People complain of pain between the shoulder blades much less often than discomfort in the lower back and neck, however, they also occur and can indicate a variety of diseases. Moreover, if pain in the lower back or neck can occur as a result of muscle strain, then discomfort between the shoulder blades is almost never of such a harmless nature, i.e. its appearance should be regarded as an unambiguous sign of the occurrence of disorders in the spine or internal organs and a reason for treatment to the doctor.
Causes of pain between the shoulder blades
Mainly, discomfort in the area of the shoulder blades is a sign of spinal diseases. At this level is the thoracic spine, which has the least mobility. This is why pain between the shoulder blades is much less common than in the lower back or neck. But they can also indicate the occurrence of:
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, protrusions and intervertebral hernias;
- spondylosis;
- scoliosis;
- kyphosis;
- myositis;
- intercostal neuralgia, etc.
Also, the cause of pain in the upper back can be diseases of the internal organs, especially the heart. But their development directly depends on the condition of the spine, therefore, in most cases, when diagnosing angina or other similar disorders, pathologies of the intervertebral discs, spinal curvature, etc. are additionally detected, since they interfere with the normal transmission of nerve impulses from the spinal cord to the heart, lungs, gastrointestinal tract and others.
This leads to disruptions in their work, which over time develops into organic changes, i.e., the development of the disease. Therefore, when pathologies of internal organs are detected, it is always recommended to examine the spine and direct efforts to restore its normal anatomy. Otherwise, therapy will be ineffective, and existing diseases will become chronic and will recur regularly.
Osteochondrosis, protrusions and intervertebral hernias
Osteochondrosis is the most common disease of the spine, in which degenerative processes occur in the intervertebral discs. It is diagnosed in almost every second person over 35 years of age, but the thoracic spine, due to its low mobility, suffers much less often than others.
Most often, the upper and last intervertebral discs of the thoracic spine suffer from osteochondrosis, protrusions and intervertebral hernias. The rest are almost never affected; this is observed mainly with extensive damage to the discs by osteochondrosis.
Against the background of dehydration of the intervertebral disc, the fibers of its outer shell (annulus fibrosus) weaken and, under the influence of high pressure of the internal contents (nucleus pulposus), gradually rupture. As a result, the disc becomes deformed and protrudes, often into the spinal canal, where the spinal cord and spinal roots pass. Thus, a protrusion is formed. If appropriate measures are not taken at this stage, the fibers of the annulus fibrosus will rupture completely and a true hernia will form, i.e., the nucleus pulposus will gain access to the spinal canal and will be able to compress the nerve roots and spinal cord.
This will lead to the development of radicular syndrome. It is characterized by irradiation of pain into the arms and body, as well as the occurrence of numbness, the feeling of goose bumps and other sensitivity disorders. The situation can be complicated by the separation of part of the nucleus pulposus from the maternal disc, which can lead to irreversible nerve damage and paralysis. This is called a sequestered hernia.
Schmorl's hernias most often form in the thoracic region, i.e. a protrusion forms on the upper or lower surface of the disc, growing inside the vertebral body, gradually destroying it. Over time, this can lead to a compression fracture of the spine.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is a complication of osteochondrosis, in which severe flattening of the intervertebral discs is observed. This leads to the formation of bony protrusions or osteophytes on the surface of the vertebral bodies. They tend to increase in size and fuse with each other, which leads to complete immobility of the affected spinal motion segments.
Scoliosis, kyphosis and their combination
Scoliosis is a curvature of the spine in which it is deformed in the lateral plane. With kyphosis, there is an increase in the natural deflection of the spine with the formation of a hump. Often these pathologies are combined with each other, in such situations kyphoscoliosis is diagnosed. In both cases, pain occurs between the shoulder blades. Without intervention, deformations progress, negatively affecting the functioning of internal organs, causing increased pain and the development of radicular syndrome.
Myositis
Myositis is an inflammatory process in skeletal muscles, which is accompanied by the appearance of local pain in the affected area. The pain intensifies with movements that use inflamed muscles and progresses over time. Their appearance is usually preceded by injuries, muscle strain, both during heavy physical labor and during a long stay in a forced position, including sitting at a computer.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is a condition in which the intercostal nerves are compressed or burst, which often results from osteochondrosis, hypothermia, and stress. Initially, muscle spasm occurs, which leads to compression or irritation of the nerves.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain is girdling, shooting in nature. They tend to intensify with breathing, sudden movement, and pressure on certain points in the ribs.
Diseases of internal organs
Diseases of the heart and gastrointestinal tract can also cause pain between the shoulder blades. They can be concentrated in the back or also cover the left side of the body, the stomach, or be encircling in nature. The main causes of pain between the shoulder blades may be:
- angina pectoris;
- IHD;
- myocardial infarction;
- gastritis and peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- pancreatitis;
- hepatitis;
- cholecystitis.
In certain cases, even pneumonia and pleurisy can make themselves felt by the appearance of back pain at the level of the shoulder blades. But this is often accompanied by a cough and fever.
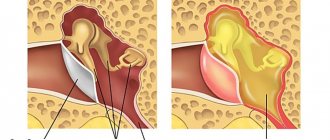
Arthroscopic release of the transverse scapular ligament
Arthroscopic decompression of the suprascapular nerve in the suprascapular notch and spinoglenoid groove has found widespread use in clinical practice. It provides the opportunity for good visualization of neurovascular structures, more accurate tissue dissection under arthroscopic magnification, and less severe pain in the postoperative period, since the tissues are subject to less trauma and the attachment site of the trapezius muscle remains intact.
Arthroscopic release of the suprascapular nerve is used both for isolated nerve damage and as part of arthroscopic restoration of massive rotator cuff injuries in order to prevent kinking when tensioning the repaired muscles.
Rehabilitation
During the first 2-3 days after surgery, a support bandage is prescribed for comfort. Pendulum exercises and exercises to restore range of motion begin immediately, and a gradual transition to full physical activity begins as the pain subsides.
Complications
The most common complications are persistence of symptoms due to incomplete release of the ligament, damage to neurovascular structures, or irreversible changes in the nerve due to its compression that developed before surgery. Good visualization and a clear understanding of the anatomy are key to performing these procedures safely.
Thorough hemostasis is achieved with the help of an arthroscopic pump that maintains the necessary pressure and fluid flow, as well as with hypotensive anesthesia. Gentle blunt spreading of the soft tissue around neurovascular structures also reduces the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Entrapment of the suprascapular nerve, isolated or against the background of another pathology (damage to the rotator cuff), is regarded today as one of the important causes of pain in the shoulder joint and dysfunction. The impingement may occur in the suprascapular notch or spinoglenoid groove.
As a result of compression of the suprascapular nerve, atrophy of both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles develops in the suprascapular notch, while pathology at the level of the spinous glenoid groove is limited to damage to the infraspinatus muscle. It is important to carefully approach the diagnosis and take this condition into account in the differential diagnosis in order for the patient to achieve an optimal clinical outcome.
Types of pain between the shoulder blades
The nature of the pain can say a lot about the reasons for its occurrence. The pain between the shoulder blades is most often aching, pulling. Therefore, they rarely force people to immediately seek medical help, which leads to the progression of existing diseases. They recur regularly and can persist for quite a long time, which indicates a chronic course of the pathology.
Acute pain in the upper back occurs quite rarely. They appear suddenly, quickly intensify and then gradually disappear. They are the ones who most often bring patients to the doctor. Although chronic mild pain is an equally compelling reason to consult a specialist.
Often the appearance and intensification of pain is facilitated by:
- physical exercise;
- prolonged maintenance of a static position, including prolonged sitting or standing;
- sleeping in an awkward position.
Pain between the shoulder blades can also be burning, which requires making an appointment with a doctor as quickly as possible, and in some situations, receiving emergency medical care.
Initially, pain between the shoulder blades can eventually begin to radiate to the neck, arms and shoulders. This is often accompanied by a feeling of numbness, goosebumps or other sensory disturbances, as well as limited mobility of the arms and body or disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, i.e. the development of radicular syndrome.
It is a consequence of compression of the spinal roots by intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies, their processes or other anatomical structures. In this case, the localization of discomfort directly depends on the level at which spinal motion segment the compressed spinal root is located. If the nerves localized at the level of the first thoracic vertebra are pinched, sensory disturbances will be observed on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder, and also in the armpit. And with compression of the nerves located at the level of the last, 11-12th vertebra of the thoracic spine, the development of pelvic organ dysfunction is possible, which may be accompanied by disturbance or loss of control over urination and defecation.
Symptoms
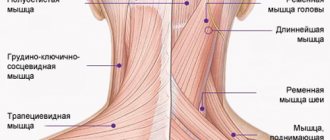
From the spinal cord, nerve endings spread throughout the body, penetrating every muscle. In the event of provoking factors, the nerve under the scapula may be pinched by nearby vertebrae or a neoplasm in the spine.
In the area where the nerve is pinched, the symptoms of the disease appear most intensely. The main symptom of the disease is considered to be painful manifestations. Moreover, they can be stabbing, sharp or aching. Another fairly characteristic sign is considered to be limited mobility in the affected area, which is connected to pinched nerve endings.
A pinched nerve under the left shoulder blade occurs most often and is characterized by peculiar painful sensations that radiate to the arm. However, in order to make an absolutely accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a doctor, since exactly the same symptoms can occur with heart disease.
Diagnosis of the causes of pain between the shoulder blades
If pain occurs between the shoulder blades, you must first make an appointment with a chiropractor, vertebrologist or neurologist. Our center’s specialists use an integrated approach to diagnosis and treatment, so they can quickly make the correct diagnosis. Diagnosis begins with a survey of the patient, during which the nature of the complaints, as well as the characteristics of work and rest, are clarified. The doctor must carefully examine the patient, palpating the spine, as well as conducting special functional and neurological tests. This allows you to get a complete picture of the patient’s condition, detect signs of neurological deficit and assess the extent of damage. The data obtained as a result of the survey and examination allow the specialist to suggest what exactly caused the pain between the shoulder blades and to prescribe additional studies to clarify the type of pathology, stage of development and general assessment of the condition of the spine.
Therefore, patients are prescribed:
- X-ray;
- CT;
- MRI.
They always try to give preference to MRI, since it is this method that allows you to obtain the most accurate and complete data on the condition of all vertebral structures, and assess the condition of the spinal cord and its roots. Using MRI, it is possible to identify not only intervertebral hernias and accurately determine their size, but also to diagnose protrusions with a size of 1-2 mm. Moreover, the method is absolutely safe and can even be used for examining pregnant women.
In our clinic, you can also learn in more detail about the composition of your body and the state of the vascular system, which is involved in the blood supply to internal organs, skeletal muscles, and the brain. Our experienced doctors will explain the data obtained to you in detail. Bioimpendansometry calculates the ratio of fat, muscle, bone and skeletal mass, total fluid in the body, and basal metabolic rate. The intensity of recommended physical activity depends on the state of muscle mass. Metabolic processes, in turn, affect the body's ability to recover. Based on the indicators of active cell mass, one can judge the level of physical activity and nutritional balance. This simple and quick test helps us identify disturbances in the endocrine system and take the necessary measures. In addition, it is also very important for us to know the condition of blood vessels for the prevention of diseases such as heart attacks, hypertension, heart failure, diabetes and much more. Angioscan allows you to determine such important indicators as the biological age of blood vessels, their stiffness, stress index (which indicates heart rate), and blood oxygen saturation. Such screening will be useful for men and women over 30, athletes, those undergoing long-term and severe treatment, as well as everyone who monitors their health.
In this case, body composition analysis gives us information that adipose tissue predominates in the body, and the bone-muscle component is in relative deficiency. These data will help the rehabilitation doctor competently draw up a physical activity plan, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
If signs of diseases of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system are detected, the patient is referred for consultation to a cardiologist, gastroenterologist or pulmonologist. These specialized specialists will help eliminate existing diseases of the internal organs, but their intervention in therapy does not eliminate the need to treat spinal pathologies that have created the preconditions for the development of disorders in the functioning of the internal organs.
Treatment of pain between the shoulder blades
In the vast majority of cases, conservative therapy is initially prescribed. It is especially effective when intervening during the pathological process in the early stages and allows you to completely eliminate the changes that have arisen. Only if severe complications develop, the patient is immediately referred for consultation to a neurosurgeon, since in case of sequestered intervertebral hernia, severe curvature of the spine or advanced spondylosis, the patient’s condition can only be improved through surgery. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor as soon as possible if pain occurs between the shoulder blades.
Conservative therapy is always comprehensive and involves taking measures to improve the patient’s well-being, as well as eliminating the cause of discomfort. Its main components are:
- drug therapy;
- osteopathy;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy (phonophoresis, carboxytherapy, ozone therapy, RF current pressure therapy);
- individual sessions with a rehabilitation doctor.
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, neurologists recommend that patients reconsider their habits and lifestyle, in particular:
- normalize weight (but strict diets and excessive physical activity are unacceptable; a transition to a balanced diet and moderate physical activity is recommended);
- refuse to lift and carry heavy objects, grueling workouts in the gym;
- workers in “sedentary” professions should increase their level of physical activity, do a warm-up every hour, and walk more;
- buy an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- introduce into your daily diet foods rich in vitamins and minerals (fresh fruits and vegetables, dairy products, etc.).
Regular swimming has a very positive effect on the condition of the spine and the body as a whole. Usually visiting the pool 2-3 times a week is enough.
Drug therapy
The main goals of drug therapy are to eliminate pain between the shoulder blades, inflammation and activate the body's recovery processes. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- NSAIDs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, widely used both to relieve various types of inflammatory processes and to eliminate pain;
- corticosteroids are drugs that have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and are prescribed to patients with severe inflammatory processes that cannot be eliminated with NSAIDs;
- muscle relaxants - medications that help eliminate muscle spasms caused by pain of vertebrogenic origin;
- chondroprotectors are drugs used in the initial stages of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs and help restore their elasticity and strength. To prevent diseases of the musculoskeletal system, we recommend to our patients the most effective drug Mermaids Marine Collagen;
- B vitamins – agents used to improve nerve conduction and improve the functioning of internal organs;
- vitamin D is a remedy responsible for the condition of bone tissue, as well as for higher brain functions, such as memory, attention, speech.
If the patient has detected pathologies of the heart, gastrointestinal tract and others, additional treatment is prescribed, which involves the use of antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors, antihypertensives or other drugs.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy can be called the basis of the treatment of spinal diseases. It should not be confused with therapeutic massage. If the latter only allows you to improve the condition of soft tissues and activate blood circulation, then manual therapy involves the direct impact of a specialist’s hands on the spine.
Thanks to the use of certain techniques of manipulation, mobilization, post-isometric relaxation, osteopathy and especially the Gritsenko technique, it is possible not only to restore the correct position of the vertebrae and the straightness of the spinal column, but also to increase the distance between them to the optimal value. Due to this, the pressure on the intervertebral discs sharply decreases, which creates optimal conditions for their regeneration. Also, a chiropractor can eliminate the pressure of various anatomical structures on the spinal roots, due to which the radicular syndrome is overcome, i.e. pain in the hands, sensory disturbances, a feeling of numbness go away, and the functioning of the pelvic organs also normalizes. There are no general standards of treatment in our clinic; an individual approach is applied to each patient.
In addition, manual therapy allows you to eliminate functional blocks and muscle spasms, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s mobility and well-being. Since normalization of muscle tone reduces pain between the shoulder blades, improves tissue trophism and transmission of nerve impulses. The manual effect itself, as well as with therapeutic massage, has a beneficial effect on the quality of blood circulation. Thanks to this, all tissues receive the maximum of the substances they need, subject to the correct diet and taking medications prescribed by a doctor, which contributes to their speedy recovery.
An additional “bonus” of manual therapy carried out according to the Gritsenko method is strengthening the immune system and enhancing the body’s adaptive abilities. Patients may notice the first improvements in well-being after the first session. But to obtain the maximum possible, and most importantly, lasting result, you need to undergo a full course of treatment, the duration of which is selected individually.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed outside the acute period of the disease. With their help, you can potentiate the effect of other therapeutic measures, as well as achieve analgesic, anti-inflammatory, reparative, antispasmodic effects, as well as improve microcirculation in tissues.
Often, for spinal pathologies, courses are indicated:
- electrophoresis;
- traction therapy;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF, etc.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy is an essential component of the treatment of almost any disease. It involves daily performance of a set of exercises individually developed by a rehabilitation doctor that will help normalize muscle tone, activate blood circulation and increase the flexibility of the spine.
It is important not to use the complexes presented on the Internet, but to contact a specialist who will individually develop a training program for a specific patient. In this case, it will take into account not only the peculiarities of the condition of the spine, but also the age of the patient, any concomitant diseases he has, as well as the level of physical fitness, which will allow achieving the maximum effect from the exercises and eliminating the possibility of harm to the person.
The first classes are recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This is necessary so that the patient can fully master the technique of performing each exercise and perform it correctly in the future at home. During exercise, it is important to avoid any sudden movements and overexertion, and if pain occurs, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Thus, pain between the shoulder blades may indicate the development of serious diseases. Therefore, when it appears, you should not hesitate to contact a specialist, otherwise the disease can lead to complications of various types, including disability. If you start treatment right away, you can almost always quickly achieve complete recovery of the body and eliminate the pain syndrome, along with the causes that cause it.
0 0 votes
Article rating
Treatment of back pain between the shoulder blades
To eliminate pain in the interscapular area, complex treatment is used, including drug therapy, physiotherapeutic methods and physical therapy. The course of treatment is selected individually, the most effective combination of methods and the scheme for their use are selected.
If interscapular back pain is caused by osteochondrosis and is vertebrogenic and neurogenic in nature, then physiotherapeutic treatment is an alternative to non-steroidal painkillers.
Physiotherapy methods:
- electrophoresis,
- electroanalgesia,
- magnetotherapy,
- ultrasound therapy,
- barolasertherapy,
- autogravitational traction of the spine,
- paraffin-ozokerite applications
reduce inflammation and pain and at the same time treat the underlying disease that caused back pain between the shoulder blades.
Manual therapy and massage are prescribed only for pain caused by diseases of the spine and nerve roots.
Physical therapy is prescribed only after pain has reduced.
It is recommended that during treatment for back pain, as well as for several days after the end of the treatment process, following a regimen that is as gentle as possible for the spine, excluding physical activity.
In the event that back pain between the shoulder blades occurs for the first time and is very severe, if the pain spreads to the chest, accompanied by any additional symptoms, nothing other than short-term pain relief should be used and you should immediately seek medical help.
Prevention measures
The only and most reliable method of prevention in this case will be an active lifestyle with the absence of bad habits and excess stress. It is necessary to maintain proper physical shape, do gymnastics, learn to move correctly, always monitor your posture, there must be comfortable and correct conditions for work, rest and sleep. If you work for a long time in an uncomfortable position, you need to do warm-up exercises and self-massage more often. Swimming in the pool will perfectly relieve muscle tension.
“Medical Center Yes!” in St. Petersburg, providing a wide range of diagnostic and therapeutic services, specializing in the treatment of neurological and therapeutic diseases. The healing process in our center is carried out taking into account the dynamics of the patient’s condition at different stages of treatment, under the supervision of specialists. Our doctors have developed complex therapy programs aimed at quickly eliminating pain syndromes and the causes of pain. Qualified specialists at our center will help the patient cope with back pain and return to normal life.
Find out about promotions by phone: +7 (812) 323-15-03
All rights reserved by copyright law. No part of the contents of the site may be used, reproduced, transmitted by any electronic, copying or other means without the prior written permission of the copyright owner.