Causes
The vast majority of cases of dysarthria are registered in childhood and are often a congenital pathology caused by the following problems:
- cerebral palsy;
- severe toxicosis and gestosis during pregnancy;
- lack of oxygen during fetal development;
- Rhesus conflict;
- maternal illnesses during pregnancy;
- difficult childbirth, birth injuries, newborn asphyxia;
- jaundice of newborns;
- prematurity.
The causes of acquired dysarthria include:
- infectious damage to the brain and its membranes (encephalitis, meningitis);
- severe purulent forms of otitis;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- brain tumors;
- acute or chronic cerebrovascular accidents;
- hemorrhages in the brain;
- autoimmune lesions;
- Parkinson's disease;
- severe intoxication;
- multiple sclerosis;
- surgical interventions on the brain or skull bones;
- alcohol or drug abuse;
- syphilitic damage to the central nervous system, etc.
Often, dysarthria occurs after a long coma that occurs after severe trauma, poisoning or a major stroke.
Diagnosis of erased dysarthria
Erased dysarthria is diagnosed using a number of medical and pedagogical studies. Be sure to study the child’s medical history, as well as the course of pregnancy and childbirth in the mother. An analysis of the outpatient card is carried out: the results of instrumental diagnostic methods may be needed.
The examination is phased and includes:
- Speech therapy examination involves assessing the state of motor skills, facial muscles, articulatory apparatus, and speech breathing. After this, the speech therapist studies the quality of sound pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, and the ability to capture various sounds. If an erased form of dysarthria is suspected, the patient is referred for consultation to a neurologist;
- An examination by a neurologist is needed to identify the nature of the disorders - hyperkinesis, paresis, dystonia, atony. The doctor also determines the location of the brain lesion. To clarify the diagnosis, EEG, electroneuromyography, CT, and MRI are prescribed.
After the baby has passed all the examinations, he will be consulted again by a speech therapist/speech pathologist. Having the conclusions in hand, he determines the type of speech disorders and draws up a plan and form of work with the child.
Types and degrees
The classification of dysarthria is based on the localization of the pathological focus, which determines the severity of certain symptoms. The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- bulbar: associated with damage to the nerve nuclei in the medulla oblongata;
- pseudobulbar: occurs when there is a pathology of the nerve fibers responsible for conducting impulses from the cortex to the nuclei of the cranial nerves;
- extrapyramidal (subcortical): the functioning of the subcortical nuclei is disrupted;
- cerebellar: occurs with pathology of the cerebellum and nerve fibers coming from it;
- cortical: pathological foci form directly in the cerebral cortex.
Depending on the severity of the pathology, there are 4 degrees of the disease:
- first (erased): problems with the pronunciation of sounds are discovered only during an examination by a speech therapist;
- second: pronunciation defects are clearly visible to others, but the patient’s speech remains understandable;
- third: the sounds are changed to such an extent that the patient is understood only by close relatives who are in constant contact with him;
- fourth: speech is impossible or is an incomprehensible set of sounds.
Types and characteristics of cortical dysarthria
There are two known types of cortical dysarthria. The first option is due to unilateral or more often bilateral damage to the lower part of the anterior central gyrus. In these cases, patients experience selective central paresis of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus (most often the tongue). Selective cortical paresis of individual muscles of the tongue leads to a limitation in the volume of fine isolated upward movements of the tip of the tongue. Patients have impaired pronunciation of anterior lingual sounds.
The cause of the second variant of cortical dysarthria is a lack of kinesthetic praxis (the ability to pronounce a series of speech sounds). This occurs with unilateral lesions of the cortex of the dominant (usually left) cerebral hemisphere in the lower postcentral cortex. Patients suffer from pronunciation of consonant sounds, especially hissing sounds and affricates (consonant sounds of a complex formation, which consist of a plosive and fricative component - the Russian “Ts” and “Ch”).
Variable and ambiguous articulation disorders occur. Finding the right articulatory structure at the moment of speech disrupts its smoothness and slows down the pace. Patients experience difficulty in sensing and reproducing certain articulatory patterns. There is a lack of facial gnosis: the patient finds it difficult to clearly localize a point touch to certain areas of the face, especially in the area of the articulatory apparatus.
The third variant of cortical dysarthria is associated with insufficiency of dynamic kinetic praxis. This is observed with unilateral lesions of the cortex of the dominant hemisphere in the lower parts of the premotor areas of the cortex. When kinetic praxis is impaired, patients find it difficult to pronounce complex affricates, which can break up into their component parts. The following speech defects are observed:
- Replacing fricative sounds with stop sounds (Z to D);
- Omissions of sounds in consonant clusters;
- Selective deafening of voiced stop consonants.
Speech becomes tense and slow. Difficulties are noted when reproducing a series of sequential movements following a demonstration or verbal instructions. The structure of the speech defect: FFND, there are no disorders of prosody (the unity of interconnected components, which include melody, duration, intensity, tempo of speech and timbre of pronunciation).
Symptoms
The manifestations of dysarthria are very extensive and largely depend on the level of damage. Changes in articulation occur against the background of the following disorders:
- increased or decreased tone of the muscles responsible for articulation (muscles of the lips, tongue, soft palate);
- spasms of the facial and neck muscles;
- restrictions on tongue movements;
- increased salivation;
- lack of complete closure of the lips or, conversely, excessive closure;
- breathing problems resulting in intermittent speech.
Each form of dysarthria has its own characteristic speech and non-speech manifestations.
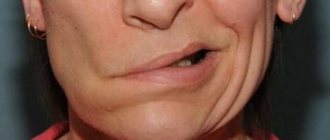
- The bulbar form, in addition to slurred speech, is manifested by dullness of the voice and severe speech breathing impairment. Patients note that it has become difficult for them to close their eyes and move their eyebrows towards the bridge of their nose. With unilateral lesions, slight asymmetry of the oval of the face is noted. Subsequently, swallowing pathology develops: when drinking, liquid enters the nasal cavity, and later similar problems appear when eating thicker foods. Many people experience headaches, dizziness, nausea and weakness.
- The pseudobulbar form is characterized by slowness and abruptness of speech. The high tone of the tongue does not allow you to normally pronounce hissing sounds, as well as the vowels “i”, “e”, “s”. The lips do not close completely, resulting in saliva constantly leaking from the corners of the mouth. As pathology develops in infancy, problems with sucking and swallowing milk are noted.
- The main feature of the cortical form is a nasal voice combined with difficult pronunciation of consonants. Speech becomes drawn out and slow. This is due to damage to the tip of the tongue, which is responsible for pronouncing the letters “t”, “d”, “s” and others. In children, this pathology causes difficulty concentrating, reading and writing; adults often become depressed due to problems with speech.
- Extrapyramidal dysarthria is manifested by a constant change in speech speed from fast to slow and vice versa. Often the patient repeats the same words, phrases or syllables. The psycho-emotional state suffers significantly. The mouth is often half-open, and saliva accumulates in the corners of the mouth.
- With cerebellar dysarthria, speech loses smoothness and rhythm, and stress disappears in words. The strength of the voice is inconsistent, and speech is difficult due to the person’s constant tension. The pathology is accompanied by impaired coordination of movements, excessive sweating and impaired chewing of solid food.
What to do if a child is diagnosed with dysarthria: advice from a speech therapist
Some parents are faced with the fact that their child - natural or adopted - has speech problems and, hearing the word “dysarthria”, feel confused. What is dysarthria, why does it occur and how to correct it, says Resource specialist, speech therapist of the highest category, member of the Russian Dyslexia Association Galina Orlova.
− Dysarthria is a disorder of the pronunciation side of speech, which is associated with damage to the central part of the speech motor analyzer and a violation of the innervation of the muscles of the articulatory apparatus. Simply put, the child cannot fully perform the movements necessary for speech. Sound pronunciation suffers from this, explains Galina. - In milder cases, this is a distortion of certain sounds. In severe cases of the diagnosis, omissions and replacement of sounds may be noticed. The pace and expressiveness of speech are impaired.
Dysarthria can also be characterized by the presence of paralysis and paresis of the organs of articulation. In this case, incomprehensible speech is a consequence of the diagnosis, up to the absence of speech due to complete paralysis of the speech motor muscles - anarthria.
The causes of dysarthria can be different - deviations from the norm during intrauterine development due to toxicosis, hypertension, nephropathy in the mother, infectious diseases suffered by a woman during pregnancy, as well as asphyxia of newborns, rapid or prolonged labor, mechanical obstetrics, a long anhydrous period in childbirth
From the very first days of life, such children are observed by a neurologist. They are often prescribed medication, massage and other rehabilitation procedures.
− How to recognize dysarthria?
− An attentive parent may suspect it by the child’s unusual facial expressions, profuse salivation, the shape and position of the tongue, the ability to fix an articulatory position, and sound pronunciation.
− When should you start working with dysarthrics?
− It is advisable to begin speech therapy work with any speech disorder in early preschool age. The earlier the disease is diagnosed, treatment and corrective classes are started, the greater the chances of success.
− What should parents do if their child is diagnosed with dysarthria?
— The first step, of course, is an examination by a neurologist. There are no special medications to combat dysarthria. The doctor only corrects some neurological symptoms with the help of medications. It is also important to consult a speech therapist who knows the technique of speech therapy massage, who, after a full examination, will give a conclusion and recommendations.
In addition, experts advise developing fine motor skills. You can assemble puzzles and Lego sets, sculpt from plasticine - there are many games that develop little fingers. You can use non-traditional methods of influence, such as su-jok therapy. The simplest method of su-jok therapy is training with special massage balls.
Logorhythmics classes are recommended for children two to three years old, for example, according to Zheleznova’s method. To correct dysarthria in children five years old, a speech pathologist is involved in the classes.
− What is the focus of the speech therapist’s work in the classroom?
— The specialist is engaged in the development of the prosodic side of speech - rhythm, strength, timbre, melody, tempo, logical stress, diction, as well as articulation and sound pronunciation, auditory attention, phonemic hearing, correction of speech breathing. The speech therapist will also pay attention to the normalization of muscle tone in the articulatory muscles and the development of voluntary facial movements.
If you do not have the opportunity to visit a speech therapist, then you can work with your child at home on your own, having previously completed a course with a specialist.
I will give examples of some elements of speech therapy massage and self-massage: take turns puffing out our cheeks, retracting our cheeks; close and open your mouth, click your teeth; suck on a small piece of sugar or candy; imitate the resorption of a lollipop; lick your lips; We hold a piece of bandage or gauze with our teeth for a long time; the adult’s task is to try to carefully remove the fabric.
It is also important to perform a complex of articulatory gymnastics - these are the “Proboscis” exercises (pull your lips forward, teeth and lips are closed, hold for five seconds), “Fence” (lips in a smile are tense with the mouth slightly open, teeth are clenched, the lower jaw is in a calm state, hold for five seconds) and their alternation, “Window” (with each count we open and close our mouth), “Spatula” (when smiling with an open mouth on a relaxed lower lip, place the tongue flat, hold for five seconds), “Needle” (smile with an open with our mouth, we put our tongue forward, trying not to bend it upward), “Needle shovel” (alternating exercises), “Clock” (we smile with our mouth open, stick out our tongue and make movements to the right and left, while touching the corners of our mouth with our tongue), “ “Swing” (smile with an open mouth, the tip of the tongue resting either on the upper or lower teeth), “Horse” (we click the tip of the tongue, imitating the clatter of hooves).
Over the years of work, I have often met children diagnosed with dysarthria of varying severity. This type of speech disorder has become a global problem in recent years, so it is extremely important to identify disorders in time and consult a specialist. But parents should know that correctional work with dysarthric children should not be limited to classes with a speech therapist. For the best results, this work should be continued at home, on a walk and in any joint activities.
Press service of the Department of Labor and Social Protection of the Population of Moscow
Diagnosis of the disease
Neurologists and speech therapists diagnose dysarthria. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following examinations are prescribed:
- a detailed survey identifying the main complaints, the time and circumstances of their occurrence; collecting information about previous injuries and diseases, the presence of chronic pathology;
- neurological examination with mandatory assessment of the condition of the pharyngeal muscles, the quality of the mandibular and pharyngeal reflexes;
- speech therapy tests to assess speech disorders;
- examination by an ENT specialist for nasal voice (to exclude other causes of this symptom);
- general tests and examinations to assess the condition of the body: general blood and urine tests, tests for underlying infections and hormones, ECG;
- electroneuromyography: assessment of the conduction of nerve impulses along nerve fibers and muscles, as well as the quality of muscle response to stimulation;
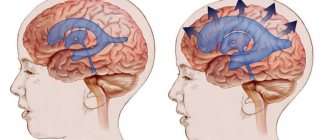
- transcranial magnetic stimulation: exposure of the cerebral cortex to magnetic radiation to assess the excitability of individual neurons and the cortex as a whole; allows you to evaluate the work of the speech and vision centers, the ability to perceive information, etc.;
- electroencephalography: registration of electrical impulses arising during the functioning of the brain; allows you to identify a number of pathological processes;
- MRI of the brain: allows you to identify abscesses, foci of necrosis after a stroke, signs of lack of oxygen, tumors and other pathological formations.
If necessary, additional tests and consultations are prescribed to exclude other causes of symptoms.
Diagnostics
A thorough examination and further therapy is carried out by a neurologist and speech therapist. In some cases, consultations with other highly specialized specialists may be required. At the initial stage, the doctor collects complete information - when the first symptoms appeared, whether there are any chronic diseases, whether family members have similar complaints.
After collecting anamnesis, the neurologist conducts a visual examination of the pharynx, checking the mandibular and pharyngeal reflex. The role of the speech therapist at the diagnostic stage is to assess speech abilities (pronunciation of sounds, changes in timbre during a conversation, disturbances in the tempo of speech).
If the patient’s voice is nasal, then to exclude dangerous pathologies in the nasal cavity, an examination by an otolaryngologist is prescribed. After a thorough visual examination, a number of diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- Electromyography (ENMG) is a diagnostic method that tests muscle activity, the functionality of the nerve innervating the damaged muscle, the affected area, and the severity of damage to the nerves and muscles.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a technique based on the activation of brain cells. The examination is carried out using a special apparatus with an alternating magnetic wave. The procedure helps determine the excitability of cortical neurons, the functionality of the cortex, and the interaction of certain parts of the brain with each other. Based on the results obtained, the doctor draws conclusions about the functioning of the speech centers, as well as the visual apparatus, cognitive functions (perception of information), and other things.
- Computed tomography (CT) is a study that allows you to examine in detail the internal organs, bone tissue and vascular system in different projections. The procedure takes only 10-15 minutes for each organ examined, after which the doctor receives a layer-by-layer X-ray image, which is used to make a diagnosis.
- Electroencephalography (EEG) is a study of the vital activity of the brain by recording impulses that come from its individual areas. The technique allows us to identify pathological processes occurring in the brain, as well as assess the nature and severity of the disorder.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is a scan of organs using magnetic waves to produce high-quality images. Diagnostics is designed primarily to identify brain abnormalities and a thorough examination of the vascular system. In addition, MRI is used to check intervertebral discs, bile ducts and other human organs.
Diagnostics is the most important stage, allowing you to make a reliable diagnosis and make the right prescription. If the type of pathology and its severity are incorrectly determined, it is impossible to make a correct prescription. This threatens that the prescribed medications will not bring the desired result, and the disease will progress.
To diagnose pathology, you can go to the Yusupov Hospital at any time of the day, where certified specialists will conduct a detailed examination of organs using the latest equipment. Thanks to the latest generation of safe devices, doctors can accurately determine the type of pathological process without harm to the patient’s health. This will allow you to select an individual course of treatment and eliminate the dangerous disease in a short time.
Treatment of dysarthria
Treatment requires an integrated approach. Classes with a speech therapist, a proven medication regimen, physiotherapy, articulation gymnastics - all this allows you to achieve a good result.
Medicines are selected depending on the specific form of the disease. Doctors use:
- nootropics (encephabol, picamilon) to stimulate brain function and improve memory;
- sedatives (persen): stabilize the functioning of the nervous system, relieve excess tension;
- calcium channel blockers (cinnarizine, gliatilin): improve blood circulation in the brain, increase the supply of oxygen and nutrients;
- means for accelerating metabolism (actovegin): improve metabolism in the central nervous system.
If necessary, drugs from other groups are used. The dosage, combination of agents and dosage regimen are selected individually.
Classes with a speech therapist are a long-term process aimed at stimulating fine motor skills and developing the muscles necessary to pronounce sounds. The complex includes:
- articulatory gymnastics;
- exercises for the development of fine motor skills (especially relevant for children);
- breathing exercises;
- restoration of writing and reading skills;
- correction of speech expressiveness.
Additional effects have:
- physical therapy (stabilizes blood circulation in the brain and improves respiratory function);
- restorative massage;
- speech therapy massage: kneading the tongue, lips, palate, cheeks to strengthen the articulatory apparatus;
- physiotherapy: magnetotherapy, laser exposure, therapeutic baths and applications;
- treatment at resorts, balneotherapy, etc.
If dysarthria is caused by any disease, the process of its treatment proceeds in parallel.
Make an appointment
Treatment in Moscow
For many years, the Yusupov Hospital has specialized in the treatment of dysarthria in children and adults. The high professional level of specialists allows us to accurately determine the type of pathology, which eliminates the possibility of incorrect prescription of therapeutic measures. An individual approach to each patient guarantees a favorable atmosphere throughout the entire course of treatment and rehabilitation. The main directions of the clinic:
- Treatment of complex neuralgic pathologies - multiple sclerosis, major stroke and other dangerous diseases that cause the death of certain groups of brain cells.
- Help for patients with cancer - chemotherapy, therapy that eliminates pain syndromes and painful symptoms.
- Treatment of progressive brain diseases - Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, Pick's disease and other rare forms of dementia.
- Rehabilitation of patients after severe operations, chemotherapy, traumatic brain and spinal injuries, major stroke and radiation therapy.
- Effective treatment and correction of speech disorders. The range of measures includes constant monitoring by specialists, physiotherapeutic measures, therapeutic exercises and classes with a speech therapist who has extensive experience in the successful treatment of dysarthria.
By contacting the Yusupov Hospital, the patient receives a guarantee of a speedy recovery and the most favorable outcome. You can make an appointment for a consultation with specialists by phone.
Make an appointment
Prevention
In order not to look for where and how to treat dysarthria, it is important to pay attention in advance to measures for its prevention:
- during pregnancy, follow all doctor’s recommendations, eat well and rest;
- develop fine motor skills;
- conduct logorhythmic exercises;
- exercise and dance;
- visit a speech therapist and neurologist for early identification of problems and their correction;
- eat well.
If we are talking about an adult, the rules for preventing dysarthria include:
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- control blood pressure levels, prevent vascular diseases;
- timely treatment of emerging pathologies, including infections;
- compliance with safety rules that exclude intoxication in the workplace;
- minimize smoking and alcohol consumption;
- adhere to the principles of proper nutrition, avoid obesity;
- take regular walks in the fresh air.
Massage for erased dysarthria
Latent dysarthria refers to mild disorders of speech function in children. Speech therapy massage for dysarthria in pictures allows parents to master exercises aimed at strengthening or relaxing articulatory muscles, stimulating proprioceptive sensations. Speech kinesthesia is important in the formation of impressive and expressive speech.
Massage for erased dysarthria enhances cerebral circulation and metabolic processes in the neurons of the brain, which improves the flow and formation of many mental processes (attention, memory), harmonizes all processes that occur in the whole organism.
When working with children suffering from latent dysarthria and speech pathology, speech therapists and rehabilitation therapists use various types of massage of reflexogenic zones (feet, hands, scalp), segmental reflex, linear, acupressure massage.
Speech therapy massage is a method of active mechanical influence. It changes the condition of muscles, blood vessels, nerves and tissues of the peripheral speech apparatus. Under the influence of massage, the elasticity of muscle fibers, strength, volume and contractile function, and muscle performance increase. Massage for latent dysarthria is one of the methods of energetic and physical influence on the human body. It soothes, relieves pain, helps overcome illness, and promotes the physical, mental and physical development of children.
The use of speech therapy massage for erased dysarthria can significantly reduce the time of correctional work, especially on the formation of the pronunciation side of speech. Thanks to the use of massage, the formation of normative pronunciation of sounds in some cases occurs spontaneously.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
The Health Energy Clinic offers each patient comprehensive treatment for dysarthria of any form and degree. Experienced specialists work in a team, complementing each other. We offer:
- full diagnostics using modern equipment;
- consultations with experienced specialists: neurologists, speech therapists, otorhinolaryngologists, etc.;
- prescription of modern drugs for the correction of dysarthria;
- restorative and therapeutic massage;
- physical therapy if indicated;
- Exercise therapy and manual therapy if necessary;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment;
- teaching relatives the rules of speech development, massage and gymnastics.
Restoration of voice and speech breathing
The basis of the orthophonic method of voice production for dysarthria is the creation of a functional relationship between breathing, articulation and voice formation. Speech therapists create an individual course of lessons, which consists of six stages:
- Rational psychotherapy;
- Corrections of physiological and phonation breathing;
- Training of kinesthesia and coordination of the vocal apparatus with phonopedic exercises;
- Automation of correct phonation with vocal exercises;
- Correction of sound pronunciation, breathing coordination, phonation and articulation;
- Full automation of new skills.
After preliminary psychotherapeutic preparation, the speech therapist directs efforts to maximize the mobility of the intact areas of the vocal and speech apparatus and develop the motor function of the vocal folds. The first part of the lesson involves articulation exercises, activation of the muscles of the soft palate and the back wall of the pharynx, and breathing exercises. The content of the work in the second part includes the development of height, duration and strength of sound, voice timbre, melodic and intonation aspects of speech.
To strengthen the muscles of the palatine curtain, exercises are used in alternating its tension and relaxation. The patient is asked to abruptly pronounce the sound “a” before the end of the yawning movement, and with the mouth wide open, move from pronouncing the sound “a” to the sound “p”, holding the air in the mouth under pressure. The patient's attention is drawn to the sensation of the condition of the velum palatine. Speech therapists use an exercise to develop the strength, timbre and pitch of the voice: counting directly in tens with a gradual strengthening of the voice and counting backward with its gradual weakening. To develop the pitch of timbre and intonation of the children’s voices, they conduct various games, dramatizations, and read fairy tales based on roles.
A popular method of treating dysarthria is breathing exercises by Alexandra Strelnikova. It allows you to adjust speech breathing and establish smoothness of speech. The essence of gymnastics is a sharp breath through the nose, which will focus the child’s attention. Inhalations should be carried out naturally and arbitrarily.
The exercises performed involve all parts of the body in the charging process, causing a general physiological reaction of the body as a whole and increasing the need for oxygen. Depending on the degree and form of dysarthria, the speech therapist individually selects breathing exercises.
Advantages of the clinic
The modern multidisciplinary clinic “Health Energy” provides high-quality medical services at an affordable price. Each patient can count on:
- reception by appointment without long waiting in line;
- polite and tactful treatment from the staff;
- assistance from general and specialist doctors;
- consultations with foreign experts if necessary;
- full range of laboratory, instrumental and functional diagnostics;
- modern integrated approaches to treatment;
- medical supervision during therapy, treatment adjustment if necessary;
- full rehabilitation using physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy, etc.;
- issuance of necessary certificates and conclusions;
- comfortable day hospital.
Dysarthria deprives a person of the opportunity to be understood by others. At the first sign of “porridge in your mouth”, do not delay in contacting a specialist, make an appointment at Health Energy.
Speech therapy massage
Speech therapy massage is one of the main elements of the rehabilitation program for patients suffering from dysarthria. Rehabilitologists at the Yusupov Hospital use various types of massage for dysarthria: probe, acupressure, facial muscles, tongue. Depending on the type and degree of dysfunction of the articulatory and facial muscles, specialists select one or another type of influence.
Any massage is aimed at improving the condition of the affected areas of the patient’s body. Speech therapy massage for dysarthria is no exception. Reviews from doctors and patients indicate that this procedure helps eliminate both increased and decreased muscle tone, changes the technique of pronunciation of words for the better, activates oxygen exchange between blood and tissues, and increases the capabilities of the articulatory apparatus.
Speech therapy massage in the rehabilitation clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is performed by qualified speech therapists and speech pathologists who have a clear understanding of the characteristics of the muscles of the speech apparatus. The program of speech therapy massage for dysarthria in patients in the acute phase of stroke, traumatic brain injury, and demyelinating diseases of the nervous system is discussed at a meeting of the expert council, in which doctors and candidates of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category take part.
The hospital's medical staff is attentive to the problems of patients with speech impairment. First of all, the speech therapist assesses the performance of the patient’s speech apparatus, palpates, and conducts exercises to determine the stage of the disease.
If performed regularly, speech therapy massage allows you to achieve the following positive changes in the treatment of dysarthria in a fairly short time:
- reducing the number of pathologies of the articulatory apparatus;
- normalization of muscle function that was not previously involved;
- improvement of diction;
- increase in the number of articulatory movements;
- normalization of facial muscle tone.