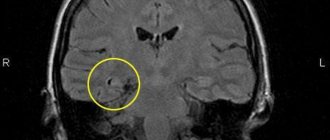
In children, dizziness is felt as a lack of coordination of movements or the room rotating around the body. Dizziness occurs in healthy children and when the baby gets sick (for example, with a high temperature).
Most often, in a healthy child, dizziness appears for a short time and is associated with a sharp change in body position (for example, the child quickly got out of bed, there was a change in body position from lying to standing).
Dizziness may occur if the child rode on a carousel or swing; such conditions are not a cause for concern.
If a child loses consciousness after or during dizziness, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
When a child is driving in a car, he feels nauseous or dizzy, perhaps this is a disease of the nervous system, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your pediatrician if:
- a child whose coordination has not been impaired develops gait disturbances and walks staggering
- the child complains of dizziness, loses balance when walking, cannot walk in a straight line
- the child often complains of dizziness and headaches, which get worse when he lies down
ATTENTION!
If dizziness is prolonged and accompanied by ringing or noise in the ears, the child should be immediately examined by a neurologist.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| The child has a high temperature, he is lethargic and moody, and feels dizzy | Reaction to temperature | Give antipyretics, if the temperature does not decrease, then call the pediatrician |
| The child had a brief loss of consciousness after feeling dizzy | Loss of consciousness due to heat, excitement or being in a stuffy room | Move the child to a cool, well-ventilated area. If the child is conscious, give him something to drink. If the child turns blue and does not come to his senses after more than 5 minutes, call emergency services immediately. |
| Against the background of ringing (noise) in the ears, the child feels dizzy (lack of coordination of movements or a feeling that the room is spinning around) | Labyrinthitis (viral infection of the inner ear) | A consultation with a pediatrician is necessary ; after examining the child, he will advise what to do. |
| After suffering from a viral disease (chickenpox), it is difficult for a child to maintain balance | Post-viral cerebellar ataxia (weakness and deterioration of motor coordination) | It is necessary to consult a pediatrician for a thorough examination |
| When driving a car, riding a boat or boat, the child experiences dizziness | Seasickness | Consult your pediatrician , he will give recommendations on how to prevent dizziness |
| The child began to complain of dizziness after a fall or injury | Head injury | Take your child to the pediatrician for a thorough examination |
| The child had short-term episodes of loss of consciousness; after dizziness, he began to complain that he was not oriented in time and place | Petite epileptic seizures | Consult your pediatrician for a thorough examination; you may need to consult a neurologist |
| The child has difficulty walking in a straight line, has nausea or vomiting, and complains of headaches that get worse when lying down | The condition is rare in children, but requires treatment and testing | Immediate consultation with a pediatrician is required for a thorough examination. |
| The child loses balance and falls with his eyes closed when standing or sitting. Cannot pick up an object, movements are not precise (misses). When asked to reach the tip of the nose with a finger, it misses | Neuromuscular ataxia, rare in children | Make an appointment with your pediatrician for a thorough examination; you may need to consult a neurologist |
FOR INFORMATION
Maintaining balance
Our ability to maintain body position is determined by the complex interaction of nerves and muscles responsible for hearing, vision and touch. The ability to hear allows us to change body position depending on the sound information received. Our limbs and muscles are equipped with sensory organs that help position the body in accordance with the shape and position of surrounding objects. Disruption of any part of the balance mechanism can lead to dizziness and nausea. Dizziness, as a rule, stops when the cause that caused it ceases to act. Dizziness caused by damage to the inner ear, on the contrary, continues regardless of external causes. In these cases, dizziness is often accompanied by ringing or noise in the ears. They are associated with concomitant damage to the auditory nerve.
Pediatrician appointment prices:
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatrician (1 hour) | 1950 |
| Examination of a child by a pediatrician to obtain a certificate + certificate | 1750 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatrician of the first category, head. department Barzenok T.A. | 2850 |
| Registration of a certificate | 700 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a leading pediatrician (Sedova M.S.) | 2500 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with the leading pediatrician, head of the breastfeeding support department, Kazakova L.V. | 2950 |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a pediatrician (Premium category) (Sergienko T.Ya.) | 4000 |
| Visit of a pediatrician, consultation at home (Moscow) | 4250 |
| Consultation with a pediatrician at home for the second child | 1950 |
| Visit to the home of a pediatrician, head of the breastfeeding department, Kazakova L.V. | 4250 |
How can you suspect dizziness in a child?
Children's behavior changes. They usually close their eyes and lie face down, pressed tightly against the wall or headboard of the crib and unwilling to move. Older children do not want to get out of bed after suffering from illnesses.
As soon as you notice any unusual behavior in your child, you need to consult a doctor. Only he will be able to identify the causes and type of dizziness in a child and prescribe adequate treatment. If this is not done in time, then a banal ailment can develop into a serious illness.
Pediatricians:
Avzalova Daria Evgenevna
Pediatrician, neonatologist
Experience: 17 years Reviews: 6
Call to home
Barzenok Tatyana Arsenyevna
Head of the pediatric department, pediatrician of the first category
Experience: 27 years Reviews: 17
Make an appointment Call at home
Belousova Elena Sergeevna
Pediatrician, nephrologist
Experience: 17 years Reviews: 14
Make an appointment Call at home
Bykov Mikhail Viktorovich
Pediatrician of the highest category, ultrasound diagnostics specialist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Experience: 24 years Reviews: 3
Make an appointment Call at home
Kazakova Liliya Valentinovna
Pediatrician, neonatologist, head of the breastfeeding consultant service
Experience: 27 years Reviews: 31
Make an appointment Call at home
Sedova Maria Sergeevna
Pediatrician, allergist-immunologist
Experience: 19 years Reviews: 30
Make an appointment Call at home
Sergienko Tatyana Yakovlevna
Pediatrician, pediatrician on duty at the pediatric hotline
Experience: 38 years Reviews: 21
Make an appointment
Symptoms of coronavirus COVID-19
Coronavirus
COVID-19
58200 January 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Definition
The SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads in microscopic particles of fluid released by a sick person during coughing, sneezing, talking, singing or heavy breathing and gets onto the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth or eyes of another person.
In addition, the virus can also spread through household contact, when particles with the virus located on surfaces or objects enter the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract through the hands.
Aerosol transmission occurs in closed, crowded and poorly ventilated areas.
The airborne dust (aerosol) transmission route is realized through the spread of aerosols (droplet nuclei) suspended in the air, the size of which is <5 microns. Due to their small size, aerosols can be transported over long distances and remain in the air for several hours. It must be remembered that aerosol-producing devices (nebulizers, halochambers, etc.) are prohibited for use in healthcare institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Symptoms of mild COVID-19
Most common symptoms
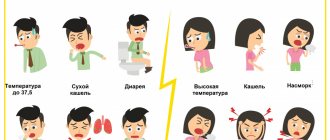
- The main symptom (80-90%) is any increase in body temperature (even low-grade - 37-37.5°C).
- The cough is dry or with a small amount of sputum (60-80%).
- Increased fatigue (40-50%).
Less common symptoms
- Sudden loss of smell and/or taste (60-80%).
- Nasal congestion or mild rhinorrhea (5%).
- Conjunctivitis or redness of the eyes (1-2%).
- Sore throat (14%).
- Headaches, dizziness (8-14%). Immediately after the end of the incubation period, migraines of varying severity may appear.
- Pain in joints and muscles (11-15%).
- Skin rashes (8%).
- Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting (up to 20%).
- Chills (11-13%).
Those who have had a mild form of COVID-19 infection compare the sensations with the course of a common respiratory disease.
Symptoms of COVID-19 in severe and moderate forms of the disease
Most common symptoms
- Shortness of breath, rapid breathing (55%).
- Increased cough, appearance of sputum (30-35%).
- Hemoptysis (5%).
- Loss of appetite (20%).
- Confusion (9%).
- Sensation of constriction and congestion in the chest (> 20%).
- Body temperature above 38°C (80%) for more than 5 days.
- Blood oxygen saturation according to pulse oximetry (SpO2) ≤ 95% (up to 20%).
Less common symptoms
- tachycardia,
- vitamin D deficiency,
- irritability,
- convulsions,
- anxiety,
- depressed state
- sleep disorders.
Important! Symptoms may not be detected during the incubation period of COVID-19 or may appear in any combination (for example, without fever). The exact diagnosis is determined by the doctor based on the results of examinations.
Patients over 65 years of age may experience an atypical picture of the disease, which includes delirium (cloudedness of consciousness), speech impairment, movement disorders, as well as more severe and rare neurological complications - stroke, inflammatory brain damage, and others.
The majority (about 80%) of patients who develop symptoms recover without hospitalization. Approximately 15% of patients develop a severe form of the disease that requires oxygen therapy, and 5% develop an extremely severe form that requires treatment in an intensive care unit.
Differences between the new coronavirus disease COVID-19 and ARVI and influenza
COVID-19 also refers to ARVI - acute respiratory viral infections characterized by similar symptoms: cough, runny nose, fever, headache, sore throat and sore throat. The most clearly defined clinical picture is caused by influenza viruses, parainfluenza, and adenoviruses. Coronavirus can be more severe than other acute respiratory viral infections, leading to complications and even death. That is why it is extremely important to distinguish the new type of coronavirus from a relatively harmless cold.
What is the difference between coronavirus and ARVI?
- Longer incubation period. For ARVI, 2-3 days are enough to go into the acute phase, but coronavirus takes up to 2 weeks.
- Unlike other acute respiratory diseases, coronavirus causes a low body temperature of 37-37.5°C, which can last a relatively long time (up to 7 days).
- A cough when infected with coronavirus is often long-lasting, dry, painful and may be accompanied by chest pain.
- Coronavirus infection can cause digestive upset (diarrhea, nausea, vomiting); such phenomena are rare with ARVI in adults.
- ARVI is usually cured in 7-10 days, and COVID-19 on the 7-8th day in a certain percentage of people can move to the next stage, when shortness of breath and respiratory failure appear.
Only a laboratory test will help you accurately name the type of pathogen and establish the disease (coronavirus, ARVI, influenza).
What is the difference between coronavirus and flu
It should be noted that COVID-19 and influenza have much in common:
- transmitted by airborne droplets and contact;
- may manifest as aching joints, headache, severe weakness and a general feeling of weakness;
- Intestinal disorders may occur.
Main differences:
- The flu begins acutely with an increase in temperature immediately to febrile values (39-40⁰C). Symptoms of general intoxication come to the fore: headache, weakness, pain in muscles and joints, lacrimation, pain in the eyes.
- Coronavirus develops gradually - from general malaise in the first days to severe symptoms, including a significant increase in body temperature after a week.
It is important that a doctor determine the difference between coronavirus and influenza, since both diseases can lead to dangerous complications, including pneumonia.
If a person has the flu and not coronavirus, he also needs medical care and treatment under the supervision of a therapist. Other diseases with similar symptoms
Pneumonia, including atypical.
Allergies. Shortness of breath, problems with smell, and other symptoms may occur as a result of exposure to allergens. The problem is solved by antihistamines, which are ineffective for viral infections.
Bronchial asthma, which also makes itself felt by difficulty breathing and a painful cough, but is non-infectious in nature.
Are symptoms different in children and adults?
Children make up only about 2% of all COVID-19 cases. At the same time, they tolerate coronavirus infection more easily and are often asymptomatic carriers.
The course of COVID-19 in children of different ages:
From 1 year to 3 years
The infection usually manifests itself as a mild illness. There are no characteristic symptoms of COVID-19. Sometimes there is a loss of appetite, which goes away after 2-3 days and does not affect the baby’s general well-being.
From 3 to 7 years
Children at this age are sick for about seven days and recover without complications. They may experience hoarseness and mild nasal congestion. There is no cough, occasional sneezing is possible.
From 7 to 17 years old
Primary schoolchildren and adolescents may experience a slight increase in body temperature and mild malaise. A dry cough is possible, and even less often - a headache.
According to Rospotrebnadzor, a mild form of the disease is usually due to the patient’s strong immunity.
The immune system of children and adolescents is usually well prepared to fight viruses. They can become infected, but their disease is milder or completely asymptomatic.
Stages of disease development taking into account symptoms
Symptoms of coronavirus in an adult by day
1-3 days. The disease begins with mild malaise, a slight increase in temperature, nasal congestion and muscle pain, as with ARVI or influenza.
3-5th day. Body temperature rises, and a mild, superficial cough is possible. The sense of smell may disappear, and taste sensations may change greatly. Digestive disorders occur, including diarrhea. This period is considered the culmination of a mild form of COVID-19.
5-10th day. An important period for determining the severity of coronavirus infection. 80% of people sick with COVID-19 experience improvements, which can lead to a full recovery in a few days. The second scenario involves a worsening of the condition, which is manifested by an increase in the number and severity of symptoms. With this development of events, the patient develops a severe runny nose, debilitating cough, chills, body pain, and shortness of breath.
10-12th day. This period is characterized by severe shortness of breath, chest pain, progression of weakness, and pallor, which indicates the development of pneumonia. Damage to the lungs leads to oxygen starvation. Hospitalization required. This condition is considered moderate.
12-14th day. With COVID-19, 75% of patients with viral pneumonia begin to recover on average 2 weeks from the onset of the disease. However, those who develop severe disease may require mechanical ventilation.
14-30th day. It takes on average up to two weeks from the onset of a serious complication to recover from a severe form of pneumonia caused by coronavirus.
But even after complete recovery, mild shortness of breath may persist, weakness and malaise may appear for a long time (up to several months).
Clinical variants and manifestations of COVID-19
- Affects only the upper respiratory tract.
- Pneumonia without respiratory failure.
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (pneumonia with acute respiratory failure).
- Sepsis, septic (infectious-toxic) shock.
- Syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation, thrombosis and thromboembolism.
- Blood oxygen saturation is less than 88%.
Patients with critical COVID-19 develop vascular endothelial dysfunction, bleeding disorders, thrombosis, and thrombotic microangiopathy.
A cytokine storm in COVID-19 is the body’s response to an inflammatory process, leading to immune cells attacking not only the virus, but also the tissues of the body’s own. The consequence of this can be the destruction of tissues and organs, and, as a consequence, the death of the body.
It is very important that sometimes COVID-19 is dangerous not only because of pneumonia and its complications, but also because it has a negative effect on blood vessels, the brain and the heart, which increases the risk of stroke. In such cases, the patient experiences dizziness, fainting may occur, the face turns blue and the muscles become numb.
Symptoms indicating the healing process
Attention!
The time intervals for the course of the disease are arbitrary; they depend on the individual characteristics of the organism. COVID-19 in mild form usually lasts no more than 14 days. But only an antibody test can confirm final recovery. Given the severity of the disease, the recovery process can take place in different ways. The criterion for recovery is if two consecutive tests for coronavirus using the PCR method gave a negative result.