Characteristics of the disease
Facial neuritis is a disease that causes inflammation and damage to the cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve, and its processes.
When sick, a person cannot control emotions and facial expressions, and has difficulty chewing food. The facial nerve is located in the canals of the facial bones and suffers from even a slight inflammatory process, as a result of which it is compressed. Under such circumstances, oxygen deprivation leads to the appearance of external symptoms. If the nerve trunk is damaged, motor disturbances and changes in sensitivity may occur. In the most severe situations, neuritis becomes a factor in the development of paralysis. According to statistics, almost all patients (regardless of age and gender - men and women equally) most often experience problems with facial expressions on one side of the face, and in some people - on both sides. The peak of the disease is diagnosed in the winter season, when the cold comes.
The peculiarity of the treatment of facial neuritis is its protracted nature; in an inpatient setting, the patient is treated for up to 30 days, the period of complete rehabilitation of the brain and central nervous system is up to six months. In at least 5% of neurologist's clients, the activity of the facial muscles cannot be restored as a result of treatment. This happens in people whose disease is caused by malignant neoplasms (oncology) of the brain or brain injury. Determining the form of severity of neurological damage in which the disease develops depends on the degree of damage to the nerve trunk and how timely the treatment process is started.
Causes of the disease
The causes of acute facial neuritis have not been proven in the scientific research world. However, doctors identify factors that provoke the development of a disease leading to a pathological condition:
- Cytomegalovirus (herpes) – often it is genetic in nature, is found in the body of most people and does not manifest itself in any way until the immune system fails. In a dormant state, the virus is located in nerve cells, in its active form it comes out (lips, nose, corners of the mouth, genitals, they are removed with antiviral drugs), and can cause severe inflammation of the facial nerve and its swelling. Other skin diseases caused by viruses - lichen, dermatitis, contribute to the appearance of neuritis.
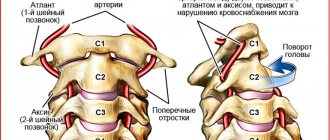
- Frequent exposure to the cold. When the body becomes hypothermic, the level of immune defense first decreases. With neuritis of the facial nerve, even a draft can lead to spasm and disruption of the functioning of blood vessels and muscle fibers. Against the background of a lack of heat, nerve nutrition is disrupted and inflammation occurs.
- Alcohol abuse. Such drinks contain alcohol, which damages brain cells and the facial nerve.
- Increased pressure. Due to jumps in upper and lower blood pressure, intracranial pressure increases, as a result of which the center of the facial nerve is affected. Such conditions lead to a risk of stroke.
- Carrying a child. The main danger awaits a woman in the first trimester of pregnancy. At this time, various hormonal changes occur in the body's systems, including the nervous system, preparing for the birth of the baby.
- Malignant neoplasms of the brain. The tumor develops and increases in size, pinching the nerve and disrupting the functioning of impulses.
- Traumatic effects in the brain area. At the site of impact, the facial nerve ruptures, which contributes to the accumulation of water, internal swelling of tissues and bones is formed, and the inflammatory process moves along the structure of the nerve.
- Tooth infection. When treating teeth, incorrect actions by the doctor or infectious diseases entering the tissue cause inflammation.
- Previously suffered diseases of the ENT organs. Other viruses in otitis, sinusitis, spread to nearby tissues, they cause damage to the nerve in the temple.
- The disease is diabetes mellitus. Disruption of metabolic processes leads to the appearance of inflammation due to the occurrence of polyneuropathy.
- Presence of atherosclerosis. Fatty plaques that form as a result of the disease clog the capillaries that supply the nerve with blood.
- Stressful and depressive conditions. When a person suffers morally, the protective functions of his body weaken, then he becomes susceptible to infections and viruses that provoke nervous diseases.
The main cause of the disease is pathogenic agents, namely viruses and bacteria. Risk factors are exogenous and endogenous.Exogenous ones include:
1. Poisoning of the body with alcohol, drugs, low-quality products. 2. Nerve compression. This is possible during surgery. 3. Injuries. In this case, post-traumatic neuritis is diagnosed.
Endogenous ones include:
1. Diseases of the endocrine system. 2. Obesity. 3. Diabetes. 4. Rheumatism. 5. Hereditary predisposition. 6. Problems with metabolism. 7. Otitis media.
The main manifestation of neuritis is pain along the nerve and in the area that it innervates. Decreased sensitivity, numbness, and impaired movement may occur.
Etiology and symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve
The main causes of inflammation of the facial nerve include:
- hypothermia (prolonged local exposure to low temperature causes vasospasm, disrupting nerve nutrition);
- herpes simplex virus, influenza, mumps;
- head and ear injuries (vascular ruptures and disruption of the integrity of muscle fibers are accompanied by swelling, which can compress the nerve, causing neuritis);
- alcohol abuse;
- dental diseases and their treatment (infection from a carious tooth spreads to nearby nerve fibers, this also includes mechanical injuries to the nerve during dental procedures);
- inflammatory processes in the middle ear (otitis) and posterior cranial fossa (meningitis, meningoencephalitis, arachnoiditis).
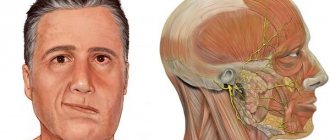
Symptoms of neuritis usually develop gradually. Initially, pain occurs in the ear area, and after a couple of days, facial asymmetry occurs. On the affected side, the nasolabial fold is smoothed out, the patient cannot completely close the eyelid (lagophthalmos) or raise the corner of the mouth. When trying to smile, a grin appears, shifted to the healthy side. There is also loss of taste on the front of the tongue and drooling. Increased hearing sensitivity on the affected side may develop.
Symptoms and treatment of facial neuritis
Various symptoms of acute neuritis of the facial nerve during primary development appear in accelerated dynamics, the signs of the disease have a characteristic course that is not characteristic of other diseases.
| Characteristics of the symptom | How it manifests itself | Cause |
| The appearance of pain behind the ear 2-3 days before facial expressions are affected | Painful sensations usually spread to the back of the head, face, eyeball, ear | Nerve nodes are compressed, swelling occurs |
| The face becomes asymmetrical | The appearance of the face changes: the eye is wide open, the corner of the mouth tends downward, the folds of the nose, lips, and forehead are smoothed out. The symptom is especially noticeable at the time of communication, expression of emotions (the desire to smile, frown, close lips tightly), perception, motor activity becomes not as sensitive as before | On the part of the brain, the ability to control facial expressions on one side is lost, the other remains healthy |
| Inability to close the eye on the affected side | Due to the inability to close the eye, a gap is visible where the mucous membrane is visible | Eyelid muscles do not respond to brain signals to close the eye |
| The corner of the mouth is downturned | At the time of eating, the liquid contents do not enter the mouth; they spill out due to the tension of the lips and tongue. The ability to move the jaw and chew is preserved | The oral muscle is not controlled by the facial nerve |
| Cheek muscles don't obey | When eating, a person may bite their cheek, causing food to remain in the mouth. | Cheek muscles do not respond to brain signals |
| Dry mouth | A person experiences a constant feeling of thirst, dry mouth, and there is a disruption in the process of wetting food with saliva. In moments of calm, the opposite situation occurs - profuse salivation occurs. | The salivary glands do not function properly due to distorted commands received from the brain. |
| Slurred speech | The mouth is not fully involved in articulation; some sounds have to be pronounced indistinctly – “v”, “f”, “b”. | The work of the cheeks, tongue and lips is partially ensured, which leads to difficulties in pronouncing sounds |
| Dry eyes or watery eyes | Due to a strongly open eye and infrequent blinking, the mucous membrane becomes dry and the production of tears is insufficient. In some cases, sometimes, on the contrary, there is a disturbance in the production of tears, which are directed not into the lacrimal canal, but outward, ending up on the face | During neuritis of the facial nerve, the lacrimal gland functions poorly, so an insufficient amount of tears is produced. In situations where the lacrimal glands are active, the outflow of tears is disrupted |
| Taste disorders | Part of the tongue cannot taste food when eating | During illness, nerve fibers become inflamed and do not transmit signals to the brain from taste buds |
| Increased auditory response | When a patient hears low tones, such sounds seem louder to him than they really are (hyperacusis) | The inflammatory process develops in the auricle, internal canal, parotid space, eardrum, and sometimes hearing loss occurs as the anomaly spreads to the temporal region |
Using an analysis of the symptoms and causes of neuritis, additional diagnostic methods, a qualified specialist determines what the prognosis is, in which zone of the facial nerve the pathology developed, establishes a diagnosis, and prepares a project for therapeutic advancement towards recovery:
- If the area of the cerebral cortex responsible for the activity of the facial nerve is damaged, the symptoms are: paralysis of facial expressions from the nose to the chin, the presence of a nervous tic, muscle disharmony during movements. When the patient cries or laughs, the disproportion of the face is not visible.
- When the functioning of the nerve nuclei is disrupted, the patient experiences uncontrolled movement of the eyeballs in an accelerated mode, the person is unable to move the forehead, the sensitivity of the skin decreases, the palate and pharynx twitch, and the motor activity of the body is not coordinated.
- At the time of pathology of the facial nerve in the skull or temple, paralysis of facial expressions occurs, dry mouth is observed due to a malfunction of the salivary glands, taste buds cannot cope with the recognition of food, there is an exacerbation of hearing, dry eyes due to insufficient tear production.
Before the first symptoms of neuritis appear, the patient feels discomfort behind the ear, spreading to the face, back of the head, and eyes. Subsequently, the center of the brain subsequently loses the ability to control the muscles at the site of the lesion of the facial nerve.
If the treatment of the facial nerve is started within the first few hours after symptoms are identified (the specialist is contacted in a timely manner), then the disease does not develop, the drugs prescribed by the doctor block the effect of the disease, so that the ability to work is restored, it will take less time.
Exercise therapy for lesions of the facial nerve
Damage to the facial nerve (VII pair of cranial nerves) is usually referred to as “neuritis.” Neuritis of the facial nerve is caused by various causes; it manifests itself as peripheral paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles of the corresponding half of the face and is accompanied by its asymmetry.
Contracture of facial muscles, the most common complication of neuritis of the facial nerve, is characterized by pathological synkinesis, persistent tension of paretic muscles and clonic-tonic or tic spasms in individual muscle groups.
The most common types of synkinesis found in clinics are:
- eyelid-frontal-labial - when closing the eyes, the forehead wrinkles and the corner of the mouth rises;
- eyelid-plethysmic - closing the eyes leads to contraction of the subcutaneous muscle of the neck;
- eyelid-nasal, or Hue's synkinesis, - raising the wing of the nose upward and outward when closing the eyes;
- eyelid-ear - squinting of the eyes is accompanied by raising the auricle;
- labio-digital - narrowing of the palpebral fissure with swelling of the cheeks;
- frontolabial - raising the corner of the mouth when wrinkling the forehead.
Objectives of exercise therapy: improve blood supply to the face, especially on the affected side, as well as the neck and collar area; restore impaired function of facial muscles, prevent the development of contractures and friendly movements; restore correct pronunciation.
In the early period of the disease (days 1-10), complex treatment uses position correction, massage and LH.
Recommendations for position correction:
- sleep on your side (affected side);
- sit for 10-15 minutes 3-4 times a day with your head tilted towards the affected side, supporting it with the back of your hand (resting on your elbow); tie a scarf, pulling the muscles from the healthy side towards the affected side (from bottom to top) and at the same time trying to restore the symmetry of the face;
- To eliminate facial asymmetry, apply adhesive plaster tension from the healthy side to the affected side. It should be directed against the pull of the muscles of the healthy side by firmly fixing the other end of the patch to a special helmet-mask, made individually for each patient.
Exercises for facial muscles
| Description of the exercise | Guidelines |
| Simultaneous and alternate cheek puffing | The cheek on the affected side should be puffed out, but not excessively. If necessary, the methodologist corrects the closing of the mouth with his hands. Avoid closing your eyes at the same time. |
| Snorting | The lips should vibrate slightly. If there is difficulty, pronounce “whoa.” |
| Pronunciation of the sound "p" | The sound is pronounced dully, followed by an extended exhalation. Before pronouncing the sound, close your lips tightly. If necessary, the methodologist helps with his hands. |
| From i.p. face down, small shakes of the head from side to side are made | The methodologist simultaneously strokes the cheeks, lips, forehead |
| Exercises in pronunciation of individual sounds | |
| Pronunciation of vowels: a, o, u, and | The lower jaw moves down freely. The muscles of the mouth work symmetrically |
| Pronunciation of consonants: b, ts, s, h, k, t | Synkinesis should be excluded. The patient's attention is paid to the movement of the lips |
| Exercises that reproduce facial movements | |
| Simultaneous and alternating eyebrow raising | When lifting at the same time, pay attention to the symmetry of the movement. The pace is slow. The amplitude of the eyebrows is moderate. When alternating, the amplitude is maximum. While moving on the affected side, the methodologist holds the eyebrow on the intact half of the face with his fingers |
| Simultaneous and alternate closing of eyes | If necessary, the methodologist helps to close the eyes tightly on the affected side. While closing the eyes, the patient tries to look down, up, to the right, etc. |
| Frowning brows | Bring your eyebrows together and form a vertical fold above the bridge of your nose. |
| Open up and show teeth | Watch for symmetry of movement. Exclude synkinesis |
| Wrinkle the back of your nose | First, the methodologist pulls down the skin of the back of the nose on both sides and then gives a line indication along the way. Symmetrical synkinesis is allowed, which facilitate the basic movement |
| Curl your lips together and blow on a lit match. | Watch for symmetry of movement. Help with your hands if necessary. Make sure that the patient can control the exhaled stream of air (the flame should fluctuate). You can ask the patient to blow into a tube placed in a glass of water. |
| Close your lips and puff out your cheeks at the same time. Release air through the left corner of your mouth. Repeating the exercise, release air through the right corner of your mouth. | Pay attention to the need to tightly close the lips and subsequent local relaxation of the area of the left and then the right corner of the mouth |
| Wrinkle the skin of the chin and stick out the lip forward | Maintain symmetry of movements |
| Pull the corners of your mouth to the sides | It is carried out when the teeth are tightly closed and the chewing muscles are tense. While simultaneously pulling the corners of the mouth to the sides, pay attention to the symmetry of the movement. When alternating movement, the maximum amplitude should be on the affected side. |
| Pull the corners of your mouth down | The movement is carried out by simultaneously lifting and slightly extending the lower lip. Watch for symmetry of facial expressions. |
| Raise the corners of your mouth up | The amplitude of movements is carefully selected to eliminate asymmetry as much as possible. In most cases, the help of a methodologist is required |
| Nostril flaring | The exercise is performed while inhaling. In the initial phase of inhalation, the methodologist compresses the patient’s nostrils and quickly releases them |
| Raising the lower eyelid | Perform the movement as isolated as possible. Completely eliminate synkinesis. When moving at the same time, pay attention to the symmetry of the face. Eliminate squinting |
Next »
How does facial neuritis develop?
Neuritis of the facial nerve develops due to improper functioning of the nerve endings. Malignant neoplasms, injuries, and infections destroy nerve fibers that are involved in sending impulses from the brain. The main consequence that occurs in connection with the progressive disease is Bell's palsy. If left untreated, the anomaly appears quickly. Its first symptom is sudden pain behind the ear, followed by numbness in the facial muscles over the next 3 days.
Paralysis due to neuritis of the facial nerve occurs in the following way:
- symptoms gradually increase (from 24 hours to 8 days), swelling, ischemic diseases appear, and a pinched nerve;
- primary rehabilitation lasts for one month – functionality returns to the facial muscles, swelling disappears;
- secondary rehabilitation (lasts up to 4 months) – restoration of the full range of muscle fibers of the facial part is carried out slowly, in this case there is a long absence of treatment;
- at the last level, the patient's facial muscles partially do not work; usually the person can move his mouth and eyes involuntarily.
The disorder quite often occurs on only one side of the face (the other remains healthy). If a patient does not have both sides functioning, there is a risk of more serious illnesses.
Is it possible to massage the face with neuritis of the facial nerve, indications for massage treatment
Massage manipulations are allowed only after confirmation of the presumptive diagnosis. The treatment course is prescribed to patients:
- with facial expression disturbances, problems with muscle function on one side of the face;
- inflammation or infections affecting nerve tissue;
- mechanical damage to nerve endings due to impacts or injuries.
Therapeutic procedures are not carried out in the acute phase of the disease, otherwise the pain will increase and the risk of permanent nerve damage will increase. The first session takes place 1-2 weeks after registration of the disease, at the first signs of disappearance of the main symptoms after the medicinal manipulations.
Important! Massage technique is designed to eliminate residual effects and strengthen muscles.
Diagnosis of neuritis of the facial nerve
The study of the causes of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out:
- When identifying symptoms of neuritis that manifest themselves in the client’s state of health, examine the face, taking into account: symmetry or asymmetry during rest, as well as in movement.
- With the help of specialized testing: a person is asked to simultaneously and alternately close and open his eyes, move his eyebrows, and frown.
- Diagnosis of the sensitivity of the tongue to taste and temperature - a person does not distinguish sweet, salty, spicy, only the bitterness of food is felt.
- Significant pathologies are revealed:
- When the patient tries to close the eye, the eyeball turns upward.
- The eyelid becomes painful because the eye does not close completely and constantly remains slightly open (there is no control over the facial muscles).
- If the patient tries to close his mouth tightly or take air into it, due to lack of control, it flies out, and the cheek takes on the shape of a “sail”.
- If it is necessary to show teeth, this works well only on the other side, where there is no paralysis.
- Through computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Using electroneuromyography to identify the site of inflammation.
Instrumental examinations
It is important for a neurologist to understand the clinical picture of neuritis, determine the localization of the inflammatory process, and assess the state of health in order to prescribe treatment.
Neurology provides a basic classification of diagnostics:
- CT and MRI are high-precision examinations that show pathology in volumetric form. In the image, the doctor sees the condition of the brain and facial nerve.
- Electroneurographic method - this method measures the speed of impulses in the nerves. The specialist receives the necessary information using sensors attached to the person.
- The electromyographic study represents the degree of interaction between the facial nerve and muscle structures.
If a neurologist diagnoses neuritis and sees other organ damage, he gives the patient a referral to specialists - an otolaryngologist (to examine the ears, throat, nose), and an ophthalmologist (to check the condition of the eyes).
Laboratory research
Testing is an important, primary step in assessing the client’s well-being and facial nerve fibers; it excludes the presence of infections and abnormalities of the autoimmune system.
What examinations are carried out:
- blood test - biochemical and general. With their help, information is obtained about the number of blood elements and their percentage. They help detect symptoms of diabetes and autoimmune system diseases.
- A study of the serological composition of the blood - it is used to determine the antibodies produced by the body after the onset of infection.
When diagnostics are used separately, the doctor, based on research results, can easily rule out illnesses with an identical clinical picture.
The treatment process of neuritis
When treating neuritis of the facial nerve, the doctor focuses on restoring the blood supply to the nervous system, the necessary outflow of lymph in the muscles of the neck and face, trying to normalize the conduction of impulses and quickly restore the activity of muscle fibers. Providing first aid (examination) within 3 days from the onset of unfavorable symptoms of neuritis to make a diagnosis is the key to successful rehabilitation and improvement of the condition; the later these measures are carried out, the less likely there is to return to a full lifestyle. The patient has the right to see a doctor for a consultation in any clinic in Moscow or the region of residence under the compulsory medical insurance policy, or for a fee, independently choose a health care institution.
Drug treatment
The conservative treatment regimen for the initial period of facial neuritis in medicine is presented with the help of glucocorticoids, anti-edema drugs, vasodilator tablets, anti-inflammatory medications, vitamin B; you cannot take medications yourself without a neurologist’s prescription. To eliminate violations of the integrity of the nerves, the blockade method is used. The reappearance of facial neuritis is immediately accompanied by treatment of the disease. To effectively treat neuritis, specialists use the following types of medications:
- antibiotics - when they enter the nervous system, they fight pathogenic organisms found in the microflora (Amoxicillin, Tetracycline);
- glucocorticosteroids – help eliminate the inflammatory process (Prednisolone, Meloxicam);
- analgesics – relieve pain associated with damage to the facial nerve (Analgin, Drotaverine);
- diuretics – relieve swelling, remove excess fluid from the body (Furosemide, Torasemide);
- Vasodilators - stimulate blood circulation (Eufillin);
- Antiviral drugs - prevent the spread of viral infections or eliminate them (if they occur) - Acyclovir, Zovirax.
In the first week of treatment for neuritis, muscle fibers should be in a calm state. In addition to the use of drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures are allowed, which involve the absence of heat contact with the body and are directly applied from the first day of treatment. On days 5-6, it is allowed to treat with UHF and physiotherapy, which involves contact of heat with the body.
Physiotherapy treatment
Physiotherapeutic treatment for the occurrence of neuritis of the facial nerve is one of the effective methods of rehabilitation. Using modern equipment, the patient receives medical care in comfortable conditions; effectiveness is achieved within the next few days after the start of the treatment process. The main methods of treating neuritis are:
- Infrared ray therapy – relieves inflammation and relieves pain;
- Electrical treatment saturates the affected tissues with oxygen and improves blood circulation.
- electrophoresis provides a dilating effect on blood vessels;
- UHF (electromagnetic field) reduces swelling of tissues, bones, and pain;
- Laser treatments accelerate tissue restoration;
- with phonophoresis, an increase in muscle tone is recorded, the body’s resources to combat neuritis are activated;
- The electrical stimulation method improves the conduction of impulses through the nervous system.
The condition of the human body with neuritis of the facial nerve and adverse symptoms that appear requires massage. It is performed both by a specialist and by the patient independently. They begin to massage with their hands from the forehead, then, with slow circular movements, move to the nose, eyes, cheeks, ending on the chin (within 15 minutes). At the last stage of treatment for neuritis, a person undergoes a set of exercises for the head: it is tilted forward and backward, gradually turned to one side, then the other. If actions are carried out without pain or discomfort, this means that the skin is being massaged correctly. It is not prohibited to engage in physical therapy and gymnastics from 2-3 weeks on an individual basis.
As a result, these measures help restore the activity of the affected facial muscles and bones, while the load should gradually increase.
In combination with massage, acupuncture significantly speeds up recovery; its one-time course lasts from 7 to 14 days. Before undergoing it, you need to consult a doctor and assess the risks of complications if there are contraindications.
Use of folk remedies
Doctors are allowed to use traditional recipes simultaneously with treatment (use of drugs) in a medical institution. The effectiveness and assistance of this type of therapy is little noticeable after two weeks. Beforehand, the patient is recommended to discuss with a specialist the methods that will be used to treat nerve cell damage. The most common recipes are:
- 50 grams of thyme in gauze pour 50 ml. boiling water, after cooling, squeeze out the contents and apply to the inflamed area of the face, hold for no more than 10 minutes. The procedure must be repeated for up to 7 days, 2 times a day.
- Pour a mixture of 15 grams of linden flowers and 15 grams of St. John's wort into 150 ml. boiling water, keep in a thermos for up to 8-10 hours, brewing like tea. The medicine should be taken in 100 ml doses. 3 times a day.
- Bay leaves (7-10 pieces) pour 400 ml. boiling water, leave for 8-10 hours. After preparing the decoction, you need to moisten a gauze bandage with it, bring it to the affected area of the face, and apply a warm towel on top for insulation. Use the compress until it dries.
- Pour a mixture of chamomile, elderberry, mint, linden flowers (1 tablespoon) into 400 ml. boiling water, leave for 2 hours. You need to drink the infusion 1/3 cup 3 times a day in the first week of inflammation.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is used more often in the presence of congenital neuritis of the facial nerve or its rupture after injury. It looks like a suturing of the facial nerve. The issue of surgery is also decided if there is no effect of drug therapy for a period of up to 10 months. It is necessary to carry out such a procedure during the first year, because after this time the process of atrophy of facial muscles can be traced. If this happens, restoration of facial fibers will be impossible.
Plastic surgery of the facial nerve is performed using the autotransplantation method. Through the graft, branches of the facial nerve located on the healthy side are installed to the muscles in the affected areas of the face. Motor impulses from intact facial muscles are transmitted and cause natural movements.
Consequences of neuritis of the facial nerve
When neuritis of the facial nerve occurs, the patient undergoes rehabilitation, taking into account the doctor’s recommendations. The most common cases are when recovery occurs completely, but when the disease lasts more than 3 months, nerve recovery is not always observed. Delaying treatment and ignoring neurologist’s prescriptions push the patient towards irreversible consequences, which often accompany the person throughout his life, and complete rehabilitation becomes impossible.
Due to damage to the integrity of the nerve and due to insufficient therapeutic measures, the following consequences arise:
- due to impaired blood flow, facial muscles atrophy;
- increased pain in the head area;
- due to constant closing of the eyelids, conjunctivitis occurs;
- the muscles contract voluntarily, periodically twitch, and tighten on one side of the face;
- ENT diseases.
How effective is massage in the treatment of facial neuritis?
Sessions are used to relieve physical and psychological stress and provide an opportunity to relax. With them, muscle function is restored, full facial expressions return. Massage for neuropathies improves local blood and lymph circulation and relaxes muscle tissue.
Procedures used:
- to increase tone;
- improving the condition of the dermis - due to the preservation of cell nutrition and trophism;
- normalization of the flow of biological fluids in the affected areas.
Important! The right approach to the problem helps to get noticeable results within a few hours after completing the session. Lasting changes require long-term manipulation.
| Before | After |