurable disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses in certain parts of the body or even to limited mobility of the limbs. The severity of the consequences after surgery for a malignant neoplasm directly depends on whether the cancer will recur in the future, and on the severity of damage to nerve tissue by the tumor. Removal of the hernia that has led to myelopathy usually leads to a complete cure, but only if serious changes have not occurred in the nervous tissue due to prolonged compression.
One of the consequences of myelopathy may be drug dependence on analgesics, as well as persistent disruption of the conduction of nerve impulses in the extremities.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Classification by type
In neurological practice, myelopathy is divided according to etiology:
- spondylogenic – on the spine;
- ischemic – disruption of blood supply to blood vessels;
- post-traumatic – a consequence of mechanical impact with the occurrence of compression on the tissue;
- infectious – for severe bacterial infections (AIDS, syphilis, enterovirus, etc.);
- carcinomatous – against the background of oncology and lesions of the central nervous system;
- toxic – due to intoxication of central nervous system cells or diphtheria;
- radiation – after exposure to radiation (including during the treatment of cancer tumors);
- demyelinating – hereditary or newly acquired demyelization of the central nervous system;
- metabolic - a rare disorder of the metabolism or endocrine system.
Depending on the cause of occurrence, the symptoms of myelopathy may give a different clinical picture.
Myelopathy syndrome with lower paraparesis
Lower myelopathy against the background of dorsopathy in the lumbosacral spine can be associated with cauda equina syndrome. The signs of these two pathologies are similar. But the essence of the diseases is slightly different. In myelopathy syndrome, compression occurs in the spinal canal. With cauda equina syndrome, compression occurs externally as the plexus of radicular nerves exits in the coccyx area. Therefore, different treatments are used.
Myelopathy with lower paraparesis is a reason for immediate contact with a neurologist or vertebrologist. Immediately after differential diagnosis, treatment must begin. With prolonged compression of the spinal cord, a person may become paralyzed in the lower extremities. It will be extremely difficult to subsequently restore the ability to move independently.
Symptoms of myelopathic processes
Symptoms of the disease are a series of nonspecific neurological manifestations that poorly reflect the etiological picture. Signs directly depend on the severity of damage to the spinal substance. General symptoms for all types of myelopathies:
- paresis, paralysis, muscle hypertonicity;
- hyporeflexia;
- hypoesthesia;
- paresthesia;
- dysfunction of the pelvic region.
Specific symptoms depend on the type of pathology, the presence of factors inherent in the underlying disease (tumors, infections, fractures, intoxication, etc.) and complications associated with this.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnostic series involves the identification (exclusion) of processes that are symptomatically similar to myelopathy and the detection of factors that provoked dystrophic spinal changes.
Laboratory diagnostics:
- CBC – general blood test;
- BAC – biochemical blood test.
Instrumental examination of the spinal column:
- X-ray;
- MRI;
- EMG – electromyography;
- ENG – electroneurography;
- lumbar puncture;
- angiography (computer or magnetic).
If it is not possible to do magnetic resonance imaging, then it is replaced by discography and/or myelography. The presumed infectious origin of the disease requires additional clinical studies of the biomaterial:
- blood sterility test;
- RPR sample;
- PCR diagnostics;
- culture of a spinal cord fluid sample.
Based on indications, the patient's neurologist can refer him for a consultation with specialized specialists - a vertebrologist, geneticist, oncologist, etc.
Treatment of the disease and consequences
Therapeutic tactics are determined by the etiological and clinical picture. It represents a complex of therapeutic measures to eliminate the causative pathology and symptoms.
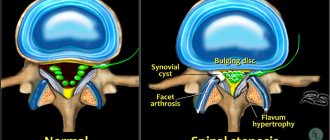
The most important goal of treatment of compression type pathology is the elimination of compression pressure. For this purpose, the following activities are carried out:
- removal of tumors, hematomas, Urban wedge;
- cystic drainage;
- laminectomy;
- spinal disc puncture;
- Fasectomy;
- micro- or discectomy (for intervertebral hernia).
The ischemic type of myelopathy is based on the exclusion of compressive conditions of the vessels. Since vascular abnormalities are the cause of most myelopathic conditions, the treatment package for almost all patients includes their therapy with special drugs:
- antispasmodics;
- vasodilators;
- supporting blood supply.
The toxic type requires detoxification procedures, and the infectious type requires effective antibacterial treatment. The greatest difficulty is in the fight against the hereditary type of demyelinating pathology and the carcinomatous type with the presence of hemoblastosis. Most often, treatment measures are aimed at relieving symptoms.
The therapeutic course necessarily includes drugs to increase metabolic processes in cells and reduce the risk of hypoxia - neuroprotective, vitamin, and metabolic agents. The treatment course includes physical procedures recommended by a physiotherapist to increase physical activity, prevent bedsores, etc.
Treatment of myelopathy
This disease is treated by a neurologist, vertebrologist, angioneurologist, oncologist, and surgeon. After diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a course of symptomatic therapy (painkillers, muscle relaxants), the main emphasis is on treating the underlying disease that provoked the myelopathy; physiotherapy, physical therapy, and massage are also highly recommended. In some cases (for example, with intervertebral hernia, oncology, vascular pathology, stage 3-4 spondylolisthesis), surgical treatment to eliminate the source of the disease may be indicated.
Complete cure of the consequences of myelopathy is almost impossible, however, completely untreated causes of myelopathy give a negative prognosis, and the disease itself will steadily progress. At the same time, with timely treatment and mandatory rehabilitation, it is possible to restore maximum sensitivity, relieve pain and restore, although often limited, freedom of movement.
Forecast and preventive measures
The prognosis for compression myelopathy is quite satisfactory if areas of tissue compression are detected and eliminated on time. If the disease is ischemic in nature, progression of the disease is possible, but regular therapeutic courses on blood vessels provide stable remission. For the radiation, carcinomatous, hereditary type, the prognosis is usually unfavorable.
To prevent myelopathic processes, it is necessary to prevent and promptly eliminate any disorders associated with vascular and spinal disorders.
You can undergo diagnostics and establish the exact cause of the disease, and receive recommendations for a course of treatment at our medical center. Specialists of the Consultative and Diagnostic Center (formerly the National Diagnostic Center) will help you cope with the developing disease. Click the “SIGN UP” button or call the numbers listed on the website and come see us.