Ear pain - mild or intense, shooting or aching - is a symptom that can indicate both a disease of the hearing organ and pathological processes occurring in nearby organs and tissues. According to statistics, otitis media is the most common cause of ear pain. However, the diversity of its forms and many other diseases with similar symptoms require accurate diagnosis and different treatment approaches. To establish the true causes of ear pain, it is necessary to be examined by an otolaryngologist, and sometimes by a neurologist, dentist, and even a cardiologist.
At CELT you can consult an otorhinolaryngologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
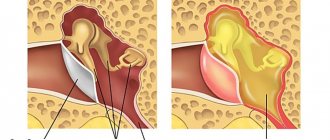
Otitis externa
Most often, inflammation of the outer ear is bacterial in nature.
The causes of infection may be:
- trauma to the external auditory canal, for example, from a sharp or blunt object, or from a hearing aid;
- skin defects due to eczema, psoriasis, diabetes and other diseases;
- too thorough removal of earwax, which creates an acidic environment that prevents the growth of microbes;
- frequent entry of water into the outer ear (“swimmer’s disease”).
Symptoms of external otitis:
- acute ear pain, aggravated by pressing on the tragus or pulling the earlobe;
- possible itching and a feeling of “stuffiness” in the ear;
- discharge of a purulent or bloody nature, sometimes having an unpleasant odor;
- examination reveals swelling and hyperemia of the external auditory canal;
- possible hearing loss;
- enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ear on the affected side.
The course of the disease may be complicated by a perforation of the eardrum, which cannot be determined without a visit to an ENT specialist.
External otitis of fungal origin is a common phenomenon, usually occurring in patients with low immune status or due to long-term use of antibacterial drops. It is characterized by severe itching, the formation of crusts, profuse thick discharge and the absence of a therapeutic effect from the use of antibiotics.
Separately, it is worth noting the localization of a boil on the skin of the external auditory canal or inflammation of the atheroma. The clinical picture is similar to otitis externa, but upon examination there is a more localized focus of inflammation with an opening from which pus and blood can be discharged.
Otomycosis - symptoms and treatment
Questioning, anamnesis collection
Diagnosis begins with collecting anamnesis. The doctor asks a series of questions:
- When did the disease begin and how did it progress?
- Has the patient previously had otitis media?
- Was there a fungal infection of other organs and systems, for example the urogenital tract.
- How long has the patient been sick, with what frequency, have there been any exacerbations.
- Does the patient take antibiotics, steroid drugs, cytostatics (most often used in the treatment of cancer) and chemotherapy drugs.
- Does the patient suffer from allergies [2][3].
- Are there any unfavorable factors in everyday life and work?
- What concomitant diseases did the patient have?
- Are there chronic infections [6].
Inspection, evaluation of complaints
When it comes to candidiasis , patients complain of whitish discharge from the ear with a cheesy consistency. During otoscopy, narrowing of the ear canal in the cartilaginous part and hyperemia (redness) of the eardrum are observed [6][11].
With aspergillus infection, the discharge is dark, almost black, and has a thick consistency. During otoscopy, narrowings in the bony part of the ear canal are observed, the eardrum may bulge and lose its identification marks [13][15].
With penicilliosis , the itching is more pronounced, the discharge resembles liquid earwax, the cartilaginous area is infiltrated, and protrusion, hyperemia or erosion may be observed on the eardrum, which falsely indicates perforation (through damage).
If we talk about mycosis of the middle ear and postoperative cavity , the main complaints are decreased hearing, discharge from the ear, periodic itching, and dizziness may also be observed [9].
As a rule, with any form of fungal infection of the outer ear, hearing is not affected or minor disturbances such as sound conduction are detected: the transmission of sound waves through the auditory canal to the middle ear deteriorates. In this case, a feeling of ear congestion occurs. Symptoms such as pain and itching can occur with any type of fungal infection [3][6][20].
Some patients in the acute period complain of headache on the affected side, increased body temperature up to 38 °C, hypersensitivity of the auricle, external auditory canal and postauricular area [6].
Laboratory diagnostics
Of the laboratory research methods, the main one is taking a smear from the ear and its mycological inoculation on special nutrient media (Saburo, Chapek, etc.). The specialist takes samples using an ATIC attic probe or a Volkmann spoon. The material is taken under visual control so as not to damage the eardrum, since the substrate is collected from the deep parts of the ear canal [12].
In addition to mycological seeding of the collected material, its microscopy using 10% potassium hydroxide, if it is native material. Sometimes Romanovsky-Giemsa staining is performed. These 2 studies together make it possible to accurately determine the causative agent of the process. To diagnose mycosis, the culture titer (amount in 1 ml) must be at least 104 CFU/ml.
A number of general clinical studies are also carried out, such as clinical and biochemical blood tests to determine the level of glucose, total protein, AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase) and creatinine. A blood test is performed for syphilis, HIV infection and hepatitis in order to exclude these diseases and identify concomitant pathologies [9].
Instrumental diagnostics
otomicroscopy of the diseased ear using binocular lenses, microscopic optics or an endoscope should be highlighted
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis must be made with inflammatory processes of the outer and middle ear of non-fungal etiology (for example, with bacterial or viral otitis media and externa), with cerumen plugs and ear tumors, such as cholesteatoma.
The final diagnosis of otomycosis can only be made with a comprehensive mycological study [9][11].
Otitis media
The middle ear communicates with the nasopharynx through the Eustachian tube, through which infection can penetrate from the upper respiratory tract due to acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, sore throat, rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases. Children are especially often affected because their Eustachian tube is short and wide, which makes it easier for infection to enter. The process can be one- or two-way.
Symptoms of acute otitis media:
- pain in the ear from moderate to severe, pulsating in nature (pain does not depend on pulling the lobe or pressing on the ear canal);
- increased body temperature;
- possible noise in the ear, dizziness, decreased hearing acuity;
- the presence of discharge (mucous, purulent, bloody) indicates a perforation of the eardrum.
With an aggressive course of the inflammatory process and the absence of adequate therapy, otitis media is fraught with such serious complications as meningitis, sepsis, intracranial abscess formation, and deafness.
How to understand the cause of ear pain
Ear pain causes unbearable discomfort. Tolerating it is not only difficult, but also dangerous to health. Regardless of what disease caused the discomfort, it requires urgent treatment. There are many ways on the Internet to get rid of ear pain at home. However, their effectiveness is questionable. And even if you manage to eliminate the pain, the cause of the pain may remain. The result of self-medication can be the addition of an infection, the appearance of purulent processes and other pathologies.
Often, after self-medication, patients still have to see a doctor, when the problem has to be solved surgically. Treatment and recovery in such situations is quite lengthy, expensive and painful.
Medicine knows a huge number of cases when a patient hesitates to see a doctor. As a result, he partially or completely loses his hearing. Don't become part of the negative statistics. Come to the Kutuzovsky Treatment and Diagnostic Center to receive high-quality medical care and prevent complications from occurring.
There are quite a lot of diseases whose symptoms include otalgia. It is better to understand the cause and understand the patient’s complaints. To make a preliminary diagnosis, the otolaryngologist can help with additional information about:
- Rate of occurrence of complaints. So, an acute, shooting pain in the ear that appears literally suddenly indicates an acute infection, inflammation of the auditory tube or eardrum. A gradual increase in the intensity of sensations is characteristic of otitis media, which occurs from a runny nose and nasal congestion.
- The nature and severity of pain. Dull, aching pain is a sign of chronic disease. Severe pain that appears and goes away on its own, repeats periodically, may indicate neuralgia. Pulsating and sharp pain occurs with acute inflammation of the ear canal, boils.
- Duration. Severe pain that does not subside for several days is a symptom of acute inflammation. The pain from the injury will go away after a few hours, but chronic processes and tumors make themselves felt with constant discomfort.
- Localizations. Otalgia can literally bother you “from inside” the head - in this case, the middle ear is affected. For superficial pain, the cause is in the auricle or ear canal.
- Variability. The intensity of pain can change with pressure on the auricle, lobe, change in body position, and swallowing.
- Additional symptoms. The doctor will definitely ask about other complaints - sore throat, nasal congestion, headaches, fever, discharge from the ears, skin changes, hearing loss, and others.
Determining the cause of ear pain begins with an examination by a specialist. In many cases, a doctor can make a diagnosis based on a combination of symptoms. However, often additional studies are required to determine the type of pathology and the degree of its development. At the Kutuzovsky Treatment and Diagnostic Center you can perform examinations of any complexity. The clinic is equipped with high-tech diagnostic equipment. Thanks to the use of modern examination methods, we are able to accurately determine the cause of pain and select the optimal treatment regimen.
By making an appointment, you can do all the necessary procedures directly at the medical center. There is no need to waste time traveling to other medical institutions. We use safe and painless research methods. Come for an appointment at the Kutuzov Diagnostic and Treatment Center to find out the cause of your pain and discuss treatment options.
All these symptoms help the doctor understand the nature and characteristics of the disease. The diagnosis can be confirmed and clarified using more precise procedures:
- Otoscopy is an examination of the ear using a special ENT instrument similar to a funnel. The procedure is painless and allows you to examine the ear and take a sample of discharge (if any) for laboratory analysis.
- Laboratory tests - bacterial culture of microflora, determination of the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics.
- Ultrasound - used to assess the condition of neighboring internal structures - lymph nodes and others.
What diagnostic methods will be needed in a particular case is decided individually by the ENT doctor.
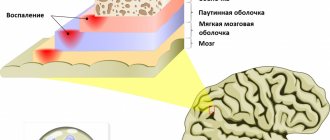
Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis)
The labyrinth is an organ of hearing and balance, is richly innervated and includes auditory and kinetic receptors, so its inflammation causes:
- severe ear pain and headaches;
- a sharp decrease in hearing, the appearance of noise, crackling, squeaking in the ear;
- dizziness, nausea, loss of orientation in space, horizontal nystagmus.
Labyrinthitis occurs as a result of the penetration of infection in various ways from different parts and cavities of the body:
- from the middle ear with untreated or advanced otitis media;
- with infected meninges during meningitis;
- with blood for diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, herpes;
- damage to the temporal region, the organ of hearing with disruption of the integrity of cells and blood vessels.
The disease requires immediate medical attention.
Etiology of the disease
The mastoid process of the temporal bone is located behind the auricle. Its internal structure consists of many interconnected cells with dense partitions. The following features of the bone structure of the appendix are considered normal:
- with a pneumatic structure - many large air cells;
- with a diploetic structure - small cells filled with bone marrow;
- with a sclerotic structure - an almost complete absence of cells.
The development of left-sided or right-sided mastoiditis largely depends on the structure of the mastoid process. The fewer cells, the lower the likelihood of inflammation and its spread throughout the bone tissue structure. More often, mastoiditis with inflammation is observed in patients with pneumatic bone structure. Its development is caused by the spread of infection from the tympanic cavity in acute otitis media or chronic purulent otitis. It is dangerous to neglect the pathology due to the possible spread of suppuration to adjacent tissues and complete hearing loss.
Eustachite
Eustachitis is an inflammation of the canal connecting the middle ear to the nasopharynx. The degree of pain varies. Characteristic features are:
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- noise and crackling in the ear, the patient hears his voice as too loud with a weakened perception of extraneous sounds;
- sensation of water pouring into the ear.
In the absence of timely treatment, eustachitis becomes chronic, causing chronic exudative otitis media.
Causes
Depending on the causes of otitis media and its complications, the following types of mastoiditis are distinguished:
- otogenic – caused by the spread of infection to the parotid tissues in the absence of timely treatment of acute otitis. The causative agents are staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci or influenza bacillus. The development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by a small hole in the eardrum, disruption of the outflow of pus and its accumulation, and closure of the ear opening with granulation tissue;
- hematogenous - a type of disease that develops as a secondary infection in syphilis, tuberculosis and other infectious diseases;
- traumatic form of mastoiditis - is the cause of damage to the mastoid process due to impact, injury or traumatic brain injury. The accumulation of blood in the area of damage and disruption of its drainage process serves as a favorable environment for the development of infection.
Activation of the inflammatory process is facilitated by:
- weakening of the body's immune defense;
- pathologies of the nasopharynx, the patient’s history of chronic diseases;
- changes in the structure of the auricle after illnesses;
- high virulence (degree of pathogenicity) of the infection that has entered the body.
Ear pain of non-infectious origin
Ear tumors
Neoplasms are most often localized in the outer and middle sections; tumors of the labyrinth are an extremely rare phenomenon. Malignant formations of the outer ear are accompanied by severe pain: the pain is burning and radiates to the temple. Possible bleeding; When the ear canal is obstructed, conductive hearing loss develops. If the middle section is affected, the symptoms are similar to otitis media; a high degree of hearing loss and intense pain, increasing in the evening, should alert you. When the process spreads, symptoms of damage to neighboring structures arise: loss of orientation in space, paresis of the facial nerve, trigeminal neuralgia.
Ear injuries
- Mechanical injuries. The auricle most often suffers with the formation of lacerations and damage to cartilage. Blunt trauma to the ear usually results in a hematoma. As a result of trauma to the ear canal, the ear hurts greatly, there is a feeling of stuffiness, and bleeding is possible. Such symptoms are an indication to consult a doctor, since rupture of the eardrum and fractures of the skull bones are possible.
- Barotrauma is caused by a difference in pressure in the external environment and the cavity of the middle ear, for example, during a sharp loud sound (explosion), take-off/landing of an airplane, deep-sea immersion (diving), climbing a mountain. As a result, the eardrum is pulled inward, which is accompanied by pain, noise or ringing, and congestion in the ears. The opposite situation is also possible, when a decrease in atmospheric pressure causes the membrane to bulge outward. As a rule, unpleasant sensations go away on their own, however, if sharp pain is noted, it makes sense to check the integrity of the tympanic membrane when examined by a doctor.
- Entry of a foreign body in the form of small objects or insects causes swelling of the skin of the ear canal, itching, pain, and sometimes hearing loss. Attempting to remove a foreign object yourself can damage the eardrum.
- With burns and frostbite of the ears, **pain // of varying intensity is observed, depending on the degree of damage.
- Conventionally, ear injuries include the formation of wax plugs, which irritate the skin of the ear canal, causing discomfort and tinnitus. Removal should be carried out by an otolaryngologist.
Causes of ear pain
Ear pain can occur for various reasons. The main reasons can be divided into three main groups:
- Inflammatory processes or injuries of the outer ear.
- Middle ear diseases.
- A situation where pain radiates to the ear due to the connection of the organ with neighboring areas of the head. For example, this happens with neuralgia, diseases of the throat, nose and other conditions.
Problems can also occur in the inner ear, but their peculiarity is that there is no pain (usually).
There is another classification of causes: pain from external or internal influence. Let's look at the main options.
Ear pain due to diseases of other organs
- Mastoiditis - inflammation of the mastoid process - causes intense throbbing pain in the ear, swelling of the tissue behind the auricle, hearing loss, and hyperthermia.
- With arthrosis and arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, the patient is bothered by shooting pains in the ear, which intensify when chewing, a crunching sound in the temple area, and over time, hearing impairment and malocclusion are possible.
- Mumps is an inflammation of the salivary gland located in front of the auricle, accompanied by acute pain in the ear, aggravated by swallowing and chewing, and swelling of the tissues.
- Inflammation of the parotid lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) develops when infection penetrates into them from diseased teeth or from other foci of inflammation.
- Inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and sinuses, malignant processes in the larynx and oral cavity are often accompanied by pain in the ear when swallowing.
- Caries, pulpitis. Since the organ of hearing, like the teeth, is innervated by the branches of the trigeminal nerve, damage to the teeth and jaw may be accompanied by pain in the ear area.
- An atypical form of heart attack, when the patient’s only subjective complaint is pain in the ear.
What to do if you have ear pain?
If you experience ear pain, you should seek medical help from our experienced doctors.
First aid
To relieve ear pain for an adult, first aid can be provided using a piece of cotton wool soaked in camphor oil or alcohol. The discomfort will decrease, but then you will still have to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
When a child needs help, he can be given a painkiller (children's Nurofen, the dosage is selected according to age, or paracetamol, the dose of which is 10-15 ml of the drug per 1 kg of the patient's weight). If there is no discharge from the ear canal and the body temperature is normal, it is allowed to use Otipax drops, an alcohol compress, cotton swabs soaked in camphor oil, and a napkin heated with an iron.
Vasoconstrictor medications will help improve the patency of the auditory tubes. An older child can be offered chewing gum, which will ease the painful syndrome. In case of bloody or purulent discharge, as well as in case of increased body temperature, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with this symptom is carried out by an ENT doctor (otorhinolaryngologist) or an audiologist (a narrower specialty in otorhinolaryngology). During the appointment, the specialist talks with the patient, examines him, conducts the necessary examination, and establishes a diagnosis.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced, highly qualified otolaryngologists. Rich clinical experience helps them make the correct diagnosis in the most difficult cases.
Our doctors
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
19 years of experience
Make an appointment
Treatment
Treatment of inflammatory ear diseases includes:
- antibacterial, antiviral agents of local and general action;
- antipyretics, analgesics;
- physiotherapy;
- in some cases - surgical intervention.
Treatment must be based on accurate diagnosis, which is impossible outside a specialized clinic. The high professionalism of CELT specialists allows us to identify various diseases of the hearing organ and choose the most effective means of solving the problem.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions