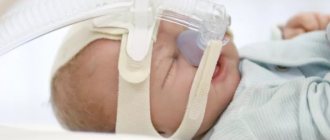
According to statistics, 2% of parents experience apnea in newborns - a disorder in which the baby stops breathing for 20 seconds or more. Apnea occurs more often in premature babies. According to various estimates, from a quarter to a half of babies born at 37-42 weeks suffer from OSA (obstructive sleep apnea syndrome).
Norm
Uneven breathing in newborns during sleep is not always a problem. Parents should not worry if breathing stops:
- occur no more than once per hour;
- breathing in a sleeping child does not cause effort;
- the baby breathes evenly and deeply during sleep;
- holding your breath for less than 5 seconds;
- the baby’s heart does not slow down, the pulse does not subside, the skin does not change color.
If your baby’s breathing causes concern, you should find time and visit a pediatric somnologist – a doctor who treats sleep disorders.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNS
If a child holds his breath for a few seconds during sleep, this does not indicate apnea.
You can suspect a symptom if the baby:
- often “forgets” to breathe in his sleep - 10-15 times per hour;
- snores, coughs and grunts in his sleep;
- often tosses and turns, sleeps with his neck stretched out;
- the child breathes unevenly in his sleep, his breathing is intermittent;
- suffers from enuresis;
- breathes through the mouth during the day: this is how a small organism tries to compensate for oxygen starvation;
- The sleeping person's chest remains practically motionless when inhaling.
Apnea should not be confused with periodic holding of a child’s breath during sleep when:
- The periodic delay interval usually does not last longer than 10 seconds.
- The sleeper is able to control inhalation and exhalation independently.
Most often, a baby before and after a year, as well as a child 3-6 years old, holds his breath in his sleep.
The disease is dangerous because it does not manifest itself in any way during wakefulness - children breathe normally. The pathology continues to progress.
Advice! In the first months after the baby is born, parents should carefully listen to the baby’s night breathing during sleep.
Parents should definitely notify their pediatrician if they suspect sleep apnea in their child.
Kinds
Infant apnea - what is it? Experts distinguish several types of this pathology.
A baby born at term may experience the following types of apnea:
- central – short-term cessation of breathing, which occurs involuntarily in infants;
- obstructive - the child stops breathing due to obstruction (blockage) of the airways.
Premature newborns may experience:
- primary apnea - observed due to difficulty in lung function immediately after the baby is born or 3-6 months after birth;
- secondary – respiratory arrest after primary ventilation.
Secondary apnea is characterized not only by cessation of breathing, but also by a decrease in pressure and a general weakening of muscle tone. This condition can provoke the further development of complications.
Sleep apnea - symptoms and treatment
Therapy for OSA is aimed at restoring oxygen levels, eliminating snoring, increasing alertness during the day, reducing respiratory arrest and normalizing sleep. In the modern world, there is a wide range of therapeutic measures, including surgical and conservative treatment, as well as lifestyle modification (weight loss, first of all, etc.). Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a full diagnosis to determine the severity of OSA.
Timely treatment begins to lead to a significant reduction in clinical symptoms, and most importantly, to preventing the progression of the disease.
Surgical methods include ENT interventions (uvulopalatoplasty, etc.) and orthognathic operations. Uvulopalatoplasty is effective for uncomplicated snoring (isolated, extremely rare) and for mild, less often moderate, OSA. It should be performed after a thorough additional examination (polysomnography, sleependoscopy). In severe cases of OSA, ENT surgery is contraindicated due to low effectiveness and sometimes worsening of the condition.
Surgeries on the upper and lower jaw (orthognathic) can be used for any severity of the disease. They are quite effective, but the preparation for them is very long (about a year), and the operation itself is very labor-intensive. This method can be used if the patient refuses CPAP therapy.
Intraoral devices are used as an alternative to orthognathy. Their goal, like surgical treatment methods, is to expand the airways at the level of obstruction. Abroad, there is a method of electrical stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve[12], which has proven effective for any severity of the disease, but it is very expensive and is currently not available in Russia.
However, the main treatment method today is non-invasive continuous positive pressure ventilation (CPAP therapy). The essence of this therapy is to create an air flow that prevents the collapse of the airways.[10] At the beginning of therapy, a trial course is conducted to select the operating mode of the device and train the patient. After which the patient uses the device at home independently and only at night. This method is recommended for patients with moderate and severe forms of OSA and has virtually no contraindications. In addition to its main goal - eliminating respiratory arrest - using this method it is possible to significantly reduce weight and reduce the number of antihypertensive drugs for resistant arterial hypertension.[13]
Symptoms
The main alarm signal is interruptions in breathing or stopping it for more than 20 seconds. You should urgently make an appointment with a doctor if your breathing pattern does not fit into the norm, and if at least one of the following symptoms is observed:
- baby's skin becomes paler or bluer;
- cyanosis appears in the mouth and nose area due to oxygen deficiency;
- snoring (indicates an obstructive type of apnea);
- The baby suffers from restless sleep not for the first night;
- enuresis (indicates disruptions in the functions of the central nervous system);
- profuse sweating occurs during sleep;
- the child convulsively gasps for air, constantly breathes through his mouth (both in sleep and while awake);
- cannot restore smooth breathing after an attack.
Due to constant lack of sleep, the baby becomes capricious, constantly cries, and gets irritated.
The main symptoms of apnea in children born prematurely include:
- episodic interruption of breathing with pauses of 20 seconds or more;
- blue/pale skin;
- slowing of the pulse (in infants it can be heard more clearly on the shoulder or fontanelle).
Doctors are well aware of when apnea in premature babies goes away, unless there are complicating factors. This occurs by 40-45 weeks of life as the nervous and respiratory systems, as well as the respiratory control center, are finally formed.
It is more difficult to understand until what age the problem will last. Seizures can occur both in infants in the first weeks of life and in children older than six months. The prognosis is given only after a complete diagnosis.
Apnea in children under one year of age: why it occurs, dangerous or not dangerous
Due to insufficient morphological and functional development of the respiratory system of a child born prematurely, he often has respiratory arrests for 20 seconds or more (pauses can be shorter), accompanied by a slow heart rate (bradycardia) and a decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood.
Apnea in premature infants is one of the most common disorders that require the newborn to be in the intensive care unit under constant medical supervision. The earlier the child was born, the more often the episodes of apnea occur and the longer their duration.
The danger of apnea of prematurity is not only the risk of sudden death due to the fact that breathing does not resume, but also the insufficient supply of oxygen to the brain tissue. A set of special measures eliminates this problem.
Neonatologists cope with apnea of prematurity using CPAP machines and masks for infants working under special programs
As a rule, the respiratory system and the mechanisms for regulating its work in prematurely born newborns are fully formed and rebuilt by 37-40 weeks from the day of conception. That is, by the time the child would have been born if the mother had carried him to term. However, in very premature infants, apnea often occurs in a later period.
Episodes of sleep apnea in full-term infants under one year of age also occur and may be a normal variant. In the first year of life, short-term pauses in breathing during night sleep should not alarm parents if:
- their number does not exceed one episode per hour;
- the baby breathes effortlessly, deeply and evenly;
- apnea lasts no more than 5 seconds;
- the child does not show anxiety, his heartbeat does not slow down, and his skin does not appear blue.
However, if you notice that during sleep your baby stops breathing for some period of time, it is best and most correct to find the opportunity to undergo a special examination - polysomnography. Or, at a minimum, get an appointment with a specialized “sleep specialist” - a pediatric somnologist.
Causes and consequences
In newborns, pathology can develop due to problems:
- with lungs or heart;
- due to disorders of the respiratory functions of the central nervous system;
- due to airway obstruction.
In premature babies, the syndrome often develops due to an immature nervous system. The reasons may also be:
- unsuccessful ventilation after primary apnea;
- birth injury;
- congenital pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- intrauterine infections affecting the fetal brain;
- immaturity of the laryngeal muscles;
- craniofacial pathologies;
- weak muscular corset of the upper respiratory tract.
In addition, apnea is often a complication of hereditary diseases, as well as diseases that the child has already had - meningitis, inflammation of the adenoids, asphyxia, oxygen starvation, etc.
Breathing problems are extremely dangerous for the baby's health. They can also threaten his life. When breathing stops for 20 seconds, neurons begin to die. With a longer absence of oxygen, irreversible problems begin with all vital organs - heart, lungs, bronchi.
In children older than six months, neurological problems develop with chronic apnea. The child cannot concentrate. Memory deteriorates. With hyperactivity, it is extremely difficult for a child to find contact with other children. There are problems with socialization on the playground or in the nursery.
TYPES AND REASONS
There are several explanations for why a child holds his breath during sleep. The characteristics of the pathology depend on its type.
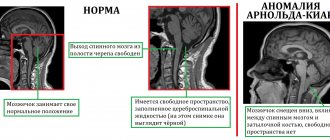
Central apnea
Diagnosed in 60% of premature babies born at 35 weeks or earlier weighing 2.5 kg or less. Pathology appears as a result of dysfunctions of the respiratory center. Located in the lower part of the brain. This center does not control the breathing muscles in children with sleep apnea. This is why a child often holds his breath for a long time during sleep at night.
Reasons for development:
- Immature nervous system of the baby;
- Hypoglycemic syndrome (low blood glucose concentration);
- Impaired pulmonary gas exchange;
- Seizures in epilepsy;
- Diseases caused by bacteria and viruses;
- Anemia;
- Smoking during pregnancy.
Interestingly, with central apnea, breathing consists only of exhalation, and inhalation seems to be lost. For this reason, a child’s breathing stops during sleep for quite a long time.
Obstructive apnea
With the obstructive type of deviation, the child breathes poorly during sleep due to narrowing of the airways. The baby sobs sharply when inhaling and often wakes up from this (several times a night). The disease often develops due to anatomical problems:
- Macroglossia. This is the name for congenital pathology of the tongue, when the organ of speech is enlarged to critical sizes.
- "Cleft lip"
- Achondroplasia is an abnormality in the development of the bones of the skull.
- Laryngeal muscle dysfunction.
- Enlarged tonsils, tonsils
- Stridor (from Latin “hissing”) is an excessively narrow larynx.
- Obesity.
Obstructive apnea can make itself felt at any age. Most often, preschoolers - children from 2 to 7 years old - suffer from its manifestations.
Mixed
The term “mixed apnea” indicates a mixture of signs of the central and obstructive type of pathology. At the same time, the central type appears at the very beginning, gradually developing into airway obstruction. This type is rare and difficult to diagnose.
Mixed apnea is often observed as a consequence of a number of problems:
- impaired body thermoregulation;
- obesity;
- disturbed sodium-calcium balance.
Intermittent breathing during sleep with a mixed version of the disease is often observed in newborns who frequently regurgitate.
Diagnostics
Sleep apnea is not a death sentence, and to understand how to treat it, it is enough to consult a doctor. Parents of a premature baby should make an appointment with a neonatologist. The rest go to a pediatrician, who will refer you to a specialist. The task of the otolaryngologist, neurologist, pulmonologist, cardiologist will be to identify the causes that provoked the disorders.
In newborns
Polysomnography is the main method that helps to identify pathology in children born at term. Diagnosis is carried out during sleep. Electrodes and sensors are connected to the baby’s body, which record the functioning of the respiratory system. The doctor visually monitors breathing pauses, their number, frequency and duration.
Additional examinations are carried out to identify the causes. For example, if you suspect:
- For obstructive apnea, anterior rhinoscopy is prescribed, which makes it possible to detect the causes of complicated nasal breathing;
- for disturbances in the functioning of the heart - ECG, ultrasound of the heart and brain;
- for pneumonia - radiography.
The doctor may also prescribe an MRI, CT scan, brain encephalogram and other examinations.
In premature babies
Most often, premature babies suffer from central apnea. Therefore, neurosonography becomes the main diagnostic method. Otherwise - ultrasound examination of the brain. The brain stem, where the respiratory center is located, is especially carefully studied. The doctor analyzes the nature and dynamics of brain processes and makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathologies.
If abnormalities are detected, a lumbar puncture is prescribed. With its help, they look for hemorrhages or inflammation in the brain.
DIAGNOSIS OF PATHOLOGY
At the slightest suspicion, parents should act together with doctors. The latter must certainly determine the diagnosis and predict treatment.
You shouldn’t put off diagnosing your baby’s condition and hope that your child’s nighttime sleep problems will go away on their own. Long pauses in breathing may indicate serious illness.
Breath holding during sleep in newborns and older children can be determined in the following ways:
- Home surveillance. Attentive parents, of course, are able to track how the child’s breathing becomes confused during sleep. If the delays are frequent and long, most likely we are talking about apnea. To track pauses with accuracy, it is better to time the duration of breathing stops using a stopwatch. However, such diagnostics may not always be accurate. A mother who is tired during the day may sleep very soundly at night and will not be able to track how often her baby holds his breath during sleep. A young patient should definitely be shown to a doctor.
- Inpatient examination (polysomnography). Helps monitor the condition of all systems of the patient’s body. In this way, the doctor determines why the child “forgets” to breathe in his sleep.
Polysomnography helps identify the following indicators:
- frequency of inhalations and exhalations;
- work of the cardiovascular system (heart rhythm, heart rate, etc.);
- electrical processes occurring in the brain;
- duration of the rapid eye movement phase;
During the examination, the patient is under continuous medical supervision. The child must also be examined by a neurologist, an ENT specialist and an endocrinologist. Only on the basis of the conclusions of these specialists is the child given a final diagnosis.
What to do for apnea: first aid
During an attack, parents should provide first aid to the baby by following simple steps:
- Take the baby in your arms, stroke or pat him on the back, rub his arms, legs, earlobes, tickle his heels or pat them.
- Spray your baby with cool water.
- To make breathing easier, place your baby on his tummy with his head turned to the side.
If the baby's breathing has not returned, perform artificial respiration:
- Place your baby on a hard surface on his back.
- Place a cushion from a sheet or towel under the shoulder blades so that the head tilts back slightly.
- Hold your head and inhale air into your mouth and nose at the same time. The air portions should be very small.
- If the child does not wake up after 6-8 breaths, perform chest compressions.
Treatment
During hospitalization, doctors perform the necessary manipulations to stabilize the baby’s condition. Premature babies are placed in an incubator. If the attacks recur there, the child is connected to a ventilator.
Medication prescriptions and clinical recommendations are made taking into account the causes of the disease. For example, to treat infant apnea caused by excessively enlarged adenoids, an ENT specialist prescribes surgery to remove them.
TREATMENT OF THE DISEASE
The causes of sleep apnea in a child may vary depending on the age of the child.
Accordingly, the treatment of nocturnal disorders should also be selected taking into account the age characteristics of children with problems with breath holding during sleep.
In newborns
Premature babies are placed in pressure chambers. Here, doctors constantly monitor the breathing of newborns and provide assistance in emergency situations.
The initial phase of treatment is the use of tactile stimulation. The doctor taps and slaps the baby's body, activating his breathing.
If the attacks are prolonged and repeated frequently, pulmonary stimulation is used on the newborn.
When the attacks are reduced and no complications are observed, the child is discharged. Doctor's supervision continues at home.
In preschoolers
When a child from 2 to 5-6 years old holds his breath during sleep often and for a long time, CPAP therapy is applied to him.
The procedure helps support the walls of the airways by accumulating air under high pressure.
Before going to bed, a mask is placed on the little patient’s face with a hose running from it to supply air. The process is controlled by a doctor. CPAP therapy can last for months or even years.
When the disease is complicated by additional pathologies, doctors recommend surgical correction of the problem. In such cases, the following types of operations are relevant:
- correction of the uvula;
- removal of adenoids;
- correction of the shape of the nasal septum;
- elimination of respiratory tract pathologies.
Operations are effective in 80-100% of cases. The next check of the little patient is carried out after 1-2 months.
In school-age children
If sleep apnea occurs suddenly in adolescents, it should be seen by a doctor to determine the cause of the respiratory system disorder.
After diagnosis, the same treatment methods are used for schoolchildren as for preschoolers: drug or CPAP therapy, surgical intervention.
Respiratory disorders are a serious syndrome that requires immediate medical intervention. But first you need to make sure that the child is not just breathing intermittently, but literally forgetting to inhale and exhale. You can track this process by observing your baby while he sleeps or by visiting a hospital for diagnosis. Therapy takes into account the age of the young patient.
Text author: Irina RALLO
Prevention
Simple recommendations will help prevent the development of apnea in infancy:
- it is necessary to regularly ventilate the room where the child sleeps;
- the air in the children's bedroom should not be excessively dry;
- Before going to bed, the child should not be overheated;
- bedding must be selected correctly: a hard thin mattress, a low pillow, pillow filling and blankets made from natural materials (filling made from natural bird feathers is not acceptable);
- It is prohibited to use aerosols (both household products and perfumes) near the baby;
- tobacco smoke is strictly prohibited.
To control a child's sleep in the first months of life, it is worth placing his crib in the parents' bedroom.