Classification of cochlear neuritis of the auditory nerve
Cochlear neuritis is the most common reason why a person's ability to perceive sound is reduced. Auditory nerve disease can affect one side, but sometimes hearing loss affects both sides. According to this, they divide:
- unilateral neuritis;
- bilateral neuritis.
Another classification of the disease concerns the degree of clinical development of cochlear neuritis. It shows how long the nerve dysfunction has been occurring and how severely it is affected. Thus, the following three forms of cochlear neuritis are distinguished:
- Acute cochlear neuritis. The period of the disease at this stage is up to four weeks. If you consult a doctor at this stage of the disease, the probability of complete hearing restoration is 70-90%.
- Subacute sensorineural hearing loss. This stage is diagnosed if the nerve damage lasts from one to three months. Treatment is also used here, the probability of recovery is about 30-70%.
- Chronic sensorineural hearing loss, which lasts for 3 months, is difficult to treat.
There are different types of cochlear neuritis according to the nature and level of damage diagnosed by the doctor. Since the disease is neurosensory in nature, nerve dysfunction can have different origins:
- peripheral cochlear neuritis - causes of impaired sound perception in the inner ear;
- central sensorineural hearing loss - the causes of hearing loss are caused by dysfunction of the corresponding structures in the brain.
According to the degree of development of the disease, four stages of cochlear neuritis are distinguished:
- Mild (I) degree, when the threshold for sound perception is 26-40 dB;
- Moderate (II) degree, the auditory limit here reaches 41-55 dB;
- Moderately severe (III) degree, sound perception threshold 56-70 dB;
- Severe (IV) degree, when the auditory limit is 71-90 dB.
If sound perception is almost completely impaired and the patient is unable to hear any sounds, the doctor diagnoses complete deafness.
According to the likely results of treatment, the nature of the course and symptoms, cochlear neuritis is classified into:
- reversible;
- progressive;
- stable.
In addition, cochlear neuritis is distinguished by the cause of the disease.
- Congenital sensorineural hearing loss, which manifests itself in childhood.
- Acquired cochlear neuritis, the cause of which can be many things. According to this, acquired sensorineural hearing loss is also considered as:
- ischemic;
- radial;
- professional;
- post-traumatic;
- allergic.
If cochlear neuritis occurs before a person learns to speak, then this type of disease is called prelingual. If it appears after, then such neuritis is classified as postlingual.
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of cochlear neuritis, and they differ for congenital and acquired hearing loss.
Causes of congenital cochlear neuritis
Congenital cochlear neuritis, symptoms of which appear from birth, may occur due to genetic abnormalities, illnesses suffered by the mother during pregnancy, or problems during the birth process.
- Hereditary hearing loss can occur due to Waardenburg syndrome, branchiootorenal syndrome, Refsum disease, Alport syndrome, Stickler syndrome.
- Diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy that can cause cochlear neuritis. Among them are: rubella, meningitis, syphilis, influenza, otitis media, mumps, herpes, ARVI.
- Problems during childbirth can cause damage to the auditory nerve. For example, such a disease can be caused by fetal hypoxia, premature birth, weakness of labor or its incoordination, birth trauma, or a narrow pelvis of the laboring mother.
Congenital cochlear neuritis
This pathological condition comes in two types: congenital and acquired. A baby may be born with a congenital form if at least one of the parents has a hearing pathology. There are also external factors that provoke the development of this disease. Let's look at some of them.
- Illness of the mother during pregnancy. The “culprits” can be measles, rubella, meningitis, influenza, mumps (mumps), acute viral infections, syphilis, inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media), herpes.
- Pregnant woman taking drugs or alcoholic beverages.
- Trauma that occurred during childbirth.
- Congenital neuritis occurs due to fetal hypoxia, premature labor, weak labor, and a woman’s narrow birth canal.
- Pathologies such as: Waardenburg, Alport, Stickler syndromes, as well as branchiootorenal, Refsum's disease.
Causes of acquired cochlear neuritis
Acquired cochlear neuritis in a third of cases is caused by inflammatory and infectious diseases. In addition, damage to the auditory nerve is caused by drugs, impaired blood supply, injury, and allergies.
- Infections and inflammatory processes that can cause cochlear neuritis include: ARVI, influenza, rubella, scarlet fever, mumps, syphilis, typhus and syphilis.
- Toxic effects of drugs, for example, antibiotics, anti-arrhythmia drugs; medications containing heavy metals or phosphorus.
- Trauma to the skull, tumors that can damage the auditory nerve.
- Arterial thrombosis, atherosclerotic plaques that disrupt cerebral circulation and blood supply to the auditory nerve.
- Long-term professional activity associated with constant exposure to noisy environments, loud sounds or vibrations.
- Age-related cochlear neuritis associated exclusively with gradual changes in the auditory nerve.
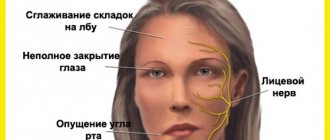
Symptoms of cochlear neuritis
Both unilateral and bilateral cochlear neuritis are characterized by two main symptoms that are constantly present:
- hearing loss (decreased);
- feeling of constant noise.
These manifestations of the disease may be complemented by other problems with the perception of sound, for example, a shift in the sense of the sound source. There are disorders of the vestibular apparatus, dizziness, vomiting, nausea. These symptoms are more characteristic of chronic cochlear neuritis.
Due to the fact that the disease affects the auditory nerve and the perception of sounds is difficult, children with cochlear neuritis suffer from psycho-emotional problems, moral disorders, and difficulties with speech. There is a decrease in the emotional background, isolation, and isolation from society.
Diagnosis of cochlear neuritis
In order to begin treatment of the disease, it is necessary to conduct a broad diagnosis of this problem. As already mentioned, cochlear neuritis exists in a wide variety of types and types and can be classified and defined into groups. Therefore, the doctor needs to conduct many tests, analyzes and procedures in order to fully describe the disease, identifying all aspects of cochlear neuritis and determining its genesis, causes, symptoms, period of occurrence, etc. This is a meticulous process, difficult at an early stage both if there is unilateral and bilateral cochlear neuritis.
The degree of damage to the auditory nerve is determined using audiometry or acoustic impedance testing. Additionally, the ability of the vestibular apparatus to respond to stimuli and load is studied. To determine the nature of the disease, various tests and analyzes are carried out; separately, using computed tomography, x-rays or magnetic resonance imaging, the vascular system, cranial bones, and human brain are studied.
To clarify the diagnosis and check its truth, manipulations are carried out aimed at detecting other diseases. Thus, the patient can be checked for otitis media, cerumen impaction, and otosclerosis using endoscopy or otoscopy.
After other possible options have been excluded from the diagnostic field, the doctor narrows the search and not only records the disease, but also characterizes it, describing the type, variety, and possible cause that caused it.
Diagnosis and treatment of cochlear neuritis
Since there are quite a lot of diseases accompanied by hearing impairment, the doctor needs to exclude other pathologies, such as Meniere’s disease, otitis media, otosclerosis, foreign body in the ear (including wax plug)
It is important to determine the degree and dynamics of decline in hearing function
The doctor performs a number of tests that allow him to suggest a pathology of the auditory nerve (audiometry, Weber test, acoustic impedance measurement), as well as other studies (electrocochleography, microotoscopy, etc.).
The main goal of treatment is, of course, to restore hearing in acute and subacute forms of the disease, and in chronic sensorineural hearing loss - to stabilize the pathological process in order to prevent further deterioration in the function of the auditory analyzer. Acute neuritis of the auditory nerve is an indication for hospital treatment. First of all, all factors that could cause the development of the disease must be excluded.
Drug treatment includes the prescription of vasodilators, antiplatelet agents, neuroprotectors, nootropics, venotonic drugs, and, if necessary, detoxification and hormonal therapy. Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment have a positive effect in treatment: acupuncture, electrical stimulation, oxygen barotherapy, phonophoresis with drugs. Treatment of cochlear neuritis is a difficult task even for an experienced otolaryngologist. Self-medication in most cases turns out to be ineffective; in addition, the patient, trying to be treated with folk remedies or hoping for self-healing, loses valuable time.
With bilateral hearing loss below 40 dB, the patient begins to experience social problems, primarily, speech communication suffers. Therefore, this condition is an indication for hearing aid.
Surgical treatment of this disease is most often carried out with the aim of cochlear implantation, removal of a hematoma, brain tumor or acoustic neuroma. Surgery is also required in case of persistent, painful tinnitus or constantly recurring attacks of severe dizziness.
Forecast and prevention of cochlear neuritis
An effective method of restoring hearing in people with acquired deafness is cochlear implantation.
With early diagnosis and timely treatment of the acute form of sensorineural hearing loss, complete restoration of auditory function occurs in 50% of patients, and in 30-40% there is a significant improvement in hearing. In the chronic form of the disease, hearing loss is irreversible; the goal of treatment is to prevent further deterioration of hearing and its correction using prosthetics.
There are no specific methods for preventing this disease. It is necessary to avoid factors that increase the risk of developing cochlear neuritis:
- timely treatment of infectious diseases;
- taking medications, especially antibiotics, only as prescribed by a doctor;
- compliance with safety rules, use of protective equipment and compliance with work and rest regimes in hazardous industries;
- prevention of coronary heart disease, hypertension, atherosclerosis, endocrine pathologies and other diseases that can lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
Treatment of cochlear neuritis
The goal of treatment for this disease is complete or partial restoration of hearing. If the patient is sick with a chronic form of cochlear neuritis, treatment is prescribed aimed at stabilizing the existing condition and preventing its deterioration. In other cases, cochlear neuritis may respond to various forms of treatment, both in a hospital and in a regular setting.
Drug treatment is used, usually prescribed intravenously. Vasodilator drugs, venotonics, neuroprotectors and disaggregants are indicated for administration over a period of two weeks. Then they move on to another stage of treatment, when the medicine can be taken orally or administered intramuscularly.
If hearing loss was caused by intoxication, first a course of procedures is carried out to remove harmful substances from the body, such as heavy metals, arsenic, phosphorus. After the toxic element is eliminated, treatment is prescribed.
The symptoms of the disease are also relieved, eliminating pain, dizziness, nausea, and vestibular disorders, if any.
In addition to treatment with medications, manipulations are also prescribed. With the wide possibilities of modern ENT medicine, procedures such as electrical stimulation, oxygen barotherapy, electro-, laser-, acupuncture, as well as phonophoresis are successfully used.
This range of treatment options is indicated for those types of disease where there is a possibility of complete or partial restoration of hearing. If the task is such that it is necessary to maintain the patient’s existing health condition, or as an additional therapy, hearing prosthetics may be prescribed.
Hearing aids are indicated not only to make it easier for patients to perceive sounds, but also to restore speech function. Linear, analog, and digital hearing aids are used. In order for the prescribed prosthesis to function correctly, its adjustment and selection must be carried out by a specialized ENT professional.
Surgical intervention, the possibility of which we mentioned earlier, is indicated if cochlear or brainstem implantation is required, or hearing impairment is caused by injury, tumor or neoplasm, the removal of which is necessary. In addition, the operation will be performed on those patients for whom the symptom of dizziness or noise becomes painful.
If the patient has a severe form of cochlear neuritis, then surgery may be aimed at manipulating the cochlea.
Treatment of the disease
The main goal of treatment of acute cochlear neuritis is to restore hearing. Treatment of the chronic form of the disease is aimed at stabilizing auditory function.
Acute cochlear neuritis and some cases of progressive chronic cochlear neuritis are an indication for treatment in a hospital. Therapy for cochlear neuritis should be carried out in conjunction with the correction of disorders that could cause it. First of all, this is the elimination of arterial hypertension and hormonal dysfunction, eliminating the effects of ototoxic factors (medicines and other substances, noise, vibration, radioactive radiation).
Drug therapy for cochlear neuritis is carried out with vasodilators, antiplatelet agents, venotonics, neuroprotectors, and detoxification solutions. Combination therapy with trental, vinpocytine, piracetam, Mexidol and Cerebrolysin in the first 2 weeks is carried out by intravenous administration, then proceeds to intramuscular injections and oral administration of drugs. The use of ginkgo biloba in the treatment of cochlear neuritis has a good effect. In the treatment of sudden onset cochlear neuritis, glucocorticoids are additionally used. To relieve dizziness, histamine-like drugs (betagistine) are used.
Physiotherapeutic treatment methods have a positive stimulating effect:
- reflexology (electropuncture, laser puncture, acupuncture);
- electrical stimulation;
- phonophoresis of drugs;
- oxygen barotherapy.
Bilateral hearing loss of up to 40 dB complicates the patient’s speech communication and is an indication for hearing aids. The prelingual form of cochlear neuritis is an indication for wearing a hearing aid at a hearing threshold of 25 dB, since it has been proven that such hearing loss causes disturbances in the development of speech in a child. For the purpose of hearing protection for cochlear neuritis, analog, digital and linear hearing aids can be used. The selection and adjustment of the device is carried out by a hearing therapist.
Surgical treatment of cochlear neuritis is carried out to perform stem or cochlear implantation, removal of acoustic neuroma, hematoma or brain tumor. The need for surgical treatment may be due to painful ear noise or attacks of intense dizziness. In such cases, removal of the stellate ganglion, resection of the tympanic plexus or cervical sympathectomy is performed; in case of deafness or IV degree hearing loss, destructive operations on the cochlea are performed.
Prognosis for cochlear neuritis
The prognosis for the effectiveness of treatment for cochlear neuritis largely depends on the duration and symptoms of the disease. Modern and proven ENT techniques show themselves very well, having proven to be truly effective and efficient solutions to this problem, however, if cochlear neuritis was diagnosed at a late stage, then no medicine can help here. However, in the case when the patient consults a doctor on time, for example, at the stage of acute cochlear neuritis, the probability of recovery and complete restoration of hearing is 50%. Partial hearing restoration is guaranteed for another third of patients.
Chronic cochlear neuritis is practically untreatable; drug and procedural intervention will help little, but the efforts of doctors will be aimed at stabilizing and maintaining the current state of human health. It is important to prevent regression and further damage to the auditory nerve. This is why such patients are prescribed hearing prosthetics: it minimizes the likelihood of further deterioration of the condition, since it significantly facilitates the functioning of the auditory system, preventing it from overstraining.
Doctors repeatedly emphasize the importance of promptly going to the hospital in case of damage to the auditory nerve. Both if cochlear neuritis occurs suddenly, and if it bothers the patient for a certain period of time, it is necessary to go to a specialist. Early diagnosis can save your hearing or prevent it from deteriorating further. Remember that your health is the most important thing, and hearing problems are far from local in nature: damage to the auditory nerve entails disturbances in speech, and therefore in socialization, behavioral sphere, emotional background, mental and moral state.
Treatment
The fight against the problem, as a rule, is long-term. The treatment tactics are determined by the doctor. Treatment of cochleovestibular syndrome is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused its occurrence, as well as restoring the functions of damaged peripheral nerves.
Patients showing signs of the disorder require hospitalization. This is due to the fact that such people can harm themselves when trying to move.
Emergency help
It is better to start treating the victim immediately after the first clinical signs appear. First, symptomatic therapy is carried out aimed at stabilizing the patient's condition. For this purpose, antiemetic drugs are used, such as Cerucal, sedatives to reduce anxiety, as well as diuretics based on torasemide to combat swelling and prevent complications.
Infusion therapy is carried out to compensate for fluid losses and correct electrolyte disturbances caused by vegetative manifestations of the syndrome and nausea. Medicines that protect the brain from the effects of low oxygen concentrations, such as Mexidol, are also used intravenously.
Review of drugs
Further treatment depends on what disease triggered the development of cochleovestibular syndrome. Hemodynamic stimulants, such as Piracetam, are used, especially for disorders caused by impaired blood supply. In these cases, antiplatelet therapy with heparin or streptokinase is also indicated. Vertigolytic medications are the basis for the treatment of vestibular disorders, which help combat dizziness. A product such as Betaserk is widely used.
Reflexology
This method enhances the effectiveness of taking medications, therefore it is actively used in the fight against the disease. Both acupuncture and special massage techniques are used. They are aimed at restoring the natural transmission of nerve impulses. This treatment has virtually no contraindications and is actively used in the fight against cochleovestibular syndrome, unlike folk remedies, which rarely show good results.
Exercises
Physical activity is the key to successful recovery from illness. It must be taken into account that excessive loads lead to a deterioration in the patient’s condition. The set of exercises is aimed at gradual restoration of the vestibular apparatus. Exercises on special platforms that allow you to regulate the speed of rotation and the degree of tilt of the patient’s body contribute to a quick recovery. You can also practice at home. It is useful to do bending and slow running exercises.