It has been proven that the female brain is approximately 8-12 percent smaller than the male brain, which, however, does not mean that the fairer sex is naturally dumber. Nevertheless, there is a difference. Male and female brains perceive some things differently. Researchers have learned why this happens and what is the main difference between the brains of men and women.
Are there differences?
For centuries, debates about the difference in thinking, behavior and perception of situations between men and women have not subsided. But if earlier discussions were more like accusations with nothing behind them, today this topic can be seriously debated, based on real scientific facts.
For the most part, gender differences between men and women are the result of the structure and functioning of the brain. It is on this that the cognitive and behavioral differences inherent in both sexes depend. There was a time when researchers even talked about the “field” of the brain. Proponents of this theory argued that the brains of all men work according to a generalized scheme, while the gray matter of all women has its own unified “program”.
Content:
- Are there differences?
- Weight and volume
- Development of the hemispheres
- Verbal skills
- Perception
- Stress
- Memory
- Teamwork
- Sexual behavior
- Our brains shrink in different ways
- So why are we so different
True, over time this theory had to be abandoned. This is because, as it turns out, there are almost no purely “female” or purely “male” brain types in nature. Although scientists do not deny the fact that the “control center” of the weaker and stronger sex has certain gender characteristics.
An international team of researchers observed the behavior of almost 500 thousand people of different ages for many years, and also studied approximately 2.5 thousand MRI images of the brains of men and women aged 44 to 77 years. This allowed scientists to make a number of amazing discoveries. Experts were able to examine and measure 68 different areas of the central nervous system. The results showed that women tend to have a thicker cerebral cortex than men, but the stronger sex has a larger brain.
Neuroanatomical features of the central nervous system
According to research, a man's brain is 8-15% larger in volume than a woman's (regardless of age). Accordingly, males have a larger volume of neuronal formations and conductive structures (neural networks). The processes of formation and development of the nervous system in women proceed faster.
A woman’s brain differs from its male counterpart in a more developed cortical region responsible for regulating emotions. Representatives of the male half of humanity have more pronounced interhemispheric asymmetry. The rates of development of central nervous system structures differ in both sexes.
General indicators
Unlike the female brain, the male counterpart has a larger volume of gray and white matter. The volume value correlates with growth and body surface area in representatives of both sexes. A pronounced dependence of these values is observed mainly in the group of men.
The dependence is explained by an increase in muscle volume and muscle size, which requires the presence of a sufficient number of neurons and the brain structures formed by them (motor centers, impulse transmission pathways) that ensure muscle contraction and, accordingly, movement. In tall people, an increase in the geometric parameters of the medulla is also due to the need to regulate somatic and autonomic functions.
To maintain blood circulation and the activity of internal organs in a large body, more neurons are needed. An increase in the volume of conductive structures in male and female populations is detected in people of large build, which is associated with large distances between the centers of neuronal networks.
Volume correction
The reasons for many of the differences between female and male brains are related to differences in body size. Researchers note that when analyzing the brain structures of representatives of both sexes with the same volume of the cranium, the differences are leveled out (smoothed out).
The geometric parameters of neural networks and conductive structures depend on the intracranial volume. When studying gender-specific neuroanatomical characteristics, a correction for brain volume or intracranial volume is used.
Rate of formation of brain structures
The difference between the male and female brain lies in the speed of formation and development of the central nervous system. In adolescence, the female brain becomes mature faster; it is so arranged that the volume of the brain matter (cortical layer, subcortical nuclei) increases during the period of growing up, then the amount of gray matter begins to decrease as a result of the maturation process. The lag for men is about 2-3 years.
For example, the caudate nucleus in girls reaches its maximum size by the age of 7.5 years, in boys - by the age of 10 years. Peak values of cortical volume in girls are observed at the age of 11.5 years, in boys - at the age of 14.5 years. The results were obtained using neuroimaging (MRI). The decrease in the amount of gray matter is due to the elimination (elimination) of excess synapses, which is observed in children and adolescents.
According to the results obtained from autopsies (post-mortems), adults have 40% fewer synapses in the cortical layer than children. Volumetric parameters of white matter constantly increase in childhood and adolescence. Transformations in white matter, including the creation of pathways connecting the prefrontal and temporal cortex with distant brain structures, continue until the age of 50.
The formation of conductive structures in girls also occurs faster than in boys. The male brain differs from the female brain in that the changes that occur during the maturation process are more pronounced in it, which emphasizes the intensity of the transformations. For example, in the age period of 6-18 years, the size of gray matter in boys is reduced by 19%, while in girls in the same time period the amount of brain tissue decreases by 4.7%.
The amount of white matter in boys in the same age period increases by 45%, in girls this figure is 17%. The ratio of the amount of brain matter (gray, white) in women is 55% and 37%. According to research results, 50% and 40% are similar in men. A larger brain is characterized by an increased number of neuronal connections, the formation of which involves white matter structures.
Interhemispheric asymmetry
The predominance of the size of the right hemisphere is equally detected in representatives of both sexes (with a more pronounced tendency for the difference in indicators in the group of men). The male group also showed asymmetric gray matter distribution to a greater extent than the female group. The difference between the male and female brain is revealed in cytoarchitectonics (the structure of the cortical layer at the cellular level).
In women, the density of neurons is higher in the medulla of the left hemisphere. In parallel, there is an increase in the proportion of large nerve cells in the morphological structure of the left hemisphere substance. In men, the highest similar indicators are detected in relation to the structures of the right hemisphere.
Regional characteristics
The male brain differs from the female brain in the size of the amygdala and putamen - in the male population these indicators are higher than in the female group. The amygdala is responsible for emotional reactions, including feelings of danger and fear. The density of the substance of the amygdala and globus pallidus is also higher in the male group. In the female group, a larger amount of thalamic substance is detected, in the male population - a larger volume of the cerebellum.
Visual and auditory cortical centers
The difference between the brains of men and women lies in the different levels of cognitive functions. Research shows that men outperform women in the processing and formation of visual patterns. In the female group, an advantage is revealed in the processing and formation of verbal information. In the male population, the size of the area of the visual cortex, which is located in the occipital zone of the head, is larger.
In the female population, the amount of substance in the area of the auditory cortex, which is located in the area of the temporal gyrus, predominates. The quantitative predominance of neurons in the visual cortex in the male population determines an advantage in processing visual-spatial information. In the female population, a thickening of the cortical layer of approximately 0.45 mm is detected in the parietal and temporal zone. Women also have higher frontal gray matter density.
Limbic, paralimbic cortical centers
The brains of men and women differ in the size of the cortical sections responsible for the formation and expression of emotions - in the female population the volume of these structures is larger than in the male group. In both groups, an increase in the volume of substance in the cingulate gyrus on the right (compared to the similar left gyrus) correlates with psychological characteristics of the individual:
- Increased anxiety.
- Excessive worry about possible problems.
- Feeling of fear in conditions of uncertainty.
- Timidity in contact with strangers, shyness.
- Increased fatigue.
Researchers note that an increase in the size of the cingulate gyrus on the right side is associated with such a psychological construct as avoidance of harm, harm, which is more characteristic of women, but is also less common in men. Information about the size of the hippocampus in men and women is contradictory.
Professor A. Ruigrok provides data that indicates an excess amount of gray matter in the hippocampal region in the male population. His colleague V. Caviness revealed an excess in the size of similar sections in girls aged 7-10 years in comparison with indicators in a group of boys of the same age.
Weight and volume
The first and most obvious distinguishing feature between male and female brains is the physiological structure of the organ. Firstly, in men it is about 100 g heavier and also larger in volume. True, researchers often explain this fact not so much by the characteristics of the organ itself, but by the general physiological characteristics of the human body.
Men's bodies are, in principle, larger and more voluminous than women's. This may be why the stronger sex has a larger brain. As evidenced by modern science, this characteristic does not in any way affect cognitive or other abilities. Just remember the brain of a Neanderthal. It was much more significant than that of a modern person. But did that make him smarter? Therefore, experts emphasize that for good brain function, it is not its volume and weight that is important, but the quality of connections between neurons.
It is also interesting that different parts of the male and female brain also differ in parameters. For example, young ladies have a larger right frontal pole, pars triangularis, inferior and middle frontal gyri, temporal plane, anterior part of the cingulate gyrus and left parahippocampal, parietal operculum, insular cortex, thalamus, Heschl's gyrus, precuneus, as well as the lateral part of the occipital cortex. bark. In males, the hippocampus, tonsils, posterior part of the cingulate and anterior part of the parahippocampal gyri, temporal poles, putamen and some areas of the cerebellum are larger in size.
Brain structure
Men on average A meta-analysis of sex differences in human brain structure have a larger volume and higher tissue density in the amygdala of the left hemisphere, hippocampus, cortex, and putamen. Certain areas of the brain are superior to similar areas in women only in volume or density.
The average woman, in turn, boasts a higher density of the frontal pole of the left hemisphere and superior volume of the frontal pole of the right hemisphere, the inferior and middle frontal gyri, the triangular part of the frontal lobe and more.
It would seem that such differences should lead to revolutionary conclusions, but everything remains at the level of unconfirmed assumptions.
For example, a woman is believed to be able to do a hundred things at once, while a man can only focus on one task at a time. The theory was based on the assumption of the Brain Connectivity Study Reveals Striking Differences Between Men and Women that women have better connections between the hemispheres of the brain, while in men neurons are more active in transmitting information within one hemisphere. But research has not confirmed this. Are women better than men at multi-tasking? . In an experiment involving 240 people, men even performed slightly better on multitasking tests than women.
It can definitely be said that men, on average, show the Influence of sex steroids on brain development better results in spatial orientation and performing tasks for rotating figures, while women are superior to them in memorizing objects and their localization. In addition, men are more aggressive and more prone to antisocial behavior.
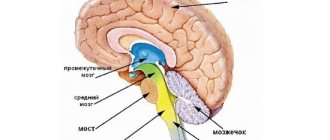
Development of the hemispheres
Many people probably know that the left hemisphere of the brain is responsible for rational thinking, logic and the ability to analyze. The right controls emotions and intuition. Both of them are developed differently in men and women. Most likely, most of those reading these lines thought that the left side of the brain is more developed in males, and the right - in females. And they were wrong.
The hemispheres of the brain in men and women are actually developed differently. Even in the womb, boys’ left hemisphere develops more slowly, but the right hemisphere “gains weight” relatively quickly. Experts suggest that this is due to the effects of testosterone. But for women, both hemispheres are equally involved in their work. As a result, it is easier for women to manage skills characteristic of the left hemisphere (verbal skills, communication), while men have more developed abilities that are controlled by the right side of the brain (active action, competition).
This feature of the brain structure affects the ability of the sexes to demonstrate spatial and social skills. Men are more focused on developing spatial thinking; it is easier for them to perceive reality and quickly coordinate their actions with it. The structure of the female brain is designed for the development of social skills, work in an analytical and intuitive mode, as well as multitasking (performing several tasks at the same time).
The difference also exists at the cellular level. In women's brains, nerve cells are located closer to each other than in men's. And this feature is crucial when it comes to the speed of signal transmission between different parts of the brain. In addition, in men, individual areas within the hemisphere “communicate” more closely, while in women interhemispheric connections are more developed. This is explained by the fact that in young ladies the right and left hemispheres are connected by denser nerve fibers than in men. This factor influences the features that we will discuss further.
Brain size and neural connections
The male brain is on average 10% heavier than the female brain.
Scientists argue that this does not provide any advantages in the intellectual sense: the relative increase in the organ corresponds to the need to control a more massive body, according to the website neboleem.net. The differences in the structure of neural connections in the brains of men and women are much more significant. Among the fair sex, transverse connections predominate, that is, those that connect the right (responsible for logical thinking) and left (responsible for intuition) hemispheres. Therefore, women do not experience any particular problems when solving problems that require the use of both instinct and a cool mind. In the male brain, longitudinal connections predominate, connecting the anterior and posterior parts of the cortex. The exception is the cerebellar zone: in this area, connections between the hemispheres in men are very well developed, which explains the ability of the stronger sex to easily learn complex physical actions and achieve great success in matters that require a high degree of control over their body.
In men, the lower parietal lobe of the brain, which is responsible for mathematics abilities, is better developed, and in women, the areas of both hemispheres that determine the ability to perceive the features of language and use spoken language.
Verbal skills
They even tell jokes about the fact that all women are great lovers of talking. But as it turns out, the desire to chat among the fair sex is inherent in nature itself. And again, it’s all about the structural features of the central nervous system.
We have already said that the cerebral hemispheres of the sexes are developed unequally. Hence the difference in working with verbal information. To “digest” what they hear, women use both hemispheres at once (including the left, responsible for the perception of verbal information). Men tend to do this predominantly on the right.
In addition (and we have also already talked about this), both hemispheres in the female body are connected with the help of powerful nerve fibers, due to which a more effective exchange of information occurs. In the male head, nature used thinner fibers for this purpose. By the way, it is precisely the structural features of the fibers connecting the hemispheres that doctors explain why women, as a rule, more easily restore verbal skills (speech) after a stroke.
This same feature of brain design explains why boys begin to speak and read later than girls.
But why did nature decide that verbal skills should be developed differently in both sexes? The theory explaining these differences was put forward by the American psychologist J. Levy. According to his hypothesis, the reason for everything is evolutionary processes. The main task of the primitive man was to hunt. And for this it was vitally important for him to navigate well in space, and not to talk.
As for the woman, even in the Stone Age she was the keeper of the hearth, took care of children and created family comfort. It was important to exchange experiences and resolve issues with other women. And in this she was helped by communication skills, which in the course of evolution were more improved along with the left hemisphere of the brain.
Men have more connections within the hemispheres of the brain, and women have more connections between the hemispheres
Men and women not only behave differently, but they also don’t think exactly the same. Thus, it is known that men are better at spatial orientation using a map.
, and women remember signs along the way.
As Gazeta.Ru wrote, analyzing the book by Dmitry Zhukov
, men are inclined to analyze objects, women are inclined to synthesis, men are rigid, women are plastic.
Women are better than men at multitasking.
If we turn to brain diseases, then there is no equality between the sexes. Gazeta.Ru has already reported that women are more likely to suffer from migraines
Parkinson's disease affects men much more often
, but otherwise
's brains age earlier
, even though women live longer.
About motivated sins and beneficial depression
Human behavior is described by the same laws as the behavior of other animals, says Dmitry...
19 November 16:18
The latest issue of the journal PNAS published
neurophysiological evidence that the brains of men and women are wired differently in some details. With the results of this study, much about gender differences in behavior and thinking becomes clear.
Some anatomical differences between the brains of men and women were already known. Men have larger skulls and larger brains, which equates to a larger body size.
White matter occupies a large proportion of the male brain
- conducting fibers (long processes of neurons - axons, covered with an insulating myelin sheath).
The male brain contains more cerebrospinal fluid. In the female brain, gray matter occupies a relatively larger volume.
- that is, nerve cells.
There are also gender differences in the size of various parts of the brain: hippocampus, amygdala
,
corpus callosum
. All these anatomical differences are laid down during the development and maturation of the brain. But so far scientists have very little ability to connect them with differences in the behavior of men and women.
Scalpel for migraines
Its German creator spoke about the surgical method of treating migraines in an interview with Gazeta.Ru...
25 September 13:43
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia used a cutting-edge method called diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
. The method, based on measuring the rate of diffusion of water, evaluates the anisotropy of the brain substance, that is, unevenness. This indicator indicates the development of conductive pathways - nerve fibers. Neurophysiologists call the totality of all pathways, all connections, the term “connectome.”
The authors studied the brains of 949 people aged 8 to 22 years using this method, including 428 males and 521 females. The subjects included white Americans, blacks, and immigrants from Latin America and Asia.
In the brains of men there were more neural connections between regions of the same hemisphere, and in the brains of women, on the contrary, there were more connections between the hemispheres.
This concerned the entire so-called cerebrum, that is, the hemispheres. Interestingly, in the cerebellum, which is sometimes called the “little brain,” the picture was exactly the opposite: men had more connections within one hemisphere of the cerebellum, and women had more connections between different hemispheres.
Old ladies get stupid earlier
Women's brains age faster than men's. This conclusion was reached by researchers who compared gene activity in...
05 September 20:19
Anatomical differences between male and female brains increase with age. Thus, in the brains of boys and girls aged 13 years and younger, the differences were very weak; they were more pronounced in the brains of 14–17 year old adolescents, and at the age of over 17 years they were much more pronounced.
From these anatomical differences, the study authors conclude that the brains of men and women are optimally adapted to different types of activities. The male brain has more connections between the perceptual and motor areas in each hemisphere, facilitating coordination between perception and action. And in the female brain, the abundance of interhemispheric connections facilitates the interaction of analytics and intuition: intuitive, imaginative information from the left hemisphere is built into the analytical activity of the left hemisphere.
Therefore, men rely more on what their eyes and ears tell them, while women rely more on intuition.
Neurophysiologists believe that this can explain women's greater attentiveness, better memory for names and faces, better communication skills, and in men - better spatial thinking and greater speed of sensory-motor processes
.
These differences begin to appear with puberty (12–14 years), when it becomes clear
that boys are better at solving problems of speed and spatial thinking, and girls are better at imaginative memory.
Perception
Did you know that women have more developed hearing, sense of smell and taste buds? But nature has endowed men (hunters by nature) with the ability to better distinguish small moving objects. And the main role in these differences was also played by the functioning of the brain.
Another difference is the different perception of colors. Remember the joke where a man sees all the dresses as blue, but for a woman it’s more than a dozen fundamentally different shades? So, don’t rush to laugh at your husband if once again he doesn’t see the color differences between two, say, red things. The fact is that this is how the male brain works - it simply does not perceive some shades as keenly as women. Take orange, for example. Any young lady will not only clearly see orange among the color spots, but will also be able to recognize several orange shades. But to the male brain, orange always looks more like red. In addition, it is difficult for the stronger sex to perceive the difference between shades of yellow, blue and green.
White and gray matter
There is also a difference in the distribution of white and gray matter. Gray matter represents information processing centers, and white matter represents the communication between these centers. Men have approximately 6.5 Intelligence In Men And Women Is A Gray And White Matter times more gray matter, and women have almost 10 times more white matter. Researchers suggest that this may be what determines men's success in solving math problems and women's verbal abilities.
Despite their differences, female and male brains have similar overall performance on broad measures of cognitive ability.
By the way, with mathematical abilities everything is not easy Culture, Gender, and Math. On average, boys are better at completing tasks than girls. But in countries that strive for equality, the average math ability of girls becomes at least the same. Therefore, the characteristics of gender socialization in this matter may be more important than the structure of the brain.
Stress
Male and female brains respond differently to stress. In a state of emotional shock in men, the left hemisphere, which is responsible for rational thinking, is activated, while the right hemisphere remains calm at this time. As for women, in stressful situations, on the contrary, the right part of the brain, which is responsible for emotions, is activated.
For this reason, men under stress tend to remember the details of the incident itself, and women tend to remember the emotions caused by it. In addition, during a scientific experiment it was proven that young ladies better remember events that caused them a surge of emotions. And this is the answer to the eternal question of men, why women pester them: “How? Don’t you remember what day it is today?!” It's simple: the reason is not that the man is bad and forgot about something, it’s just that his brain classifies events and memories associated with them using a different system.
How is a woman's brain different from a man's?
There are many different fantasies and myths on this topic. Very often, women are attributed to frivolity, irresponsibility and emotionality, although in fact research shows that women cope well with difficult and serious problems - even leading combat squadrons, and men are no less emotional, they are just taught to express only certain emotions, and the rest - somatize. Men are credited with being responsible, rational, and focused, when in fact men, for example, are much more likely to miss project deadlines, generally absent themselves more and quit more often, make logical errors with the same frequency, and are quite often absent-minded - more often distracted than women.
However, modern studies of MRI images are revealing true structural differences. We'll talk about them today. So, scientists identify the following types in the differences between the male and female brains: the ratio of white and gray matter, physiology, blood supply and innervation.
From a scientific point of view
The ratio of white and gray matter is different in men and women: men have slightly more gray matter, and women have slightly more white matter. Gray matter is localized, grouped and responsible for analysis, it is a kind of processor. White matter is the connection, it is responsible for the communication of neurons with each other. Men have more processing areas, women have more connecting areas.
Too many different tasks for women also leads to burnout and procrastination, just like for men, and many men are unable to concentrate on one thing for a long time and need breaks.
That is, this relationship is from the category of “rather” and “to some extent”, and not “women are designed for a large number of tasks, and men have perfect focus.”
Physiology
The bodies of men and women contain the same substances, but in different quantities - primarily we are talking about serotonin, testosterone, oxytocin and estrogen.
Women have more serotonin, oxytocin and estrogen - it is due to this that they have greater perseverance, sensitivity, emotional competence and the ability to create stronger human relationships. Female friendship is in vain ridiculed: statistically, it is women who have the longest, most trusting and warm contacts with women - in contrast to intergender contacts or “strong male friendships.”
Testosterone and lower levels of other hormones are associated with less perseverance and more aggressiveness in men, as well as decreased empathy when absorbed in tasks. This leads to men having a harder time coping with stress, being more likely to suffer from depression and being more likely to commit suicide. Paradoxically, this also means that men are encouraged to cry more to reduce the level of cortisol in the blood, a stress hormone that, when accumulated in the body, weakens the immune system, breaks down muscles and causes depression.
Structural differences
Women have a larger hippocampus, as well as more areas responsible for language; in men they tend to be mainly concentrated in one hemisphere, and in women - in both. Due to this, women have better access to information received from different senses, can more easily describe their experiences and emotions, and also remember more sounds, smells, sensations and visual details.
Blood supply and innervation
With a more efficient blood supply, women's brains tend to be less drained and better able to process memories, experiences, and emotions. Men get tired of this process faster and prefer to move on to active actions. This is why their actions tend to be less thoughtful, especially in areas related to relationships with other people: men are less able to predict the impact of their words and actions and the consequences in the form of changes in other people's attitudes. Women have higher social competence.
To summarize: women cope better with stress, make more informed decisions regarding other people, switch from task to task more easily, analyze and use past experiences better, and build relationships with other people better.
Men are more impulsive, less able to handle stress, less empathetic, and less understanding of other people's actions. At the same time, they focus better and move to action faster.
In general, according to research by Gregory Janz, men and women have more than 100 differences in the brain (do not forget about individual differences within the sexes). As a rule, the consequences of these differences lie not in the area of “smarter - dumber”, but in the area of “rather more inclined” and “rather less inclined”. Despite the average indicators, in life there are sensitive, reasonable men and indifferent, impetuous women.
Gregory Jantz believes that because of these differences in the nervous system, it is important to teach men stress management, perseverance, and greater emotional competence, while helping women gain more confidence to better use their brain strengths.
Memory
By the way, about memory. For most women it is indeed better than for men. But only up to a certain age. After menopause, when the concentration of estrogen in the female body decreases, memory deteriorates sharply. With changes in hormonal levels, women lose their superiority over men in terms of memory, and in old age, representatives of both sexes are “on an equal footing.” In addition, women of menopausal age have a reduced ability to learn and assimilate new information; it can be difficult to remember what she knew and remembered well before. Therefore, in old age, women are more susceptible to cognitive impairment, including dementia, than men.
In 2021, researchers found that women perform better than men on tests of word memory and language proficiency. But what's most interesting is that in some cases this ability of the female brain does its owner a disservice. The fact is that the early stages of Alzheimer's disease are usually diagnosed using just such tests - for memorizing words. So it turns out that the female brain, which has good verbal memory, can mask the initial stage of the disease. For this reason, diagnosing the early stages of Alzheimer's in women is much more difficult than in the stronger sex.
Interaction with the outside world
The structural features of a woman’s brain allow her to hear 2.5 times better and distinguish smells and tastes more acutely. Ladies perceive colors a little differently - they have access to more shades of color than men.
A man is more capable of distinguishing small objects in motion (hunter's vision).
Feelings, emotions, joint activities
The average man’s brain reacts to a stressful situation by activating the right hemisphere, the female brain activates the left, for the stronger sex the essence of the stressful state is more important than the details of the experience. Women, on the contrary, remember the details of their sensory experiences; they have “sensory memory”; memories of events result in memories of emotions.
The brain of women, more than men, depends on changes in hormonal levels. During menopause, women's ability to learn new skills and remember information decreases.
When it comes to joining forces to achieve a goal, women show better performance - they interact better with each other. Men achieve mutual understanding better in large groups.
When cooperation is needed, women's brains activate the temporal cortex, while men's brains activate the lower right prefrontal zone.
From the editor: Causes of pain in the top of the head
Oddly enough, when it is necessary for a woman-woman pair to interact, the central nervous system is tuned to mutual cooperation; in a man-woman pair there is no such process, although this does not affect the achievement of the final task. Whether this is a confirmation of the initially different roles of men and women in the process of survival of the species is unknown.
Teamwork
Research has shown that women and men adapt differently to working in teams. Representatives of the fair sex are more prone to what is jokingly called “being friends against someone.” Women easily form groups only if they understand that other women are observing their behavior. Under normal circumstances, it can be quite difficult for two ladies to find a common language. It is much easier for men to work in pairs, although, as research shows, the stronger sex is more predisposed to work in a large team rather than being divided into “groups.” It is also interesting that if a couple of a man and a woman have to work on the same project, then the lady is usually more friendly and ready for peaceful cooperation, which cannot be said about her colleague.
In addition, the researchers compared brain activity and team performance. It turned out that the performance of men and women is regulated by different groups of neurons, so the performance efficiency is higher in same-sex groups of partners. Compared to men's, women's brains are able to quickly and easily adapt from one task to another. The stronger sex requires quite a lot of energy and effort to switch between tasks; men find it difficult to perform several tasks at the same time.
Behavioral and social differences
Men and women not only feel and think, but also behave differently. Representatives of the fair sex are naturally sociable and tend to establish trusting relationships. Women are considered the best organizers, capable of unobtrusively uniting people to solve a common problem. Men are more likely to be “loners”, more adapted to competition, ambitious and aggressive. In a conflict situation, a woman prefers to solve the problem through negotiations, and a man prefers to resolve the conflict by escalating the conflict.
The female tendency to somewhat disperse attention to details also has a positive side: any representative of the fairer sex easily combines several streams of information and is able to do several things at the same time. The male way of thinking involves complete concentration on a specific topic, and moving from one thing to another requires some effort and time.
Knowing the features of the brain of men and the brain of women is very useful. In fact, this is the easiest way to understand each other and stop conflicting over trifles. Remembering how another person differs from you, you can become his support, and save yourself from far-fetched grievances and disappointments. Take care of each other and be happy!
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Sexual behavior
The statement that men love with their eyes has a very real scientific basis. The male brain is programmed to perceive visual images better. Smells also have a good effect on the stronger sex. That's the whole secret of how to win the affection of a man.
The female brain is configured differently and tends to evaluate a sexual partner comprehensively. Evolution has made sure that a woman subconsciously chooses a mate, taking into account how healthy the offspring he can give her.
Our brains shrink in different ways
Brain volume is not a static indicator. With age (after about 30 years), the organ begins to dry out. Over the course of a year, a person can lose up to 0.2% of their total gray matter volume. Thus, by age 70, the brain may weigh about 200 g less than at age 25. But what’s interesting is that the brain dries out differently in representatives of different sexes.
In 2021, Finnish scientists discovered in a study that women's brains age faster than men's. Moreover, this trend continues throughout life, starting from about 35 years of age. Experts have determined which parts of the brain shrink the most. As it turns out, this process follows different patterns in men and women.
Over the years, the male brain loses volume mainly due to shrinkage of the frontal and temporal lobes of the organ. They are responsible for emotionality and cognitive functions. The female is reduced by the hippocampus and parietal lobe, involved in visual and spatial perception, memory function and language learning.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
To date, experts have no consensus on how these age-related changes affect overall health. Scientists suggest that these transformations are the reason why older women are more prone to Alzheimer's disease, and men are more often diagnosed with Parkinson's disease.
Study: Gender differences in the brain are not confirmed
Everyone knows how the female brain differs from the male brain. One is talkative and a little nervous, but remembers everything well and takes good care of other people. Another is calmer, albeit more impulsive, but may put aside chatter to get the job done.
These are stereotypes, of course, but they have a surprising impact on what happens in real brain science and on how the results are interpreted. With the advent of MRI, neuroscientists are continuously working to find differences between male and female brains. This type of research gets a lot of attention because it is easiest to link a particular finding to gender differences in behavior.
I am a neuroscientist with extensive experience in this field, and my colleagues and I recently completed a painstaking analysis of 30 years of research into sex differences in the human brain. And it turned out that virtually none of these statements have been proven.
Other than simple differences in size, there are no significant differences between the brain structure or activity of men and women that persist across populations. None of the supposed differences actually explain why men and women have personality and behavioral characteristics.
More similar than not
My colleagues and I called our study “Breaking Dimorphism” to debunk the idea that the human brain is “sex dimorphic.” Sexual dimorphism is a scientific term used by biologists to describe characteristics that appear in two different forms in males and females, such as deer antlers or human genitalia.
When it comes to the brain, some animals do exhibit sexual dimorphism. For example, some birds have a nucleus in their brain that controls song. It is six times larger in males and is responsible for singing during courtship. But as we discovered in our exhaustive review, there is nothing even remotely similar in the human brain.
Yes, the overall brain size of men is about 11% larger than that of women, but unlike some songbirds, men or women do not have disproportionately larger individual brain regions. The size of the brain is proportional to the size of the bodies, and women's brains differ in size from men's smaller than other organs such as the heart, lungs and kidneys, which are 17-25% larger in men.
No single brain region differs by more than 1% between men and women, and even these tiny differences are not consistently found across geographically or ethnically diverse populations.
Other widely discussed sex differences in the brain are also explained by size rather than gender. These include the ratio of gray matter to white matter and the ratio of connections between and within the two hemispheres of the brain. Both of these indicators are higher in people with smaller brains, regardless of whether they are male or female.
What's more, recent research has completely rejected the idea that tiny differences in connectivity between the left and right hemispheres actually explain differences in behavior between men and women.
Zombie concept
And yet “sexual dimorphism” will not die. It's a zombie concept, and its latest revival involves artificial intelligence determining whether brain scans are male or female.
Computers can do this with 80% to 90% accuracy, although this drops back to 60% (not much better than flipping a coin) when controlling for head size. What's even more alarming is that these algorithms don't work across populations such as Europeans and Chinese. This discrepancy shows that humans do not have universal characteristics that differentiate male and female brains—unlike deer antlers.
Neuroscientists have long hoped that larger studies and better techniques would finally reveal “true,” or cross-species, sex differences in the brain. But the truth is that the more research is done, the less evidence there is for sex differences.
This failure is a clear sign of a problem known as publication bias. Small early studies that found significant sex differences were published more often than those that found no difference between the brains of men and women.
Software vs Hardware
We must be doing something important, because our challenge to the brain sex dogma has received pushback from both ends of the academic spectrum. On the one hand, we are called “science deniers” and ridiculed for being politically correct. On the other hand, it is rejected by women's health advocates, who believe that we have not studied women's brains thoroughly enough and that we should intensify the search for sex differences to better treat disorders that dominate women, such as depression and Alzheimer's disease.
But there is no denying evidence, accumulated over decades, that shows that sex differences in the brain are tiny and are negated by the much greater variation in the brains of individuals in a population. The same can be said for most behavioral indicators.
About a decade ago, teachers were encouraged to separate boys and girls in maths and English classes based on perceived learning differences. Fortunately, many refused, arguing that the range of abilities between boys and girls was always much greater than that of each sex in the group.
In other words, gender is a very imprecise indicator of what type of brain a person will have. Each individual brain is a mosaic of circuits that control many indicators of masculinity and femininity, such as emotional expressiveness, interpersonal style, verbal and analytical reasoning, sexuality, and gender identity itself.
Or, to use a computer analogy, gendered behavior results from running different software on the same underlying hardware.
The absence of binary gender characteristics in the brain may also be associated with an increase in the number of people who identify as non-binary, queer, non-conforming or transgender. Whatever influence biological sex has directly on the circuitry of the human brain, it is clearly not sufficient to explain the multidimensional behavior that we attribute to the complex phenomenon of sex.
The human brain is not a “dimorphic” organ, but a monomorphic one—much more like the heart, kidneys, and lungs. And they, as you may have noticed, can be very successfully transplanted between men and women.
Source
Interesting article? Subscribe to our Telegram channel to receive more educational content and fresh ideas.