In this article we will look at how to saturate the brain with oxygen.
Brain hypoxia is a lack of oxygen, which is necessary for its correct functioning. It occurs as a result of a lack of O2 in the air or the inability of human blood to transport it. Next, we will talk about how to saturate the brain with oxygen and outline the consequences that starvation of this human organ leads to.
How is lack of oxygen expressed?
We’ll tell you below how to saturate the brain with oxygen at home, but for now let’s talk about the consequences of its lack.
Lack of O2 in the brain is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of frequent dizziness and a feeling of near fainting.
- The appearance of cold sweat, which does not go away even if the person is covered with a warm blanket.
- The presence of pale skin along with marbled palms.
- The appearance of weakness and a constant desire to go to bed. It is not possible to overcome drowsiness even with long and regular sleep.
- Constant pain in the head. Sensation that there is a pressing cloud in the brain that is in contact with the walls of the skull.
- Deterioration of memory and speech. Decreased alertness and concentration.
Causes of cerebral hypoxia
Approximately 20% of the total volume of blood circulating in the body enters the brain. Together with blood cells, oxygen and other useful substances that are necessary to maintain its functionality are delivered to the organ.
There are endogenous and exogenous types of hypoxia. The reason for the development of exogenous oxygen starvation of the brain is a decrease in oxygen concentration in the environment, namely, in the inhaled air. Often a similar situation is observed when climbing mountains, which is why this state of the body is called Altitude or Mountain Sickness. A sharp drop in barometric pressure can also lead to exogenous oxygen starvation. In this case, they talk about the development of decompression sickness in a person.
Endogenous oxygen starvation is indicated when the level of oxygen in the air is low, but barometric pressure remains normal. This situation can happen when a person is in mines, wells, in a submarine, or during an operation due to errors in the operation of the apparatus responsible for supplying oxygen to a patient under anesthesia.
Brain hypoxia can also develop in pathological conditions of the body. In this regard, there are:
- Hypoxia of the brain, which develops against the background of disorders in the organs of the respiratory system.
The following reasons can lead to respiratory hypoxia of the brain:
- Alveolar hypoventilation. This can be observed when the airway is obstructed, for example, against the background of an inflammatory process in the lungs, when a foreign body enters the airways, or due to a spasm of the airways. The following can also lead to brain hypoxia: pneumonia, pulmonary edema, pneumothorax, accumulation of exudate in the pleural cavity. Moderate hypoxia of the brain is often caused by disturbances in the mobility of the chest, paralysis of the respiratory muscles, as well as its spasm against the background of tetanus or myasthenia. Alveolar hypoventilation can lead to oxygen starvation of the brain when respiratory regulation processes are disrupted when the respiratory center is affected by pathogenic factors. Other reasons include: hemorrhages in the respiratory organs, the presence of a tumor in them, injury to the medulla oblongata, overdose of narcotic or sleeping pills, severe pain that occurs in a person during breathing movements.
- Failure of ventilation-perfusion connections develops due to obstruction of the airways due to bronchospasm, pulmonary emphysema, and pneumosclerosis.
- Excessive shunting of venous blood, which is observed with congenital anomalies of the heart.
- Difficult oxygen diffusion. The cause is emphysema, asbestosis, pulmonary sarcoidosis, interstitial pulmonary edema.
- Hypoxia, which develops against the background of certain circulatory disorders, leading to insufficient blood supply to brain tissue. The reasons are: massive blood loss, dehydration due to burns or cholera, etc. This also includes disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle, for example, myocardial infarction or cardiosclerosis, cardiac tamponade, cardiac overload. Often factors can occur in various combinations. Circulatory hypoxia of the brain develops against the background of severe infectious diseases, severe allergic reactions, electrolyte imbalances, when taking glucocorticoids, with increased blood viscosity, with acute and chronic heart failure, with collapse, etc.
- Reduced oxygen capacity of the blood, leading to the development of brain hypoxia, can be a consequence of factors such as: severe anemia with a sharp drop in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. This is often observed in diseases such as tuberculosis, peptic ulcers of the stomach and intestines, poisoning with hemolytic poisons, massive burns, malaria, when the body is exposed to ionizing radiation, against the background of a lack of vitamins and iron from food.
- Tissue hypoxia of the brain develops when body tissues lose the ability to absorb oxygen from the blood. A similar situation develops against the background of cyanide poisoning, an overdose of barbiturates, antibiotics, and exposure to toxic substances of various origins. Deficiency of thiamine, riboflavin and other vitamins can also provoke tissue hypoxia of the brain.
- Mixed type brain hypoxia develops when several factors lead to it simultaneously. It is worth noting that any severe hypoxia occurs of a mixed type, for example, with various types of traumatic shock or during coma.
Consequences of long-term oxygen starvation
Hypoxia can be chronic. In this case, it can proceed smoothly and will haunt the person throughout his life. Lack of oxygen can be accompanied by the symptoms described above and lead to early aging disease. Fulminant hypoxia can occur when respiratory function is impaired. Acute hypoxia can manifest itself as a result of poisoning with toxic vapors, however, with timely assistance it is completely leveled out. Next, we’ll find out how to saturate the brain with oxygen using special exercises.
Special training
How to saturate the brain with oxygen through exercise?
Let us next consider chronic hypoxia, when the lack of oxygen is a consequence of depression or stress. It is not very dangerous and can be cured with training. True, a person is not satisfied with exercise alone. The fact is that in the presence of hypoxia, contacting a doctor to prescribe medications is a prerequisite. It is necessary to additionally perform exercises at home, which should be consistent. Each new exercise should be started immediately after the previous one has been fully mastered.
So, how to saturate the brain with oxygen?
They sit up straight. Press your back against the wall so that there is no desire to hunch your spine. Then start the stopwatch, holding your breath for as long as possible. When a person feels that he is suffocating, he should slowly exhale the rest of the air and take ten shallow exhalations and inhalations. Repeat this five times. Do breathing exercises three to four times a day. After a person learns to hold his breath for two minutes, move on to the next exercise.
Perform the previous exercise, albeit in dynamics. In this case, the breath-hold is done less than at rest, with a permissible maximum of sixty seconds. Then they master breathing inclinations, namely, lower the body down while exhaling, then stop breathing. Next, take a small breath, rise and repeat the exercise again.
Next, start running training. They do it on a simulator under the strict supervision of a trainer in case you suddenly feel dizzy and urgently need help. Hold your breath and run until you stop. Afterwards, take three minutes of calm, normal steps with shallow breathing. The workout is repeated six times.
Chronicles of a pandemic: three causes of hidden hypoxia in COVID-19
Research continues into many unclear aspects of the pathogenesis of coronavirus disease. One of the most important open questions remains the mechanism of development of “silent hypoxia”, a low-symptomatic oxygen deficiency in cells and tissues. If this condition continues long enough without appropriate medical intervention, irreversible changes in vital organs can occur. A group of biomedical engineering specialists from Boston University, working in collaboration with colleagues from the University of Vermont (USA), are trying to find answers using computer modeling technologies.
In many cases, people who are infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus and have dangerously low levels of oxygen saturation in their blood do not show any signs of shortness of breath or difficulty breathing. The term “silent hypoxia” appeared precisely in connection with this trend. It is generally accepted that the virus initially damages the lungs, depriving certain areas of them of the ability to fully perform their functions. Affected lung tissue loses oxygen and can no longer oxygenate the bloodstream. But exactly how this effect occurs was until now unclear. Of particular concern was the fact that in cases of hypoxia incompatible with life, lung scans often revealed virtually no serious abnormalities.
The joint research team tested three different scenarios using mathematical models to explain how and why the lungs stop delivering oxygen to the bloodstream. The results, published in Nature Communications, suggest that with CoViD-19, several pathological processes occur simultaneously in the lung tissues of patients.
It is known that the lungs perform the vital function of external gas exchange, when inhaling, providing oxygen to each cell and when exhaling, ridding the body of carbon dioxide. Healthy lungs saturate the blood with oxygen at a level of 95-100% of the maximum possible. A saturation level below 95 percent is already an alarming signal, and a drop below 92 percent creates an indication for artificial oxygenation. In the early stages of the pandemic, when the first reports of the phenomenon of silent hypoxia began to appear in the flow of medical information, household pulse oximeters were literally swept off pharmacy shelves: many people realized that they might have to fight the infection at home, and were preparing to monitor yourself and your loved ones the level of blood oxygen saturation.
The primary focus of the study was the effect of CoViD-19 on the ability of the lungs to regulate basic blood flow. It is normal that in an infected area of lung tissue, if it is unable to collect enough oxygen, the blood vessels will narrow. This mechanism was developed during evolution, and its task is to redirect blood flow to the most oxygenated areas of the lungs, due to which the consequences of infection are partially or completely compensated. But with COVID-19, the authors suggest, in some patients the lungs lose the ability to restrict blood flow to already damaged tissue; on the contrary, the blood vessels there further expand, i.e. something is happening that is very difficult to see with a standard CT scan.
Computational modeling confirms this hypothesis.
The effect of blood clotting on the blood supply to various parts of the lung was also studied. When the mucous membranes of the vascular walls become inflamed in response to coronavirus infection, microscopic clots can form inside the lungs, the size of which does not allow them to be seen on tomographic scans. Computer modeling also confirms this possibility, but this pathogenetic mechanism alone would not be enough to reduce blood oxygenation to the levels actually observed in patients.
Finally, the effect of coronavirus disease on the efficiency of oxygen transfer to the blood was studied - in volumes sufficient for the normal functioning of the body. This proportion is violated in many diseases of the respiratory system, for example, in bronchial asthma, which may be one of the factors of silent hypoxia in COVID-19. The results of computational modeling indicate that for the development of silent hypoxia, the efficiency of oxygen transfer to the blood must be reduced, including in those areas of the lungs that do not appear damaged or altered during imaging diagnostics.
In general, the simultaneous combination of all three factors is most likely the cause of severe hypoxia in patients with CoViD-19. Currently, taking into account the data obtained, the possibility of preventing such a scenario is being studied, including through the so-called. low-tech intervention - for example, in a prone position, the posterior parts of the lungs absorb more oxygen and, to some extent, compensate for the insufficient proportion between air flow and blood saturation. According to the authors, it is very important to understand all possible causes of hypoxia in order to select the most effective therapeutic response in each specific case, in particular, prescribe vasoconstrictor and/or thrombolytic drugs.
Based on materials from the Science Daily website
How can you cleanse blood vessels using traditional methods?
What methods cleanse blood vessels and saturate the brain with oxygen?
It is impossible to cure oxygen starvation using folk techniques, but you can significantly alleviate the symptoms and improve the overall well-being of the body:
- Pour a glass of hot water over the dry herbs of thyme, motherwort and horsetail. After half an hour, filter and cool. Drink 30 grams of infusion every four hours for severe symptoms of oxygen deficiency. This decoction must be taken with you if a person goes to the mountains.
- Boil 40 grams of fresh birch leaves for fifteen minutes in half a liter of water and drain the broth. Take one glass in the morning and evening.
- In summer they eat fresh lingonberries, and in winter they make lingonberry tea. To achieve a greater effect, add currants.
Many people are interested in how to saturate the brain with oxygen using medications?
In addition to exercises and folk techniques, there is an excellent way. To do this, take a course of glycine. They exhibit the properties of an energetic antihypoxant, which is correlated with the ability of this supplement to prevent a lack of oxygen. This property of glycine was proven in a study of its effect on the occurrence of hypoxic syndrome. Next, we’ll find out what drugs should be used to normalize blood circulation in the brain, saturate it with oxygen and cleanse blood vessels.
Risk factors
Neurologists warn that each peak of oxygen deprivation can cause irreversible consequences. Therefore, it is worth adhering to preventive measures. The following categories of people are at risk:
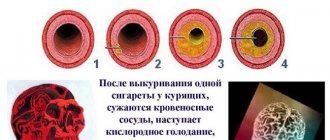
- Smokers
. Cigarettes cause vascular spasms, which impair blood circulation in the brain. - Patients with unstable blood pressure
. Regular increases in blood pressure lead to swelling and disruption of blood vessels. - Having a genetic predisposition
. Hypertensive patients, people with anemia, and those who have had heart attacks.
The higher the risk factor, the more likely a person is to experience symptoms of oxygen deprivation. If you do not contact a neurologist, it may develop into a chronic form. Over time, hidden complications appear and disruptions in the functioning of body systems are formed.
With pneumonia, inflammatory damage to the pulmonary alveoli occurs, leading to a decrease in oxygenation and the appearance of areas of fibrosis. Timely treatment is required to prevent the development of complications, including death. Read more in the article: “how to treat pneumonia at home.”
Acute manifestations may be characterized by loss of sensation in the extremities, hearing, speech and vision impairment. Paralysis of limbs and parts of the face is possible. Weak manifestations are similar to the symptoms of severe fatigue and overwork.
General manifestations
The symptoms of various manifestations of hypoxia vary. Ranges from fatigue and drowsiness to loss of coordination. Depending on the degree of damage, doctors distinguish several types of hypoxia:
- chronic;
- hypoxic;
- comatose.
Each type is characterized by its own symptoms, which differ in severity and duration. Residents of megacities and industrial zones suffer from a lack of oxygen. If a person regularly encounters symptoms, but does not consult a specialist, then the disease can provoke a stroke, heart attack, cardiac arrest, blockage of blood vessels, and paralysis.
With hypoxia, sudden changes in mood, paleness of the skin and difficulty focusing are possible.
When monitoring their own condition, a person with hypoxia may pay attention to convulsions, flickering before the eyes and rapid heartbeat. In rare cases, erratic muscle activity, cold sweat, and yawning may occur. With a short-term lack of oxygen, trembling occurs in the limbs, feeling like a fever.
Hypoxic symptoms
You can understand that the brain does not have enough oxygen by the symptoms. The hypoxic type is formed over a long period of time. The disease occurs in people who often change altitudes (climb mountain slopes, fly on an airplane), or are in a room with minimal access to oxygen. First of all, problems arise with water-salt balance and vascular tone. Typical symptoms include:
- Breathing disorders
. Rapid breathing, excessively sharp breaths, or the inability to exhale fully. - Coordination problems
. Uncontrolled muscle activity, accelerated movements, slow reactions. - Brain disorders
. Memory loss, inability to concentrate, decreased performance.
Lack of oxygen in the brain during the hypoxic type can manifest itself as paresis, shortness of breath, and memory impairment. A person develops a desire to sleep constantly, and weakness in the limbs occurs. Attacks of involuntary urination are possible if left untreated. As the situation worsens, patients lose consciousness or fall into a coma.
The hypoxic type is conventionally called acquired, since it occurs against the background of an incorrect lifestyle and is provoked by external factors. It is treated with medication and physiotherapy.
Comatose reactions
In adults, symptoms of oxygen starvation of the brain in comatose type appear a minute after the cessation of oxygen supply. The disease itself develops gradually, but more often it has a hidden type. The patient feels symptoms of overwork, stress, fatigue. Experiences drowsiness, loss of previous performance, shortness of breath appears during normal activities, and a feeling of lack of strength arises.
As the situation worsens, the following symptoms occur:
- dysfunction of the cerebral cortex;
- the patient is not oriented in space, the heart rate increases;
- control over bowel and bladder function is impaired;
- convulsions appear and speech is impaired.
If medical assistance is not provided in time, the situation may worsen. A sluggish coma gradually develops. Muscle tone and blood pressure drop sharply, and cramps become more frequent. Temperature and blood pressure continue to fall, and atony occurs. Artificial ventilation is often required.
In a serious condition, the transition to a coma begins, the brain gradually dies. At the last stage there is a high risk of death. Doctors recommend promptly contacting a specialist. He will select a medication and help you change your lifestyle. It is important to eat foods that help saturate the brain with oxygen, be in the fresh air more often and ventilate the room.
Drugs for treatment
Another way to saturate the brain with oxygen?
To restore vascular circulation to the brain, medications are used that can relieve severe symptoms of the pathology, improve metabolism in brain cells, and restore mental abilities along with lost coordination of movements. There are several groups of drugs that saturate the brain with oxygen with different mechanisms of action that help normalize cerebral circulation:
- vasodilators (their effect is based on the ability to relax vascular walls);
- anticoagulants that prevent platelets from sticking together;
- nootropics that prevent irreversible changes in nervous tissue.
Everyone should know how to saturate the brain with oxygen at home.
Treatment
Photo: neurolikar.com.ua
Therapeutic measures are prescribed depending on the cause of hypoxia, aimed at combating the lack of oxygen and correcting disorders that occur in the hemostatic system.
In some cases, to combat hypoxia, it is enough to walk in the fresh air or ventilate the room in which there is a person suffering from lack of air. However, if hypoxia is associated with diseases of the lungs or cardiovascular system, more serious measures are required.
If necessary, various oxygen equipment is used, for example, oxygen masks, oxygen pillows or oxygen cartridges. In some cases, a person needs to be connected to a ventilator. The ventilator provides a forced supply of a gas mixture to the lungs, due to which the blood is saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide is removed from the lungs.
The following medications can be used:
- bronchodilators;
- antihypoxants;
- respiratory analeptics;
- drugs with a cardiotropic effect (for example, cardiac glycosides);
- antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants.
If the cause of hypoxia is poisoning of the body, special antidotes are introduced, the action of which is aimed at weakening or completely stopping the effect of the poison on the human body. The choice of antidote depends on the nature of the action of the substance that caused the poisoning. The effectiveness of application depends on the accuracy of identifying the appropriate antidote and the time of assistance.
In emergency situations, surgical interventions are performed to eliminate acute hypoxia.
Basic exercises to improve brain function
What exercises do experts recommend focusing on if a person wants to improve the functioning of his brain? To do this, you need to choose one of the following simple methods:
- Exercising daily thirty minutes of walking.
- Do a fifteen-minute jog every day.
- Dance classes.
- Passion for fifteen-minute bike rides.
- Performing aerobic exercises at home.
This perfectly cleanses the blood vessels of the brain, saturates it with oxygen, and trains.
Treatment of cerebral hypoxia
Since brain hypoxia is most often associated with a number of factors, complex therapy is necessary, which depends on the cause that led to this pathological condition.
If hypoxia is the result of a lack of oxygen in the inhaled air, then the person should be switched to breathing normal air as quickly as possible. Provided that the brain cells have not been destroyed, recovery will not take much time, and all functional disorders will be eliminated. Sometimes patients are advised to add 3-7% carbon dioxide to regular oxygen. This will expand the blood vessels of the brain and stimulate the functioning of the respiratory center.
If there is a foreign object or other obstruction in the airway, tracheal intubation and tracheotomy may be required. The patient is placed in a position that facilitates breathing.
In case of severe respiratory failure, or complete absence of breathing, auxiliary or artificial respiration and artificial ventilation of the lungs are necessary. Oxygen therapy should be continuous and long-lasting until it is no longer needed.
Blood transfusions, cardiac and hypertensive medications are required for circulatory hypoxia. In this case, it is important to normalize blood circulation. If the patient has suffered cardiac arrest, chest compressions and the use of a defibrillator are required. The doctor may administer adrenaline, atropine, and take other resuscitation measures. All these measures must be carried out as quickly as possible, so it is possible that they can be carried out while still in the ambulance.
To treat and prevent cerebral hypoxia, medications with an antihypoxic effect can be used. These are narcotic and neuroleptic drugs, drugs to reduce body temperature, etc. Sometimes glucocorticoids can help.
It is imperative to restore the acid-base and electrolyte balance in the body, but this already applies to symptomatic treatment. Seduxen, which is administered intravenously, allows you to relieve convulsions. If this does not help, then the introduction of muscle relaxants is indicated.
To eliminate the consequences of brain hypoxia, it is possible to use drugs such as:
- Dibazol.
- Galantamine.
- Sodium hydroxybutyrate.
- Nerobol.
- Pyridoxine.
- Cerebrolysin.
- ATP.
- Tranquilizers.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
The patient will definitely have to visit the massage therapist’s office and perform therapeutic gymnastic complexes.
First aid for a person with cerebral hypoxia
The only thing a person who does not have a medical education can do for a victim with cerebral hypoxia is to provide him with a flow of fresh air and call an ambulance as quickly as possible. Until doctors arrive, you should ventilate the room and remove from the victim all items of clothing that may interfere with breathing.
What other exercises should you do to train your blood vessels?
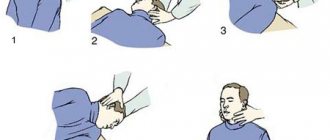
The starting position should be as follows: place your arms along the body, then raise them to your shoulders, clench your hands into fists and tilt your head forward. Next, raise your elbows up and tilt your head directly forward. Return to the starting position. The exercise is not performed quickly or slowly, but is done exclusively at an average pace.
As part of the second exercise, the starting position looks like this. Arms to the sides, then bend them at the elbows and make jerks with bent limbs. The right hand is directed forward, and the left hand is directed back behind the back. Return to the starting position. They do exactly the same thing several times, changing hands: right - back, left - forward. This exercise is not done quickly or slowly, it is performed at an average pace.
During the next exercise, the starting position looks like this: the arms are placed along the body, and the head is held straight. The head is then tilted towards the right shoulder, returning further to its original position. Then the head tilts towards the left shoulder and the person returns to the starting position. Next, keep your head straight, do not tilt your neck, and look in front of you, turning it to the right, then return to the starting position. Then, in the same way, keep your head straight, do not tilt your neck, and look in front of you, turning it to the left, then return to the starting position. Do this exercise at a slow pace.