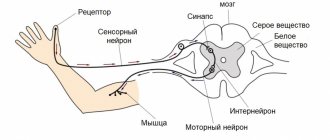
How does a “heavy” head feel?
It’s not just a headache that can interfere with normal perception of the colors of the world around you and living in peace. Sometimes a tedious heaviness in the head is perceived worse than a migraine attack. After all, a migraine will go away after a certain period of time, and the feeling of a burden in the head can torment a person for a very long time.
How do patients describe their feelings?
- In the morning, my head pulls towards the pillow.
- There is a feeling that the skull has been filled with stones.
- It was as if blood from the whole body had collected in the skull.
- Metal disks move heavily in the brain.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Information is not perceived adequately.
- I want to put my head in my arms and sleep, sleep, sleep.
- Nausea creeps up my throat.
- Lethargy falls on the body, it is difficult to even raise an arm.
Often the headache does not hurt, but it is heavy and cottony. Unpleasant sensations can occur in the morning and do not disappear even after a long sleep.
Diseases accompanied by heaviness in the head
Heaviness in the head may be a sign of brain damage. Also, unpleasant sensations, a feeling of lethargy and weakness indicate that a person is developing a serious illness.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
With this disease, any unusual load can cause discomfort. The tone of brain vessels is disrupted, the outflow of venous blood is hampered, and the supply of oxygen to brain cells deteriorates. The result is a feeling of overcrowding in the skull.
A person suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia often has panic attacks that worsen the general condition. Depressive thoughts arise that literally make your head explode. If there is no opportunity to rest and relax, the feeling of heaviness is accompanied by a headache: bursting, aching, throbbing.
Meniere's disease
Damage to the vestibular system can also cause a person to have a feeling of heaviness in the head. Meniere's disease is an inflammation of the inner ear, labyrinthine dysfunction develops, in which an excess amount of fluid is released. Liquid accumulates in the labyrinth, pressing on the nerve endings. Symptoms of the disease:
- Ear noise, feeling of fullness in the ears.
- Constant dizziness.
- Loss of balance when walking.
- Nausea.
- Hearing loss.
Due to the fact that the vestibular system sends distorted signals to the brain, a person has a feeling of a cotton head. It is difficult for the patient to stand up; when bending over, he is pulled forward.
Osteochondrosis
If the cervical spine is affected by osteochondrosis, then the person’s blood supply to the brain is disrupted. Most often the vertebral artery is compressed. This can provoke an increase in intracranial pressure and lead to oxygen starvation of the brain. A gradual deterioration in blood flow causes the following symptoms:
- Drowsiness, lethargy.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Intrusive headaches.
- Feeling of stiffness in the neck.
- Feeling of heaviness in the skull.
Those at risk include office workers, athletes, people engaged in monotonous work that requires constant repetition of the same actions. Even a nursing mother who regularly falls asleep in an uncomfortable position while breastfeeding may experience a feeling of “fullness” in her head.
Dizziness and heaviness in the head are frequent companions of teachers who spend the entire working day at the blackboard. The static and heaviness of the posture affects the pose - a raised hand with chalk, which performs monotonous movements.
Neurosis-like conditions
Chronic fatigue, constant stress, and depression can lead to a person beginning to develop neurosis. Complaints of patients suffering from neurosis:
- Feeling empty in the head.
- “Muddy” head, like jelly in the skull.
- Tightening, pressing headache.
- The feeling that a heavy hat or a cast-iron helmet was put on your head.
The patient is easily irritated and may start shouting for no apparent reason at his family or just strangers. The patient has difficulty in crowded places where there is a lot of noise and light. They cause increased discomfort; in addition to the symptoms listed above, a feeling of confusion and, at the same time, anger is added.
Sleep disturbances are noted: a person has difficulty falling asleep, often wakes up at night, and lies awake for a long time. The next morning he finds it difficult to get up, even if sleep lasted until lunch, he has a feeling of a “heavy head”, a thick “fog”.
Neoplasms
One of the main symptoms of brain cancer is a daily morning headache. In addition, patients complain of heaviness in the head and drowsiness. Pressing pain occurs in one area of the head due to the fact that the growing tumor puts pressure on the nerve endings and compresses the blood vessels. Due to poor circulation, a feeling of “fullness” and heaviness in the head appears.
The morning nature of the discomfort is due to the fact that when a person changes body position, intracranial pressure rises and cerebral edema increases. Minor physical activity increases the discomfort.
A headache can occur even at night, become stronger in the morning when waking up and subside in the evening. Dizziness, vomiting, feeling of lethargy, apathy are accompanying symptoms of the disease.
Injury
A skull fracture, concussion, neck or head injury can lead to cerebrovascular accident. Heaviness in the skull, accompanied by an annoying bursting headache, is most often a symptom of a complication that develops after a whiplash injury.
Whiplash occurs when unexpected acceleration or deceleration is applied to a person's body. Possible triggering situations:
- Falling from the stairs onto your feet.
- Car accident.
- A quick push from another person when playing football, volleyball, or hockey.
- "Shaking" the baby.
Unpleasant sensations in the head can disappear literally an hour after the injury and appear delayed: after a month, six months, a year, several years. As a result of a whiplash injury, a person experiences dysfunction of the occipital bone and its sutures. In this case, a person develops symptoms such as frequent dizziness, headaches, and heaviness in the head.
Other diseases
Experts identify several other diseases, one of the indirect symptoms of which is a feeling of “fullness” in the head. This type of discomfort does not necessarily appear as the disease progresses, but can sometimes accompany it.
These diseases include:
- Damage to the cardiovascular system.
- Injuries, ruptures of the eardrum.
- Neoplasms in the ocular apparatus, in the middle ear.
- Damage to nerve nodes.
- Migraine.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Aneurysm rupture.
- Colds and infectious diseases: flu, rhinitis, otitis media.
- Prolonged lack of oxygen caused by bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, suffocation.
If a person constantly experiences heaviness in the head, the causes of which cannot be determined at home, you should seek help from a doctor.
Identifying the cause is a priority
It has already been emphasized that all of the above sensations are just symptoms that indicate the development of a particular disease.
To accurately determine which disease causes heaviness and fogginess in the head, you should contact an experienced specialist.
Also, for your own education, you should familiarize yourself with the most common reasons why the head becomes heavy, and lead and weakness spread throughout the body.
In addition to feeling leaden, some patients experience fatigue, trouble sleeping, and loss of appetite. The person becomes irritable. All this is a sign of neurasthenia - a common phenomenon in our time.
Although the technological progress characteristic of the 21st century has made it possible to facilitate human physical activity, it has contributed to the development of stress on its mental component. Every day, a modern city resident experiences severe stress, both at work and on the way home.
The patient does not immediately detect a nervous breakdown. As a rule, it develops gradually. As stress accumulates, it reduces physical and mental activity. A person begins to experience difficulties in performing seemingly the simplest everyday tasks. He suffers from headaches and dizziness. The head feels like cotton wool, there is fog and cloudiness in the eyes. It becomes difficult to think and do something.
Osteochondrosis of the neck
It would seem that lead in the skull and compression in the temples are a direct indicator of brain disease, but this is a misconception.
It turns out that these and similar symptoms occur with degenerative disease of the discs located between the vertebrae.
Cervical osteochondrosis negatively affects not only the head, but also the upper internal organs. With this disease, the spinal cord receives more damage, and it, in turn, sends painful impulses to other parts of the body with which it is connected by nerve endings (in other words, throughout the body).
In addition to cloudiness and heaviness with osteochondrosis, the patient experiences ringing in the ears, which can either subside or intensify. This phenomenon is facilitated by pinching of the vessels supplying the brain. Disruption of neuron nutrition provokes auditory hallucinations, as well as:
- drowsiness;
- painful sensations in the back of the head and temples;
- visual impairment;
- memory losses.
Due to compression of the vertebrae, causing disruption of circulation in the brain, the patient feels not only heaviness and cloudiness, but also periodic dizziness. This, in turn, may be accompanied by sweating, burning in the face, and pain in the neck.
Unfortunately, not everyone is aware of all the pathogens that can cause this phenomenon in the body. An allergy is a malfunction of the immune system when a person interacts with something or someone. And it can happen at any time.
Swelling, swelling, nasal and mucous congestion are not the only symptoms of allergies. Often this reaction in the body begins with the appearance of congestion and fogginess in the brain.
At the moment of an unexpected deterioration in health caused by one or another pathogen, it is necessary to take timely measures in order to prevent anaphylactic shock.
The penetration of infection contributes to the deterioration of well-being. Often this process manifests itself through headaches and deterioration of visual function. The infection spreads very quickly in the body, which emphasizes the need for prompt medical intervention.
Athletes and people whose work activities involve constant health risks are most susceptible to this phenomenon. Bruise, concussion and fracture - all this causes unpleasant sensations. Moreover, a varying period of time may pass before these signs appear from the moment of injury.
You don't have to be in an accident to get injured. One sudden movement is enough for the discs in the vertebra to shift. This can happen both during training and in public transport (during sudden braking). A person will not immediately feel a deterioration in health. Only a gradually heavier crown and growing fog in the eyes will indicate a deterioration in blood flow.
The reasons for this phenomenon can be many factors:
- alcohol consumption;
- smoking;
- past injury;
- increase/decrease in pressure;
- displacement of discs in the spine;
- and much more.
The bottom line is this: due to the compression of the channels that supply the brain with oxygen, a gradual deterioration in well-being occurs. Fog appears in the eyes, the body is overcome by weakness, and the head becomes like a stone. A person feels better only in a supine position. Possible loss of consciousness.
Even an ordinary runny nose can contribute to this condition. Due to the blockage of the airways, the brain does not receive the proper dose of oxygen.
Older people are susceptible to this process. Due to multiple changes, both in bone tissue and in the vascular system, the channels through which the brain is nourished are blocked.
Third-party factors that provoke heaviness in the head
Is it hard to raise your head, but you have not been diagnosed with any diseases? Perhaps the cause of discomfort is a person’s lifestyle or some external factors. Unpleasant sensations appear if:
- For a long period of time you don’t sleep enough, go to bed late and get up early.
- Sit at the computer every day, avoiding physical activity.
- Drink alcoholic beverages in large quantities.
- Spend your nights in clubs and sleep during the day.
- Use drugs.
- Use certain medications in large quantities.
Toxic damage to the body (from food, alcohol, drug poisoning) causes oxygen starvation of the brain, and is therefore accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness of the skull. Allergic reactions that occur with cerebral edema can also cause discomfort. When the weather changes, a sudden cold snap, a weather-dependent person may experience heaviness in the head.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you experience headaches, you should consult a general practitioner. The therapist will conduct an examination, perform diagnostics and determine a preliminary diagnosis.
Depending on the suspected cause of severity, consultation with doctors will be required:
Read also: Why there is a lump in the throat and how to get rid of it
- ENT: infectious diseases of the ENT organs, Meniere's disease.
- Neurologist: osteochondrosis, VSD, migraine, stroke.
- Allergist: allergic reactions with cerebral edema.
- Cardiologist: pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Angiologist: cerebral aneurysm.
- Narcologist: drug and alcohol addiction.
- Psychologist: stress, neurotic conditions, overwork.
- Oncologist: neoplasms of the eye, middle ear, brain.
Heaviness in the head can be the cause of many pathologies, so you will have to see a lot of different doctors
For cotton head in children, you should consult a pediatrician and family doctor.
How to eliminate discomfort?
Did you get up in the morning with a heavy head and can’t recover? There are several methods you can use to improve your condition.
- When a headache is added to the unpleasant sensations, it makes sense to take a pain reliever (analgesic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug).
- A cool or contrast shower, which should be taken for at least 15 minutes, helps to get rid of discomfort.
- You can conduct a massage or self-massage session, gently rubbing the neck, back of the head, and temple area.
- To alleviate the condition, you can use aromatherapy: apply a couple of drops of mint, rosemary, lavender oil, tea tree oil, lemon.
- Breathing exercises effectively eliminate discomfort.
- Some yoga exercises can reduce discomfort.
- You can try to relax using self-hypnosis: sit or lie down with pleasant music and imagine yourself on the seashore, in a rustling forest, in a meadow.
Sometimes, in order to eliminate discomfort, you just need to get a good night's sleep in a dark room and normalize your working day: if your job is sedentary, periodically take breaks, exercise minutes, and regulate psychological and physical stress. It is advisable to change the pillow and mattress, choosing bedding that helps you relax while sleeping.
Features of treatment
If a patient constantly complains that he has a heavy head, the causes of discomfort are vegetative-vascular dystonia, osteochondrosis or another disease, it is best to entrust treatment to a specialist. The following therapeutic measures are carried out:
- Cerebral circulation is normalized with the help of nootropic and vasotropic drugs.
- Blood circulation is improved with the help of physiotherapy: electropheresis, phonopharesis, and magnetic therapy are used.
- Muscle spasms in cervical osteochondrosis are relieved through massage and manual therapy.
- Nervous tension is eliminated - with the help of tranquilizers, sedatives, sedatives.
- To relieve muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are taken, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory gels and ointments are applied topically.
- Allergic reactions are relieved with antihistamines.
If the cause of discomfort is the growth of a tumor, surgical intervention may be required.
In case of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, it is necessary to strengthen blood vessels and normalize blood pressure. If the discomfort is due to a cold, the patient’s condition will return to normal after recovery.
Regular use of painkillers is required only if the heaviness in the skull is accompanied by a headache. It is advisable not to rely only on medications, but also to change eating habits and give preference to natural products. Spicy, salty, sour foods can increase discomfort, as can caffeinated drinks and chocolate.
Do you want the heaviness in your head to go away? Play sports, preferably swimming. It helps not only to get a feasible load on all muscle groups, but also to relieve accumulated negative emotions, “wash away” stress and a depressive mood. Walking in the fresh air, good sleep and the absence of nervous overload will help avoid unpleasant sensations.
What to do when your head is spinning?
04.03.2020
Dizziness is a feeling of uncertainty when a person, without moving, feels a sense of movement. A distinction is made between spinning vertigo (merry-go-round), swaying vertigo (movements like on a ship at sea) or vertigo when rising (feeling of sinking or lifting).
The work of the vestibular apparatus
Even with your eyes , the body with its balance organs (vestibular apparatus) determines exactly what position it is in the room. The organs are located on both sides in close proximity to the auditory organs. They consist of two gravity sensors and three semicircular channels that can measure acceleration in any direction.
Diseases or injuries with dysfunction of the balance organ on one side affect the balance between the two balance organs. If the impulses on one side outweigh, this is perceived as an erroneous rotational movement.
Causes
Damage to the balance center in the brain , such as after a stroke, multiple sclerosis , or even temporarily due to alcohol, often causes dizziness .
If the brain does not coordinate the movement felt by the balance organ with the visible image, dizziness and double vision .
Dizziness is caused by anxiety or mental illness.
Symptoms
In addition to dizziness, we are talking about:
- nausea and vomiting;
- profuse sweating ;
- headaches;
- tinnitus ; _
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- lateral involuntary eye or flickering.
Clinical picture
Low blood pressure is characterized by an attack of dizziness with possible brief loss of consciousness. Some people experience severe dizziness when traveling by car, bus, or boat.
Temporary successive tears in the mucous membrane of the auditory organ also lead to dizziness . The reason for dizziness can be a stressful situation: being at high altitude, a family quarrel, or a fear of flying on an airplane. Chronic otitis and medications can also cause dizziness .
If a person experiences the symptoms described, then they should definitely consult their doctor .
Attacks of dizziness are one of the most common complaints that bring older people to their family doctor . The important thing is that a person should move as much as possible, despite the fear of dizziness .
A common diagnosis is benign positional vertigo , which causes small crystals to invade the semicircular canal of the inner ear . They suddenly activate the semicircular canals that normally register head movements, resulting in severe impact vertigo . Phobic dizziness is caused by other reasons: uncertainty, anxiety. Activity and movement help with phobic dizziness , fueled by fear and uncertainty. If a person does not move, they are in poor physical condition, which impairs balance and walking.
In old age, there is another feature - unstable blood circulation, which causes dizziness . Before getting out of bed after sleep, you need to sit on the edge of the bed, cross your legs , relax your body muscles, and only then consciously, without jerking, stand on your feet .
Moderate daily exercise prevents dizziness . If this is a violation of the balance reflexes, you need to practice slow head movements while fixating the visual target. Polyneuropathy is more related to training balance. There are cases when just one exercise dizziness slowly disappear. Examples include inflammatory disease of the inner ear or vestibular neuritis. The person becomes weakened, exhausted, and can hardly perform any exercise. But even in this case, it is important to start moving so that the compensation of the brain and healthy balance organ of the opposite side is not unduly delayed.
Depending on the cause of the dizziness , medications are also used in young and elderly people. Drugs that improve blood circulation, glucocorticoids or antibiotics are used.
Published in Neurology Premium Clinic