How physiological is the sensation of tinnitus?
The causes of constant or periodic ringing in the ears can be pathological. So and physiological. Often people of different ages experience some ringing in the ears in complete silence; such ringing is normal and arises as a result of the functioning of the neurosensory system of the inner ear and cochlear organ. Physiological noise occurs in more than 90% of people, regardless of gender and age. Difficulties in assessing the intensity of physiological noise lie in the subjectivity of the assessment by each individual person. Usually a person adapts to such noise and does not pay attention to it at all, however, with the development of any pathological condition on the part of the neurosensory part of the hearing aid or any other, as well as with some vascular diseases, the intensity of tinnitus can increase significantly, which leads to to the formation of tinnitus symptoms.
Pathological causes of tinnitus
A number of diseases can cause tinnitus to increase in intensity. The duration of the ringing can also vary significantly, from rare transient noises to a constant pronounced ringing that causes discomfort in the patient. The most common cause of ringing in the ears is a sharp loud sound, as a result of which the sensory apparatus of the inner ear does not have time to rebuild and adapt to the loud sound, thereby forming a transient or short-term ringing in the ears. Which we've all heard, it's like a squeak. This form is especially common among people who work in loud environments, for example: guitarists, rock musicians, DJs and hosts of festive events. However, severe tinnitus often occurs in one ear and goes away on its own.
The following more serious causes of pathological ringing in the ears can be diseases such as:
- Otosclerosis is a disease in which bone tissue grows in the cavity of the ear canal.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the outer, middle and inner ear.
- Arterial hypertension is increased blood pressure in the vessels of the brain.
- Taking medications with an ototoxic effect.
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Injuries and contusions of the head and hearing organ.
- Blockage of the auditory canal.
All of the above diseases often lead to tinnitus, which becomes a painful companion for the patient. Tinnitus can occur with preserved hearing or be accompanied by a decrease in hearing.
Otosclerosis
If you are bothered by a constant ringing in the ears and head, the causes of which remain unclear, then most likely it occurs due to the proliferation of bone tissue among the structures of the inner ear. This process is called secondary ossification and leads to the gradual formation of otosclerosis. The disease occurs more often in females and does not depend on age. Often, with otosclerosis, patients, in addition to noise and ringing in the ears, experience sensorineural hearing loss.
With otosclerosis, tinnitus is the first symptom and appears much earlier than the development of sensorineural hearing loss and other symptoms, however, the diagnosis of this symptom is much more difficult, since the symptom is purely subjective.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ear
Diseases in which inflammation occurs in the ear are called otitis media. Otitis can be of different localization, and therefore external, middle and internal otitis are distinguished. If you are wondering why there is a ringing in your left ear or why there is a ringing in your right ear, then the cause may be a history of otitis media in the past. Ringing most often results from damage to the inner ear. As a result of inflammation, especially if it is accompanied by a purulent process, disturbances in the hydrodynamic physical parameters of the transmission of sound information are formed. Such changes occur only on the side of the affected ear, which ultimately leads to the unilateral occurrence of the symptom of ringing in the ears. Tinnitus associated with previous inflammation can develop at a young age, and the interval between otitis media and the manifestation of ringing can be very long, it is for this reason that it is important to give due importance to a thorough collection of anamnesis of the disease.
Hypertonic disease
The cause of constant ringing in the ears on both sides can be significantly increased pressure, this is especially true for people over 50 years of age. According to statistics, more than 70% of patients with hypertension have a symptom of tinnitus, and in a permanent form. If the cause of ringing in the ears is arterial hypertension, then you should not delay contacting a specialist for advice and specialized treatment. Typically, tinnitus occurs when blood pressure is high. Moreover, the leading role in this situation is played by the level of systolic pressure, which corresponds to myocardial contraction. Often, ringing in the ears or in a separate ear is associated not only with hypertension. But also with concomitant atherosclerosis of the vascular wall.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is often accompanied by ringing in the ears. The mechanism for the formation of this symptom in osteochondrosis is a significant bending of the vertebral arteries, which feed the pyramid zone and the cochlea of the inner ear. With osteochondrosis, vertebrobasilar insufficiency develops, which is also accompanied by a feeling of spots flashing before the eyes and dizziness. In some cases, with vertebrobasilar insufficiency, tinnitus may precede a short-term loss of consciousness.
Atherosclerosis of cerebral arteries
A constant ringing in the ear on the left side of the head or a similar noise on the right side may indicate serious atherosclerotic changes in the cerebral arteries, namely in the internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries. With the development and progression of atherosclerosis, cholesterol accumulates under the inner layer of blood vessels - the endothelium, which in turn leads to compaction of cerebral vessels and a significant decrease in the elasticity of the vascular wall. Even with moderately elevated blood pressure in combination with atherosclerosis, tinnitus may occur. Particularly characteristic is the one-sided manifestation of noise during the formation of atherosclerotic changes in vessels anatomically close to the pyramid of the inner ear.
Use of medications with side effects
Taking some drugs with ototoxic effects can cause temporary or permanent symptoms of tinnitus. The most common drugs that have such serious side effects include:
- Group of antibacterial drugs of the tetracycline series;
- Some psychotropic drugs - Haloperidol, Levodopa, Nicotine, Marijuana;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs of a steroid nature - Prednisolone;
- Diuretics such as Furosemide (Lasix);
- Cardiac glycosides – Digitalis and non-selective beta blockers.
The use of tetracycline antibiotics in early childhood or non-compliance with dosage can lead to dystrophic changes in the cochlear apparatus and brain nuclei responsible for analyzing sound stimuli.
Blockage of the ear canal
The mechanism of perception of sound stimuli in humans is a complex mechanism in which mechanical and chemical processes are involved. If an obstacle occurs in the path of a sound wave, not only sound distortion may occur, but also noise may be generated due to the resonance mechanism. Any foreign body or substance in the area of the external auditory canal can cause tinnitus. Often noise occurs in children when liquid or solid particles of dust or sand enter the ear. Small insects may also enter the outer ear, which will also lead to the formation of ringing in the ear. With insufficient hygiene and treatment of the external auditory canal, the formation of cerumen plug is possible. Which can also cause noise in the ear on one side.
Causes of tinnitus
Acoustic trauma
The appearance of noise is provoked both by a single sound impact of prohibitive volume (shots from large-caliber weapons, fireworks, rock concerts), and by the constant influence of sounds, which is often found among people listening to loud music through headphones, workers in factories and sewing workshops. In case of acute injury, a person temporarily loses hearing, which causes a monotonous ringing or squeaking in the ears. May cause severe throbbing pain in the temporal part of the head and dizziness.
With chronic exposure to sound stimuli, symptoms increase gradually. First, complaints appear about short-term noise (within 1-2 hours), which begins after being in a room with loud sounds or using headphones. As the condition progresses, the ringing in the ears becomes constant and is accompanied by hearing loss. The frequent occurrence of noise, which disrupts performance, is combined with headaches and hearing loss, is an indication for seeking medical help.
Age-related changes
Among people 55-65 years old, every fifth person periodically notes the appearance of extraneous sounds; after 65 years, the number of people suffering from humming and ringing in the ears increases to 40%. Typical complaints are bilateral noise, which at first feels very quiet and practically does not interfere with everyday activities. Then the sounds seem more intense. Due to the intensification of symptoms at night, patients usually suffer from insomnia. Tinnitus in the elderly is caused by degenerative changes in the inner ear and is combined with decreased hearing, which requires consultation with a doctor.
Hypertonic disease
The appearance of tinnitus is typical for patients suffering from high blood pressure, and the intensity of auditory sensations depends on blood pressure levels. Extraneous sounds are caused by the turbulent movement of blood through narrowed vessels with thickened walls. Hypertensive patients periodically hear a slight hum, which usually occurs against the background of a headache and a deterioration in their general condition. Increased noise, accompanied by painful nausea, flashing “spots” before the eyes, is a symptom of an incipient hypertensive crisis.
Pathological processes in the ear
Ear noise may indicate damage to the auditory analyzer, which is caused by disturbances in the perception and analysis of sounds, and discoordination of the work of different parts of the hearing organ. These reasons often cause temporary sensations of humming or ringing, which cease to bother you after the underlying pathology is relieved. With some lesions of the inner ear that are difficult to treat, the noise becomes constant. Tinnitus is caused by:
- Inflammatory diseases
: external and otitis media, eustachitis, labyrinthitis. - Blockage of the ear canal
: wax plugs, foreign bodies, water ingress. - Inner ear diseases
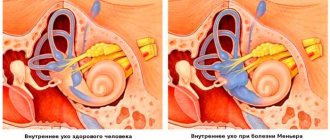
: Meniere's disease, otosclerosis.
Vascular disorders
Most often, the symptom occurs with atherosclerosis: the deposition of lipid plaques on the walls of the vessels of the inner ear disrupts the normal movement of blood, which is felt as a moderately intense “pulsating” noise. In most patients, the hum is more pronounced on one side, which is associated with the degree of damage to the vascular wall. Unilateral loud ear noise is observed in patients suffering from temporal artery aneurysm. In this case, uncomfortable auditory sensations are combined with periodic headaches and dizziness.
Tumor causes
Tinnitus is most characteristic of a benign formation—acoustic neuroma. With this neoplasia, unilateral tinnitus becomes the first symptom. A person notices the appearance of a weak constant hum in one ear, which does not disappear even at night. As the disease progresses, hearing on the affected side gradually deteriorates, and sound sensations become more intense. Pulsating one-sided noise in combination with swallowing disorders and asymmetry of the palpebral fissure occurs with glomus tumor of the ear.
Cervical osteochondrosis
In case of problems with the spine, the occurrence of ringing or humming in the ears is associated with sharp turns or tilts of the head, or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. The causes of noise are compression of individual vessels that go from the neck to the ear and brain. The symptom is observed periodically, the intensity of the sounds is low, so the performance of most patients does not suffer. With severe deformation of the cervical vertebrae, a monotonous strong ear noise is possible, combined with dizziness, fainting, and sharp pain in the neck.
Traumatic brain injuries
Mild head injuries may be accompanied by a short-term noise or ringing in the ears, which does not cause severe discomfort. With more significant damage, unusual auditory sensations are detected against the background of severe nausea and vomiting, intense headaches. Sometimes the symptom does not appear immediately after the injury, but several days later. The noise that occurs after hitting the head is grounds for an urgent visit to the doctor, since with a traumatic brain injury there is a risk of destruction of bone structures and intracranial hemorrhages.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Tinnitus most often develops 1-2 weeks after the start of etiotropic treatment of severe bacterial infections, which is due to the strong ototoxic effect of drugs. The symptom also occurs in patients with hypertension who are forced to take medications from several groups daily. Side effects from the auditory analyzer are provoked by such groups of medications as:
- Antibiotics
: aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides. - Diuretics
: furosemide, ethacrynic acid, hydrochlorothiazide. - NSAIDs in high doses
: indomethacin, diclofenac, aspirin. - Tranquilizers
: flurazepam, tranxene, phenazepam.
Rare causes
- Malformations of the auditory analyzer
: Goldenhar syndrome, microotia, congenital sensorineural hearing loss. - Endocrine pathology
: hypothyroidism, pituitary adenoma. - Diseases of internal organs
: digestive system, kidneys. - Neurological causes
: multiple sclerosis, age-related degenerative processes in the brain. - Damage to the temporomandibular joint
. - Allergy
.
Types of tinnitus
Despite the fact that the vast majority of forms of tinnitus are subjective, it is still possible to identify objective ones. The objective symptom of tinnitus is that it is audible not only to the patient, but also to the specialist who diagnoses the disease that caused it. Objective tinnitus is quite rare and occurs as a result of gross and pronounced disturbances in the activity of the patient’s cardiovascular system; in even more rare cases, this form occurs with muscle pathology. The nature of the noise helps to distinguish what is causing the ringing in the ears. If the ringing is rhythmic and pulsating, then most likely the noise is generated by a vascular component; in the case of a crackling noise, it is generated by a muscular component.
Much more often in the practice of otorhinolaryngologists we encounter a subjective form of tinnitus, the differential diagnosis of which is a much more serious task. The patient's answers help in diagnosis. Since a number of diseases are characterized by either constant noise, or periodic or transient noise, the situation is similar with the localization of the process, which can be unilateral or bilateral.
Tinnitus Treatment Methods
Drug therapy for tinnitus does not bring significant relief to patients, since drugs with pathogenetic and etiotropic effects do not exist today. Only a doctor can determine the most appropriate course of therapy after determining the causes of ear noise. In practice, the following conservative methods of treating tinnitus are used to improve the well-being of patients:
- physiotherapy;
- hearing aids;
- psychotherapeutic courses;
- reflexology;
- audiomaskers.
Decompensated forms of the disease are treated with anti-anxiety and sedatives. To improve the psycho-emotional state of patients, cognitive behavioral psychotherapy is often used.
In modern clinics, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is used to treat tinnitus, but the effectiveness of physiotherapy is relatively low. The severity of auditory effects can be significantly reduced only if the causes of their occurrence, which can only be determined by an otolaryngologist, are eliminated.
Character of the ringing
Questioning a patient who complains about this symptom helps in diagnosing the underlying disease that caused it. To determine the disease, an otorhinolaryngologist asks the patient leading and clarifying questions to determine the nature of the ringing.
- A monotonous noise resembling a whistle, hissing, squeaking or buzzing.
- Multicomponent noise - resembles the ringing of a bell, voice timbre, and various musical elements.
Noise can be of vibrational or non-vibrational nature, which directly affects the nature of the noise.
- Vibration ringing - occurs mechanically due to the anatomical formations of the inner ear and cerebral vessels. This noise may be objective.
- Non-vibrational - always subjective, occurs as a result of improper functioning of the conductive nerve fibers in the central nervous system. May occur with mental disorders.
Ringing degrees
Despite the difficulty of assessing the intensity of tinnitus, this symptom can be determined by the degree of noise intensity. Russian otorhinolaryngology has developed its own classification of noise intensity, thanks to Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences I.B. Soldatov. This classification includes 4 degrees of tinnitus intensity and reflects the practical significance of this symptom.
- Degree. At this degree, the patient easily tolerates noise, it does not affect the general condition and well-being of the patient and is noted only in the quietest conditions.
- Degree. The patient experiences frequent distractions by noise in quiet areas or at night. In some cases, there is difficulty going to bed.
- Ringing in the ears constantly bothers the patient, as a result of which the patient’s behavior is disrupted. He becomes irritable, the emotional background is constantly tense.
- The patient experiences unbearable noise, which almost completely deprives him of sleep and makes daily activities difficult. The patient's ability to work is significantly reduced.
This classification, despite all the subjectivity, allows you to most effectively assess the severity and degree of ringing in the ears, which turns out to be very valuable in the rational planning of treatment measures and the elimination of this symptom.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing the symptom of tinnitus is important. Since the symptom may be associated with serious diseases. The intensity of the noise and its location, as well as its duration, are important in diagnosis.
Ringing in the right ear causes and treatment
In this case, the ringing is most likely associated with diseases such as otosclerosis, otitis interna, the presence of a foreign body in the outer ear on the right side, or damage to the cerebral vessels. Ringing in the right ear can be constant or periodic; the periodic appearance of a symptom speaks in favor of the vascular component of the disease, for example, in atherosclerosis and hypertension, but constant noise speaks in favor of otosclerosis and disorders of the nervous system. Why is there a ringing in my left ear? The reasons will be the same as with the right one. To clarify the diagnosis, the specialist will necessarily collect an anamnesis, examine using otoscopy, and determine bone conductivity using a special medical tuning fork. To clarify the diagnosis, special additional research methods are sometimes required, such as:
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography - allows you to determine the degree of damage to the anatomical structures of the inner and middle ear;
- Tone threshold audiometry - in this study, an audiogram is compiled, which can be used to judge the degree of perception by the central nervous system of various sound stimuli;
- Angiography of cerebral vessels - allows you to determine the degree of damage to the arteries.
Often, to establish an accurate clinical diagnosis, it is sufficient to determine the accompanying set of symptoms that help in differential diagnosis.
Types of noise
Constant noise in the right ear varies. Sound manifestations can be in the form of:
- constant pulsation;
- clicking;
- hissing;
- whistling;
- high-pitched squeak;
- buzzing insects;
- the fluttering of a butterfly's wings;
- dull hum.
These noises are called simple. Voices and musical sounds are a serious type of noise. These manifestations may be symptoms of mental disorders, which require treatment under the supervision of a neurologist or psychiatrist.
Doctors advise not to ignore the problem, believing that it will go away on its own. It is necessary to identify the cause, and this requires contacting a specialist. Such symptoms may be signs of serious pathologies in the body that cannot be ignored.
Treatment for tinnitus
Since tinnitus is just a symptom of some other disease, it makes no practical sense to get rid of it alone. It is important to start fighting the underlying disease that caused it. Depending on the disease, the treatment will be completely different. However, regardless of the cause of the noise, there are some general principles for treating tinnitus. A number of medications are used to treat tinnitus:
- Nootropic drugs;
- Angioprotective drugs;
- Anticonvulsants;
- Antihypoxants and antioxidants;
- Antihistamines;
- Drugs affecting cerebral circulation.
In addition to medications, a mandatory component of conservative therapy is the use of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Nootropic therapy
The use of nootropics allows you to increase the metabolism of brain neurons, which improves the functioning of the neurosensory apparatus of the inner ear and pathways. In medical practice, drugs such as Piracetam, Phezam, Cortexin are used. Nootropic therapy helps elderly patients with a predominance of dystrophic processes in the central nervous system.
Antihistamines
They help fight if the cause of tinnitus is an inflammatory process occurring in the inner ear or in cases where noise is associated with increased sensitivity of body tissues and the occurrence of allergic changes localized in the middle and inner ear.
Anticonvulsants
Prescribed in cases where tinnitus is caused by a vibrational muscle component. Stopping the clonic contraction of the muscles of the soft palate or the muscles of the middle ear can effectively combat vibrational tinnitus. For therapy, drugs such as Difenin and Konvulex, as well as their analogues, are used.
Antihypoxic and antioxidant therapy
With pronounced trophic and degenerative changes in the inner ear in elderly people, the use of antihypoxants and antioxidants helps alleviate the symptoms of tinnitus, and also slows down the progression of degenerative disorders in the inner ear, improving its blood supply.
Drugs that increase cerebral circulation
As a result of age-related changes in older people, the vessels become less elastic, and the thickness of their walls increases, which reduces the degree of perfusion of the tissues of the inner and middle ear. To combat atherosclerotic changes in the cerebral arteries, the following drugs are used: Cavinton and Vinpocetine.
Noise in ears
Tinnitus is one of the most common and quite difficult problems in otorhinolaryngology for differential diagnosis. With this pathology, the patient perceives sound effects that actually do not exist in the external environment. According to statistics, about 15% of people around the world complain of tinnitus, which significantly affects their quality of life.
Determining where this noise comes from can be quite difficult, since the symptom can be characteristic of a very wide range of diseases. Only an ENT doctor cannot always help; you may have to visit several specialists.
Pathology or not?
We need to start with the fact that tinnitus is not always a pathology. Sometimes we simply hear the processes that occur in our body: muscle contraction, blood movement, etc. Usually these sounds are hidden behind other, external sounds, but in some situations, for example in complete silence, they can manifest themselves as unusual auditory sensations. As a rule, such noises are short-lived and do not disturb the usual rhythm of life.
But, alas, often tinnitus is a manifestation of some pathological process occurring in the body, and due to its intensity and duration, it forces you to consult a doctor.
Types and causes of tinnitus
There are two main types of pathological noise - objective, which is actually present in the human body and can be recorded using instrumental studies, and subjective, which is heard only by the patient.
The causes of noise are very diverse and can affect the sphere of professional interests not only of the otorhinolaryngologist, but also of such specialized specialists as a cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, etc.
Objective tinnitus often occurs with pathologies of the temporomandibular joint, arterial stenosis, heart defects, abnormal arrangement of blood vessels, etc. In this case, the hearing organ and sound-conducting nerve pathways are not damaged, and the sounds produced by “improperly” functioning organs are perceived like noise in the ear.
But subjective noise is already the jurisdiction of the lore. If only the patient hears the noise, it means that something is wrong with his hearing organs. The following factors can provoke the development of tinnitus:
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathology, vascular atherosclerosis);
- brain tumors;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- taking certain medications (antibiotics from the aminoglycoside group, diuretics, antidepressants);
- exposure to toxic substances (methyl alcohol);
- injuries;
- and, of course, ear diseases (external - foreign body, cerumen plug; middle - otitis, tumors, otosclerosis; internal - sensorineural hearing loss, Meniere's disease, labyrinthitis, etc.).
Practical advice
If you experience ringing in the ears, and even more so it bothers you and interferes with your activities, you should not delay in contacting a specialist for professional help, otherwise you may miss the progression of a serious disease that may be accompanied by ringing in the ears. Only a specialist - an otorhinolaryngologist will be able to accurately determine the cause of tinnitus and plan subsequent treatment. By the way. Following the advice of your doctor is a prerequisite for effective relief from an unpleasant symptom. Take care of your body and health, be happy!
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 139 votes
Share article on social networks