Many patients and even doctors do not pay due attention to the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). As a result, the necessary diagnostic measures and therapy are not carried out. However, this opinion is wrong. If at first the symptoms of the pathological process turn out to be harmless, very soon they begin to signal serious disturbances in the functioning of the internal organs.
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
The main condition for eliminating the risk of complications and negative consequences is timely identification of the primary process, which is accompanied by vegetative-vascular dystonia. However, diagnosing VSD is not so easy, since such a concept does not exist in official medicine.
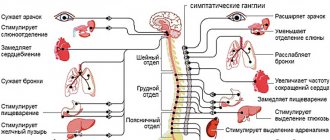
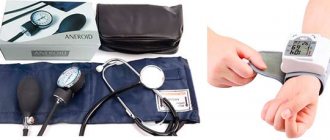
When visiting a doctor for the first time, a person’s blood pressure is measured and information is collected about how long ago symptoms occurred, their frequency, and severity. A general or clinical blood test is also required. To exclude heart disease or vascular pathologies, an electrocardiogram is performed. An ECG reveals an increase in heart rate, disturbances in the heartbeat such as extrasystole.
Typical clinical manifestations of cerebral vascular dystonia are decreased ability to work, malaise, shortness of breath, increased or decreased blood pressure, which the doctor takes into account when making a diagnosis. One of the main diagnostic measures is an ECG with stress
If vascular dystonia is present, the body will react in the form of increased release of adrenaline and norepinephrine.
In the presence of frequent dizziness or fainting, consultation with a neurologist, rheoencephalography and ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head are required. REG helps to identify pathological changes in blood vessels, for example, obstruction of venous outflow. If necessary, an MRI of the brain is performed.
If numbness or coldness of the extremities occurs, the doctor will refer you for rheovasography - a study of blood flow. In this case, it is possible to identify narrowing of the arteries, which causes disruption of blood flow.
Vegetative tests are often prescribed - a special study of the ANS.
Causes of the disease
According to statistics, women suffer from VSD much more often than men - the reason for this is hidden in the characteristics of the female psyche. The main factors under the influence of which vegetative-vascular dystonia develops in girls include:
- Features of the body. A person’s congenital predisposition to VSD should also be considered.
- Constant stress. A long stay in a regime of severe psycho-emotional stress can provoke the development of the syndrome.
- Changes in hormonal levels. In women, they are observed during adolescence, during pregnancy or menopause. At this time, the nervous system is rebuilt, which can cause attacks of VSD.
- Chronic pathologies and infectious lesions. For example, for stomach ulcers, bronchial asthma, cholelithiasis, ischemia and other diseases. The body is constantly struggling with chronic pain, which over time will cause disruption of the autonomic nervous system.
- Patient activity. Sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle, bad habits and constant lack of sleep can cause the development of VSD syndrome.
- Psycho-emotional characteristics of the patient. Psycho-emotional instability, suspiciousness and excessive anxiety can also cause the syndrome.
It is believed that VSD is not an independent disease, but becomes a consequence of other diseases. And in order to identify a specific disorder in the functioning of body systems and prescribe appropriate treatment for VSD in women, a thorough diagnosis of the patient is required.
How long does the VSD crisis last?
The frequency and nature of clinical manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia occur differently for each patient, and the complexity of the disease depends on these factors. Therefore, doctors highlight:
- mild attacks;
- attacks of moderate severity;
- heavy.
Mild attacks of the disease usually last no more than 15 minutes and are accompanied by a small range of clinical symptoms. In this case, most often one organ system is involved. There is no post-crisis asthenia, that is, after an attack, a person quickly returns to normal life.
Symptoms of an attack of moderate VSD last less than an hour, but are accompanied by multiple indicators with persistence of post-crisis asthenia for up to a day and a half.
Severe attacks last more than an hour and are accompanied by a vivid clinical picture in combination with tics, convulsions or other hyperkinesis. Post-crisis asthenia persists for several days.
Treatment methods for VSD
Treatment of VSD in Moscow is carried out using medication and physiotherapeutic methods. The choice depends on the characteristics of the patient’s condition and symptoms of disorders.
Drug therapy
Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in adults should be comprehensive. The following groups of drugs are used for this:
- Sedatives. Medicines relax, calm, normalize sleep, and relieve anxiety. Good results are obtained with preparations based on medicinal herbs or containing synthetic relaxants (barbiturates).
- Cardiovascular. The drugs relieve arrhythmia, normalize blood pressure, and improve cerebral circulation. To increase their effectiveness, patients need to sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Medicines to normalize the functioning of the nervous system. There are several groups of drugs. For VSD, the following are used: tranquilizers (drugs relieve anxiety), sleeping pills (normalize sleep), antidepressants (treat the symptom complex of depression, including increasing mood), neuroleptics (reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings, are used to treat severe emotional and mental arousal), nootropics ( to improve cerebral circulation).
- Vitamin complexes. The drugs normalize the balance of vitamins and minerals and strengthen the nervous system.
- Antispasmodics. Necessary for muscle weakness, stomach cramps, headaches.
- Hormonal drugs. The drugs are used if VSD has developed against the background of hormonal imbalance.
- Diuretic medications. These drugs remove excess fluid, prevent stagnation and swelling, and ensure good blood and lymph circulation.
When choosing medications, the patient’s age and existing diseases are also taken into account.
Physiotherapy
In addition to medications, the symptoms of the disorder are relieved by physiotherapeutic procedures. Treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in Moscow includes:
- bioresonance therapy;
- reflexology;
- Exercise therapy according to a special course of exercises;
- massage;
- acupuncture;
- laser and magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis with sedatives;
- electrosleep;
- darsonvalization;
- aeroionotherapy.
Massage, exercise therapy, acupuncture should be carried out by specialists. Procedures are selected individually.
Prevention
After a course of VSD therapy, as well as to prevent nervous breakdown, doctors recommend the following measures to patients:
- various exercises, sports;
- walk as often as possible;
- start doing yoga, meditation, and other techniques aimed at relaxation;
- vitamin therapy courses;
- contrast shower (if there are no contraindications).
Patients are advised to avoid overexertion, find time to rest, and get enough sleep. At the first attacks or intensification of symptoms of the disorder, it is better to consult a doctor. In case of severe manifestations of dysfunction of the autonomic system, the patient is hospitalized.
Prevention
Many people know that preventing a disease is much easier than getting rid of it later. Therefore, in order not to treat VSD, you should take care of its prevention in advance. Especially if there have already been cases of such a disorder in the family, for example, on the female side of the mother or grandmother.
You can overcome VSD by following simple rules:
- adjust physical/intellectual stress;
- introduce more vegetables and various fruits into the diet;
- observe drinking regime;
- take an annual vacation - go on vacation, travel out of town;
- ensure a good night's rest - in a ventilated, cool room;
- avoid stressful situations.
Of course, autonomic dysfunction, if it has formed, can remain with a person for life. However, it is better to ask your doctor in advance how to get rid of VSD and whether it can be defeated.
Clinical manifestations
The signs and symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia in a child and an adult are the same. However, in each person the pathology occurs differently, which is influenced by the predominance of a certain part of the ANS and the type of neurocirculatory dystonia. For some, headaches predominate; for others, dizziness occurs when the ambient temperature changes. Fainting is possible, but after being brought to consciousness the person experiences relief and relaxation.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is often accompanied by nausea and a feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the throat. Taking into account blood pressure indicators, the following types of VSD are distinguished:
- hypertensive: blood pressure increases;
- hypotonic: blood pressure decreases;
- mixed: jumps in indicators are observed.
Each type of VSD is characterized by its own symptoms.
Hypertensive type
Pathology of the hypertensive type occurs with the following clinical manifestations:
- increased blood pressure;
- headache and cramps;
- dizziness;
- weather dependence with increased severity of headaches, increased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- impaired thermoregulation;
- weakening of intestinal motility, constipation;
- decreased production of tear fluid.
With VSD of the hypertensive type, a person quickly gets tired, even with light physical exertion.
Hypotonic
Vegetovascular dystonia of the hypotonic type occurs with the following symptoms:
- decreased blood pressure;
- rare pulse (bradycardia) or increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- pain syndrome in the heart (cardialgia);
- dizziness;
- frequent fainting conditions;
- headache, the intensity of which increases depending on weather conditions, during physical and mental stress;
- increased fatigue;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- digestive dysfunction;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- feeling of lack of air;
- paleness of the skin;
- increased cold sweating;
- symptoms of epilepsy - episyndrome, which is expressed in mild convulsive seizures.
With VSD of the hypotonic type, the risk of developing allergic reactions increases.
Mixed
In the absence of agreement between the structures of the ANS (sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions), various symptomatic manifestations arise. For example, when blood pressure jumps, redness of the face is observed or, conversely, paleness of the skin.
With VSD of mixed type, the clinical picture of the pathology combines symptoms characteristic of the other two types. Which department of the ANS will prevail in a certain period, such manifestations will be inherent in the human condition.
Vegetative crisis
With a severe course of vegetative-vascular dystonia, a crisis may occur - a condition characterized by the maximum severity of symptoms. It could be:
- increased sweating;
- severe nausea and headache;
- sudden illness;
- the appearance of a veil before the eyes;
- a pronounced decrease or increase in blood pressure;
- slowing heart rate.
After a crisis, a person’s condition does not recover immediately: for the next 2-3 days he will feel unwell, weak, and periodically dizzy.
Diagnosis of VSD in women
To diagnose the syndrome, an integrated approach is practiced, which includes not only collecting anamnesis and listening to the patient’s complaints, but also examining the patient by related specialists. This is done in order to reliably establish the cause of the development of VSD, which will make it possible to select the most effective treatment for vegetative-vascular dystonia in women, simultaneously eliminating some organic pathologies that require separate therapy.
Thus, in addition to the neurologist, the following doctors may be involved in examining the patient:
- cardiologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- ophthalmologist;
- endocrinologist;
- ENT;
- urologist;
- psychiatrist;
- gynecologist.
In addition, to identify disorders of the ANS, the patient must undergo a number of special tests. They are assigned strictly individually.
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia VSD
The symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are very diverse and differ in one direction or another depending on the cause, as well as the organ or system in which this disorder occurred. Thus, according to the same criteria, the VSD group included the following syndromes with their own characteristic features.
Parasympathicotonia (Vagotonia)
Vagotonia, or the vagus nerve, is characterized by the following symptoms: depression, increased fatigue, sleep disorders (insomnia or excessive sleepiness), memory impairment, decreased performance, apathy, fearfulness, abdominal pain, appetite disturbances, nausea, feeling unwell in a stuffy room or in the cold, dizziness, leg pain, acrocyanosis, increased sweating, frequent urination, constipation, transient swelling under the eyes and allergic reactions.
From the cardiovascular system, the following symptoms were noted: pain in the heart area, low blood pressure (80/50 mm Hg), bradyarrhythmia, muffled heart tone (pulse up to 45-50 beats/min), increased heart size.
Sympathicotonia
Sympathicotonia is characterized by the following symptoms: paleness of the skin, chills, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, anxiety (feelings of fear and anxiety), short temper, inattention, increased sensitivity to pain, mydriasis, polyuria, constipation.
Neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD)
Neurocirculatory dystonia is divided into three types: cardiac, vascular and mixed, each of which is characterized by its own symptoms.
Cardiac type of NCD (functional cardiopathy): disturbances of the rhythm and conduction of the heart (sinus bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystole, atrioventricular block of the I-II degree), some forms of mitral valve prolapse and disturbances in the processes of ventricular repolarization.
Vascular type of NCD: arterial hypertension (hypertension) and arterial hypotension (hypotension).
Mixed type of NCD: a combination of symptoms of cardiac and vascular types.
Other signs of autonomic dysfunction
Cardiovascular syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms: heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystole), paleness of the skin, constant changes in blood pressure, various types of discomfort or pain in the heart area that does not go away when taking nitroglycerin.
Hyperventilation syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms: a feeling of suffocation, lack of air, as if it is difficult to take a deep breath, muscle spasms, dizziness, sensory disturbances in the limbs and perioral area.
Irritable bowel syndrome is characterized by: pain in the lower abdomen, flatulence (bloating), frequent urge to defecate, pain or discomfort in the pit of the stomach, appetite disturbances, nausea and vomiting, dysphagia.
Cystalgia is a painful urge to urinate and the act itself, while urine tests do not show the presence of any diseases;
Impaired sweating, especially increased sweating is observed on the soles of the feet and palms;
Sexual disorders, which are characterized in women by vaginismus and anorgasmia, in men by erectile dysfunction and ejaculation;
Violation of thermoregulation, which is characterized by daily temperature changes, from normal to a slight increase (up to 37.5°C), and slight chills.
Vegetative crises
Under the influence of unfavorable factors - overwork (mental and physical), acute infectious diseases, stress and others, which we will talk about a little later, a person can be attacked by various kinds of vegetative crises - panic attacks, vegetative storms, paroxysms. They can occur both short-term and long-term, up to several days. Let's consider the most common vegetative crises.
Sympathoadrenal crisis. It is characterized by the following symptoms: headache, increased blood pressure (up to 150/90-180/110 mmHg), rapid pulse (up to 110-140 beats/min), increased excitability, numbness of the extremities with a feeling of coldness in them, pain in the heart area, frequent urination, polyuria, dry mouth, sometimes elevated body temperature (up to 38-40°C).
Vagoinsular crisis. It is characterized by the following symptoms: sudden pallor of the skin, increased sweating, decreased blood pressure and body temperature, abdominal pain, flatulence, nausea and vomiting. Sometimes angioedema may develop. Attacks of suffocation, pain in the heart area, syncope, and migraine are also possible.
Symptoms of VSD in women
The symptoms of the syndrome are varied, which often requires consultation with various specialists to accurately determine the cause of the disorder. The main symptoms include:
- Pathologies of the heart muscle, the appearance of pain in the heart area, irregular heartbeat;
- Changes in blood pressure, Raynaud's syndrome, attacks of fever or chills, redness or paleness of the skin;
- Breathing problems that get worse with physical or emotional stress;
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Headaches of various origins, dizziness, tinnitus, impaired vision, weather sensitivity and sleep disturbances;
- Increased body temperature or its decrease for no apparent reason or underlying disease;
- Increased sweating or dry skin;
- The appearance of trembling of the upper and lower extremities, a feeling of chills, muscle cramps throughout the body (traditionally, cramps of the calf and facial muscles are observed), shuddering;
- Changes in sensitivity: feeling of numbness, tingling, goosebumps;
- Problems with urination, decreased libido and sexual dysfunction, anorgasmia, menstrual irregularities;
- A feeling of painful weakness and lethargy throughout the body, high fatigue and decreased attention, difficulty concentrating. There is also increased irritability and tearfulness, and the appearance of phobias.
When these symptoms are observed, immediate treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia in women , since in the future the syndrome can only progress, which will lead to intensification and the appearance of new symptoms.
The course of VSD syndrome can be divided into permanent (in this case, symptoms appear sporadically), paroxysmal (it is characterized by paroxysmal onset of symptoms) and latent - in which the symptoms of the syndrome can be identified only after examination.
Treatment
In most cases of vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is possible to normalize the patient’s condition with the help of physiotherapeutic measures, lifestyle correction, and elimination of factors that provoke VSD.
Medicines for the treatment of symptoms of VSD in adults are used only after a thorough examination according to indications. As a rule, tranquilizers and antidepressants are prescribed, as well as nootropic drugs and antihypertensive drugs to normalize blood pressure.
Medicines
When treating vegetative-vascular dystonia in adults, characteristic symptoms can be relieved by the following groups of drugs:
| Group of drugs | Product name | What is it used for? |
| Sedatives |
| They have a calming effect on the nervous system. Prescribed for anxiety and psycho-emotional stress. |
| Tranquilizers |
| They are used strictly as prescribed by a doctor for severe mental and anxiety disorders. |
| Neuroleptics |
| Normalizes blood pressure and heart rate. Reduce irritability, aggressiveness and nervousness. |
| Sleeping pills |
| Prescribed for sleep disorders. They also help in relieving headaches. Long-term use is not recommended, as the body gets used to these drugs. |
| Antidepressants |
| They help fight depressive disorders, apathy, and hypochondria. |
| Nootropics |
| Prescribed to restore memory, improve concentration, and relieve nervousness. |
| Cerebroangiocorrectors |
| Used to restore blood circulation in the brain. |
| Vegetotropes |
| They improve the general condition of the body due to their effect on the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems - relieve sweating, various pains, and dizziness. |
Along with these drugs, vitamin preparations of group B are often used in the treatment of VSD, such as Neurovitan, Neurobex, Neurorubin, which help in the restoration and healing of the body.
Physiotherapy
For vegetative-vascular disorders, physiotherapeutic methods are prescribed such as:
- electrophoresis,
- electrosleep,
- darsonvalization,
- laser therapy,
- inductothermy,
- galvanotherapy,
- magnetotherapy.
These methods are aimed at improving vascular tone and normalizing metabolic processes. The duration and intensity of the procedures are selected by the doctor depending on the degree of disorder. Physical therapy, swimming and various types of massage also have a positive effect.
ethnoscience
An important role in the treatment of VSD is assigned to traditional medicine recipes. At home, infusions and decoctions of herbs are prepared that have a calming and blood pressure-regulating effect:
To increase pressure the following are used:
- ginseng,
- lure,
- Leuzea,
- eleutherococcus,
- bearberry,
- lemongrass
To reduce blood pressure it is recommended:
- sage,
- mint,
- motherwort,
- Melissa,
- peony root.
To normalize cardiac activity:
- hop,
- hawthorn,
- Sophora,
- cottonweed.
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs have a mild effect and do not cause addiction. They can treat VSD for a long time without fear of side effects. However, for the sake of your own peace of mind, it is necessary to clarify the presence of contraindications to the use of folk remedies in each specific case.
VSD in the elderly
A pathology such as VSD (or its signs) is most often found in representatives of the younger generation. In elderly people, vegetative-vascular dystonia is observed much less frequently.
The reasons for the appearance of this pathology in the elderly are the following:
- a history of diseases associated with disruption of the digestive, nervous, cardiovascular, respiratory and other systems - their symptoms often coincide with the symptoms of VSD;
- lower potential of the body to adapt to increased physical and mental stress;
- The patient was taking medications, the side effects of which coincide with the signs of VSD.
If you suspect the presence of VSD in an elderly person, you should collect an anamnesis from the patient as quickly as possible and conduct a detailed interview with him in order to establish the heredity factor. To diagnose the disease, instrumental and laboratory tests are performed. For older people, a full examination is important, since the signs of VSD often coincide with other, more serious diseases.
Therapy for VSD
Is VSD treatable? This question worries hundreds of people, because the disorder causes many problems and significantly worsens the quality of life.
With VSD, it is important to eliminate emotional stress and streamline your daily schedule. Treatment of VSD in adults is a complex therapy that includes various methods
However, before deciding how to deal with VSD, you need to make a correct diagnosis.
Patients with signs of vegetative-vascular dystonia have to go through many specialists before they are given a final diagnosis. Depending on the symptoms, the attending physician prescribes a consultation with specialists, as well as tests.
How to defeat VSD? If you have vegetative-vascular dystonia, you can get rid of it forever only if you follow certain rules. When a diagnosis is made, treatment is carried out by a neurologist. It is he who develops a treatment strategy, which may include the following measures:
- Examinations for concomitant diseases and their treatment by specialists.
- In moments of crisis, the patient is prescribed medications to relieve symptoms.
- Also, in order to get rid of VSD, the patient often needs to take sedatives.
- Physiotherapy is an integral part of treatment for VSD; it perfectly combats the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms in the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Work and rest schedule. Each person has his own reserve of strength. Many patients, asking the question of how to cure VSD, do not even think about the fact that they themselves provoke the development of crises by overstraining their body. All people, regardless of whether they have VSD symptoms or not, need quality rest. Mental and physical stress is one of the factors in the development of abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system. Sleep should last at least 8 hours a day.
Passive lifestyle. It is impossible to cure vegetative distance by sitting in a chair all day. With a sedentary lifestyle, all human organs suffer, because muscles weaken, structural changes occur, organs are displaced, the spine and, as a result, the nervous system suffer. Daily exercise can solve this problem. The nerve fibers will receive the necessary nutrition, and the muscles will gain tone, which will ensure good health.
Emotional peace. Effective treatment of dystonia is impossible if a person is constantly under stress. Any nervous tension can turn into a crisis and a significant deterioration in the condition. A huge number of negative facts that we learn from the media form fears, anxiety, excitability and depression in us. Any scandals, tension in family relationships and at work also have a negative impact on health. Of course, life without worries is not possible, but you need to learn to control your emotions and, if necessary, visit a psychotherapist.
Nutrition
Before wondering how to treat vegetative-vascular dystonia, you need to pay attention to your diet and eating schedule
Many people underestimate the importance of healthy food. We are used to eating in fits and starts, eating fast food and neglecting healthy food.
However, we must remember that nutrition is the only way to a healthy life. We are what we eat. This is a truth that every person should remember. A lack of vitamins, microelements and nutrients can cause various disorders, including nervous system failures. In adults, treatment also involves complete cessation of bad habits.
We are used to eating in fits and starts, eating fast food and neglecting healthy food. However, we must remember that nutrition is the only way to a healthy life. We are what we eat. This is a truth that every person should remember. A lack of vitamins, microelements and nutrients can cause various disorders, including nervous system failures. In adults, treatment also involves complete cessation of bad habits.
VSD during menopause
The manifestations of dystonia at 30, 40 and 50 years of age will always differ. That is why pathology in women of different ages requires an excellent approach to treatment. If for young women it is enough to adjust the work and rest schedule, then during menopause the emphasis is mainly on normalizing blood pressure and preventing coronary disease.
The course of VSD during menopause is also complicated by fluctuations in the well-being of the woman herself. Attacks of tachycardia and pressure surges increase the likelihood of developing myocardial ischemia and circulatory disorders in the brain. After 45 years, the course of dystonia in women comes under special control. This allows you to prevent complications when the main manifestations of menopause occur.
Treatment of VSD in adults
Treatment of VSD is carried out comprehensively and includes the following points:
- Normalization of daily routine, sleep, rest;
- Elimination of physical inactivity using dosed physical activity (PT);
- Therapeutic massage and water procedures;
- Balneotherapy (treatment with mineral waters);
- Phototherapy;
- Limiting sources of emotional experiences - computer games, TV shows;
- Counseling and family psychological correction;
- Normalization of nutrition (regular consumption of food enriched with vitamins);
- Electrophoresis;
- Drug therapy.
The most difficult stage in therapeutic intervention is eliminating the causes that led to the autonomic disorder. Reviews from patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia indicate that a person is often independently able to determine the factors contributing to the manifestation of the syndrome. They indicate stress, overwork, quarrels and conflicts in the family, leading to an attack of VSD.
Drugs for vegetative-vascular dystonia
If non-drug methods are ineffective, pharmaceutical drugs are prescribed. These drugs are selected individually for each patient, starting with minimal doses and gradually increasing to the desired concentration
Particular attention is paid to getting rid of chronic foci of infection in the body, treating endocrine and other pathologies
Drug treatment is determined by the predominant symptoms in a particular patient. The main group of drugs for VSD consists of drugs with a sedative effect:
- Herbal remedies – valerian, motherwort, novo-passit, etc.;
- Antidepressants – cipralex, paroxetine, amitriptyline;
- Tranquilizers - seduxen, elenium, tazepam, grandaxin.
Depending on the disturbing complaints, the doctor may prescribe tablets for vegetative-vascular dystonia of the following drug groups:
- potassium and magnesium preparations (Magne B-6, Panangin, Asparkam) - to improve vascular tone and the relationship between nerve cells;
- beta-blockers (Metaprolol, Anaprilin) – for persistent arterial hypertension;
- nootropics (Piracetam) - to normalize metabolic processes and improve blood circulation;
- antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Cipralex) – for severe symptoms of depression to regulate the functioning of the central nervous system;
- tranquilizers (Diazepam) - to provide a sedative effect in cases of anxiety and panic attacks.
Physiotherapy for VSD
Physiotherapy in the treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia is aimed at regulating vascular tone, normalizing metabolism and eliminating pain. The nature, systematicity and intensity of the procedures are selected by the doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the disease.
The effects that physiotherapy produces on a patient with vegetoneurosis are:
- calming – electrosleep, electrophoresis of sedative drugs, aeroionotherapy;
- tonic – magnetic and laser therapy, inductothermy;
- vasodilator - galvanization, local darsonvalization;
- vasoconstrictor - electrophoresis of adrenaline and other adrenomimetic drugs (drugs that stimulate adrenergic receptors);
- antiarrhythmic - electrophoresis of potassium chloride, lidocaine.
Therapeutic massage and water treatments
Physical effects on the body, in particular therapeutic massage and water procedures, improve blood circulation, improve the functioning of the lymphatic system, if necessary, restore the structure of the spine (in the case of osteochondrosis), and along with the spine, the nerve channels with the vessels that pass through it are aligned. In addition, massage allows you to relax, relieve stress, and improve muscle tone.
Physical exercise
Most experts in the field of prevention and treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia agree that physical rehabilitation should be put in first place.
It is various physical exercises that can significantly help in the fight against the disease.
But what is important here is the correct balance between the complexity of the physical exercise and the abilities of a particular patient. This is the only way to achieve the best results
What should you avoid?
Some actions of the patient can aggravate the condition of VSD. Thus, if there are already existing disorders in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, you should not:
- excessively involved in meditation;
- create additional stress for the body or exhaust yourself with increased physical activity;
- go on diets for a long time or even starve;
- be an inveterate pessimist;
- drink alcoholic beverages, smoke;
- listen to recommendations from people who do not have the appropriate medical education (especially in matters of drug treatment of the disease).
Preventive actions
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a serious pathology that requires competent treatment. Otherwise, its symptoms will significantly worsen a person’s quality of life. In order not to encounter their manifestations, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- Try to engage in feasible sports every day. Regular physical activity is the best way to relieve stress or depression. Yoga, swimming in the pool and even evening walks are suitable.
- Experts recommend paying more attention to cardio exercises. For example, exercise on an exercise bike or just ride a bike in the park.
- Any physical activity should exclude heavy lifting and sudden movements.
- You need to spend 1-2 hours a day in the fresh air. A regular walk in the park with a dog or with a child on the playground is suitable for this.
- It is important to harden the body. You can start healing procedures at any age. It starts with a contrast shower, gradually changing the water temperature to a colder one.
- To avoid physical exhaustion, you must try to avoid overwork.
- Experts recommend paying more attention to your work and rest schedule. Everyone benefits from getting 8 hours of quality sleep. A few hours before rest, you need to turn off all gadgets and not watch TV.
- If necessary, you can take courses of soothing compounds. Most people prefer options made from herbal ingredients. They are absolutely harmless, but effective. Before starting use, it is better to consult a doctor; many formulations have contraindications.
- If possible, avoid stressful situations and strong emotional experiences.
Almost every second adult faces a dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Unfortunately, for most of them this problem remains without proper attention. Patients consult a doctor only when their condition worsens and more alarming signs appear. However, following basic preventive recommendations allows you to avoid this pathological condition.