General information
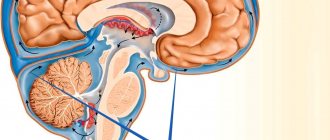
Glioblastoma is a malignant neoplasm that forms from brain ganglion cells. It is characterized by rapid growth.
Glioblastoma is a malignant tumor that affects brain tissue. The clinical picture depends on the stage of development of the pathological process.
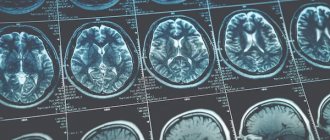
Diagnostic measures include computed and magnetic resonance imaging, PET, radiography, and biopsy.
Treatment - radiation, chemotherapy, gamma knife, drugs, surgery.
Symptoms are pronounced only at the second stage of development of the pathology, when the brain tumor reaches a significant size and begins to put pressure on neighboring structures.
Causes of glioblastoma of the brain
Glioblastoma of the gray matter is a tumor-like lesion of the central nervous system of a malignant nature.
The signs that appear at stage 4 are clearly visible. The pathological process of glioblastoma spreads rapidly, affecting healthy tissue.
Experts distinguish primary neoplasms of this type, which arise under the influence of negative factors, and secondary ones, which are formed as a result of the spread of metastatic lesions.
Treatment of glioblastoma
The current gold standard, or ideal treatment, for patients diagnosed with glioblastoma is surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by chemoradiotherapy (chemotherapy and radiation) once the surgical wound has healed.
Surgery to remove glioblastoma
The neurosurgeon will try to remove as much of the tumor as possible by performing a partial resection. It is difficult to remove the entire tumor in the case of glioblastomas because:
- they are diffuse, that is, they have thread-like elements that spread into the brain;
- It may be difficult to tell the difference between the edges of the main part of the tumor from normal brain tissue. This means that parts of the tumor may remain after surgery.
Recent advances in oncology have improved surgeons' ability to remove more tumors. Before surgery, patients in some hospitals are given a substance called 5-ALA to drink. It causes brain tumor cells to glow pink under violet light. This allows the surgeon to identify tumor cells in an area of normal cells, and thus remove more diseased tissue. It is effective in adults with high-grade gliomas, such as glioblastomas.
note
The extent to which a tumor can be safely removed also depends on its location in the brain, deep in the brain and near important parts of the brain are very difficult to operate on.
Chemoradiation treatment
Treatment includes several weeks of radiation therapy and periods of chemotherapy with the drug temozolomide. It is used to slow the growth of any tumor cells that cannot be
removed surgically. Temozolomide works by stopping tumor cells from making new DNA (the material that carries all of their genetic information). If they cannot synthesize DNA, they cannot divide into new tumor cells, so the tumor cannot grow. The drug is also believed to make tumor cells sensitive to radiation. Temozolomide is usually taken for an additional 6 months after radiation therapy.
From the editor: Causes, signs and treatment of bad blood vessels
Implants with drugs
Gliadel implants are small plates coated with the chemotherapy drug carmustine, which is injected directly into the brain at the end of surgery. This means the treatment crosses the blood-brain barrier, which prevents many chemotherapy drugs from reaching the brain.
New in treatment
There is evidence of the use of a drug called bevacizumab in the treatment of glioblastomas. However, there is not yet sufficient evidence of its effectiveness in brain tumors, so it is used as an experimental treatment.
Electrical field therapy for glioblastoma, also known as Optune, is a relatively new, non-invasive technique for adults with glioblastoma. It uses an alternating electric field generated by sensors glued to the skull. It is designed to disrupt the division of tumor cells or cause their death. This helps prevent the tumor from growing or spreading quickly.
Immunotherapy is a personalized cancer vaccine that is produced for each patient from their own dendritic cells. Dendritic cells are a type of immune cell that helps the body's immune system recognize and attack tumor cells.
Classification
In accordance with the characteristics of the pathology, experts distinguish three forms of glioblastoma of the brain. This allows you to establish a more accurate diagnosis and determine the correct course of therapy.
Multiform
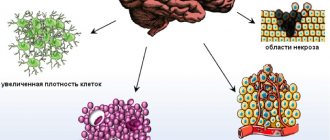
In the medical literature it is called multifocal. The peculiarity of this form is that neoplasia cells acquire increased plasticity.
As the tumor increases, the lumen of the blood vessels decreases, which leads to the spread of tissue necrosis and hemorrhages.
Glioblastoma multiforme also contains many small vessels inside.
Gliosarcoma
When carrying out instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods, the presence of elements of sarcoma is determined.
Specific symptoms arise at the second stage, as a result of which identifying the disease at the first stage of development is difficult.
Giant cell
This form got its name due to the fact that the tumor contains large multinucleated cells.
Symptoms
The morphological features of the tumor (infiltrative, “penetrating” growth, the rate of increase in the mass of glioblastoma) lead to the rapid development of symptoms.
The main symptoms can be divided into two parts: general cerebral and focal manifestations. General cerebral syndromes include hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome (expanding headaches, nausea, weakness), vestibular (uncertainty of gait, dizziness). Focal manifestations depend on the specific location of the tumor and include speech disorders, changes in the mental sphere, memory loss, inability to perform complex actions, etc.
Sometimes, against the background of a short period of general weakness and headache, a picture of a hemorrhagic stroke may develop due to extensive hemorrhage into the tumor tissue. If the brain stem is damaged, the patient's life and death are quickly threatened.
Based on the size of the tumor, its cytological nature (immaturity of the cells that make up the tumors and the rate of their growth) and some other parameters, four degrees of glioblastoma are distinguished.
Stages
Glioblastoma, which affects the brain, has 4 stages of development, each of which is characterized by certain features.
Stage 1
There are no signs of a malignant process during diagnostic measures. The neoplasm gradually affects new cells, but grows slowly.
With treatment, the patient has a chance for a full recovery.
Stage 2
The tumor acquires symptoms of malignancy, but its increase in size is also slow.
Timely treatment can achieve a complete cure in some cases.
Stage 3
The tumor begins to affect the deep layers of brain tissue, which provokes the appearance of severe symptoms.
Glioblastoma begins to grow rapidly and is characterized by a pronounced malignant nature. Recovery can only be achieved in exceptional cases.
Stage 4
Glioblastoma g4 has a severe course and is characterized by rapid growth. The symptoms are severe.
At stage 4, decay begins to occur. The tumor is most often inoperable. Patients are given maintenance therapy.
Diagnostics, prognosis
When you suspect that a person has a brain blastoma, you need to urgently undergo diagnostics. After this, the doctor will be able to tell you about the prognosis and chances of a full recovery. The sooner all examinations are completed, the higher the likelihood of a positive prognosis.
Diagnostics
A tumor and its level of spread can only be identified through diagnosis. It is especially important in the initial stages of glioblastoma development, because Symptoms in the first weeks may be very mild. To undergo the examination, you will need to contact a specialist in the field of oncology.
Diagnostics include:
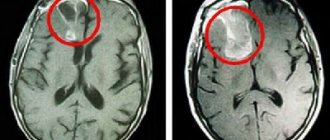
- MRI or CT scan with contrast will help determine the location and size of the tumor.
- PET (positron emission tomography) is effective in detecting relapses.
- Biopsy - allows you to laboratory examine the tumor and determine its type.
After making a final diagnosis, the doctor will be able to talk about the prognosis and prescribe precise treatment.
Forecast
Recovery can only be achieved with grade 1 or 2 glioblastoma. This will require a large number of medical procedures, but even then there will be a high probability of relapse with a fatal outcome.
Survival rates for grade 3 or 4 glioblastoma are extremely low. After successful treatment, only 10% of patients can live for 2 to 5 years. If the tumor is multiform, then death will occur in the first 40 weeks after the onset of tumor development. Such sad statistics are due to the fact that it is impossible to completely get rid of the tumor, which is why glioblastoma often reappears in the patient even after surgery. Moreover, relapse occurs in 80% of cases.
Very often, grade 4 glioblastoma turns out to be completely inoperable. In this case, life expectancy may be very short, but to increase its duration, doctors prescribe medications or undergo special procedures. If the cancer began to occur with other serious pathologies, then the consequences and prognosis will be even worse.
What causes the greatest fear among patients is the fact that almost everyone has to live out their last days and die in severe pain. They experience extremely severe headaches, lose intelligence, and experience hallucinations and seizures.
Children under 2 years of age who are diagnosed with low-grade glioblastoma have a high chance of a full recovery. However, treating a small child can be quite difficult, and a positive prognosis is only possible with complete removal of the tumor, after which all symptoms will subside in the coming days. If glioblastoma is highly malignant, then the baby’s lifespan will not exceed two years.
The prognosis for a woman during pregnancy will also be unfavorable. Many methods of therapy will not be applicable for her, because... the body may react negatively to them, causing the baby to suffer. But in most cases, the patient manages to give birth to a baby and live for some more time if she receives full treatment immediately after childbirth, while using some techniques even during pregnancy.
Causes
Experts have not established the exact reasons for the development of formation on brain tissue. But many years of research have made it possible to identify a number of provoking factors. According to scientists, they can significantly increase the risk of developing malignant tumors.
Of the glial tumors, glioblastoma is considered the most aggressive and common neoplasm, which leads to disability.
Life expectancy after diagnosis usually does not exceed 14 years. Even a combined treatment does not improve this indicator.
Hematologist, oncologist
Khazova Olga Vladimirovna
5 years experience
A large group of patients had loved ones suffering from similar cancers. As a result, experts concluded that genetic predisposition is of great importance in the development of the disease.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Scientists believe that factors such as smoking and drinking alcohol in large quantities, living in areas with an unfavorable atmosphere can be provocateurs.
The reasons for the development of the process of cell mutation include various injuries to the skull and brain. They can provoke the spread of inflammation, which leads to cell transformation.
The influence of toxic chemicals, radiation, and ionizing radiation also has a negative effect on the body when a person has been exposed to it for a long time or received radiation in large doses.
Causes of glioblastoma
Cancer is an unpredictable phenomenon. It is difficult for doctors to determine the causes of the development of the disease and the occurrence of tumors. However, among the most likely are:
- genetic predisposition (presence of the disease in close relatives);
- the effect of ionizing radiation on body tissues;
- as a concomitant pathology of neurofibromatosis, astrocytoma (grades 1 and 2), etc.;
- when interacting with chemical reagents (for example, regular inhalation of vapors of harmful substances);
- congenital pathology in children that appears during the formation and development of the child (embryo).
The risk group includes:
- men from 40 to 60 years old;
- those who have close relatives with this disease (or with low-quality formations in general);
- people working in the production of harmful substances (PVC, chlorine compounds, etc.);
- patients who previously had cancer (including glioblastoma).
Clinical picture
Glioblastoma, especially the multiforme type, may be accompanied by specific signs already in the first stages that allow one to suspect the presence of brain damage.
Specific signs
The cause of the clinical picture is the spread of the pathological process to important parts of the organ responsible for motor and speech functions.
In the early stages, headache occurs. At first it is temporary and appears after physical activity.
Over time, when the tumor increases in size and begins to put pressure on neighboring structures, the painful sensations become constant and severe. They cannot be relieved with painkillers.
Prognosis for glioblastoma
Glioblastoma of the brain is a neoplasm that belongs to the 4th degree of malignancy.
With glioblastoma, the patient sleeps all the time and becomes lethargic. Nausea also occurs in the morning.
Over time, the neoplasm also affects the visual apparatus, which manifests itself in the form of deterioration in the quality of vision and double vision. In later stages, complete loss of vision is possible.
Patients experience memory problems and decreased intelligence, which is due to the effect of cancer cells on the meninges. The sense of smell is impaired, as a result of which a person ceases to perceive odors and their perception changes. Often this sign becomes a reason to contact a specialist.
When conducting a neurological examination, a violation of movement coordination is established. This symptom indicates damage to the vestibular apparatus.
As the disease progresses, paralysis, decreased sensitivity of the limbs, and numbness of the skin are noted.
There is also a disturbance in speech, breathing, and the appearance of hallucinations. In some cases, death may occur during sleep as a result of asphyxia.
General signs
In addition to the occurrence of specific symptoms, in the presence of a malignant tumor, general symptoms also appear. First of all, weakness, nausea, apathy, and irritability are observed. Patients experience loss of appetite, resulting in weight loss.
If hemorrhages occur, laboratory testing confirms anemia. This condition is accompanied by weakness, headaches and dizziness.
Classification of tumors
Based on cell type, there are three types:
- giant cell glioblastoma (large cells containing two or more nuclei);
- multiform (different tissues, many hemorrhages and blood vessels);
- gliosarcoma (the tumor affects only glia).
Based on localization in the brain, malignant tumors are divided into 5 types:
- stem;
- isomorphic cell glioblastoma;
- multiform;
- polymorphocellular;
- Grade 4 glioblastoma.
The first type is not curable. Operations in this case are impossible. Malignant cells are located in the trunk connecting the spinal cord and brain.
Surgical intervention in such a delicate area is dangerous and leads to disruption of the musculoskeletal system. For this reason, in most cases, stem glioblastoma is inoperable. They are usually detected by the presence of problems with heart rate and breathing.
The isomorphic cellular form is less common than the others. The tumor consists of cells of one type - round or oval. It is characterized by unclear contours and numerous centers of neoplasms.
Multiforme is characterized by a variety of atypical cells that arise from glia (the connective tissue of the network of neurons). As a result of exposure to unfavorable factors, healthy cells transform into malignant ones.
It is possible for head cancer to descend down the trunk, engulfing the spinal cord and further spreading to other neural systems. A third of brain glioblastoma tumors are of the multiforme type.
The most common type is polymorphocellular. Cells, as a rule, are large, single-celled and of different shapes. Histological examination does not clearly reveal the cytoplasm of the cells due to its low content, so this species is not easy to detect.
Based on the number of malignant cells, tumors are divided into 4 grades. The first stage is transitional. Some benign ones turn into cancerous ones. This type is the easiest to treat.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to diagnose glioblastoma at this stage. This is due to the complete absence of symptoms. Only a random examination reveals this degree of brain cancer.
At the second stage, slow growth of cells occurs, among which atypical ones are increasingly found. The third is characterized by a large number of malignant tumors. Growth occurs much faster. Photos of the patients' brains before and after treatment are shown below.
The most dangerous grade 4 glioblastoma (Grade 4) is the most common. Simply because the last stage is easier to diagnose. Usually at this stage, pronounced syndromes appear, with which the patient consults a doctor. Once diagnosed, people die within months.
The more malignant tumors there are, the less chance of recovery. Of course, this also depends on the location of the tumor in different lobes of the brain and on many other factors.
Diagnostic methods
In order to determine the location of brain glioblastoma and its course characteristics, it is important to conduct a comprehensive study.
MRI or CT
The procedure is carried out using a contrast agent, which allows the tumor to be visualized in the images, its size, location and borders to be determined.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are highly informative methods of instrumental diagnostics, as they allow layer-by-layer scanning of tissues and analysis of the structure of the tumor.
Biopsy
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed a biopsy, which is carried out by sampling a section of tumor tissue. The resulting samples are sent for laboratory testing.
Analysis of the biopath allows you to confirm the presence of cancer cells in the tumor and make an accurate diagnosis. The procedure in this case is complex and is carried out only by a highly qualified doctor.
PAT
Chitron emission tomography is used to detect the re-development of pathology if the patient has a history of treatment for such a formation.
PET is also used to determine the presence of a primary tumor.
Radiography
X-ray examination is prescribed to identify metastatic lesions. But with glioblastoma, metastases do not always occur in distant organs. Most often, the disease spreads only to brain tissue.
But x-rays also make it possible to determine the extent of the spread of the pathological process and determine the presence of necrosis.
The patient will also have to undergo a blood test. Laboratory testing is prescribed to determine tumor markers, the inflammatory process, and various changes in composition.
Treatment
Therapy when glioblastoma is detected is aimed at removing the tumor, achieving long-term remission, and reducing the risk of complications. But not all treatment methods achieve a favorable prognosis.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
The treatment method is selected by the attending physician, taking into account the characteristics of the course, form and degree of development of the disease.
Surgery
Surgery to remove the tumor is the most effective treatment method. During the procedure, the surgeon removes the glioblastoma, which improves the prognosis and prolongs the patient’s life.
But surgical intervention is one of the most complex procedures, and not every highly qualified specialist will be able to completely remove the affected tissue. This is due to the fact that the tumor grows strongly into the structure of the brain and in certain areas the changed cells are almost impossible to notice.
Today, a special solution is used during surgery. It allows you to visualize the affected areas.
Radiation therapy
The technique is used after surgical removal of glioblastoma. The use of ionizing or radioactive exposure can destroy the remaining cancer cells and improve the prognosis.
Treatment of glioblastoma
Glioblastoma of the brain is an oncological disease that requires complex and long-term treatment, the result of which is not always positive.
The duration of treatment is about 6 weeks. In this case, the radiation dose is about 60 Gy for the entire duration of therapy.
Targeted radiation exposure not only destroys malignant cells, but also has a negative effect on healthy tissue. This results in a number of unpleasant side effects.
Complications after radiation therapy occur in rare cases, since the radiation is administered gradually.
Chemotherapy
The technique involves the use of special chemotherapy drugs that have a destructive effect on pathologically altered cells and can improve the prognosis for brain cancer.
Therapy includes several courses of 5 days. The break between them must be at least 23 days.
Often six courses are prescribed. Drugs are selected individually depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the course of the disease.
Gamma Knife
This is a modern technique that is carried out using radiation exposure on a tumor.
Nutrition for glioblastoma of the brain
Glioblastoma of the brain is a cancer that requires systemic treatment and an integrated approach to it.
The radiation dose is insignificant, but has a negative effect on the tumor. Thus, the likelihood of damage to tissues unaffected by the pathological process is minimal.
As a result, the procedure allows you to achieve stable remission, improve the prognosis and eliminate the occurrence of unpleasant side effects.
Drug therapy
It is impossible to cure the disease with the help of medicines. The drugs are used to relieve severe symptoms and maintain immunity after chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Patients are prescribed medications in the form of tablets or intravenous solutions that improve blood supply to the brain. Multivitamin complexes are also recommended.
All medications are prescribed only by the attending physician, who also determines the dosage and duration of use.
How is radiation therapy performed for glioblastoma of the brain?
Before the treatment process, a comprehensive examination is carried out: laboratory tests, magnetic resonance spectroscopy, positron emission tomography, biopsy. Based on these data, doctors of leading specializations (oncologist, neurosurgeon, radiotherapist) draw up a clear plan, which indicates the dose of ionizing radiation, exposure time, number of fractions, and cycle duration.
The principles of radiation therapy are to cover areas of the brain located on the periphery of the tumor with radiation, which increases the effectiveness of therapy for glioblastoma . That is, radio rays destroy malignant cells and affect healthy structures. Over the course of subsequent sessions, the cancer cells die, while all the others are restored, thanks to their high regenerative ability.
The procedure is carried out in a special room, where the patient is positioned on a couch and fixed. Using a remote device, the radio beam is directed locally to the marked area or to the entire brain in case of widespread metastasis. The medical staff is in another room and monitors the procedure. Communication is possible through a microphone. The manipulation is absolutely painless and does not cause discomfort. The number of sessions for glioblastoma reaches 30, the course takes at least 6 weeks. The total dose is no more than 65 Gy, 2 Gy per fraction. Unfortunately, a lower dosage will not give the expected result.
Complications
The disease is accompanied by severe pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers. Lack of treatment leads to brain swelling, and mental disorders also occur with glioblastoma.
When the tumor begins to disintegrate and the disease becomes grade 4, treatment is no longer carried out. In this case, patients most often completely lose self-care skills. Memory loss, impaired concentration, and partial or complete loss of vision are observed. Personality disorder also occurs.
But even after treatment, relapse is observed in more than half of the cases. The recurrence of glioblastoma is caused by cancer cells remaining after surgery. Sometimes it is not possible to completely remove them.
The most severe consequence is death, which occurs 30-40 weeks after the transition to the last stage.
Forecast
Complete recovery or long-term remission can be achieved only in cases where the disease is at stage 1 or 2. Surviving a diagnosis of glioblastoma is possible only with timely treatment.
Symptoms of glioblastoma
Glioblastoma is a malignant intracranial tumor of the central nervous system (CNS).
If the pathology is at stage 3, only about 10% of patients manage to survive for 2-5 years after treatment. But when a multiform type of tumor is established, death occurs 3-4 months after the formation of the tumor begins. This is due to the fact that it is impossible to completely remove glioblastoma. Relapse is observed in 80% of cases.
At the last stage, the tumor is inoperable and begins to disintegrate. Treatment in this case is aimed at relieving symptoms and alleviating the patient’s condition. The prognosis is unfavorable. Patients often die due to complications.
Prognosis for glioblastoma
This type of brain tumor is not only the most aggressive, but also the most common. About 52% of primary brain tumors are glioblastomas.
When treating cancer abroad, the doctor usually announces to the patient and his relatives the prognosis of the effectiveness of the treatment. In its compilation, it is based on the histological type of tumor, stage of the disease, age and general health of the person. Glioblastoma is a dangerous disease with not the most positive prognosis. However, in younger patients the chances are much higher; the five-year survival rate is:
- for children and adolescents under 19 years old - 66%;
- for adult patients from 20 to 45 years old - 50%;
- for patients over 75 years old - 5%.
If the tumor is relatively benign and the patient refuses treatment, he has 3-5 years left at his disposal, during which the tumor will continue to actively grow and invade more and more new areas of the body. By seeking help in a timely manner, the patient has every chance to continue living for up to 10 years. If the tumor is relatively malignant, the patient's life expectancy is about 2-3 years. When the tumor is malignant and is at the last stage, the average life expectancy is from 4-12 months.
Despite new treatment methods, the disease can be dangerous due to its relapses, which is why brain cancer is one of the key problems of modern oncologists. The search for the most effective ways to treat glioblastoma continues.
Prevention measures
Since experts have not established the exact reasons for the development of the tumor, no special preventive measures have been developed. In order to reduce the risk of developing the disease, it is recommended to follow general rules, including:
- Timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases when the pathological process affects the head area.
- Elimination of exposure to radiation, ionizing radiation, chemicals and toxic substances.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Patients are advised to stop smoking and drinking alcohol, as they have a negative effect on the entire body.
- Avoiding hypothermia and overheating. In the cold season, you need to wear a warm hat, and in the summer, wear a Panama hat, scarf or cap.
It is also important to undergo regular preventive examinations. This will help to promptly identify the disease and carry out treatment. If unpleasant symptoms occur, there is no need to postpone visiting a specialist. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Glioblastoma of the brain is a malignant lesion. In the initial stages, it develops slowly, which allows treatment and full recovery.
But already at stage 3 the prognosis is unfavorable. That is why, when identifying a pathology, it is important to follow all the doctor’s clinical recommendations and undergo treatment. After surgery, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations to exclude relapse.