Flashes in the eyes are a false sensation in which a person sees luminous objects of various sizes and shapes. As a rule, these are flickering spots, lightning, balls, sparks.
Lightning before the eyes is not an independent disease. This is a symptom that, depending on the circumstances, may indicate harmless eye fatigue or cervical osteochondrosis, or a serious eye catastrophe - retinal detachment. It is one of the most common complaints of patients and, as a rule, is accompanied by another symptom - spots in front of the eyes, the appearance of a “curtain”.
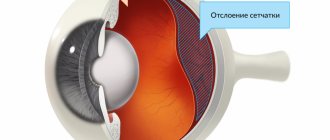
Fig. 1 Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is one of the common causes of lightning in the eyes (not dangerous)
Causes of flashes before the eyes
Sometimes such complaints are a benign condition associated with excessive visual stress or age-related changes in the eye. However, more often than not, the cause of outbreaks is a serious problem that requires immediate medical attention. The causes of the condition may be:
- Posterior vitreous detachment. The gel-like substance that fills the central part of the eye and is attached to the retina is called the vitreous body. With age, it gradually shrinks, peeling off from its original place. This process retracts the retina, causing flashes to appear in the eyes. Similar symptoms are noticeable when moving the eye. There is no specific treatment for this condition. However, patients with this diagnosis must undergo regular ophthalmological examinations. Sometimes, such symptoms hide a more dangerous pathology - retinal detachment, which can cause irreversible vision loss - blindness.
- Retinal detachment or tears. Very often, flashes of light are a symptom of a violation of the integrity of the retina and the beginning of its detachment. It is necessary to pay special attention to the situation if such a condition appears after physical activity (heavy lifting) or serious nervous stress. In this case, flashes of light are often accompanied by the appearance of a veil in front of the affected eye and a sudden decrease in visual acuity. In case of retinal detachment, urgent medical attention is required - surgery.
- Migraine. Similar visual symptoms may precede headache attacks. In this case, flashes of light take the form of bright white zigzags, sparks or geometric shapes. As a rule, they are localized in the periphery of the visual field in one eye or two at the same time. Light flashes of light in the eyes occur without headache attacks. This phenomenon is called ocular migraine. They do not fall within the competence of an ophthalmologist; they are dealt with by neurologists.
- Vascular diseases. Such pathologies include: hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, etc. Patients note the periodic occurrence of flashes before closed eyes or in the dark. The condition is caused by short-term vascular spasms with impaired blood circulation in the retinal tissue. As a rule, in this case, manifestations of angiopathy or retinopathy are visible in the fundus.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. When the vertebral arteries (pass in the bone canals of the cervical vertebrae) are compressed, the blood supply to the brain (including the cerebellum) is disrupted, so not only visual disturbances appear, but also dizziness. Often, vertebral artery syndrome (VAS) occurs in people who work at a computer for a long time and lead a sedentary lifestyle.
- Intracranial tumors of the occipital lobe of the brain. In this case, visible phenomena differ in shape and color and have a constant nature of occurrence.
- Inflammatory processes in the retina and choroid of the eye. The diseases that cause them are called retinitis and choroiditis and always occur against the background of accompanying signs of inflammation: blurred vision, decreased visual acuity.
Treatment
As noted earlier, flashes and lightning in the eyes in 80% of cases are the result of various ailments. Therefore, possible treatment for photopsia is selected taking into account the diagnosis made by doctors.
If the patient has significant damage to the retinal tissue or hemorrhages occur, then surgical intervention is performed. Vitrectomy involves the removal of blood clots, fibrovascular strands, and areas of the vitreous that have become clouded as a result of the disease.
Flashes caused by cataracts are eliminated by removing the clouded lens and replacing it with a special artificial lens.
If the cause of photopsia is inflammation of the retinal vessels (chorioditis), then treatment is usually carried out in a hospital and consists of antibiotic therapy and drug management of symptoms.
Macular edema of the visual organs can be treated conservatively (use of effective anti-inflammatory drugs) or with surgical intervention (surgery and laser method).
Flashes of light when your eyes are closed can be caused by frequent migraines. This phenomenon can be stopped with serotonin receptor agonists. For ocular migraine, the ophthalmologist will prescribe drugs with sedative properties and drugs that improve the movement of blood to the main vessels of the brain.
Doctors also call the cause of outbreaks osteochondrosis, degenerative processes in the spine (in its cervical region). Treatment consists of taking muscle relaxants and drugs intended for the prevention of ischemic syndrome of brain tissue, normalizing blood circulation, and B vitamins.
Any treatment must be supported by the recommendations of a doctor. Under no circumstances should you select medications yourself.
Treatment used
Before starting treatment, the patient undergoes a complete ophthalmological examination, including the fundus with a dilated pupil. For this purpose, traditional and the latest diagnostic research methods are used (including OCTA - optical coherence tomography in angiography mode).
If necessary, the patient receives consultation with a neurologist, endocrinologist, and other specialized specialists.
Fig. 2 If lightning appears in your eyes, you should consult an ophthalmologist. If necessary, he will refer you to other specialists.
Very often, the symptom of a “flash of light in the eyes” is a one-time occurrence; once it occurs, it does not recur and is not treated.
In the case of posterior vitreous detachment, flashes in the eyes occur periodically, they practically do not bother the person and do not require special treatment.
For inflammatory processes (retinitis and chorioretinitis) that cause flashes before the eyes, doctors at our clinic prescribe pathogenetic, specific and nonspecific hyposensitizing therapy, use physical (laser coagulation) and physiotherapeutic methods of influence.
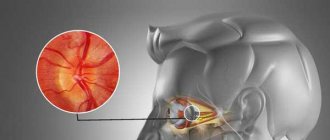
In case of retinal dystrophies and ruptures, our laser surgeons perform its strengthening - a restrictive laser coagulation procedure (a painless procedure that can be done on the day of treatment).
Fig. 3 Rupture and detachment of the retina - situations requiring urgent surgical treatment
For retinal detachments, vitreoretinal surgeons at our clinic use the most modern surgical methods:
- laser coagulation;
- cryotherapy;
- scleral filling;
- pneumoretinopexy;
- vitrectomy.
Thanks to the clinic’s equipment with innovative diagnostic and surgical equipment, the necessary medical care can be provided immediately and urgently. The professional experience of the center's microsurgeons guarantees patients minimizing the risk of possible intra- and postoperative complications and rapid recovery even in the most serious cases.
What treatment is prescribed?
Medication
Dietary supplements can be included in the therapeutic complex of drugs for infectious-inflammatory pathology of the visual organs. If sparks in the eyes are a consequence of the progression of an infectious-inflammatory disease, then drug therapy will be required. The following groups of drugs are used for treatment:
- antibiotics;
- antiseptics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- antihistamines;
- decongestants;
- painkillers;
- vitamin and mineral complexes, dietary supplements.
Surgical
If flashes in the eyes are a consequence of vitreous detachment, retinal dissection or other intraocular disorders, surgical treatment is required to prevent the progression of degenerative processes. The most common eye surgeries are:
- vitrectomy;
- scleroplasty;
- laser coagulation.
In the presence of a tumor, brain surgery is the only sure way to solve the patient’s problem. The most severe and dangerous disease that causes flashes in the field of vision is an oncological tumor localized in the brain. In this case, a radical operation is prescribed, during which the tumor is removed. The procedure will be followed by rehabilitation, during which the patient will need to undergo a course of chemical, radiation and restorative therapy. If the tumor is diagnosed in the early stages and does not metastasize, the prognosis for successful recovery is favorable.
Folk remedies
Non-traditional methods of therapy can be used as auxiliary and preventive treatment. For frequently recurring infectious and inflammatory eye diseases, it is recommended to take a vitamin infusion for a course of 2 months, the preparation method of which is simple:
- Pour 3 tbsp into a thermos. l. fresh blueberries and pour 2 liters of boiling water over everything.
- Close the container tightly with a lid and leave to infuse for 3 hours.
- You need to drink the finished product a day, use the infusion as tea, you can add a little honey or sugar to taste.
If conjunctivitis is diagnosed, you can prepare an herbal decoction to wash the eyes. The recipe is:
Chamomile and calendula can be added to the medicinal decoction.
- Boil 300 ml of water, add 2 tbsp. l. a mixture of chamomile, calendula, sage and thyme flowers, taken in equal proportions.
- Cover the container with a lid, reduce heat and simmer for 5 minutes.
- Remove the broth from the stove and let it brew for another 1 hour.
- Strain the product and cool to room temperature.
- Using a pipette or syringe, rinse the eyes with a bactericidal decoction daily, 4-6 times a day, until the pathological symptoms disappear.
Color vision impairment
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
17002 October 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Color vision impairment: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Description
Impaired perception of colors and their shades in medicine is called color blindness, or chromatopsia. The ability of the human eye to distinguish many colors and shades opens up enormous possibilities for orientation in space, knowledge of the surrounding world and fine art.
The conductor that helps a person perceive surrounding objects with the help of the organ of vision is light. Light is electromagnetic radiation, visible to the human eye, whose wavelengths range from 380 to 700 nm. Each object can reflect and absorb certain wavelengths of light. Those waves that are reflected pass through the transparent structures of the eye and excite special cells - cones, which are responsible for the perception of color.
The human eye can distinguish almost all color shades resulting from mixing the three basic ones - red, blue and green.
Depending on the percentage of excitation of a particular type of cone, a sensation of color arises in the brain. So, for example, when the brain perceives the color orange, then at that moment an impulse is transmitted from 99% of red cones, 42% of green and 0% of blue, and in the case when the brain perceives green, 31% of red, 67% of green and 36 % blue cones. If all cones are excited equally, then we see white color.
Color vision disorders occur due to a disruption in the excitation of cones and the transmission of impulses to the brain. If this condition is congenital, then a violation of color vision may remain unnoticed for a long time, because a person is guided by brightness and color saturation. Life experience and communication with people provide information about color: grass is green, the sky is blue, strawberries are red. Errors are detected at low brightness and object sizes.
A condition where a person has a reduced or completely absent ability to distinguish all or some colors is called color blindness.
.
Types of color vision impairment
There are congenital (most common) and acquired color blindness. Depending on the clinical manifestations, i.e. Depending on the characteristics of color perception, the following types of color blindness are distinguished:
- Achromatopsia is a complete lack of color vision, when a person perceives everything in black and white. Very rare.
- Deuteranopia is a complete loss of perception of the green part of the spectrum. Most common.
- Protanopia is a complete impairment of recognition of the red part of the spectrum. Deuteranopia and protanopia give similar color perception because... mixing red and blue, blue and green gives rise to a similar interpretation in the brain - swamp green.
- Tritanopia is a complete impairment of the perception of the blue spectrum. Rarely seen.
In addition to color blindness, there is a weakness in color sensitivity, when a person needs much more time and strong color saturation to recognize the color of an object.
Decreased perception of red is called protanomaly, green is called deuteranomaly, and blue is called tritanomaly.
Possible causes of color vision impairment
The most common cause of color vision impairment is damage to the genes involved in color perception on the X chromosome. As you know, men have a chromosome set of 46XY, and women have 46XX. If a boy received a damaged X chromosome from his mother, then there is nothing to compensate for the defective genes (there is no second X chromosome), and a violation of color perception occurs. In women, congenital color blindness is quite rare - in the case when a girl receives a damaged X chromosome from both her father and mother. The color blindness gene can be passed on through generations, manifesting itself in grandchildren and great-grandchildren. To make sure there is no genetic predisposition to color vision impairment, you can take a DNA test. This method is applicable in cases where conventional visual tests cannot be used, for example, for newborns and children in the first years of life.
Acquired types of color vision disorders are relatively rare and occur with various damage to the visual analyzer at one of the stages of receiving, transmitting or processing information.
Among their reasons are the following:
- damage to the retina by ultraviolet light if safety precautions for using UV lamps are not followed;
- Diabetes mellitus is one of the common causes of acquired color vision impairment as a result of diabetic macular degeneration. With a constant increase in blood glucose levels, damage occurs to all blood vessels, and especially to the small vessels of the fundus. Due to lack of oxygen, the retina ceases to perform its functions. Along with the symptoms of color vision impairment, distortions of straight lines and blurred vision occur;
- inflammatory diseases of the retina and optic nerve;
- cerebral atherosclerosis;
- taking certain medications (for example, cardiac glycosides can lead to seeing objects in yellow-green tones);
- cataract and glaucoma;
- retinal burns;
- chemical poisoning;
- lack of vitamin A, which results in a change in sensitivity to light and the perception of yellow-blue hues;
- mechanical damage to the retina, optic nerve, as well as traumatic brain injury;
- typhoid fever;
- neurological disorders: multiple sclerosis, previous stroke or cerebral infarction, brain tumors.
Which doctors should I contact if I have color vision problems?
If color vision is impaired, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and the necessary tests to evaluate vision and color vision. If acquired color blindness is suspected, he will prescribe a set of laboratory and instrumental research methods and refer you to the necessary specialists.
Diagnosis of color vision impairment
There are several methods for diagnosing color vision disorder:
- tables E.B. Rabkin, or “polychromatic” tables, which consist of circles of different colors and brightness, which a person with color vision impairment will not be able to navigate. The circles are arranged so that some of them form a number or figure that needs to be recognized;
- the Ishihara test involves cards with spots of different colors that form numbers and shapes;
Ishihara test
- anomaloscopy;
- biochemical blood test to determine glucose levels, control cholesterol levels, very low, low, and high density lipoproteins, blood electrolytes - potassium, sodium, calcium, creatinine levels, liver enzymes - ALT and AST, total and direct bilirubin levels);
Causes
Sparkles in the following pathologies:
- Injuries, bruises. Damage to the head area most often affects the visual apparatus. According to statistics, the largest percentage of causes of outbreaks is given to injuries and bruises. In case of damage, the following symptoms are observed: clouding of consciousness, headache, nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, general discomfort, weakness.
- Migraine is a headache that strikes a person in “attacks” with a certain frequency. The person is exhausted. During such attacks, it is difficult for him to engage in any activity. The eyes get tired quickly, it is harder to concentrate on things, and with pain it is almost impossible to work with small things.
- Damage to the retina (the inner layer responsible for color perception). The retina can be damaged due to a blow, chemical poisoning, or burn. The reasons are not important. Any defeat causes a “sparkle” in the eyes. Retinal damage may not manifest itself for a long time. The development of pathology takes some time.
- Detachment of the vitreous humor (the clear membrane between the lens and the retina). Peeling is directly related to a change in the shape of the visual apparatus. Therefore, most often a similar reason appears in older people, when the eye narrows and undergoes biological changes. Flashes appear when tilting (turning) the head.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. A disease associated with deformation of the cervical vertebrae. Accompanied by aching pain and discomfort in the neck area. The manifestation of glows occurs due to a person feeling severe pain.
- Brain tumors (benign and malignant formations). Sparkling is one of the symptoms of the development of a tumor in the body. A similar symptom appears when the tumor grows. The tumor begins to put pressure on the eye apparatus and a sparkling effect occurs.
- Inflammations and infectious diseases of an ophthalmological nature. Such pathologies are accompanied by decreased vision, the appearance of a veil, fog, increased tearing, pain and discomfort in the eyes, irritation, pain, and bright flashes. They are treated in accordance with the prescription prescribed by the ophthalmologist (eye drops, ointments).
- Diseases associated with blood vessels. Coronary heart disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), neurocircular dystonia, varicose veins, diabetes mellitus and a number of others. Defects in the functioning of blood vessels lead to outbreaks. These flashes come in a variety of colors (from pale yellow to bright red).
Single flashes flicker for the following reasons:
- sudden turns of the head;
- fatigue due to long-term stress and concentration;
- after sitting at the computer, TV;
- when watching fireworks;
- due to damage to the optics.
If the glow occurs sporadically, it is not necessary to contact an ophthalmologist. But if sparkling regularly appears, consult a doctor immediately for consultation and treatment.
With eyes open
Flashes only when the eyes are open due to the development of pathologies in the body with the visual apparatus:
- vitreous detachment;
- retinal pathologies;
- injuries, damage that affect the eye;
- development of neoplasms (tumors in the brain);
- inflammation and infectious diseases.
The occurrence of flashes when the eyes are open can be a symptom of other diseases. Lightning appears individually. The occurrence and patterns of such an effect have not been fully studied.
With your eyes closed and in the dark
When the eyes are closed, flashes are determined by the presence of pathologies:
- vascular system;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- migraine.
Flashes before the eyes in the dark are accompanied by:
- blurred vision in a poorly lit room;
- difficulty concentrating on individual objects in the dark.
In a lighted room, the visual impairment disappears. The person concentrates well on objects and does not notice any discomfort.
In other words
The fire of the soul in the eyes can be compared to a mirror, because it reflects what is currently inside you. If you are angry with someone or, conversely, are delighted with something, then the interlocutor will be able to notice characteristic highlights.
The lights in the eyes are contagious. Those around you will feed off your positivity and will fight for their happiness, even if they were previously insecure or lazy. But be careful, because the same thing happens with negative highlights.