Author
Eremin Dmitry Sergeevich
Radiologist (CT)
Doctor
Radiologist
until September 30
Total Body Scan (MRI of the whole body) with a 48% benefit + free consultation with a GC doctor* More details All promotions
MRI
(magnetic resonance imaging) is a modern type of diagnostics that uses a magnetic field and radio waves (rather than ionized radiation, which is used in X-ray machines and computed tomography). Therefore, MRI is safe and can be performed as often as necessary.
Magnetic resonance imaging is a highly informative diagnostic method, most revealing in the study of soft tissues, which allows obtaining images in the form of tissue sections of a particular organ.
What you need to know about the principle of MRI and the design of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner
The patient is placed on a movable table that moves through a tunnel-shaped magnet. The magnet creates a powerful magnetic field; Radiofrequency pulses are sent to the examined area of the patient in a magnetic field. As a result of this radio wave exposure, hydrogen atoms resonate in the tissues of the body.
Our body is mostly composed of water and fat, and these substances, in turn, are characterized by a high hydrogen content. The amount of hydrogen varies in different tissues; including in tissues affected by pathological processes, it differs from what is characteristic of healthy tissue of a given organ.
Information about atomic resonance is read by special sensors (coils) and processed using a computer program that reconstructs an image in the form of a slice of the organ under study.
HealthQuestion to an expert: Is it necessary to do an MRI just in case and what are the risks?
Text: Gayana Demurina
answers to most of the questions that concern us online. In a new series of materials, we ask exactly these questions: burning, unexpected or common ones - to professionals in a variety of fields.
Examination methods that allow you to see various organs and systems without pain or incisions, including even before a person is born, are called imaging techniques (or imaging techniques in English). True, many still doubt that these methods are safe: there are rumors about the dangers of even such an ordinary thing as ultrasound. As a result, two extremes arise: some are afraid of imaging studies, others insist on regular “imaging of everything.” How justified are the fears? Who needs such research and when? Should pregnant women be afraid of them? We asked an expert to answer these questions.
Sergey Morozov
Chief freelance specialist in radiation diagnostics of the Moscow Department of Health, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Director of the Scientific and Practical Center for Medical Radiology of the Moscow Department of Health
Concerns about the safety of hardware examinations are quite understandable, because they somehow affect the cells of the body. The first thing we think about is how this will affect our health in the future (especially if the word “radiation” appears in the sentence). But in fact, not all types of imaging diagnostics use radiation: ultrasound and MRI have nothing to do with it at all.
In the case of ultrasound, the machine creates vibrations, or waves; When an ultrasonic wave reaches tissues with a certain acoustic resistance, it is refracted. That part of the wave that acts on tissues with less resistance will be absorbed by them and will travel further, and the other part, in front of which the resistance of the tissue is stronger, will be reflected. Roughly speaking, the more ultrasonic waves are reflected, the brighter and clearer the picture on the device screen will be. With MRI, the story is a little different - but the main role here also belongs to waves, only electromagnetic ones. They create a strong magnetic field and record the response to it from some particles (the nuclei of hydrogen atoms are responsible for this). Essentially, the device registers the body’s response electromagnetic radiation and displays an image. This is not a “photograph” of the organ being examined, but rather a map of its electromagnetic signals.
Such methods are safe for the patient’s health because they propagate sound or electromagnetic waves that cannot change the structure of cells. Ionizing radiation (such as X-rays or gamma rays, which CT scans use) works differently: the wavelength of such exposure can turn neutral particles in our tissues into charged ones, that is, ions (hence the name). This is dangerous for health because the tissue structure changes. If ionization takes dividing cells by surprise and affects a protein synthesized using DNA, then the resulting anomaly will be repeated many times, like on a conveyor belt. This is how mutations arise, which can lead, for example, to cancer.
Of course, this is not a reason to categorically refuse X-rays or CT scans. It's a matter of radiation dose; for structural changes to start, it must be very large (symptoms of acute radiation sickness appear at radiation levels of 300 millisieverts, and the safe dose is up to 100 millisieverts). Modern diagnostic devices are gentle on the body in this regard: for example, during an X-ray of the lungs, a patient may receive less than 1 mSv of radiation; with a CT scan, the numbers will vary depending on the area being examined, but in general should not exceed 16 mSv. Higher doses of radiation are used to treat cancer - this is called radiation therapy. At the same time, the risk of developing a second tumor cannot be excluded, although this happens extremely rarely.
It turns out that it is difficult to achieve a dangerous dose of radiation, but there is no need to be afraid of examinations. Firstly, the harmful effects of ionizing radiation have so far been recorded only in the context of major disasters, such as Chernobyl, where the radiation doses were incredibly high. Secondly, we receive a certain amount of radiation without medical examinations: a person who regularly leaves the house receives up to 2–3 mSv of radiation per year. Our body has adapted to this type of stress and copes with it using protective mechanisms, including immune cells that capture and destroy abnormal cells, as well as apoptosis (programmed cell death).
Using only safe methods so as not to encounter radiation at all is more of a utopia than a reality
On the other hand, it is definitely not worth doing radiation diagnostics in any unclear situation: although the harm of radiation in small doses remains in question, experts try not to expose patients to radiation in vain. Some organs are especially sensitive to radiation - the thyroid gland, skin, retina, glands (including mammary glands), and pelvic organs. To protect patients, certain protocols are followed: for example, lead aprons are used to block X-rays, and the machines are adjusted to use the minimum dose necessary to produce a good image.
Experts treat children and pregnant women with special caution: if an examination is recommended, but there is no urgent need for it, it may be postponed for some time. On the other hand, dental x-rays are safe for pregnant women if performed according to all the rules - the source of infection in the mouth, that is, caries or pulpitis, is much more dangerous for both the mother and the fetus. Ultrasounds and MRIs can be done safely during pregnancy - and ultrasound is used to determine not only the sex of the baby, but also the risk of developing Down syndrome or congenital anomalies. The dangerous effect of ultrasound and MRI on the fetus is no more than a harmful myth, because there is no ionizing radiation from such studies.
Using only safe methods so as not to encounter radiation at all is more of a utopia than a reality. If only because different types of diagnostics allow you to look at the area under study in different ways. The mechanisms of CT and MRI are not the same, but they have the same task - to display an object in three-dimensional form. At the same time, with the help of computed tomography, fractures, hemorrhages, vascular function, and the condition of the abdominal cavity are better diagnosed, although in general this method is suitable for other cases. MRI is better for soft tissue, allowing you to see tumors and study, for example, the brain and spinal cord, although again this method can be used in other parts of the body.
Ultrasound, on the contrary, has a limited spectrum of action. It is believed that it does not see organs that are hidden behind the bones (the ultrasound wave simply does not reach them). It is also not yet amenable to automation, meaning a specialist is needed to interpret the ultrasound results. However, the device can be easily installed right at the patient’s bedside, which is not possible with, for example, a massive MRI tunnel. Classic x-ray diagnostics are now used less frequently than before, but sometimes you cannot do without it, for example, before complex operations. In fact, a lot depends not only on the purpose of the study, but also on the price, time spent and, in fact, the availability of the device in the clinic.
A healthy person under forty does not need to undergo regular CT scans. It's worth making an appointment with a doctor when something really bothers you. If it seems that you need something like a medical examination, it is enough to go through a simple check-up program (this usually includes ultrasound of various organs, ECG and echocardiography - ultrasound of the heart, but may also include a chest x-ray). For older people, X-ray examinations are indicated as part of regular examinations. For example, after fifty to sixty years of age, everyone is recommended to undergo annual screening for lung cancer - that is, a CT scan of the lungs, and for women after forty - also breast cancer using mammography.
Photos: dmitrysteshenko - stock.adobe.com, Mandrixta - stock.adobe.com
Types of MRI studies
The most popular types of MRI studies are:
- MRI of the spine
. Allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord, cartilage, ligaments and back muscles. Circulatory disorders, consequences of injuries, developmental anomalies, changes in intervertebral discs, etc. are identified. An MRI examination of a specific section or the entire spine may be performed. - MRI of joints
. A specific joint is examined: knee, shoulder, hip. MRI allows you to study in detail the structure of the articular joint, visualize intra-articular (menisci, joint fluid) and periarticular formations (ligaments, muscles). Developmental anomalies, inflammatory and degenerative changes in the joint, and pathologies of periarticular tissues are diagnosed. - MRI of the brain
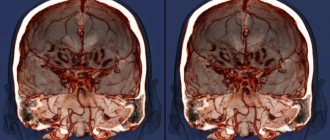
. MRI examination of the brain is highly sensitive and allows you to visualize both hemispheres of the brain, its stem part, the ventricular system and other structures. Using MRI of the brain, vascular abnormalities, vasodilation, hemorrhages, tumors, foci of inflammation and degeneration, fluid accumulations, etc. can be identified. - MRI of the pituitary gland
. MRI shows the condition of the pituitary gland itself and the sella turcica (anatomical area in which the pituitary gland is located). MRI can detect adenomas and other pituitary lesions. - MRI angiography of the brain
. MRI provides an opportunity to assess the condition of cerebral vessels without the introduction of a contrast agent. This is possible because the method allows one to distinguish a substance in motion (blood) from stationary structures (vascular walls). - MRI cholangiography
– study of the patency of the bile ducts. The intrahepatic ducts, cystic duct and common bile duct are examined, as well as (partial) liver and pancreatic tissue. Allows you to identify stones, polyps, tumors and narrowing of the bile ducts. - MRI of the prostate
. MRI allows you to evaluate in detail the structure of the prostate gland, identify prostate adenoma (benign hyperplasia), foci of inflammation and prostate tumors. - MRI of the pelvic organs
(uterus and ovaries). MRI can detect changes in tissue structure, endometriosis, adhesions, fibroids, polyps, tumors, and helps determine the type of ovarian formation.
What does MRI show?
Sometimes MRI can detect pathological abnormalities or conditions that are impossible or difficult to diagnose using other non-invasive methods. Thus, tomography successfully detects degenerative changes in the white and gray matter of the brain, and pathology of the pituitary gland. MRI scans clearly show areas of the brain that are damaged by a stroke. Using an MRI of the spine, a neurologist can easily detect hernias, protrusions, osteochondrosis and spondylosis. Because magnetic resonance imaging allows you to see minute differences between healthy and diseased tissue, MRI images clearly show:
- Brain diseases such as epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, tumors, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease. This test method allows you to determine the dead tissue in the abscess and the presence of metastatic cancer cells.
- Malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity.
- Liver diseases, in particular cirrhosis, abnormalities of the bile ducts and pancreas.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Heart problems, including congenital abnormalities.
- Malformations of the vascular bed, the presence of blood clots, narrowing of the arteries, inflammatory processes of blood vessels and wall injuries.
- Polyps, cysts, tumors of the genital organs.
- Degenerative disorders of the bone tissue of the spine, injuries of ligaments, cartilage, osteomyelitis, arthrosis and arthritis.
Previous Next
Harmlessness of MRI
To date, there have been no cases where the magnetic field or radio waves used in MRI scans have caused harm to a patient. MRI is not done in the first trimester of pregnancy, but this is just a precaution; the facts when an MRI would cause any harm to the fetus are also unknown to medicine.
contraindications for MRI
.
First of all, they are determined by the presence of electronic devices implanted into the body (hearing aids, artificial heart pacemakers), as well as any metal structures and fragments (joint endoprostheses, metal plates, knitting needles, consequences of metal osteosynthesis and gunshot wounds, etc.). Dental implants, vascular stents and umbrella filters produced in the last 5-7 years are usually made from MRI-ready materials. Therefore, for such patients, an MRI examination can be performed after presenting a certificate or confirmation from the medical institution that performed the installation.
MRI is not done if you have a pacemaker (an absolute contraindication).
An MRI cannot be performed if the patient is afraid of confined spaces (suffers from claustrophobia).
Sometimes during the study, a burning sensation or irritation of the skin occurs due to the applied cream, ointment, or certain types of tattoos, in these cases the study must be stopped and, if the cause cannot be eliminated, the study may be stopped.
Breastfeeding, menstruation and the presence of an intrauterine device are not an obstacle to undergoing an MRI.
Preparing for an MRI
No special preparation is required for MRI. The only exception is MRI of the liver and gall bladder, which are performed strictly on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning.
The patient should be prepared for the fact that he will have to spend quite a significant amount of time (from 15 minutes to almost an hour, depending on the type of study) inside the tomograph tunnel. At the same time, the installation produces noticeable noise (this is an inevitable consequence of the technology used). Clothing in which you can undergo an MRI must not contain metal parts (zippers, fasteners, buttons). All accessories (watches, hairpins, hairpins, jewelry, etc.) will need to be removed. It is also necessary to leave electronic magnetic cards and any other magnetic media (flash drives, memory cards, etc.) in a special booth, otherwise all information on them will be erased in the magnetic field.
MRI or X-ray, which is better?
Both diagnostic methods are used to see the condition of the internal organs of the human body, but x-rays are an outdated research method. It continues to be used only because it is cheap. In cases where a detailed picture is needed, the MRI method is used, which allows you to obtain more complete information.
The main difference between these methods lies in the physical phenomenon underlying the operation of the equipment. When using radiographic examination, ionizing flows are used, which are transmitted by soft tissues and reflected by dense ones. Therefore, x-rays are used when it is necessary to examine bones or determine whether there are stones in the patient’s kidneys.
Unlike X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging does not use high-frequency radiation, but magnetic waves. Under the influence of magnetic radiation, hydrogen molecules located in the organs and tissues of the human body change the direction of movement. With this, the doctor can see a more detailed image of the desired organ.
What are the differences between MRI and X-ray?
What is the difference between tomography and x-ray? If we compare diagnostic methods with each other, we can note the following points:
- Features of creating photographs . The tomography method makes it possible to image the area under study from any angle. If required, the specialist can take several photographs in different planes and then combine them into a complete three-dimensional image.
- Duration of the process . An X-ray examination is completed in less than a minute. Tomographic diagnostics, even on the most modern equipment, takes 15–45 minutes. Therefore, it is better not to use MRI for those people who suffer from severe pain or have a fear of closed spaces.
- Purpose . The tomography method is universal. With its help, you can obtain images of any areas of the human body, regardless of the type of tissue. In this case, X-rays are used exclusively for diagnosing dense tissues - bones, solid formations in organs, identifying foreign bodies, etc.
- Harm to the body . Although a single x-ray exposure does not cause significant damage to the human body, if you perform 3-4 such studies in a row, the patient will receive an annual dose of radiation. The magnetic radiation of the tomographic method causes absolutely no harm to the patient, and it can be used as many times as desired.
- The advantage of radiographic diagnostics is the possibility of its application to people who have electronic and metal implants, as well as its use for examining severe patients who cannot tolerate a longer examination.
Advantages of MRI at Family Doctor
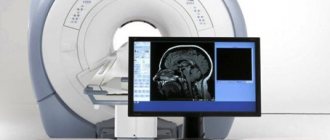
The “Family Doctor” uses a Brivo MR355 Inspire tomograph, manufactured by GE Healthcare (the medical division of the American company General Electric), to conduct magnetic resonance imaging. Brivo MR355 Inspire is a world-class MR scanner with a magnetic field of 1.5 Tesla (the higher this figure, the more detailed the resulting image can be). This tomograph belongs to the class of equipment with high magnetic field power. Thanks to modern technologies, Brivo MR355 Inspire provides high-quality visualization to help make the diagnosis as accurate as possible.
MRI is performed at the Diagnostic Department of the Hospital Center (Baumanskaya metro station). Research is carried out on the orders of Family Doctor doctors, as well as third-party medical organizations.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.