Dental factors
A feeling of a “stiff” jaw that spreads throughout the chin is a sign of problems inside the mouth. When paresthesia covers the gum tissue, lips and tongue, a burning and tingling sensation occurs - the best solution in such a case would be to consult a doctor for diagnostics and identification of pathology. Possible dental factors include the following.
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process localized in the area of the tooth root, the occurrence of which is facilitated by the development of pulpitis or improper placement of a filling. Characteristic signs are aching pain, aggravated by pressure, a general increase in body temperature, as well as numbness of the gums and jaws.
Prosthetics and implantation are complex procedures, during which technical errors may occur, both at the preparation stage and during the installation of a replacement structure. Incorrect installation of the implant can cause damage to the jaw nerve, the symptom of which is discomfort and loss of sensitivity in the chin area.
Use of anesthetic drugs. Anesthesia, better known among patients as “freezing,” is designed to prevent discomfort that occurs during dental procedures. As a rule, the effect lasts for 2-4 hours after the procedure, however, if tissue sensitivity has not recovered after the specified period of time, you should contact your treating specialist again.
Filling of dental canals - if composite materials get on the surface of the bone tissue, as well as poor-quality cleaning of the problem area that has become infected, an inflammatory process may develop, which negatively affects the condition of the jaw region. In critical cases, a transition to a toxic state is even possible, when the patient’s body is poisoned by the elements contained in the used material.
Mechanical damage. Another common occurrence is injuries caused by excessive force applied to the jaw. Most often, injuries are diagnosed in patients belonging to a high-risk group - athletes, car enthusiasts, stuntmen, etc. If numbness in the chin or teeth occurs after a blow or fall, it is likely that surgical intervention will be required for treatment.
Numbness of the face
Stroke
Diabetes
28960 March 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness of the face: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Numbness of the face occurs when the sensitivity of skin and muscle receptors to various impulses is impaired. This symptom may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Loss of facial sensitivity is described as burning, tingling, sometimes pain, and in some cases as a complete absence of sensation. When the face is numb, the color of the skin over the affected area may change in the form of pallor or redness.
In severe cases, sensory impairment is accompanied by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles.
Types of facial numbness
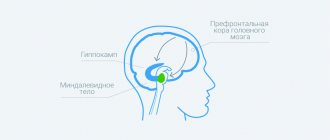
Any external influence, be it heat or cold, light touch or strong pressure, leads to activation of skin receptors and muscle structures. Each receptor is associated with a specific type of nerve fiber that transmits a specific type of sensitivity (sensation of pressure on the skin, vibration, stretching of the skin, and temperature sensitivity). An impulse is generated in the receptor, which is sent through nerve fibers at high speed to the nerve ganglia, which are a collection of sensory neurons. This is where primary information processing occurs to activate vital reflexes. Subsequently, the impulse goes to the brain, where it is processed in special nerve centers, and the person feels pain, pressure, vibration, etc. Thus, we can talk about the following types of sensitivity disorders:
- Violation of surface sensitivity
occurs when receptors (temperature, tactile, pain, etc.) and nerve fibers of the facial skin are damaged. - Violation of deep sensitivity
occurs when the receptors and nerve fibers of the facial muscles are damaged. - Violation of complex types of sensitivity
. A similar type of disorder occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. There is no recognition of two different stimuli that simultaneously affect the skin, or the person cannot determine the location of the touch.
Possible causes of facial numbness
In many cases, numbness in different parts of the face is short-term, passing within a few minutes.
Such episodes can occur when the head is positioned in an awkward position, for example during sleep.
This occurs due to compression of the nerve fibers and a temporary disruption of impulse conduction. There is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Partial loss of sensitivity is observed with prolonged exposure to the cold due to vasospasm. After gradual warming of the skin, sensitivity is restored.
However, facial numbness can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Acute cerebrovascular accident, or stroke
– a common cause of sudden numbness of the face in combination with a violation of facial activity. Hemorrhage or blockage of brain vessels by a thrombus (blood clot) occurs, acute oxygen deficiency and damage to neurons with disruption of their functions develops. Symptoms develop unexpectedly, sometimes accompanied by headache.
The main signs of a stroke are: numbness of the face and limbs on one or both sides, sudden weakness, speech impairment (inability to clearly pronounce words), drooping of the corner / corners of the mouth, uncoordination of movements.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. A cerebral aneurysm
can cause numbness in the face due to compression of nerve fibers and sensitive centers of the brain. It usually develops gradually; at the onset of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Numbness first affects one area of the face (for example, perioral), and with further growth of the aneurysm, the affected area gradually expands. Sensations may also change: from tingling, burning at first - to a complete absence of sensations later.
There is a danger of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm; in this case, the symptoms are similar to those of a stroke and appear quickly.
Trigeminal neuritis
often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis), ear (otitis), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis), parotid glands (mumps). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated, which can lead to numbness in the corresponding areas of the face.
Impaired sensitivity with increased tone of the masticatory muscles
occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by muscle fibers. Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is characteristic of damage to the temporomandibular joint due to arthritis and arthrosis, incorrectly selected braces, and certain diseases of the pharynx, for example, peritonsillar abscess.
Diabetes
– with this disease, the process of utilization of glucose from the blood is disrupted, which leads to damage to the vascular wall and disruption of the nutrition of nerve bundles. In the absence of maintenance therapy, tingling and partial loss of sensitivity in areas where the blood supply is impaired may occur.
Numbness of the face in multiple sclerosis
occurs due to demyelination (disappearance of the outer sheath) of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve. Numbness is often preceded by severe pain not only in the face, but also in the limbs.
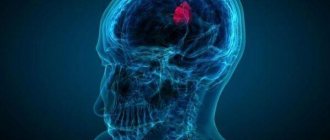
Tumors of the brain and its membranes
lead to impaired sensitivity in the facial area due to compression of the neurovascular bundles or tumor growth in them.
Which doctors should I contact if I have facial numbness?
If your face becomes numb, you should consult a neurologist or therapist. In some cases, consultation with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, or dentist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for facial numbness
Depending on the suspected cause of facial numbness, the following laboratory and instrumental studies may be required:
- clinical blood test;
Non-dental factors
However, the above list is not exhaustive - in addition to the causes of loss of sensitivity of the maxillary region directly related to dentistry, there are other problematic factors.
Trigeminal neuralgia. A chronic pathology characterized by sharp exacerbations of painful sensations when mechanical triggers are activated. The main symptoms of the disease include pain during facial activity, the occurrence of involuntary tics, disruption of facial symmetry, as well as numbness of the jaw and chin.
Insufficient intake of minerals and vitamins. An unbalanced diet, with a deficiency of nutrients important for the metabolic process, leads to disruption of the functioning of nerve endings, the functionality of which directly depends on the quality of metabolism.
Development of neurosis. Psychogenic disorders are accompanied by numbness of certain areas of the face, the development of tics and involuntary muscle contractions.
Additionally, potential sources of the problem may include:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical region, causing excessive compression of nerves and blood vessels, leading to loss of sensitivity;
- Impaired blood flow caused by dystonia or atherosclerosis;
- Hypertension, sinusitis, edema, as well as gestosis that occurs during pregnancy.
Causes of paresthesia
Goose bumps on the face are not a disease, but only a symptom of another primary process or a consequence of a provoking factor. It can occur in various areas of the face and occurs in combination with other manifestations, for example, burning, muscle rigidity, swelling. Paresthesia is sudden, temporary or permanent, mild or severe. In the latter case, there is not paresthesia, but complete paralysis of the face.
Most cases of numbness on the right or left side of the face are due to circulatory problems in the head or neck and diseases associated with the central nervous system. However, temporary factors are no exception, after the elimination of which the symptom disappears.
Temporary, not caused by diseases
Only a doctor can rule out diseases of the central nervous system and other body systems as the cause of tingling on the face based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis. Temporary causes of paresthesia include:
- Sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow. If for a long time, for example, throughout the night, you take one position of your head to sleep (on your side), you can wake up in the morning with a feeling of numbness and trembling. This can be explained by the fact that nerves and blood vessels are compressed. This causes the development of paresthesia.
- Increased irritability, behavior characteristic of stress. Often, during an emotional conversation, a person contracts his facial muscles, which contributes to the appearance of muscle hypertonicity and, as a result, numbness in this area.
- Anxiety syndrome, anxiety before an important event, for example, before an exam. In such cases, sensitivity is lost due to nervous overstrain.
- Engagement in professional activities that require the head and neck to assume a monotonous position for a long time. These could be professions that require long periods of work at a computer; reading, handicrafts for several hours in a row. In such cases, it is recommended to take breaks from time to time and perform exercises for the cervical spine and head.
- Colds. The right or left side of the face becomes numb as a result of muscle inflammation, which is a complication of ARVI or acute respiratory infections.
- Hypothermia. The symptom is caused by vasospasm. After the end of the cold and warming, it disappears.
In other cases, the left side of the face (or right) becomes numb due to the development of a vascular or neurological disease.
Pathological, requiring medical assistance
If the left side of the face is numb, and the symptom occurs frequently or on an ongoing basis, or is present for a long time, self-medication is not recommended. Paresthesia in this case may signal the development of a dangerous pathology. You should immediately call a doctor if the symptom occurs suddenly; in addition to the cheek, part of the lip, nose, chin, forehead, or head is numb. This may be a sign of a stroke, requiring urgent medical attention and specific treatment.
Other pathological reasons why the left side of the face goes numb:
- trigeminal neuritis;
- migraine;
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia);
- neurosis;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- multiple sclerosis;
- syringomyelia;
- shingles;
- inflammation of the facial nerve, for example, the temporal nerve.
In most cases of diagnosing pathological causes of paresthesia, stroke and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine occur.
In the latter case, a violation of the sensitivity of one side of the face occurs against the background of constant compression of the spinal nerve or vessel by formed salt stones. Chronic pain in the cervical region, pain in the head, slight dizziness, malaise, and a crunch in the neck when turning the head also occur.
Another common reason why numbness in the left side of the face occurs in women and men is poor circulation in the brain. This condition is considered dangerous and occurs against the background of various factors, for example, when small capillaries are blocked by cholesterol deposits, blood clots, or an aneurysm.
In adult women, acute cerebrovascular accident often occurs with long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, smoking, alcohol abuse, poor diet, and frequent migraine attacks.
Stinging on one side of the face can occur with trigeminal neuralgia. The disease develops against the background of irritation or compression of the nerve during the inflammatory process in the nose, mouth, ear area, as well as due to its contact with a tumor-like neoplasm, adhesive formations after injury. In most cases, the inflammatory process occurs in the lower branch of the nerve, so the symptom manifests itself in this area.
Often, numbness on the left or right side of the face occurs due to a stagnant process in the lymphoid fluid. The inflammatory process in the lymph nodes develops when the infection intensifies and spreads into the lymphatic system. Along with paresthesia, swelling is observed, compressing the nerves.
A less common cause of tingling on the face is sinusitis. The disease is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the upper maxillary sinuses, caused by an acute respiratory infection (signs - nasal congestion, sore throat, fever, etc.). In addition, the source of inflammation is the spread of infection from another primary focus, for example, from a gum pocket or a carious cavity of a tooth.
Disruption of the functioning of the central nervous system occurs against the background of insufficient content of useful substances in the body, in particular vitamins B and E. A decrease in the level of these is observed due to the development of pathologies in the digestive system (hepatitis, gastritis, enteritis, etc.). With vitamin deficiency, not only the cheeks tingle, but also the lips and chin.
Poor blood circulation in the facial area occurs after surgery or trauma to this area. In addition to superficial disorders, that is, paresthesia, there is an increased risk of developing secondary infections, the formation of abscesses, and phlegmon.
A disruption in the process of conducting nerve impulses along sensory fibers occurs due to the use of agents from the group of anesthetics. These include Lidocaine and Novocaine, and other drugs used to relieve pain symptoms in dentistry and endoscopy. A consequence of the use of these drugs is the thinning of nerve fibers due to the development of an allergic reaction.
If numbness occurs in the left side of the face and arm, this may be a sign of multiple sclerosis. Each disease of the peripheral nervous system develops against the background of activation of viral pathogens, immunodeficiency or due to food allergies. Multiple sclerosis is characterized by paralysis and impaired visual and auditory function. If left untreated at the initial stage, the disease progresses and clinical manifestations intensify.
Risk group
Relevant studies have proven that in the presence of certain diseases in the body, the risk of paresthesia increases several times. The type of life a person leads is also important.
Persons at risk are:
- females, who more often develop neurological pathologies accompanied by symptoms such as impaired skin sensitivity;
- female during pregnancy (body weight increases, swelling occurs, including on the face, which increases the risk of paresthesia);
- those who are obese and overweight (in this case, an additional load is created on the body; fat accumulations in the face and neck can put pressure on the nerves);
- those suffering from diseases of the endocrine system that cause hormonal imbalance and neurological complications;
- those suffering from diabetes mellitus, which is complicated by damage to the nerves in the face and neck;
- those suffering from rheumatoid arthritis, which occurs with compression of the nerve endings of the jaw joint and, as a result, a violation of the sensitivity of this section.
Also at risk are people whose profession involves the need to sit for long periods of time (office workers, etc.).
When to see a doctor
To restore sensitivity and get rid of numbness in the chin or jaw, it is recommended to visit the dentist at the first signs of discomfort. Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible to establish the root cause of the pathology and begin targeted therapy that helps restore the natural state of tissues. To prevent paresthesia, it is also recommended to periodically do short facial exercises that stimulate internal processes and restore the functionality of the facial muscles.
Conditions that cause numbness of the lips and tongue
| Headache | Sensory disorders | Features of the blood test | Additional examinations | |
| Migraine | Appears an hour after numbness | My hands are going numb | No changes | Taking triptans, monitoring results |
| Bell's palsy | Doesn't appear | Half of the face loses sensitivity | In rare cases, markers of inflammation are present | Perform MRI, CT |
| Stroke | Long-lasting, intense, appears before numbness | Most often, sensitivity is impaired in one half of the body | The parameters of the coagulation system change. Possible increase in platelet | Perform MRI, CT |
| Hypoglycemia | Doesn't appear | Diabetic polyneuropathy | Blood glucose levels drop to 3 mmol/l or less | MRI, CT to rule out insulinoma |
| Anemia (B12 deficiency) | Doesn't appear | Peripheral polyneuropathy | of hemoglobin decreases , in some cases leukopenia and thrombopenia | A bone marrow puncture is performed |
| Anxiety disorders | Does not manifest itself, dizziness | Possible short-term disturbances in the sensitivity of parts of the body associated with the stress experienced | No changes | Schedule a consultation with a psychotherapist and conduct tests to determine anxiety and depression |
| Angioedema | Does not appear if the swelling is extensive, discomfort in the head area is possible | Loss of sensitivity in the area of edema | Inflammatory markers may appear | If allergic edema develops, tests are performed with allergens; if it is hereditary, an examination for defects in the complement system is performed. |
| Formations benign and malignant | Pain at the site of the tumor or diffuse pain if the meningeal membrane is involved in the process. It is poorly controlled with analgesics. | Not with all formations, sometimes | If the process is malignant, all blood counts decrease; if it is benign, there are no changes. | CT, MRI of neck, head, brain |
Causes of numbness of lips and tongue
Why your tongue tingles, why your lips go numb - the reasons for this can be determined by a doctor after a comprehensive examination. A blood test, MRI, and CT Dopplerography of blood vessels will help to specifically determine why the lower lip is numb and the reasons for the numbness of the tongue. The treatment regimen depends on the underlying disease.
All diseases in which the tongue goes numb, numbness of the lower lip and chin manifests itself, are divided into several groups.
Nervous system diseases
Diseases of the central departments
Often the patient notes that the lip or tongue is numb if formations, both benign and malignant, appear in the brain structures. These symptoms also occur with degenerative changes in the brain .
Peripheral nerve diseases
The answer to the question of why the upper lip is numb may be idiopathic neuritis of the facial nerve . Also, the causes of numbness of the upper and lower lips may be associated with neuralgia of the facial, trigeminal and other facial nerves.
Diseases that are not related to the nervous system, but affect it
Swelling and numbness are possible with vascular pathologies leading to acute disruption of blood flow ( transient ischemic attack , stroke ). This symptom also manifests itself in diseases of the circulatory system, in particular anemia associated with a lack of vitamin B12 .
If the lower or upper lip is swollen or the tongue is numb, this may be associated with infectious-allergic processes - allergic manifestations, herpes .
Mechanical damage
When the upper lip becomes numb or twitches, or the tongue curls, this may be a consequence of head or facial injuries. This is also possible after recent dental surgery.
Numbness after dental procedures
Those who are interested in why the tongue goes numb can also find the reasons for this phenomenon in the recent performance of any dental manipulations with “wisdom teeth”. Surgical removal of eighth teeth, especially if they have assumed a horizontal position, is difficult and requires anesthesia .
The causes of tongue numbness may be associated with local anesthesia. Sensitivity on one side disappears for a while. If the palate becomes numb, the reasons may also be related to dental procedures. This manifestation is not dangerous, but can be repeated for up to six months, causing a person to feel discomfort. In this case, treatment is not required. However, a person must clearly know why the tongue becomes numb and that this is due specifically to dental procedures, so as not to miss the development of serious diseases.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
One of the most serious reasons why the tongue and lips go numb is associated with the so-called “vascular accident”. Stroke is one of the leading diseases in terms of mortality. Therefore, it is very important to know the symptoms of this terrible disease, including numbness of the lips and tongue. The causes of this disease can be different. The signs are as follows:
- Paralysis and numbness of the right or left side of the face, while one eye may be closed and the corner of the mouth droops.
- Numbness on the left side of the body or on the right side.
- Speech is absent or slurred.
- A person cannot move his leg and arm on one side, or it is very difficult for him to do so.
- Coordination is impaired.
- Possible manifestation of depression of consciousness.
It is necessary to provide assistance to a person with such symptoms very quickly: it is important that this is done within 6 hours from the onset of the attack. If adequate assistance is provided on time, there is a high probability of restoration of speech and muscle function.
Conservative therapy is practiced in rehabilitation centers where recovery after a stroke is carried out. The following actions are also important for recovery:
- blood pressure within normal limits (no more than 140/90).
- Control of fluid intake - its amount per day should be 1.5-2 liters.
- ACE inhibitors are considered the drug of choice.
- Balanced diet.
- Monitoring glucose levels, since when its level is more than 11-12 mmol/l, rehabilitation becomes more complicated.
- Preventive measures to prevent blood clots.
- Sedative treatment to ensure psycho-emotional comfort.
To the question of whether blue lips are a sign of what disease, the answer may also be problems with the heart and blood vessels.