Human nerves are built just like electrical wires. Just like any cable, the nerve has its own insulation - it is called the myelin sheath. Only its functions are slightly different. While conventional insulation is primarily needed to ensure that no one gets electrocuted, myelin plays an important role in the normal functioning of the nerve.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disease in which the myelin sheath is destroyed. This leads to neurological disorders that worsen over time.
What are the possible consequences of multiple sclerosis in men and women?
The disease has a chronic course. The prognosis and possible consequences depend on the gender, age of the patient, the course of MS, and what the symptoms were at the onset of the disease. On average, sick people live 5-10 years less than healthy people. Almost half live to age 60 or older.
Over time, serious complications may arise:
- convulsions, fits, as in epilepsy;
- muscle stiffness;
- paralysis, usually in the leg muscles;
- severe memory impairment;
- mood swings;
- urinary and stool incontinence;
- depression.
Multiple sclerosis is a serious disease and requires individually tailored treatment. The patient should be regularly monitored by a neurologist.
Treatment of multiple sclerosis in Moscow at the international clinic Medica24
During an exacerbation of the disease, corticosteroids are used - preparations of the adrenal cortex. They suppress immune reactions and inflammation. If the symptoms are very severe and medications do not help cope with them, they resort to plasmapheresis, a blood purification procedure.
To prevent attacks and slow down the progression of the disease, special drugs are used that change the course of multiple sclerosis - DMTs. They began to be widely used at the end of the 20th century. Treatment of PED is a rather complex process. The doctor must have the appropriate competence, be able to select the right combination of drugs, and guide the patient on them. Today in Moscow there are multiple sclerosis treatment centers that deal with this area of therapy.
Treatment of multiple sclerosis (MSD) should begin as early as possible, after the diagnosis is established - in this case, the best effect can be achieved. But even if the patient’s condition has deteriorated significantly, this is not a reason to give up. Contact a specialist.
At the Neurology Center of the International Clinic Medica24 you can get a consultation with an experienced neurologist. Call +7 to make an appointment with a doctor on a weekday or weekend.
Depending on which nerve fibers are affected, the manifestations of multiple sclerosis may vary. In addition, the course of the disease varies. As a rule, the first symptoms begin to bother you at the age of 20-40. Women get sick more often than men.
New in the treatment of multiple sclerosis
Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences N.V. Kazantseva
How to defeat multiple sclerosis when the patient himself has been underestimating the dangerous neurological manifestations of the disease for many years, because at the beginning of the disease, the symptoms of the disease can disappear quite quickly on their own. How to change the tactics of medical intervention when the use of pulse therapy with neurotoxic hormones almost always initially leads to complete recovery, but becomes less effective and more dangerous over time.
Why, even with early diagnosis using publicly available MRI, is the number of disabled people with MS growing, despite the enormous amounts of money spent in all countries on the treatment of this disease? The increase in progressive forms of MS in the last decade is most likely associated with the widespread use of large doses of hormones. Hormone pulse therapy is a standard approach to the treatment of exacerbations of MS; it causes dysregulation of hormone synthesis in the patient’s body, increases adrenal insufficiency, which is always present in MS, disrupts metabolic processes, promotes atrophy of the cerebral cortex and the development of dementia in MS. Often, 1-3 months after a course of pulse therapy with hormones, an exacerbation of MS develops again. Less aggressive treatment tactics for MS, which were used earlier, more often led to long-term remission with preservation of patients' ability to work.
Repeated courses of pulse therapy early lead to the ineffectiveness of the body's defense against disease progression. With a progressive form of the disease, the patient, as a rule, has been ill for a long time and the treatment undertaken has led to the depletion of the body’s own resources and to the ineffectiveness of hormonal therapy. The disease becomes, as it were, incurable - it does not go away on its own, and drugs that could help end the autoimmune inflammation in the brain no longer help.
Hormone therapy, despite its severe health consequences, is used because it is considered indispensable for exacerbation of MS, while other treatment methods that can stop the progression of the disease are ignored as they have not undergone multicenter randomized trials. But the drugs introduced into the standard treatment for MS (which have undergone expensive testing) do not even allow to slow down MS and only benefit their manufacturers and distributors.
More than 30 years of experience in treating patients with progressive forms of MS has shown that treatment of MS should be comprehensive and aimed at all pathological changes in the patient’s body. A central place in treatment should be occupied by a method that restores the body’s own protective resources, increases the effectiveness of medications and reduces the pathological consequences of hormone therapy and antibiotics. This method is normoxic therapeutic compression (NLC) developed by us. The combination of NLC with a modern antiviral drug that penetrates the blood-brain barrier has proven to be so effective that it gives hope for victory over this complex disease. The results of using the complex antiviral treatment method we developed undoubtedly testify in favor of the viral nature of MS.
How can viruses cause the development of MS, and why do symptoms of the disease accumulate with age? Symptoms of the disease are associated with the destruction of myelin and damage to pathways and nerves, and as a result, disruption of the transmission of signals from the brain to the periphery. Myelin destruction occurs due to a disruption of the barrier between the brain and blood (blood-brain barrier), which in a healthy body prevents blood lymphocytes from contacting brain matter. When lymphocytes enter the intercellular space of the brain, an autoimmune conflict develops - the brain substance is considered by activated lymphocytes as foreign. Normally, neuroviruses that enter the brain are destroyed by brain cells by histiocytes, but when the brain’s own defense is ineffective, neuroviruses begin to multiply in the histiocytes, surrounding themselves in an area where blood circulation is reduced due to thrombosis of small veins and subsequent swelling of the brain tissue surrounding the site of virus reproduction. Blood lymphocytes, penetrating into the brain, begin to actively fight neuroviruses, but as a result of this constant inflammatory process, myelin is destroyed and myelin formation in the brain is disrupted, and neuroviruses remain in the area of reduced blood circulation. The process of myelin destruction begins to prevail over its restoration, and clinical symptoms of MS appear, which at first are easily eliminated. On MRI, there are foci of reduced density in the area where viruses multiply, associated with swelling around foci of inflammation, but not with the fact that the brain in this area has undergone destruction. With active autoimmune inflammation, contrast introduced into the blood during MRI penetrates into these lesions, indicating a violation of the permeability of the barrier between the brain and blood.
Factors that contribute to disruption of the barrier between the brain and blood vessels - infections, injuries, hypothermia, stress - usually cause an exacerbation of MS.
At what point does the complex of pathological changes in MS become irreversible and what determines the severity of the disease? The number of inflammatory lesions on MRI often does not correlate with the severity of neurological symptoms, but increases significantly with the course of the disease. As with other autoimmune diseases, in MS there is always a violation of energy metabolism in the form of a genetic or acquired defect in mitochondrial oxidation. Such diseases are called mitochondrial or age-related because the number of abnormal mitochondria tends to accumulate with age. The impaired immunity observed in MS is caused not only by the presence of chronic infections, viruses and pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, but also by a defect in energy metabolism.
With progressive MS, characteristic changes in the immune system are observed, which are a consequence of the accumulation of pathological changes in the brain in MS and indicate, on the one hand, the presence of an inflammatory process, and on the other, the ineffectiveness of the body’s fight against infections and viruses. In this case, impaired energy metabolism and impaired microcirculation determine a decrease in immunity. Therefore, the use of normoxic therapeutic compression (NLC) is always accompanied by a noticeable improvement in the condition of patients with MS and a slowdown in the progression of the disease. Therapeutic compression with antioxidants restores energy metabolism by increasing the proportion of healthy mitochondria and improves microcirculation, so the therapeutic aftereffect of the method is long-lasting. However, only when NLC was combined with a modern antiviral drug that penetrates the blood-brain barrier, the effectiveness of treating MS increased so much that it became possible to even “defeat multiple sclerosis” with timely use of the method.
Treatment for MS should be aimed at reducing autoimmune inflammation in the brain. To do this, it is necessary to restore the blood-brain barrier, restore energy metabolism and microcirculation, and, if possible, destroy viruses that have entered the brain. Naturally, this difficult task is unattainable using only pulsed doses of hormones.
An analysis of many years of experience in treating MS in our clinic indicates the high effectiveness and long-term therapeutic aftereffect of the MS treatment method we developed.
Of 85 patients with progressive MS (protracted exacerbation, primary and secondary progressive MS) who received a course of complex antiviral therapy in combination with normoxic therapeutic compression (NLC), 55.3% experienced complete or significant recovery of lost functions; 37.6% experienced a noticeable regression of neurological symptoms and only 7.1% showed slight positive dynamics. No negative dynamics were observed.
The control group consisted of 10 patients with multiple sclerosis who received complex antiviral treatment without NLC and hormones. We did not detect any noticeable regression of symptoms in the control group. When using NLC without complex antiviral treatment, complete regression of symptoms was not observed in any patient with secondary or primary progressive forms of MS (out of 115 patients we observed previously).
When using a new method of treating MS, as a rule, each session of therapeutic compression leads to a decrease in the severity of neurological symptoms. Even in severe cases of the disease and in long-term ill patients, the therapeutic effect of the method increases with repeated courses of treatment. Complete and long-term remission after 1-2 courses of treatment was observed, as a rule, with a short duration of the disease or its remitting course. Repeated courses for severe forms of the disease were carried out by us after 3, 6 and 12 months and were accompanied by an increase in the therapeutic effect. In case of primary and secondary progression of MS, a long-term therapeutic aftereffect of the method of 6 or more months was observed, when the symptoms of the disease did not increase. Even in long-term ill patients with MS, normalization of the immune status, a significant decrease in the number of lesions accumulating contrast on MRI, and a noticeable regression of neurological and cognitive impairment were observed. The effectiveness of the new method of treating MS, used in our clinic, is confirmed by a noticeable restoration of immunity and a significant decrease in apoptosis (CD 95), i.e. stopping or slowing down the neurodegenerative (destructive) process. The new method not only makes it possible to change the course of MS, but also restores performance and significantly improves the quality of life.
The pronounced and persistent therapeutic effect of complex antiviral treatment in combination with therapeutic compression in MS undoubtedly indicates that neuroviruses remaining in the brain are the cause of MS. A decrease in the titer of antiviral antibodies after a course of treatment, including NLC and complex antiviral therapy, correlating with the severity of the therapeutic effect of the method, indicates the leading role of antiviral therapy in achieving a therapeutic effect. On the other hand, the absence of noticeable regression of neurological symptoms and dynamics of antiviral antibodies with the isolated use of antiviral therapy indicates the important role of NLC in the complex treatment of MS.
The presence of viruses remaining in the nervous system undoubtedly causes primary and secondary immunity disorders, which are apparently impossible to restore without antiviral drugs that penetrate the brain. Why are the use of these drugs not accompanied by an independent therapeutic effect in MS? Apparently, due to disruption of microcirculation and even blood stasis in the area surrounding the focus of inflammation in the brain, and the associated deterioration in the access of drugs to the area of the brain where viruses are stored. Improved microcirculation in the area of incomplete autoimmune inflammation caused by NLC may be the reason for such a significant antiviral effect of the new method.
Normoxic therapeutic compression with antioxidants restores microcirculation and energy metabolism, which allows you to end autoimmune inflammation and restore the brain’s own protective functions in the fight against hidden viruses. The absence of noticeable progression of the disease when using therapeutic compression was noticed by us earlier, i.e., with regular use of the method, the disease is, as it were, limited to the range of existing pathological changes, which can resume during an exacerbation, often even to a lesser extent than previously observed.
Studies have shown that NLC is a pathogenetic therapy for MS, aimed at restoring the barrier properties of cell membranes. The combination of NLC with etiological therapy aimed at destroying viruses that persist in the brain can significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment for patients with MS and even talk about the possibility of “defeating multiple sclerosis,” since after repeated courses of treatment it is possible to predict the absence of exacerbations of the disease.
Clinical experience has shown that treatment of MS should be aimed at eliminating all pathological changes in the patient’s body. For active inflammation in the brain, indicating a disruption of the blood-brain barrier, the treatment complex included short courses of small doses of dexamethasone. Antibiotics and symptomatic therapy were used in complex treatment for almost all patients with MS.
Thus, early, active complex antiviral therapy in combination with NLC can significantly increase the effectiveness of MS treatment, stop the progression of the disease at the very beginning of the disease and significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients with MS. Repeated courses of complex antiviral therapy provide long-term and complete remission of MS without neurological and psychological disorders and exacerbations.
Pulse therapy
In cases of exacerbation of symptoms of multiple sclerosis or the appearance of new symptoms, pulse therapy is used - intravenous administration of loading doses of a hormonal drug.
The best results are shown by the administration of 6-methylprednisolone. This drug has powerful anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous and immunomodulatory effects.
The hormonal agent is administered intravenously through a dropper. The duration of the course is from 3 to 7 days. Pulse therapy at the international clinic Medica24 is carried out according to protocols that have proven their effectiveness based on the results of clinical randomized studies, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
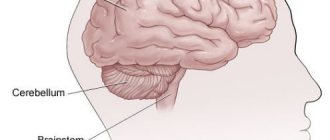
Indications for pulse therapy are symptoms of damage to the brain stem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. The goal of treatment is to relieve acute symptoms, improve the condition and slow down the development of multiple sclerosis.
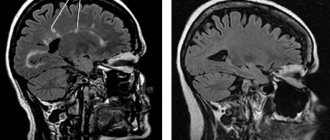
The decision to conduct pulse therapy at the Medica24 international clinic is made on the basis of MRI data (with a contrast agent), in the presence of active foci of demyelination, the appearance of new foci or the growth of old ones. MRI data must be confirmed by changes in the clinical picture of the disease.
As a result of pulse therapy for multiple sclerosis at the international clinic Medica24, a significant improvement in the condition is achieved - dizziness, unsteadiness of gait, numbness and weakness of the arms and legs disappear, and vision improves.
The development of the disease slows down, regression of symptoms and even achievement of remission is possible.
On the other hand, the use of loading doses of a corticosteroid may lead to side effects. Some of them are minor - insomnia, slight euphoria or anxiety, nausea, hiccups, headache, increased appetite. Others are more dangerous - cardiac arrhythmia, hyperglycemia, sudden fluctuations in blood pressure, bleeding.
Therefore, a course of pulse therapy for multiple sclerosis is best carried out in a hospital setting, where the patient is under constant medical supervision. This allows you to adjust the treatment course in time and eliminate side effects.
The international clinic Medica24 has extensive experience in treating multiple sclerosis with loading doses of glucocorticoids, achieving maximum results with minimal side effects and timely correction of the patient’s condition.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis in women and men
The severity of manifestations of multiple sclerosis varies. Most people experience the following:
- Unusual sensations in different areas of the body. This may be numbness, unpleasant tingling (“like needles”), burning, itching. Similar signs occur in approximately 50% of patients.
- Bladder disorders. Occurs in approximately 80% of patients. Often has the urge to go to the toilet, including at night, and is bothered by the feeling as if the bladder is not completely emptied.
- Intestinal disorders. Manifests itself in the form of constipation.
- Walking disorder. The disease is often accompanied by weakness and muscle cramps, along with numbness in the legs, dizziness, and problems maintaining balance. This makes it difficult to walk.
- Dizziness.
- Constant fatigue. It is especially disturbing in the afternoon, even if the person had rested all day before. The patient may feel tired even after sleep. This manifests itself in the form of difficulty inhibited thinking, muscle weakness, and drowsiness. This condition occurs in approximately 80% of patients.
- Muscle spasms. Occur in approximately 40% of cases, usually affecting the leg muscles. Feelings range from tension, stiffness to painful spasms.
- Problems with thinking. About 50% of patients are bothered by symptoms such as slow thinking, memory impairment, and decreased concentration.
- Speech disorders. The patient may speak through his nose, slurred, and take long breaks between words.
- Swallowing disorders. Occurs in the later stages of the disease.
- Problems in the intimate sphere. Signs of multiple sclerosis in women may include vaginal dryness, and in men - weakening of erections.
Fortunately, many symptoms of multiple sclerosis have effective treatments and can be kept under control. To do this, you need to constantly be under the supervision of a neurologist and conscientiously follow all prescriptions and recommendations.
If symptoms from this list appear, especially if they continue for a long time, you should immediately contact an experienced neurologist. It may not be multiple sclerosis, but there is always a risk, and if the diagnosis is confirmed, it is better to start treatment immediately.
How does multiple sclerosis occur?
Due to remyelination, the disease occurs with exacerbations and remissions for a long time. The above symptoms appear abruptly, but subside over time. As MS develops, symptoms do not completely regress, and a persistent neurological deficit develops.
There are also more severe forms of the disease:
- there is no deterioration and subsequent improvement, a neurological deficit forms immediately and gradually worsens (progressive course);
- demyelination occurs very quickly and affects large areas of the brain (this condition requires immediate treatment as it can be fatal).
Causes of multiple sclerosis in men and women: factors that increase risks
There is no clear reason why some people develop the disease and others do not. However, there are some known risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing multiple sclerosis:
- Female. For unknown reasons, women get sick twice as often as men.
- Age. The first signs of the disease usually appear at the age of 15-60 years (most often at 20-40 years).
- Some infections. For example, it is known that the risks are increased by infectious mononucleosis, a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus.
- Having sick relatives. You are at greater risk if one of your parents or siblings has already been diagnosed with multiple sclerosis.
- Ethnicity. The disease is most common among the indigenous people of Northern Europe. Asians, Africans and American Indians have the lowest risks.
- Some diseases. The risk is increased by certain thyroid diseases, inflammatory pathologies in the intestines, and type I diabetes.
- Smoking. Smokers develop MS more often than non-smokers.
If you or your relative experience the first suspicious symptoms, immediately contact an experienced neurologist.
Frequently asked questions about multiple sclerosis
Is multiple sclerosis a hereditary disease?
-No. Multiple sclerosis is not passed on from parents to children, but it is possible that more than one family member develops the disease. To date, about 150 DNA sections have been identified that are thought to play a role in the development of the disease, but the presence of each of them only slightly increases the risk of developing the disease.
Is it true that a patient with multiple sclerosis is constantly getting worse?
—No, the condition of a patient with multiple sclerosis can change in different ways: worsen, improve, or remain unchanged.
What determines the frequency of exacerbations of multiple sclerosis?
Convincing evidence has been obtained that exacerbations can be triggered by infections and psycho-emotional stress. There is preliminary data on the safety of vaccinations against influenza, hepatitis B and tetanus. Surgeries, general and epidural anesthesia, and injuries do not increase the risk of exacerbations. The frequency of exacerbations decreases during pregnancy and full breastfeeding. Exposure to direct sunlight and high levels of vitamin D reduce the frequency of exacerbations. Smoking has been shown to increase the rate of disease progression (both clinically and as measured by magnetic resonance imaging).
It has been suggested, but not proven, that moderate alcohol consumption and exercise may reduce the severity of brain damage.
Is there really no cure for multiple sclerosis?
—It remains unknown why multiple sclerosis develops. Scientists first need to establish the cause of multiple sclerosis, and then move on to searching for a cure. Despite this, there are treatments available to slow the progression of the disease's symptoms. Their regular use affects the immune system, reducing the severity and frequency of exacerbations.
How to solve your psychological problems associated with the disease?
Help your loved ones come to terms with the idea that you have an illness.
Find someone other than you to tell them about your illness.
Tell them how you are feeling, both physically and emotionally.
Help your loved ones understand and express their emotions, do not try to influence their feelings.
Discuss important decisions with your loved ones, allow them to take part in your destiny.
If necessary, contact professional psychologists.
How does intimate life change with multiple sclerosis?
Communication with a loved one is an important component of a healthy, fulfilling life. It should not stop in a couple if one of the partners has multiple sclerosis.
The disease may impair the ability or desire to have sexual relations.
Sexual desire arises in the brain, then signals are sent to the genitals through the spinal cord and nerves. Changes in the body caused by multiple sclerosis can cause both physical (spasticity, erectile dysfunction or lubrication) and psycho-emotional problems (lack of sexual desire, feelings of one’s own sexual attractiveness).
How do oral contraceptives affect the course of multiple sclerosis?
According to a small study, taking oral contraceptives in combination with immunosuppressive therapy led to a decrease in the severity and rate of progression of the disease.
It has also been shown that taking oral contraceptives is associated with a later onset of the first symptoms of multiple sclerosis. The longer the duration of oral contraceptive use, the older the age at which the first symptoms of the disease appeared.
Multiple sclerosis: causes of disease symptoms
Sometimes there are three groups of manifestations of multiple sclerosis, each of which is caused by certain reasons:
- Initial disorders are associated with damage by the immune system to the sheaths of nerve fibers. As a result, the passage of nerve impulses is disrupted, and corresponding neurological disorders occur.
- In turn, this leads to disruption of the functioning of internal organs and the development of secondary disorders. For example, if the bladder stops functioning normally, the risk of genitourinary tract infections increases.
- All this cannot but affect the quality of life, performance, and social adaptation of a person. The resulting disorders lead to psychological problems.
Treatment should target all of these causative factors in multiple sclerosis. It is necessary to keep the main symptoms of the disease under control, combat complications from internal organs and carry out rehabilitation treatment, and strive to ensure that the sick person lives as full a life as possible.
Since the causes of the disease in multiple sclerosis are not fully known, there are no effective methods of prevention. It is extremely important to notice the first symptoms in time and immediately consult a doctor. If you need a consultation with a neurologist, you can make an appointment with a specialist at the international clinic of modern neurology Medica24 around the clock. Just call.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
An appointment with a doctor begins with a conversation. The neurologist needs to figure out what symptoms bother the patient, when and how they arise, what provokes them, whether there are exacerbations, and how the condition changes over time. A neurological examination is then performed.
It is important that the neurologist carefully evaluates the patient’s condition and excludes all other possible diseases.
In a relapsing-remitting course, when the disease periodically goes through stages of exacerbation and improvement, the diagnosis is relatively easy to establish based on the clinical picture of multiple sclerosis and MRI data. If the patient is concerned about unusual symptoms or the disease is constantly progressing, other tests may be needed.
Causes of multiple sclerosis
There is still no clear understanding of the causes of MS. It is believed that the disease is multifactorial and is caused by a combination of many factors, such as genetic predisposition, geography and ecology of the place of residence, and some viruses. These factors provoke the production of antibodies and facilitate their penetration from the blood into the tissues of the nervous system.
In MS, antibodies attack the myelin sheath of neurons, demyelination of nerve fibers occurs, and signal transmission between neurons is disrupted. The body is able to fight the disease for a long time - the myelin is restored ( remyelination ), and the signal again passes through the fibers. Symptoms appear and disappear; these processes can be observed in almost any part of the brain or spinal cord. The symptoms are dispersed in time and space, which explains the name of the disease.
What studies and tests help diagnose multiple sclerosis?
For diagnostic purposes, the doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- Blood tests. Helps rule out other diseases. There are no specific substances that would indicate multiple sclerosis; scientists are currently busy developing such diagnostic tests.
- Spinal tap. Between two vertebrae in the lower back, a needle is inserted into the space around the spinal cord and a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid is obtained for analysis. It detects antibodies associated with MS, which also helps rule out other diseases.
- MRI. The test reveals damaged areas in the brain and spinal cord. MRI with contrast is sometimes used.
- Evoked potential method. During the study, a special device records electrical signals that arise in the nervous system in response to stimuli.
Under no circumstances should you engage in self-diagnosis. Visit a neurologist.
Is there a way to prevent multiple sclerosis?
Scientists do not fully know the causes of the disease, so there is no effective prevention of multiple sclerosis. But you can minimize the risks of many neurological, and not only, diseases if you lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well, treat any diseases and infections in a timely manner, stop smoking and minimize alcohol consumption.
If any disorders of the nervous system occur, it is better to immediately contact the neurological center and consult a doctor. If you need a consultation with a neurologist, make an appointment with a specialist right now by calling +7. We can also provide diagnostics.
The material was prepared by Natalya Yurievna, a neurologist at the international clinic Medica24, Candidate of Medical Sciences Lasch.