Causes of the problem
“There are a number of major nerve clusters that connect your brain to different parts of your face and head. When nerves are inflamed, compressed, or damaged, numbness can occur. Reduced or blocked blood supply can also cause numbness,” says Irina Ryabokon.
The reasons why numbness of the head may develop, says the neurologist, are varied. So, for example, if such a symptom appeared due to a cold, headaches or because of an uncomfortable sleeping position, then there is no need to worry. But if a person suffers from some illness, takes a number of medications, or has suffered an injury, you need to be wary. Head injuries or concussions can cause numbness if nerves are damaged.
“By the word “numbness,” which actually means loss of sensitivity, patients often understand various sensations, such as crawling, burning, tingling (so-called paresthesia). To find out the cause of such sensations, it is extremely important to determine what exactly is meant - a decrease, lack of sensitivity or paresthesia,” explains Ryabokon.
Sclerosis, but not that one. By what signs are multiple pathologies recognized? Read more
The neurologist notes that with paresthesia, sensitivity can be preserved, sometimes even enhanced. Less common are situations where paresthesia is combined with a violation of sensitivity in this area (sense of touch, pain sensitivity - injection, feeling of vibration, etc.).
“Paresthesia (without loss of sensitivity) can have numerous causes, and the cause cannot always be determined. For example, they may be side effects of certain medications or associated with severe anxiety or anxiety. Especially when the localization of sensations changes,” notes the neurologist.
But impaired sensitivity in a certain area of the head or face requires a detailed examination. “The cause may be vascular disorders, nerve damage, or brain diseases. The unilateral and persistent nature of the disorders requires seeing a doctor and a detailed examination,” she says.
Quite serious illnesses can also cause this symptom. “Diabetic neuropathy can cause permanent nerve damage. Numbness is also a common symptom of multiple sclerosis, a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system,” says the specialist.
In addition, in the list of what numbness in the head may indicate, the following items:
- allergic rhinitis;
- cold;
- sinusitis;
- brain tumor;
- arterial hypertension;
- stroke;
- epilepsy attacks;
- use of prohibited substances;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking anticonvulsants.
“You should see a doctor immediately if head numbness occurs after starting medication,” says the neurologist. The specialist also notes that the list of reasons for the feeling of numbness in the head can be supplemented with headaches and cluster pains (severe pain syndrome), tension pain, migraines, encephalitis, Lyme disease, shingles, as well as dental infections.
“Numbness in the head sometimes occurs only on one side. Or only the temple or back of the head may suffer. Typically, such conditions signal the following diseases: Bell's palsy, infections, acute migraine,” the doctor notes.
My head hurts! When to take your child to a neurologist Read more
Head goes numb: causes, sign of what disease
If your head goes numb, this is due to a deterioration in the sensitivity of the scalp, the causes being diseases:
- cerebral vessels - inflammation (vasculitis), blockage with deterioration of blood supply (stroke or temporary ischemic attack);
- traumatic origin - cranial, cervical spine;
- hereditary - for example, narrowing of the openings through which the spinal cord root passes;
- with compression of the nerve fiber - by muscles (with spastic contraction or prolonged tension), bone outgrowths with osteochondrosis, space-occupying formation (tumor, blood accumulation, inflammatory compaction, aneurysm);
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- infectious (herpes, meningitis);
- metabolic – diabetes mellitus, lack of vitamin B12, B1;
- against the background of lead poisoning, other toxic compounds, and medications.
Most diseases occur with concomitant symptoms, the patient feels severe weakness, dizziness, speech, vision, and movements may deteriorate. If the general condition is normal, but only, for example, the scalp under the hair becomes numb, then this is usually a manifestation of prolonged muscle tension. This happens with sedentary work, incorrect body position during sleep, headaches and after a long trip on a bus, train or plane.
The location of the numbness zone is also important. In neurological and vascular diseases, it has clear and permanent outlines; by its location, a neurologist can determine the location of nerve damage.
If there is a variety of symptoms (tingling in different parts of the face, burning, heat, numbness), then a suspicion of neurosis or neurocirculatory dystonia arises. They often occur against the background or after stress overexertion.
Leather
If the scalp becomes numb, then most often you need to look for the cause in the cervical spine. Osteochondrosis is the most common cause; it causes irritation of the spinal cord roots by bone outgrowths (osteophytes), which patients call “salt deposition.”
If the size of the osteophytes increases, then compression begins with pain during movements and impaired sensitivity. Usually the numbness spreads to the head, neck, and sometimes extends to the arm.
If it shrinks (squeezes) the scalp, this sensation may be confused with a decrease in sensitivity. This is especially common in the setting of tension headaches. Patients describe it as tension, tightening or squeezing. Most often it is symmetrical, sometimes bringing the head and face together on one side. This disease is characterized by the appearance of symptoms after the action of a provoking factor:
- stress, lack of sleep;
- incorrect static posture;
- visual strain;
- long break in meals;
- staying in a stuffy room, heat, cold;
- anxiety, depression;
- high blood pressure;
- infection;
- hormonal disorders (usually premenstrual syndrome, menopause).
Forehead, frontal part
Trigeminal neuralgia
Numbness of the forehead (frontal part of the head) is possible with trigeminal neuralgia. This disease is characterized by painful attacks of the type of electric discharges, after which the sensitivity of the facial skin is impaired. Since the forehead is innervated by the superior orbital branch of this nerve, when it is damaged, skin numbness, tingling, and a feeling of cold occur. Causes of neuralgia include:
- vascular diseases - congenital tortuosity, aneurysm (expansion of the area), arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis;
- tumors of the brain, skull bones;
- sinusitis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- changes in bite, dental procedures;
- herpes.
Neuralgia can be suspected if pain occurs after touching the skin of the face or contraction of facial muscles when eating or talking.
Right side or left
If the right or only the left side of the head hurts and goes numb, then the cause may be neuritis of the facial nerve. It is also called Bell's palsy, since one of the manifestations is weakness of the facial muscles. The patient experiences pain behind the ear, then half of the face goes numb, on the affected side the nasolabial fold is smoothed, the corner of the mouth is drooping. Then a skew of the facial part of the head occurs on the healthy side, and on the affected side, movements of the facial muscles become impossible.
Unilateral numbness and asymmetry of the face also occurs with acute cerebrovascular accident. Then, when trying to smile, one half lags behind the other (a crooked smile), the eyebrows rise to different heights, and if you ask the patient to stick out his tongue, it deviates to the side. There may be loss of vision in one eye. Speech becomes slurred. Usually, with a decrease in sensitivity, weakness is felt in the arm or arm and leg on one side, the patient will outgrow the sensation of touching half of the upper lip.
Symptoms may disappear within a day, then a diagnosis of transient (transient) ischemic attack is made. If symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, a stroke develops. The causes of deterioration of cerebral circulation include atherosclerosis, hypertension, and osteochondrosis.
Crown, upper part of the head
Numbness and tingling in the crown and upper part of the head can be associated with pinching (neuralgia) of the occipital nerve. This disease is provoked by:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- infectious diseases (sore throat, mumps);
- inflammation of the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) of the occipital, behind-the-ear group;
- neck injuries, surgeries;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged muscle tension.
Painful shooting sensations from the back of the head to the crown, from the neck to the shoulders and shoulder blades are typical. Most often they are one-sided, but they can spread to both sides.
Ear and head part
Numbness that starts from the ear and then covers half of the head is typical of neuritis of the facial nerve.
The most common cause is hypothermia and inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media). Similar signs may also appear against the background of herpes, mumps, or after an injury. Less commonly, such symptoms occur due to an acute cerebrovascular accident (ischemic stroke), a tumor, or an infectious lesion of the brain (encephalitis).
Half head, whiskey
Numbness of half the head or a predominant deterioration of sensitivity in the temples is typical for a migraine attack with aura. At the same time, there may be tingling in the fingertips.
Sometimes numbness spreads to the entire arm, part of the neck and body. You may experience ringing in the ears or unusual sounds or smells. Half of the head also goes numb in patients with an epileptic attack, a transient disorder of cerebral circulation.
Also hands
Numbness of the head and arms is a typical sign of cervical osteochondrosis, and can also be caused by:
- trauma, especially vertebral subluxations;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the spine;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- scoliosis.
In older people, the height of the intervertebral discs may decrease (spondylosis).
Damage to the cervical and upper thoracic roots occurs with herpes zoster. Impaired sensitivity of the scalp and hands is caused by circulatory disorders (for example, diabetes mellitus, vasculitis). Less commonly, tumors of the spinal cord or brain are found in the patient.
Numbness in various parts of the body is typical of the onset of multiple sclerosis. This is a disease of autoimmune origin. When it occurs, the body produces antibodies to the nerve sheath, an inflammatory reaction develops, followed by damage to the nerve fiber, replacing it with scar tissue.
Most often, the patient is initially concerned about weakness in the legs, back pain, tingling in the limbs, blurred vision, and dizziness are also possible. As the disease progresses, muscle spasms are observed, making it difficult to walk, the functioning of the intestines and bladder is disrupted, and problems with swallowing food arise.
Physiological state
“Often a feeling of numbness in the head occurs during sleep. When you wake up with a numb head, it may be a sign that you are sleeping in a position that restricts blood flow to your head,” notes the neurologist. Here you can try to cope with the problem of sleep correction. “In this case, try sleeping on your back or side, placing your head and neck in a position that will not cause discomfort. If you are lying on your side, try putting a pillow between your knees, this will help straighten your back,” advises Irina Ryabokon.
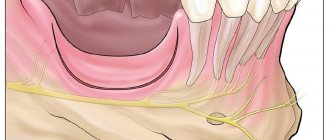
Pinched nerves of the head
Description
The pathology is expressed
by pinching of the occipital nerve
, due to inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
Localization and nature of pain
When turning the head, the pathology makes itself felt with piercing pain in the occipital region, gradually spreading over the back of the head and neck.
Additional syndromes
- Neck pain with numbness.
- Pain occurs when touching the skin in the neck and back of the head.
- Inability to tolerate bright, sudden lighting.
Who should I go to for treatment?
The only highly qualified doctor capable of providing specialized care is a neurologist.
The doctor has carried out the required examination and will periodically monitor the patient’s recovery process. Diagnosis
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Radiography.
- CT scan.
A course of treatment
In case of severe neuralgia,
it is effective to use blockades
that quickly eliminate a painful attack. Among these drugs, the following drugs stand out: “Kenalog”, “Hydrocotrisone”, “Metypred”.
Drug treatment can be continued with anticonvulsants (Gabapentin, Carbamazepine).
A specialized relaxing massage will not be superfluous.
How can a neurologist help?
If you have such a symptom and exclude physiological reasons for its development, you should visit a specialist. You should contact a neurologist. He will examine you and ask about your symptoms and medical history. He may also order one or more of the following tests to help determine the cause of the numbness in the head: blood tests, nerve conduction studies and electromyography, MRI, CT scan, nerve biopsy.
Since quite a few conditions cause numbness in the head, it may take some time to determine what exactly is causing the characteristic symptoms. You should not leave the situation unattended, because you can waste time, and then you will have to undergo treatment longer and more difficult.
There are contraindications. Be sure to consult your doctor.